BIOL 1406 EXAM 1 (CH 1-4)
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
For an atom to be electrically neutral, it must be true that the number of _____.
protons equals the number of electrons
The chemical formula for carbon dioxide is CO2. How would you modify the formula to show six molecules of carbon dioxide?
6CO2
The atomic number of an element is the number of _____.
protons in the nucleus
The chemical formula of a molecule of glucose is C6H12O6. One glucose molecule has how many atoms of oxygen?
6
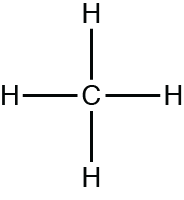
Methane is a molecule made of one carbon and four hydrogens. Identify the chemical formula for methane.
CH4
Identify the components of an atom found in the nucleus.
neutrons and protons
Identify the example(s) of energy from the choices provided.
Electricity, light, sound, and heat
Something that has mass and occupies space is referred to as _____.
matter
An atom that has one proton, one neutron, and one electron would have an overall charge of _____.
0
Water can occur in three states: as a solid (ice), as a liquid, and as a gas (water vapor). Which state of matter has a defined volume and a defined shape?
Solid
Matter is something that _____.
has mass and occupies space
If an atom has a net negative charge, it must have _____.
more electrons than protons
Energy is often explained as the ability to _____.
do work
Oxygen has an atomic number of 8. What does this indicate?
Oxygen has 8 protons in its nucleus
What is the difference between nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15?
Nitrogen-15 has one more neutron than nitrogen-14
Which elementary particle is found orbiting outside the nucleus of an atom?
Electrons
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called _____.
isotopes
Interpret the chemical formula 6H2O.
Six molecules of H2O
Glucose has a chemical formula of C6H12O6. What would be the proper way to identify two molecules of glucose?
2C6H12O6
Carbon-12 and carbon-13 have the same number of _____.
protons and electrons
If an element has an atomic number of 7 and an atomic mass of 15, that element has _____.
seven protons and eight neutrons
The value that identifies the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is the _____.
atomic mass
What type of elementary particles have negative charges?
electrons
Glucose has the chemical formula C6H12O6. Which element is not found in glucose?
Nitrogen
What type of elementary particles have positive charges?
Protons
A compound is a molecule composed of atoms of more than one type of element. Which of the following would be classified as compounds?
CO2
H2O
What elements are found in the compound NaCl?
Sodium Chlorine
What would be the expected number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 6?
6
For each of the functional groups shown, R represents the remainder of the molecule the functional group is part of.
Which functional group is called an amino group?

Differences in electronegativity lead to _____.
polarity
Which type of bond is formed when one atom loses one or more electrons and another atom gains those electrons?
Ionic
Which type of bond involves the interaction of atoms that carry full negative and full positive charges?
Ionic
Which element listed has the lowest abundance in living organisms?
Magnesium
The formation of which type of bond requires the presence of a catalyst called an enzyme in order to occur at a biologically relevant rate?
Covalent
The electronegativities of the most common elements in biology are as follows:
| |
Hydrogen | 2.1 |
Carbon | 2.5 |
Oxygen | 3.5 |
Nitrogen | 3.0 |
Which element above has the greatest attraction for electrons?
Oxygen
Which type of bond is created when atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons?
Covalent
Identify the most appropriate term for the molecule below.
amphipathic
Hydrogen is much less electronegative than nitrogen. In an N-H bond, the hydrogen would be _____.
partially positive
Which molecule possesses an ionic bond?
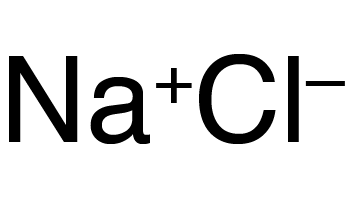
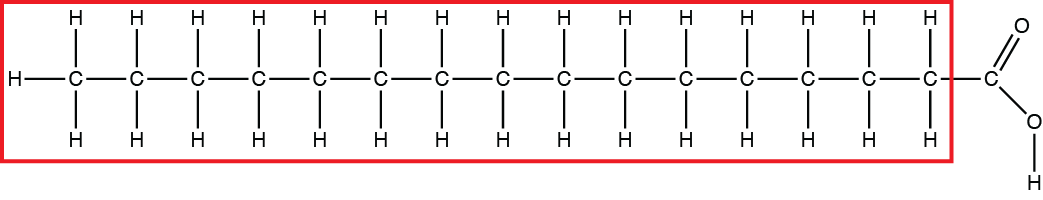
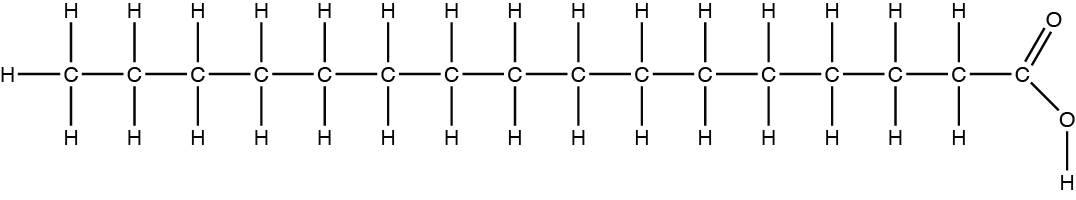
The portion of the fatty acid below bound by the red rectangle is _____.
hydrophobic
Which element listed has the lowest abundance in living organisms?
Calcium
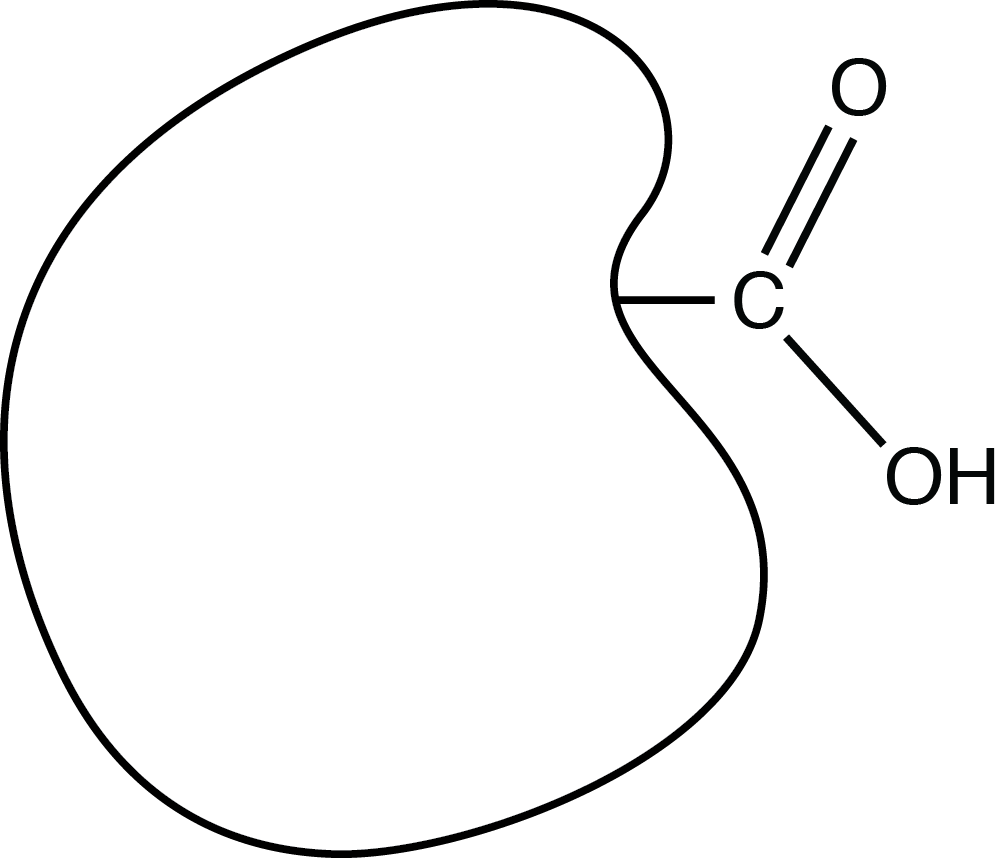
The shape below represents an organic (carbon-based) molecule with a functional group consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen:
The functional group is called a _____ group.
carboxyl
Recall that the primary elements in biology are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorous (P), and sulfur (S). C, H, P, and S have biologically similar electronegativities, while O and N are significantly higher than the others in electronegativity.
Which bond is least likely to demonstrate polarity (partial charge)?
C-H
The shape below represents an organic (carbon-based) molecule with a functional group consisting of oxygen and phosphorous:
The functional group is called a(n) _____ group.
phosphate
Bonds formed from the equal sharing of electrons are called _____.
nonpolar covalent
Bonds formed from the unequal sharing of electrons are called _____.
polar covalent
For each of the functional groups shown, R represents the remainder of the molecule the functional group is part of.
Which functional group is called a methyl group?
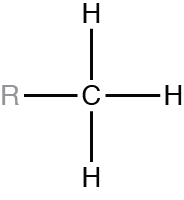
In what way do hydrogen bonds differ from covalent bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are the result of the weak attraction of the hydrogen in a polar bond with a more electronegative atom in another polar bond.
Which red arrow identifies a hydrogen bond?
For each of the functional groups shown, R represents the remainder of the molecule the functional group is part of.
Which functional group is called a hydroxyl group?
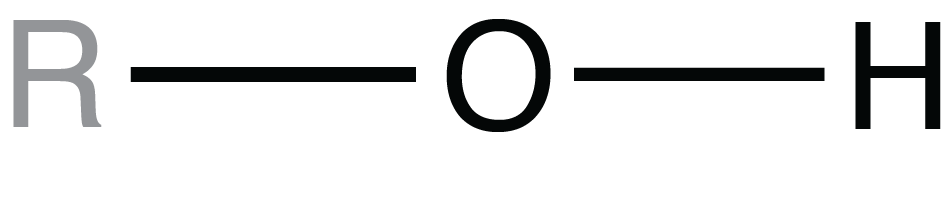
Covalent bonds are formed when _____.
a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms
When the pair of electrons in a covalent bond spend more time around one atom than the other, this is due to a difference in _____ between the two atoms.
electronegativity
Which of the covalent bonds shown is a polar covalent bond?
O-H
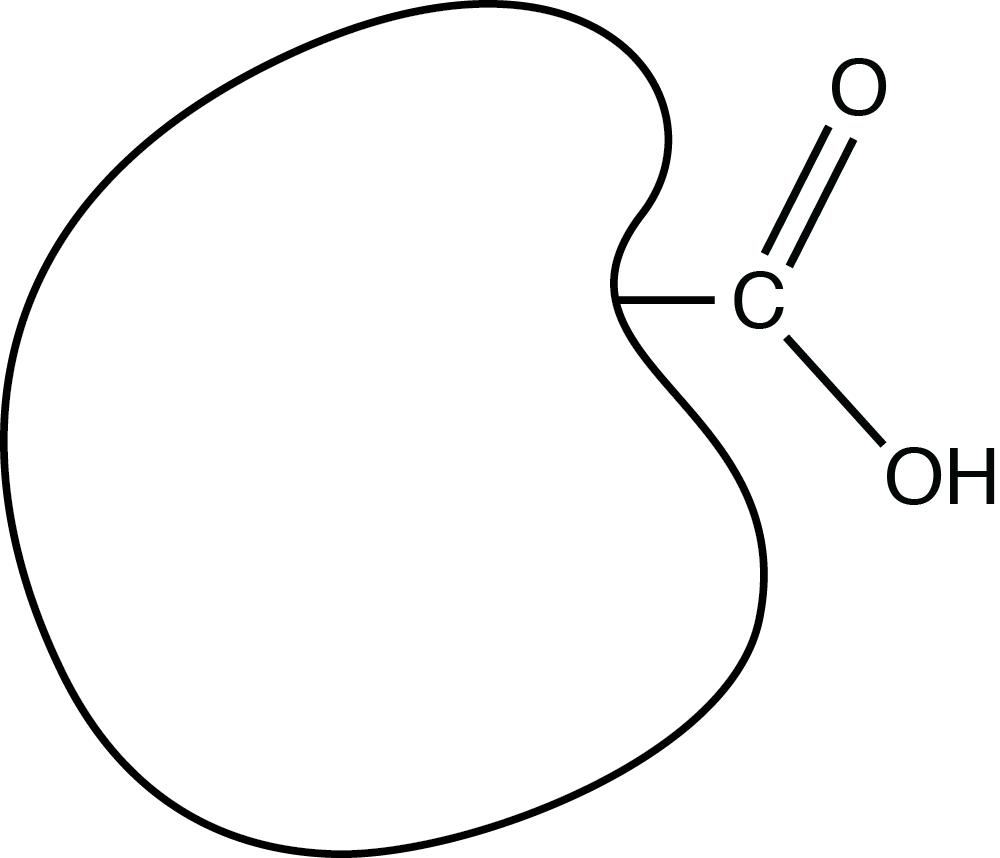
The shape below represents an organic (carbon-based) molecule with a functional group consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen:
The functional group is called a _____ group.
carboxyl
Which element listed has the highest abundance in living organisms?
Carbon
The human body is composed primarily of _____.
water
Water exists in three states, solid, liquid, and gas. Identify the state(s) where hydrogen bonding occurs among water molecules.
liquid and solid
The evaporation of sweat cools skin because of the _____ of water.
high heat of vaporization
Identify the property that describes the attraction of water molecules to molecules other than water.
Adhesion
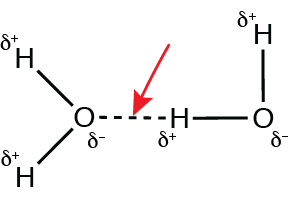
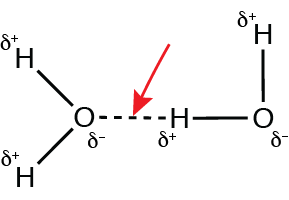
The figure below represents two water molecules interacting with each other:
What type of bond is identified by the red arrow?
Hydrogen bond
When a narrow glass tube is placed in a beaker of pure water, what will happen?
The water will rise in the tube above the level of the water in the beaker
When NaCl (table salt) is dissolved in water, _____ is the solvent and _____ is the solute.
water, NaCl
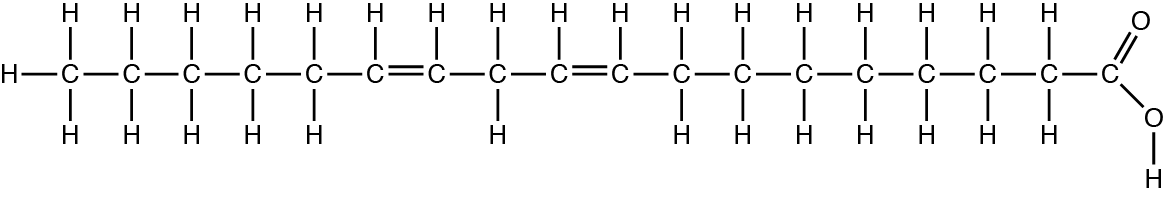
The figure below is linoleic acid, a common fatty acid in sunflower oil:
If drops of sunflower oil are placed into a beaker of water, what is most likely to happen? (Hint: the electronegativity value of carbon is 2.5 and the electronegativity value of hydrogen is a biologically-similar 2.1)
The droplets of oil will accumulate in the center of the beaker of water and form a layer dividing the water in half.
The curved surface of water in a clean glass tube is due to _____.
the high surface tension of the water
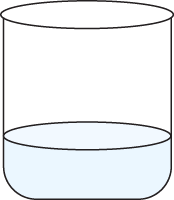
Both beakers below contain pure water. The beaker on the left contains 500 ml of water, and the beaker on the right contains 200 ml of water:
The specific heat of the water in the beaker on the left is _____ the specific heat of the water in the beaker on the right.
the same as
Identify the property that describes the attraction of water molecules to other water molecules.
Cohesion
Which molecule would be insoluble in water?
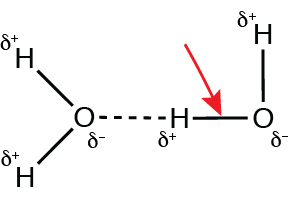
The figure below represents two water molecules interacting with each other:
What type of bond is identified by the red arrow?
Polar covalent bond
The substance in a solution which is dissolved into the other substance is called the _____.
solute
When oil and water are mixed, why do they immediately begin to separate?
Oil is mostly hydrophobic, and will not dissolve into the water by forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Why does ice float on water?
Ice floats because water molecules in ice are further apart than water molecules in liquid water, and thus less dense.
The substance in a solution which dissolves the other substance is called the _____.
solvent
In a molecule of water, the oxygen is _____ and the hydrogens are _____.
partially negative, partially positive
The evaporation of sweat cools skin because of the _____ of water.
high heat of vaporization
What property of water allows it to moderate the temperature of the Earth?
High specific heat
An insect's ability to walk on water is due to what property of water?
High surface tension
Cohesion in mercury is higher than cohesion in water. If mercury is placed in one container and an equal volume of water is placed in a second container, what is the relationship between the distance traveled for each in similar sized capillary tubes place in the respective containers?
Water will travel a greater distance than mercury.
Which factor or factors contribute to the movement of water from the roots of a tree to the leaves?
Adhesion, capillary action, and cohesion
When a drop of water is placed carefully on a microscope slide, it forms a bead-like drop instead of flattening to a thin layer. This is due to the _____ of the water molecules.
cohesion
Which statement about water is correct?
Water has cohesive properties
A solution with a pH of 2 has a proton concentration _____ than a solution with a pH of 4.
100 times higher
In an aqueous solution, the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+] times the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH–] equals _____.
10–14 M
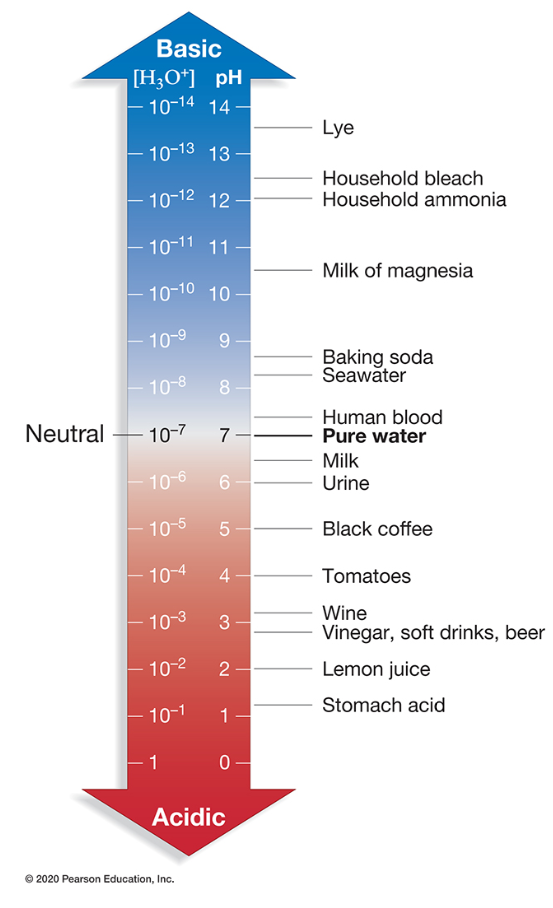
Which substance is the most acidic?
Tomatoes
Every unit on a pH scale represents what change in hydrogen ion concentration?
10-fold
A substance that donates hydrogen ions in solution is referred to as a(n) _____.
acid
A substance with a pH value of 8.5 is _____.
basic
Buffers are commonly _____.
weak acids
For simplicity, hydrogen ions are represented as H+. What is a more chemically accurate representation of hydrogen ions in pure water?
H3O+
A substance with a pH value of 4.5 is _____.
acidic
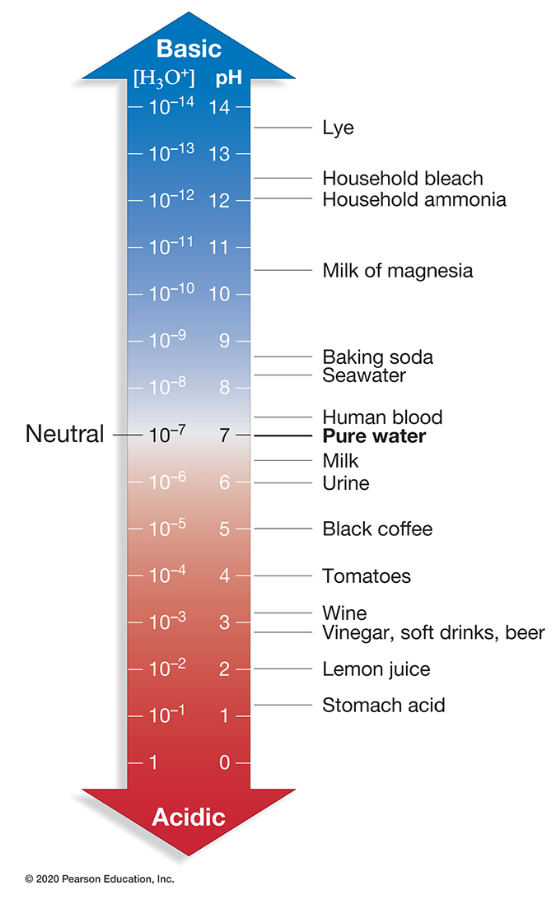
What substance has a hydrogen ion concentration of 10–2 M?
Lemon juice
What is the pH of a solution with a proton (H+) concentration of 0.1 M?
1
A base can reduce the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution by _____.
directly accepting hydrogen ions
releasing hydroxide ions which combine with hydrogen ions to form water
What is the reason that NaCl is not considered an acid when it dissolves in water?
No hydrogen ions are released into the solution.
A solution with a pH of 8 has a proton concentration _____ than a solution with a pH of 5.
1,000 times lower
A solution with a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) _____.
is an acid and has a low pH
Identify the correct statement(s) about a hydronium ion.
It is one of the products of the dissociation of water in solution
It has a formula of H3O+
What is the H3O+ concentration of pure water?
10–7 M
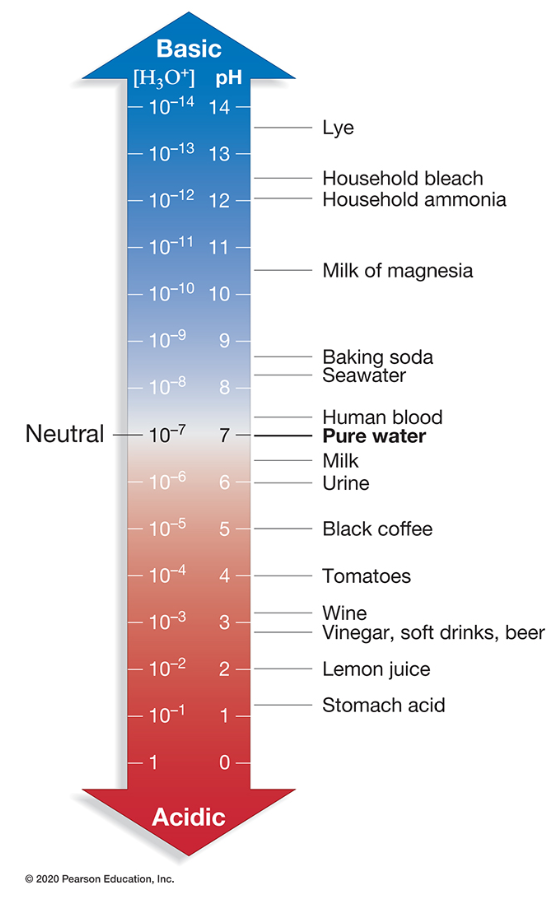
What is the hydrogen ion concentration of household ammonia?
10-12 M
Which substance has an equal concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions?
Pure water
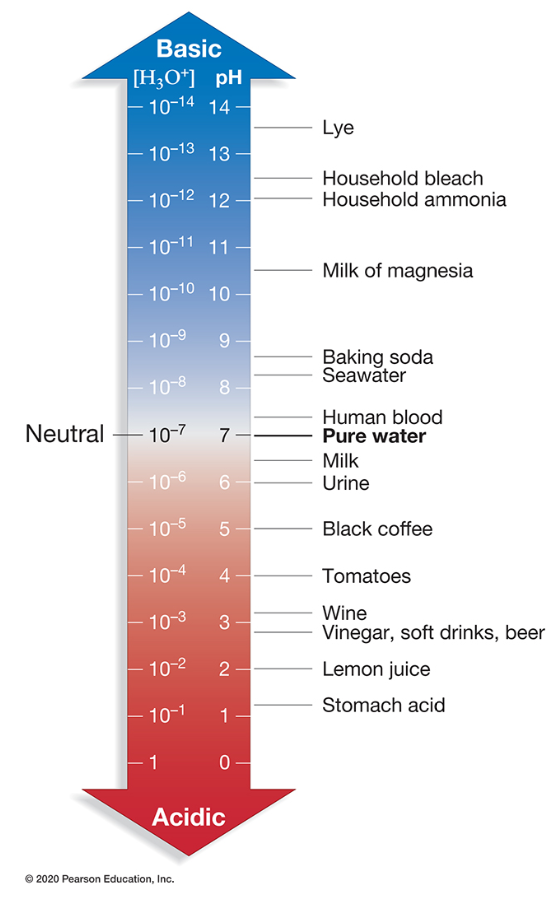
Baking soda has a hydrogen ion concentration _____ than lye.
105 times higher