WJEC AS Biology - Unit 2.3 Adaptations for Transport
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Types of circulatory system
Open
Closed
Open circulatory systems
Blood is not carried around the body in blood vessels
Blood bathes tissues directly while held in a cavity, allowing oxygen to be transported/delivered directly to respiring cells
Oxygen diffuses directly to cells from tracheoles so blood does not need oxygen → no respiratory pigment
Advantages of open circulatory systems
Less energy needed to pump the transport medium
Disadvantages of open circulatory systems
Substances are transported at lower pressures and therefore transported slower
Example of open circulatory systems
Insects
Circulatory system of insects
Open circulatory system
Long, dorsal tube-shaped heart running length of body
Heart pumps blood → haemocel (cavity), where materials are exchanged between the blood and body cells
Blood returns slowly to the heart and open circulation starts again
Lack of respiratory gases and respiratory pigment in blood as oxygen diffuses directly from tracheoles so blood does not need oxygen
Closed circulatory systems
Blood is carried in vessels (VASCULARISATION) to transport molecules/substances to and from exchange surfaces/tussues
Pumps/hearts used to pump blood
No direct contact with cells therefore resp pigment needed to carry respiratory gases in the blood
Advantages of closed circulatory systems
Blood pumped at higher pressure so blood travels at greater velocities, delivering oxygen and materials quickly to respiring cells
Disadvantages of closed circulatory systems
Contraction of a pump requires a large amount of energy
Types of closed circulatory systems
Single
Double
Single closed circulatory systems
Blood passes through the heart once in a single circuit around the body
Advantages of single closed circulatory systems
Requires less energy to operate the single pump than a double pump
Less complex single pump therefore less likely to have issues with values as exposed to lower pressures
Disadvantages of single closed circulatory systems
Lower pressure transporting oxygen to respiring cells → less velocity to blood → transporting oxygen to cells more slowly
Examples of single closed circulatory systems
Fish
Earthworms
Circulatory system of fish
Single closed
Ventricle of heart pumps deoxygenated blood → gills, where capillary network reduces it pressure
Oxygenated blood returns to atrium of heart
Blood moves to ventricle and circulation starts again
Circulatory system of earthworms
Respiratory gases carried
Blood moves forward in the dorsal vessel and back in the ventral vessel
5 pairs of pseudohearts (thickened, muscular blood vessels) pump blood from dv to vv
Double closed circulatory systems
Blood passes through the heart twice in its circuit around the body
Fastest type of delivery
Cells are more metabolically active and mammals need to maintain a constant body temperature
Advantages of a double closed circulatory systems
High pressure → fast delivery
Blood is repressurised when it leaves the gas exchange surface, giving a faster and more efficient circulation to the tissues
Disadvantages of a double closed circulatory system
Require lots of nerve transmission → requires lots of ATP
Issues with valves due to higher pressure
Contraction requires a lot of energy
Example of closed double circulatory system
Mammals - Blood pigment; haemoglobin
Types of circulation in mammals
Pulmonary
Systemic
Pulmonary circulation
Serves the lungs
Right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left side of the heart
Systemic circulation
Serves the body tissues
Left side of heart pumps the oxygenated blood to the tissues
Deoxygenated blood from the body returns to the right side of the heart
Pathway of blood
Heart
Artery (pulmonary or aorta)
Arteriole
Capillary
Venule
Vein (Vena Cava or pulmonary)
Blood vessels
Artery, Arteriole, Capillary, Venule and Vein
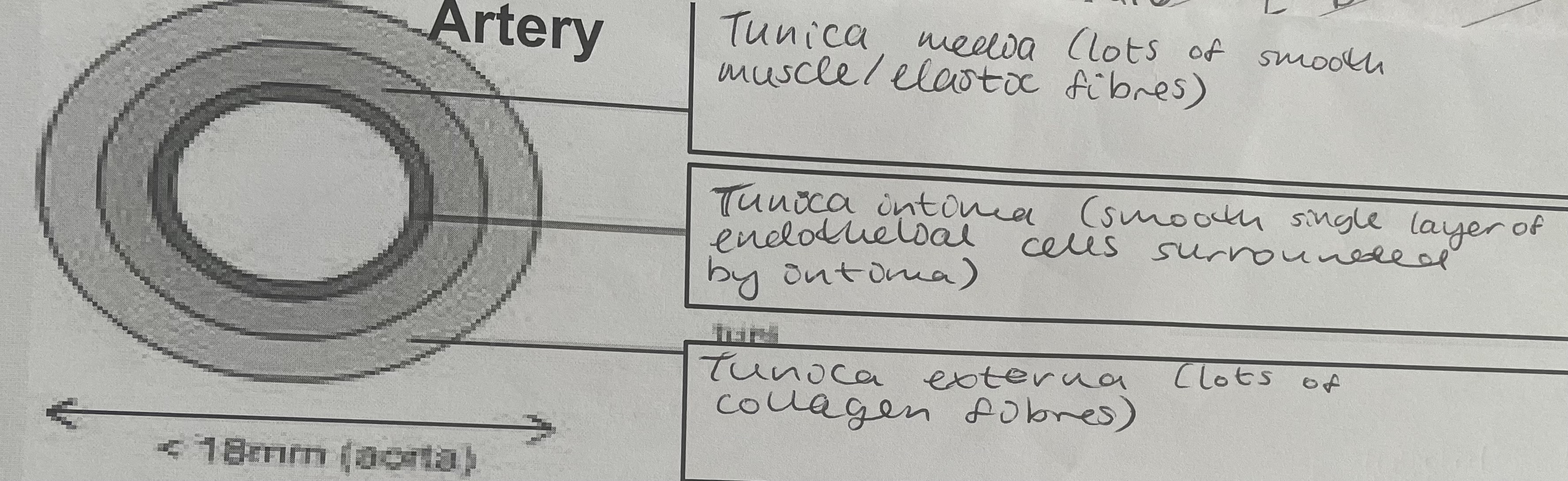
Arteries
adapted to carry blood at higher pressure
Have thick tunic externa; contains collagen fibres. Resists overstretching under pressure
Layer of muscle and elastic tissue = thick to provide elastic recoil aiding propulsion of blood and maintaining blood pressure
Lumen is relatively small to the maintain the pressure of the blood
Function of arteries
Supply oxygenated blood to respiring organs in the body
Structure of arteries
thick elastic walls; withstand higher pressures in arteries
Lots of elastic fibres; allow the arteries to expand and then recoil, helping to maintain arterial blood pressures and maintain a continuous flow of blood (ELASTIC RECOIL)
The smooth endothelial lining is undulating and elastic
Tunic externa, thick and contains many collagen fibres; numerous collagen fibres in tunica externa prevents rupture
Diagram of arteries
Function of arterioles
supply oxygenated blood to tissues/capillary beds.
Narrowing (VASOCONSTRICTION) and widening (VASODILATION) regulates blood flow to tissues
Increasing total surface arterioles, causes frictions slowing the blood and reducing the blood pressure
Arterioles
similar in structure to arteries but have more muscle
Construct and dilate to control the flow of blood to capillaries
Structure of arterioles
thicker tunica media in comparison to arteries. Therefore had a greater proportion of smooth muscle; allows narrowing and widening. Allows regulation of blood flow to tissues Increasing tissues
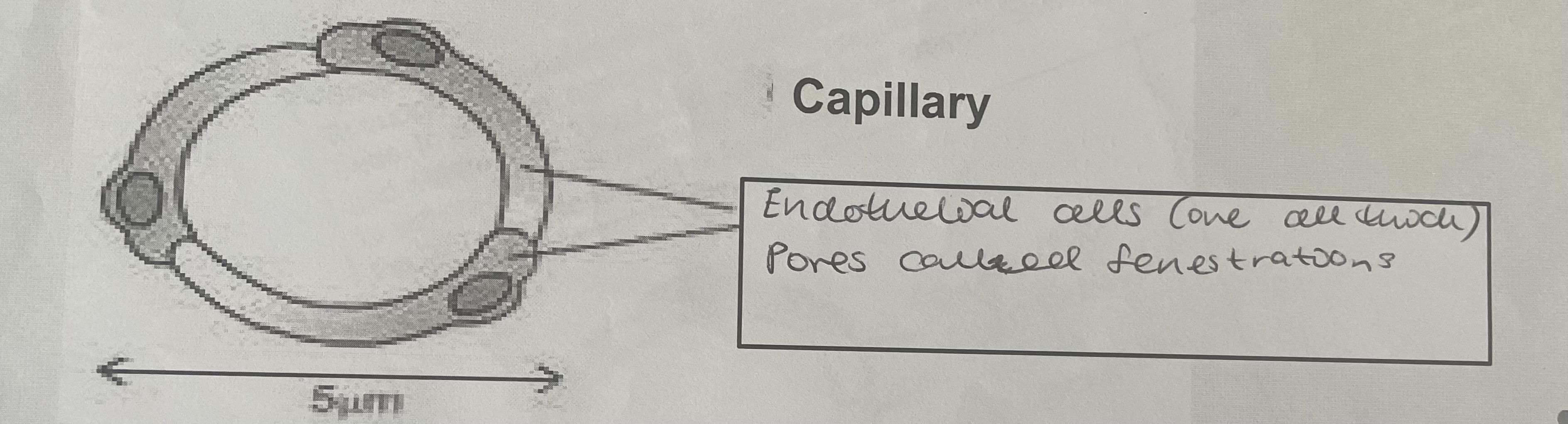
Capillaries
Consists of a single layer of endothelial cells
Tissue rather than an organ
Site of gas exchange; single layer of flattened cells gives a short diffusion path
Function of capillaries
Exchange of materials. This is where tissue fluid is formed
Structure of capillaries
Structure of endothelial cells; reduces diffusion path, increasing the rate of exchange of substances
Microscopic pores - generations; allow fluid to leave and return to the capillaries. The fluid will carry with it dissolved substances such as glucose and oxygen
Diagram of capillaries
Venules
Veins
Function of veins
Return deoxygenated blood to the heart
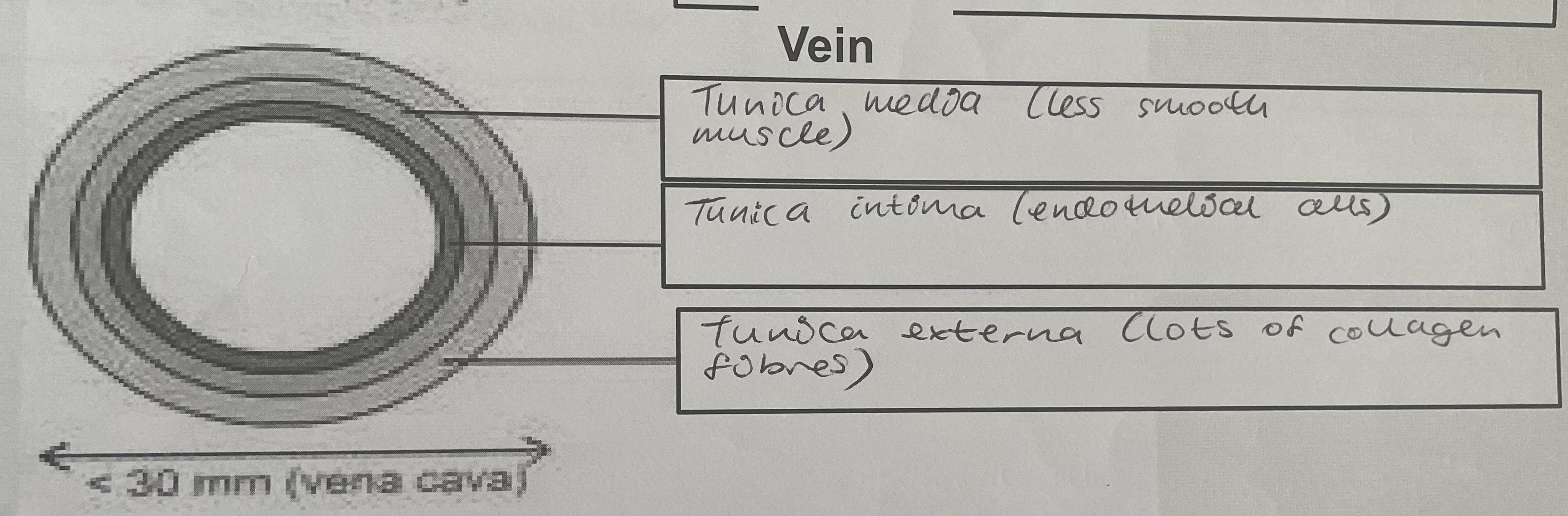
Structure of veins
thinner walls as they do not need to withstand the higher pressures as pressure are lower, backflow of blood is a potential issue
Contain semilunar valves; prevent backflow of blood
Larger wider lumens; reduces friction, increasing the velocity of the blood
The contraction of skeletal muscle close to the veins helps to return blood to the heart
Diagram of veins
Tunica intima
innermost layer of blood vessels
Single layer of endothelium
In some arteries, supported by elastin-rich collagen
Smooth lining, reducing friction, producing minimal resistance to blood flow
Tunica media
middle layer
Contains elastic fibres and smooth muscle
Thicker in arteries than in veins
Arteries, elastic fibres allow stretching to accommodate changes in blood flow and pressure as blood is pumped from the heart. Recoil, pushing blood on through the artery
Contraction of smooth muscle regulates blood flow and maintains blood pressure as the blood is transported further from the heart
Tunica externa
Outer layer, containing collagen fibres which resist overstretching
External structure of the heart
Internal structure of the heart
Myogenic
Layers of blood vessels
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Function of atrioventricular valves
Function of semilunar valves
The cardiac cycle
Sequence of events of one heartbeat
Stages of the cardiac cycle
Atrial systole
Ventricular systole
Diastole
Atrial systole in the cardiac cycle
Atrial walls contract to move blood further into the ventricles
Blood pressure in the atria increases
This pushes blood through tricuspid and bicuspid valves down into the ventricles, which are relaxed
The AVVs are open as greater pressure in the atria than the ventricles
Ventricular systole in the cardiac cycle
Ventricle walls contract from the bottom upwards
Increase blood pressure in the ventricles
The AVVs close as pressure greater in the ventricles than the atria
The SLVs are open as pressure is greater in the ventricles than the arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta)
The blood flows into the arteries (aorta and pulmonary artery)
Ventricular diastole in the cardiac cycle
Ventricles are relaxed
Volume of ventricles increases and so pressure in the ventricles falls
Most blood flows passively into the heart as pressure is greater in PVs and VC than the heart
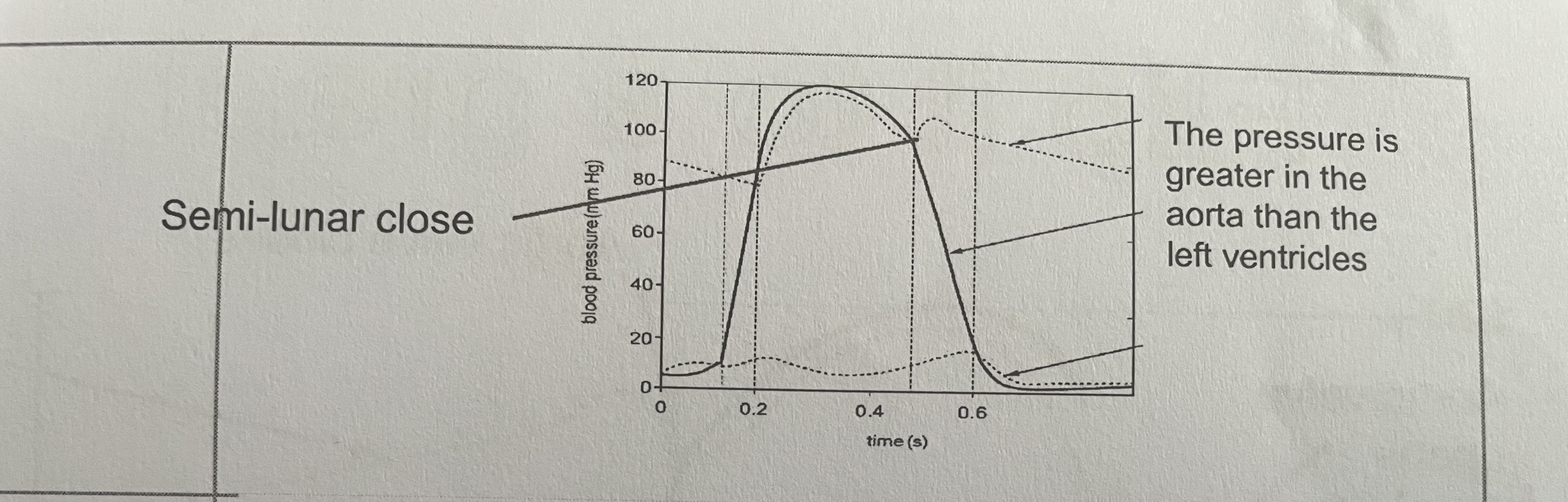
Greater pressure in the arteries then the ventricles means the SLVs are shut
Cardiac cycle graph
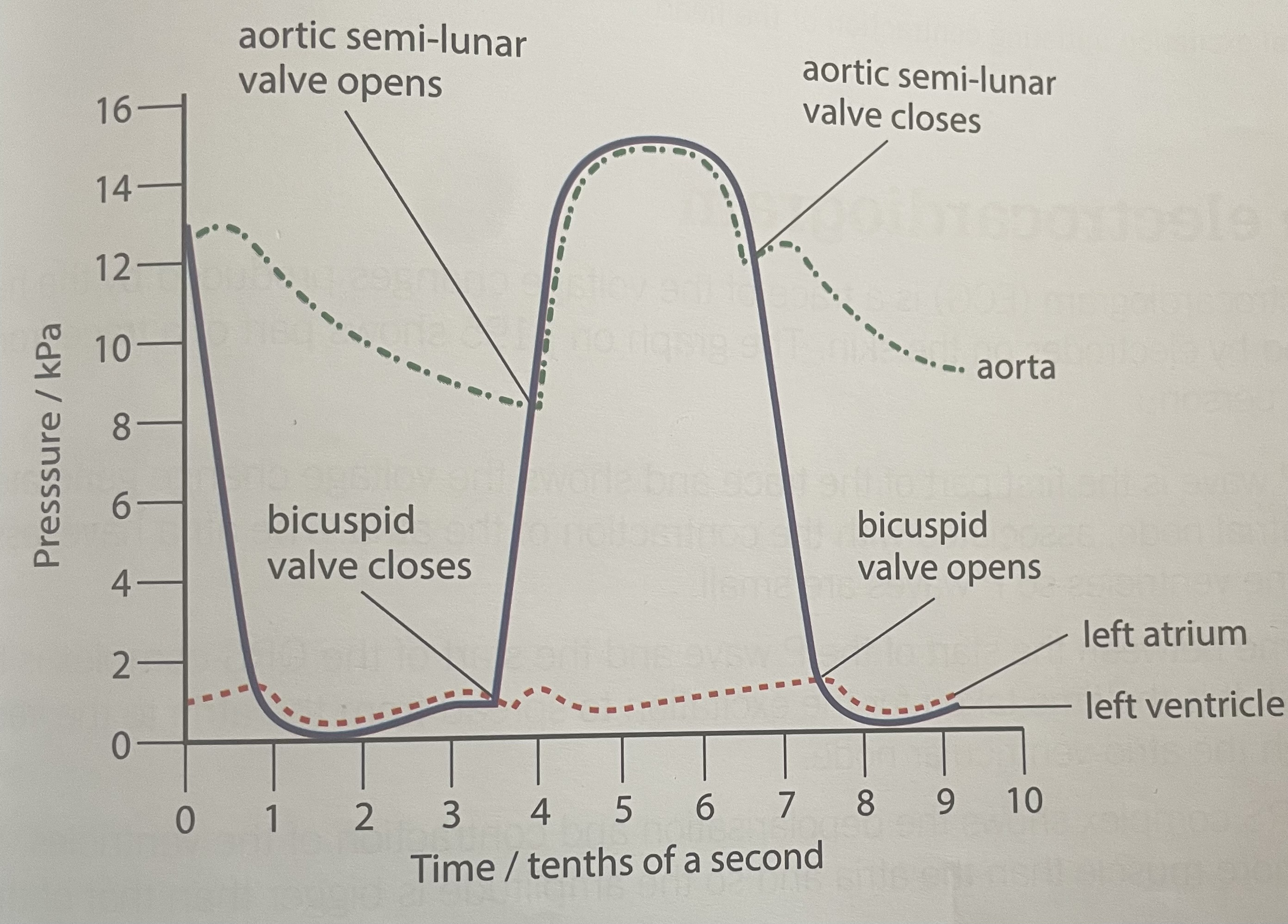
X on cardiac cycle graph
Aorta
Y on cardiac cycle graph
Ventricle
Z on cardiac cycle graph
Atria
When the AVV closes in the cardiac cycle graph
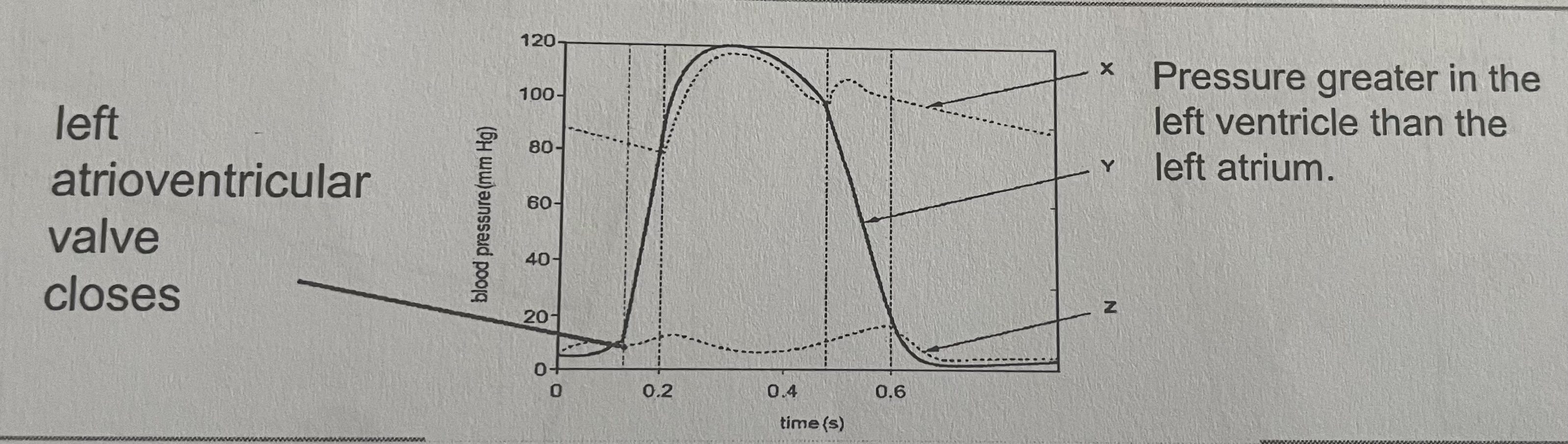
When the SLVs open in the cardiac cycle graph
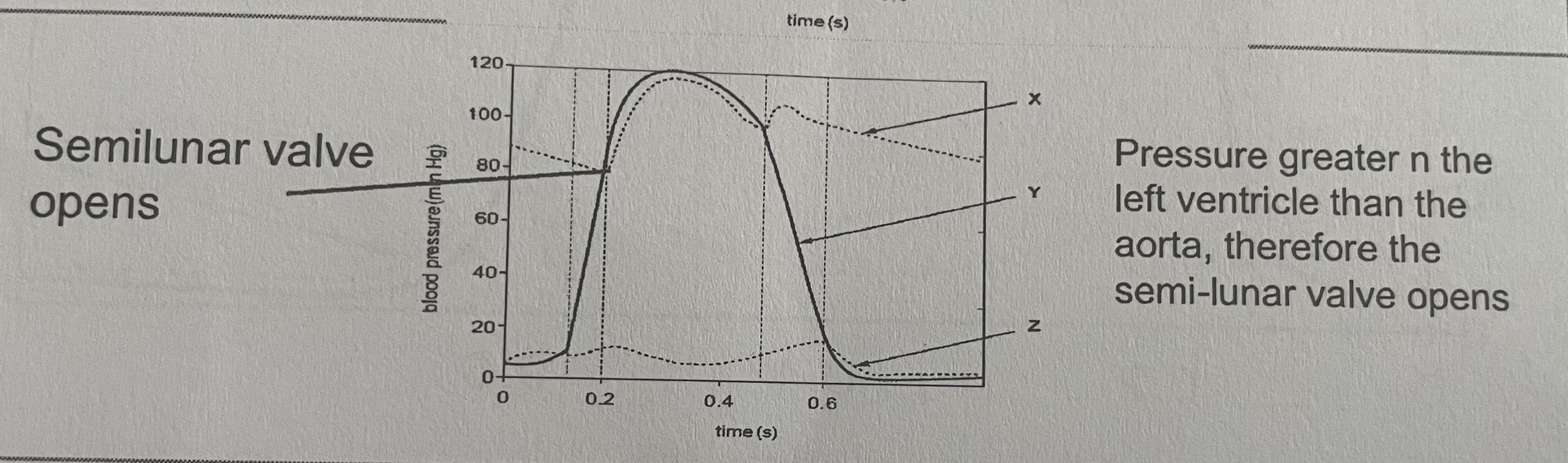
When the aortic valve opens on the cardiac cycle graph
Atrial systole on the cardiac cycle graph
Reason for the delay between atrial systole and ventricular systole
Ventricular diastole on the cardiac cycle graph
Sounds made in cardiac cycle graph
Electrical control of the heartbeat
Sino-atrial node
Atrio-ventricular node
Atrial systole (electrical)
Ventricular systole (electrical)
Ventricular diastole (electrical)
ECG
P wave on an ECG
QRS region on an ECG
T wave of an ECG
Irregularities in ECGs
Atrial fibrillation causes
Atrial fibrillation effects on normal heart function
Atrial fibrillation symptoms
Arrhythmia causes
Arrhythmia effects
Arrhythmia symptoms
Tachycardia causes
Tachycardia effects
Tachycardia symptoms
Pressure changes in the blood vessels
Pressure changes graph
Functions of blood
Composition of blood
Role of white blood cells
Role of red blood cells
How SA:Vol ratio of RBCs is increased
Why it is important that RBCs are flexible
How lack of a nucleus increases the RBC’s ability to transport oxygen
Benefits of small RBCs on efficiency of transport of oxygen
Adaptations of RBCs to low oxygen concentrations
Binding properties of haemoglobin
Affinity
Plasma