Biology Unit 5 test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/84
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
Frederick Griffith (what did he study and what was his experiment)
Studied the connection between bacteria and pneumonia
Experiment: Injected mice with different strands of bacteria
Experiment: Injected mice with different strands of bacteria
2
New cards
What happened when mice were injected with Rough Bacteria?
Survived
3
New cards
What happened when mice were injected with smooth Bacteria?
died
4
New cards
What happened when mice were injected with heated smooth Bacteria?
survived
5
New cards
What happened when mice were injected with Rough and smooth heated Bacteria?
died
6
New cards
What were the results of Griffith’s experiments?
Some “factor” changed the harmless - rough bacteria into the disease causing bacteria
7
New cards
What did Oswald Avery want and what was his experiment and results?
Wanted to figure out what “factor” caused transformation
Experiment:
Tested to see if transformation occurred without a specific macromolecule
Conducted the same experiment as Griffith, but included specific enzymes that broke down each of the four macromolecules
Result:
Determined nucleic acids caused transformation
Experiment:
Tested to see if transformation occurred without a specific macromolecule
Conducted the same experiment as Griffith, but included specific enzymes that broke down each of the four macromolecules
Result:
Determined nucleic acids caused transformation
8
New cards
what did Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase do?
Worked with bacteriophages to determine if DNA or RNA carried genetic information
9
New cards
What are bacteriophages? And how do they infect becterium?
Viruses that infect bacteria
Usually composed of a DNA core and protein coat (RNA)
How a bacteriophage infects a bacterium:
By injecting their DNA into a bacterium and it gets incorporated into a bacteria plasmid
Usually composed of a DNA core and protein coat (RNA)
How a bacteriophage infects a bacterium:
By injecting their DNA into a bacterium and it gets incorporated into a bacteria plasmid
10
New cards
what experiment did Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase do? And what were the results?
Used isotopes of sulfur and phosphorus as markers to determine what holds genetic information.
Sulfur - 35 marked the protein coat to see if touch caused the transformation
Phosphorus - 32 marked the DNA core to see if injection caused the transformation
Result:
DNA contained the genetic information
Sulfur - 35 marked the protein coat to see if touch caused the transformation
Phosphorus - 32 marked the DNA core to see if injection caused the transformation
Result:
DNA contained the genetic information
11
New cards
What monomer makes up DNA?
Nucleotides
12
New cards
What are the 3 components of DNA?
5 - Carbon Sugar: __**Deoxyribose**__
Phosphate Group
Nitrogenous Base
Phosphate Group
Nitrogenous Base
13
New cards
What are purines and their structure?
Purines have a 2-ring nitrogenous base.
Adenine
Guanine
Adenine
Guanine
14
New cards
What are pyrimidines and their structure?
Pyrimidines have a 1-ring nitrogenous base.
Cytosine
Thymine
(and uracil when applicable)
Cytosine
Thymine
(and uracil when applicable)
15
New cards
What did Erwin Chargaff do and notice?
Studied DNA and noticed that:
There were equal amounts of Adenine & Thymine
There were equal amounts of Cytosine & Guanine
There were equal amounts of Adenine & Thymine
There were equal amounts of Cytosine & Guanine
16
New cards
What did Rosalind Franklin do and notice?
Took a detailed picture of DNA by using x-rays
First noticed that DNA was double stranded
First noticed that DNA was double stranded
17
New cards
What did Watson and Crick do and notice?
Used Franklin’s picture to construct a 3D model of DNA and claimed that it was in a double helix shape
Noticed hydrogen bonds connected the two strands (nucleosides)
3 hydrogen bonds between C and G
2 hydrogen bonds between A and T
Noticed hydrogen bonds connected the two strands (nucleosides)
3 hydrogen bonds between C and G
2 hydrogen bonds between A and T
18
New cards
Double helix structure
Twisted ladder of DNA on a molecular level
19
New cards
Histone structure
individual protein
20
New cards
Nucleosome structure
Cluster of DNA wrapped around histones
21
New cards
Chromosome structure
Condensed DNA
22
New cards
Chromatin structure
Less condensed DNA
23
New cards
What direction do you read a DNA strand?
5’-3’
24
New cards
What does it mean for DNA to be anti-parallel
It means that the DNA strands are the complement to the ones they are opposite of.
25
New cards
Why do we need to replicate DNA before cells divide?
So that each cell has a copy of our DNA
26
New cards
DNA replicates in what phase of the cell cycle?
Interphase
27
New cards
After replication, how many strands of DNA will be made?
2
28
New cards
What does Helicase do?
An enzyme called helicase unzips the DNA strand by depolarizing the hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA together
29
New cards
What is DNA naturally?
Hydrophobic
30
New cards
The point where the DNA is unwound is called what?
\
\
Replication fork
31
New cards
After the DNA is unzipped, what happens?
It will rotate 180 degrees
32
New cards
How are new strands of DNA created?
DNA polymerase binds to the original strand of DNA with the help of a primase(which act as signal markers) and creates new strands of DNA.
33
New cards
What will the new strands do?
Each new strand will complement the nucleotides of the original strand of DNA.
34
New cards
How is the leading strand made?
\
\
Continuously
35
New cards
How is the lagging strand made?
\
\
In chunks
36
New cards
What are the “chunks” of DNA fragments called?
\
\
Okazaki Fragments
37
New cards
What enzyme connects bases?
An enzyme called DNA Ligase connects the bases to form the new DNA strand.
38
New cards
What does helicase do (simple version)?
unzips the DNA
39
New cards
What does Primase do?
puts down primers to show where DNA Polymerase needs to begin
40
New cards
What does DNA polymerase do?
creates the new strand of DNA; proof reads and checks the DNA
41
New cards
What does DNA ligase do?
connects the strands together
42
New cards
Why is the process of DNA replication described as semi convservative?
Because after DNA is replicated, the new DNA will have one strand that is new and one that is the original.
43
New cards
DNA vs RNA
DNA: Deoxyribose, Double stranded, has Thymine
\
RNA: Ribose, Single stranded, Uracil
\
RNA: Ribose, Single stranded, Uracil
44
New cards
What is the main purpose of transcription?
\
\
To turn DNA codes into RNA codes
45
New cards
Where does transcription occur?
\
\
In the nucleus
46
New cards
What is RNA Polymerase’s role in transcription?
\
\
RNA polymerase binds to a strand of DNA and makes an mRNA copy of the DNA strand
47
New cards
What does Messenger RNA (mRNA) do?
Carries copies of instructions on how to turn amino acids into proteins
48
New cards
What is Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
Located on the ribosome and feeds in the mRNA strand
49
New cards
What does transfer RNA do (tRNA)?
Transfers mRNA code into to the ribosome and releases an amino acid
50
New cards
What are introns and extrons?
Introns: the parts that are removed.
Exons: the parts that remain and get expressed
Exons: the parts that remain and get expressed
51
New cards
What is the main purpose of translation?
\
\
So that mRNA connects with the ribosome.
52
New cards
Where does translation occur?
\
\
In the ribosome (the cytoplasm of the cell)
53
New cards
How many bases make up a codon?
3
54
New cards
When dealing with Deciphering the Genetic Coding the codon ciphers, which type of RNA would you use?
I would use the original RNA not the anticodon that comes from the tRNA
55
New cards
Steps of Translation
1. mRNA brings the information to the ribosome through the rRNA
2. A tRNA corresponding to the mRNA binds to the mRNA
1. The anticodon for the tRNA binds to the codon of the mRNA
3. Once the anticodons attach, the tRNA releases its amino acid
4. The ribosome connects the different amino acids together to form a polypeptide (polymer)
56
New cards
What kind of bond holds amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
57
New cards
what happens during replication transcription and translation
Replication
DNA is copied
Transcription
turns DNA codes into RNA codes
Translation
mRNA connects with the ribosome.
DNA is copied
Transcription
turns DNA codes into RNA codes
Translation
mRNA connects with the ribosome.
58
New cards
what is epigenetics?
the study of how DNA interacts with epigenetic tags inside the cell
59
New cards
List the two ways that DNA/histone expression can be changed:
\
1. DNA Methylation: Methyl groups added to turn off the DNA
2. Histone Modification: Chemical groups can be added or removed from histones to make the histones more tightly or loosely
1. DNA Methylation: Methyl groups added to turn off the DNA
2. Histone Modification: Chemical groups can be added or removed from histones to make the histones more tightly or loosely
60
New cards
What do Hox Genes do?
These tell the order and how an organism will develop
61
New cards
What is a mutation?
any change in the genetic material of an organism
62
New cards
Gene mutations:
Changes in one or a few nucleotides that affect a gene.
Also known as a point mutation because they occur at a single point in the DNA
Also known as a point mutation because they occur at a single point in the DNA
63
New cards
Chromosomal mutations:
mutations that can change a chromosome’s structure or number.
64
New cards
Why are gene mutations also known as point mutations?
Because they occur at a single point in the DNA
65
New cards
Point Mutation: Substitution
Switching a nucleotide for another
Types:
Silent - No change in AA sequence
Nonsense - changes sequence into a stop codon
Missense - changes the Amino Acid
Types:
Silent - No change in AA sequence
Nonsense - changes sequence into a stop codon
Missense - changes the Amino Acid
66
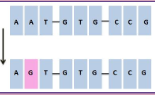
New cards
Point Mutation: Inversion
When sequences of DNA are reversed
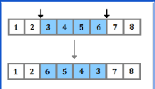
67
New cards
Insertion
Adding a base into the DNA sequence
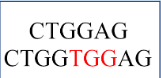
68
New cards
Deletion
Removing a base from the DNA sequence
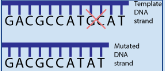
69
New cards
What type of mutations are deletion and insertion?
Frameshift
70
New cards
What happens in Deletion Duplication Inversion and Translocation
Deletion:
The loss of a section of a chromosome.
Duplication:
Produced extra copies of a section in a chromosome.
Inversion:
The reversal of a section in the chromosome
Translocation:
Only mutation that involves 2 different chromosomes.
The swapping of sections between two chromosomes
The loss of a section of a chromosome.
Duplication:
Produced extra copies of a section in a chromosome.
Inversion:
The reversal of a section in the chromosome
Translocation:
Only mutation that involves 2 different chromosomes.
The swapping of sections between two chromosomes
71
New cards
Nondisjunction
A numerical chromosomal disorder.
Failure of chromosomes to separate correctly during meiosis (sex cell reproduction).
Causes sex cells (sperm and eggs) to have too many or too few chromosomes
Failure of chromosomes to separate correctly during meiosis (sex cell reproduction).
Causes sex cells (sperm and eggs) to have too many or too few chromosomes
72
New cards
Switch cards around
Yup
73
New cards
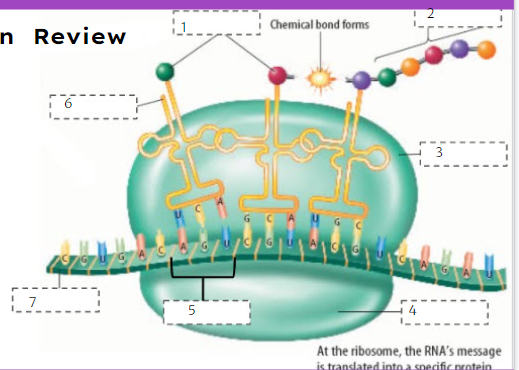
nuclear membrane
What is number 1?
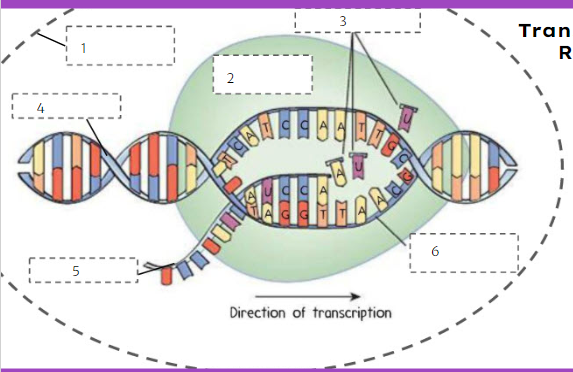
74
New cards
RNA polymerase
What is number 2?
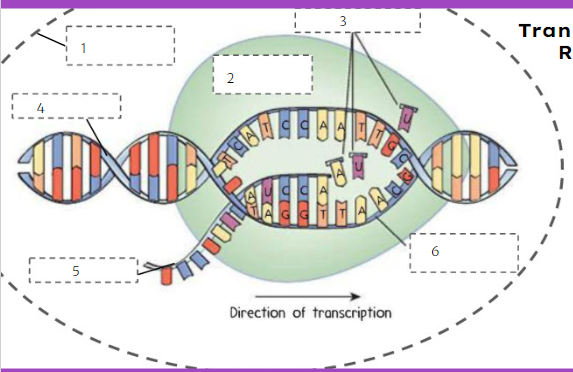
75
New cards
RNA nucleotides
What is number 3?
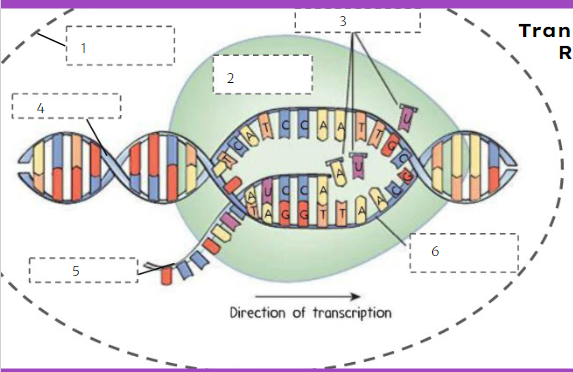
76
New cards
DNA
What is number 4?
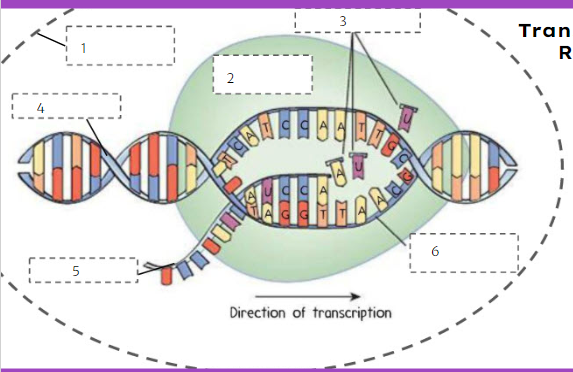
77
New cards
mRNA
What is number 5?
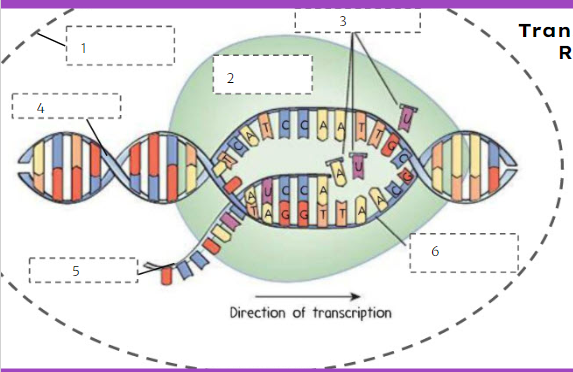
78
New cards
template strand
What is number 6?
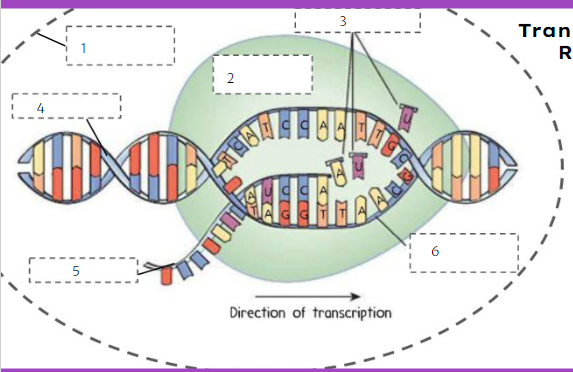
79
New cards
Amino acids
What is number 1?
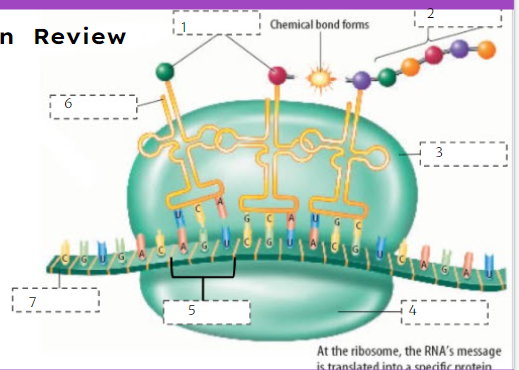
80
New cards
Protein
What is number 2?
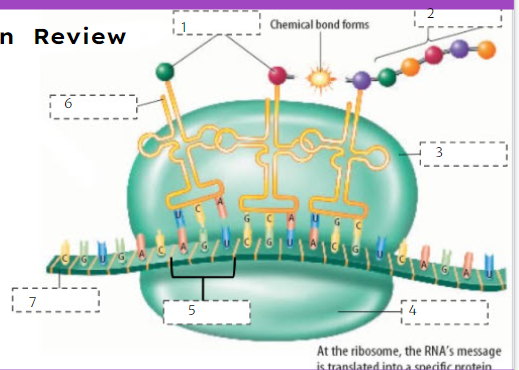
81
New cards
Large subunit
What is number 3?
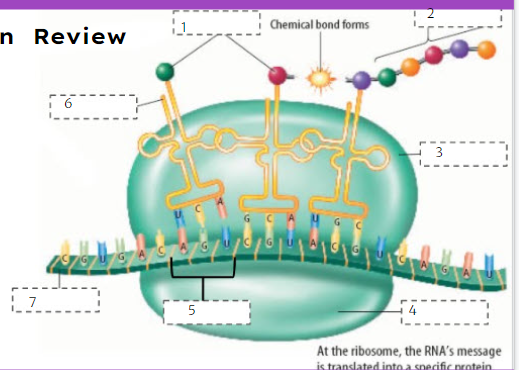
82
New cards
Small subunit
What is number 4?
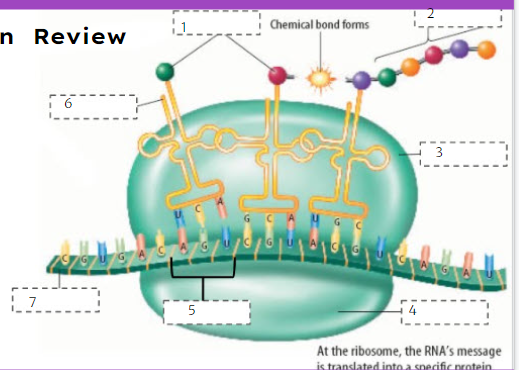
83
New cards
Codon
What is number 5?
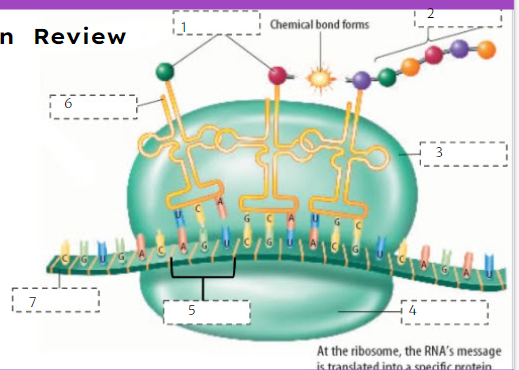
84
New cards
tRNA
What is number 6?
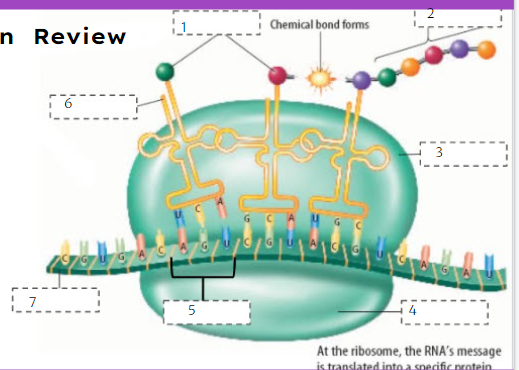
85
New cards
mRNA
What is number 7?