DLA 3: DNA Packaging/Supercoiling and Telomerase
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How does DNA packaging occur in Prokaryotes?
DNA Supercoiling
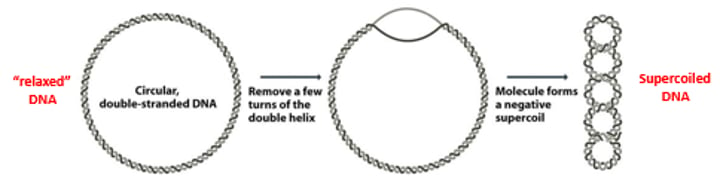
Prokaryotic DNA supercoiling is accomplished by the action of what 2 enzymes and association with what proteins?
1- DNA Topoisomerase I
2- DNA gyrase
Hu proteins
What is the structure of a Bacterial nucleoid?
Supercoiled DNA loops are attached to a protein core
the protein core contains: Topoisomerase I, DNA gyrase and Hu proteins
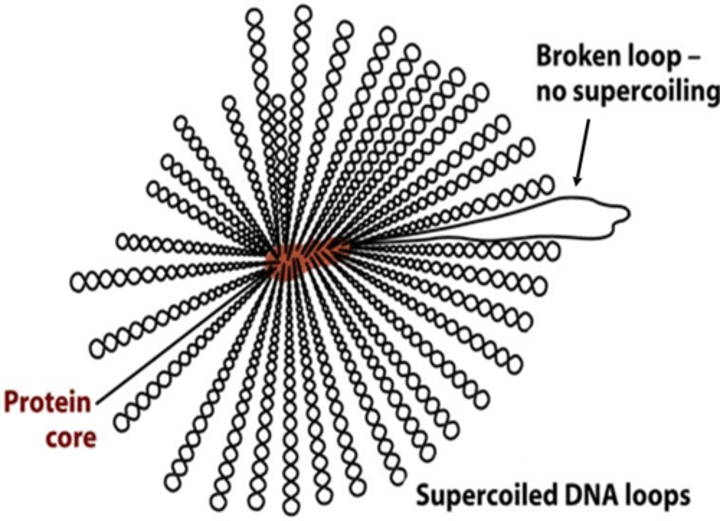
What are the main function of Supercoiling of DNA?
Compacts the DNA so that it can be packaged into the cell
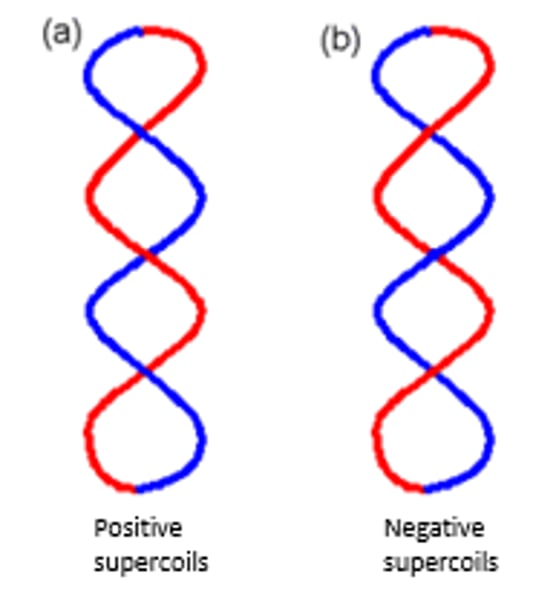
What does Negative supercoiling promote?
Strand separation ie DNA replication
When are Positive supercoils introduced? What effect do they have?
During DNA replication and transcription
Positive supercoiling makes DNA strand separation more difficult
image: a) Positive supercoils (the front segment of a DNA molecule cross over the back segment from left to right). (b) Negative supercoils
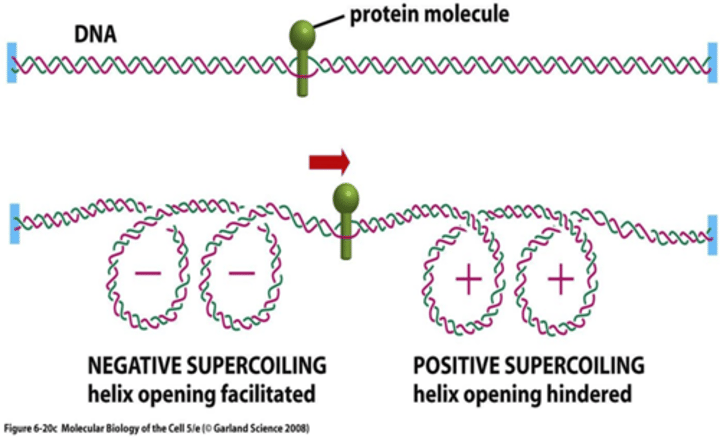
Where are Positive supercoils introduced? Negative supercoils? What corrects these supercoilings?
Ahead of the protein
Behind the protein
Topoisomerase I and DNA gyrase
What is an example of a drug that inhibits DNA gyrase?
Cirprofloxacin
prescribed as an antibiotic
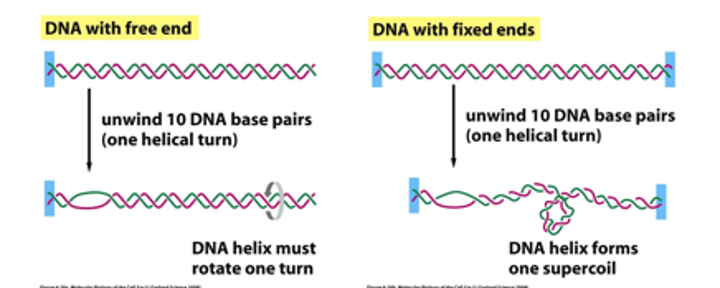
Supercoiling can be relieved in a DNA double helix containing what? What is the issue with this?
A free end by rotation of the entire molecule
most DNA molecules do not contain a freely rotating end as DNA molecules in the cell are often associated and bound to various matrix or scaffold proteins
As a result DNA supercoiling is a common phenomenon
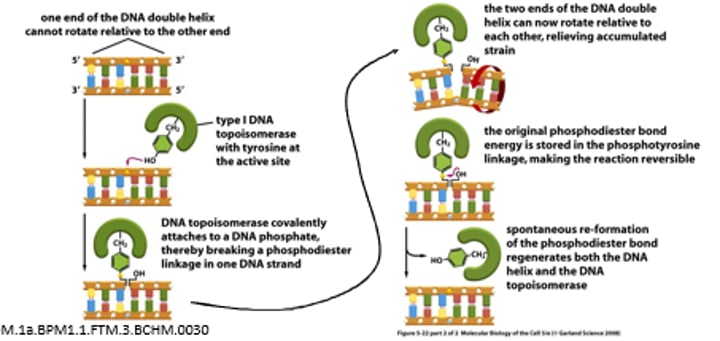
What is the MOA of Topoisomerase I ?
1- Forms a single covalent bond with the DNA and breaking a phosphodiester bonds in one DNA strand
2- The two ends of the DNA double helix can now rotate relative to each other, relieving accumulated strain
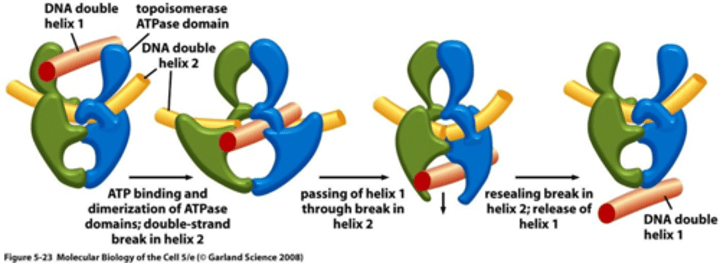
When is DNA Gyrase (Topoisomerase II) activated? Does it require energy?
When 2 double helices cross over each other
Yes, this reaction requires ATP hydrolysis
What is the MOA of DNA gyrase in relieving strain?
1- DNA gyrase makes a covalent linkage to both strands of one DNA helix and making a double stranded break
2- The second DNA helix is passed through the break
3- The break is resealed and the enzyme dissociates
What are the 3 main functions of Chromatin?
1- Packaging of DNA to allow the genome to fit inside the eukaryote
2- Maintain the structure of chromosome during metaphase and protect it from damage
3- Regulate gene expression by making regions of the genome accessible to transcription (uncondensed DNA) or repressing transcription by forming a condensed DNA structure and making that region of the genome inaccessible to the transcriptional machinery.
What are the 2 main types of chromosomes based on chromosome staining properties?
1- Heterochromatin
- Condensed
- stains dark
- transcriptionally inactive
2- Euchromatin
- Uncondensed
- stains light
-transcriptionally active
What components make up the structure of the Nucleosome? What is the Nucleosome core made up of?
Histone protiens + DNA
Octamer: 2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3 and 2 H4 histone proteins
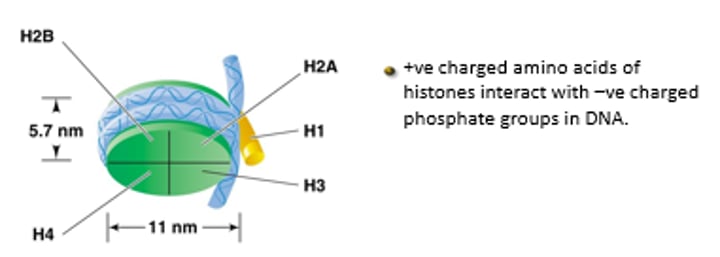
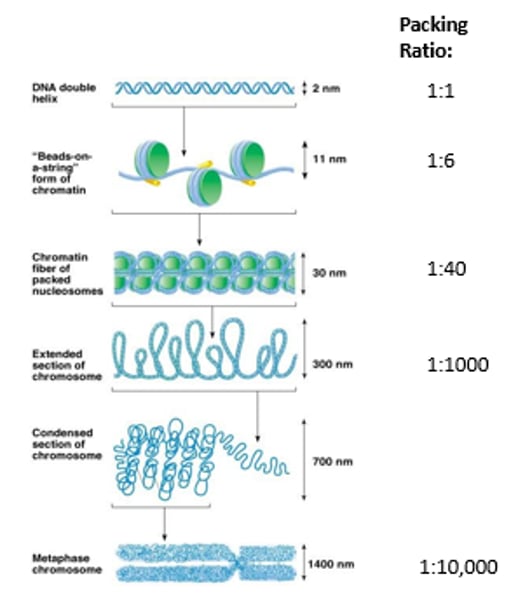
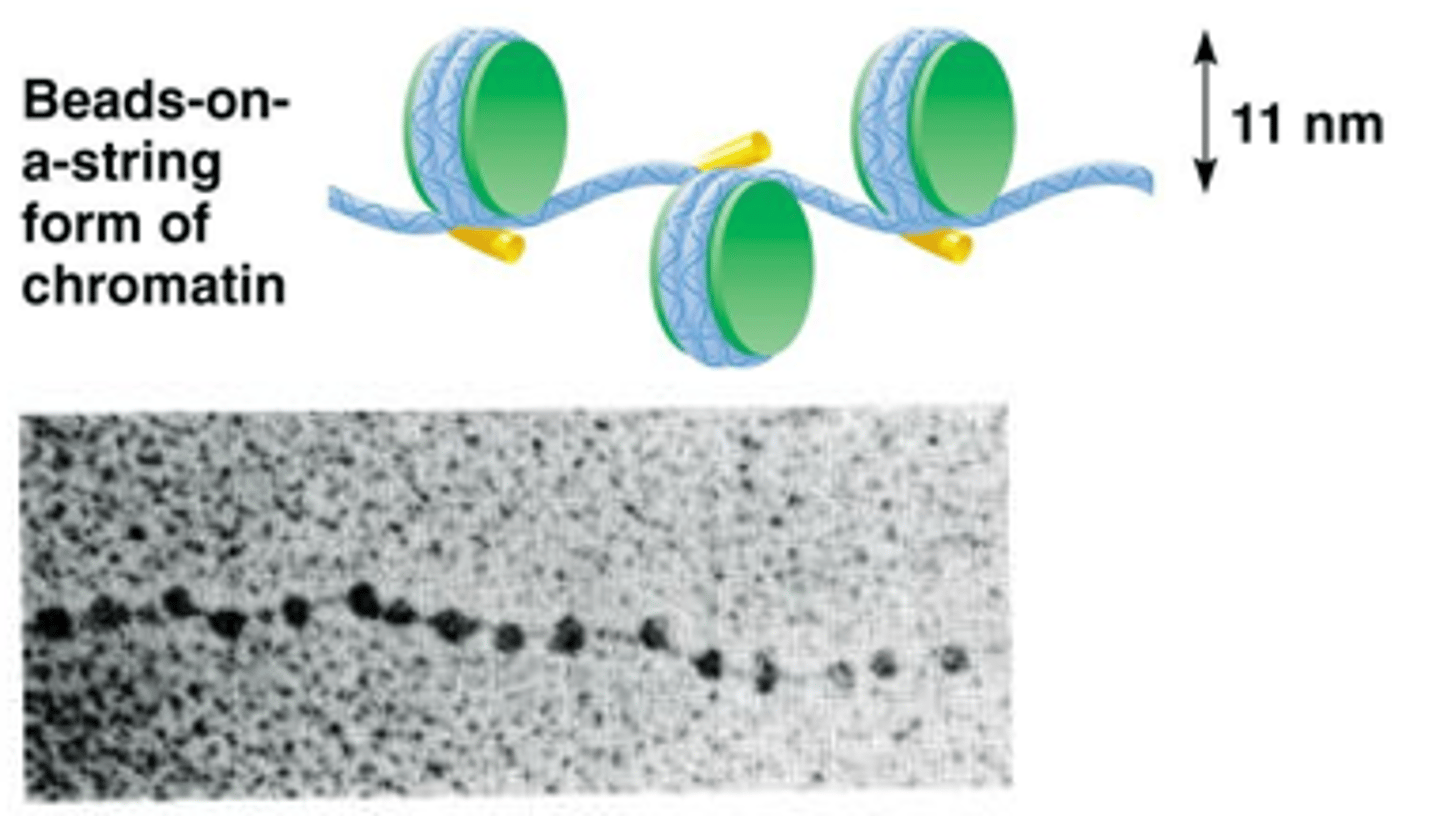
What are Nucleosomes connected together by? What structure do they produce?
Linker DNA and H1 protein
Beads on a string (11nm)- more condensed chromatin
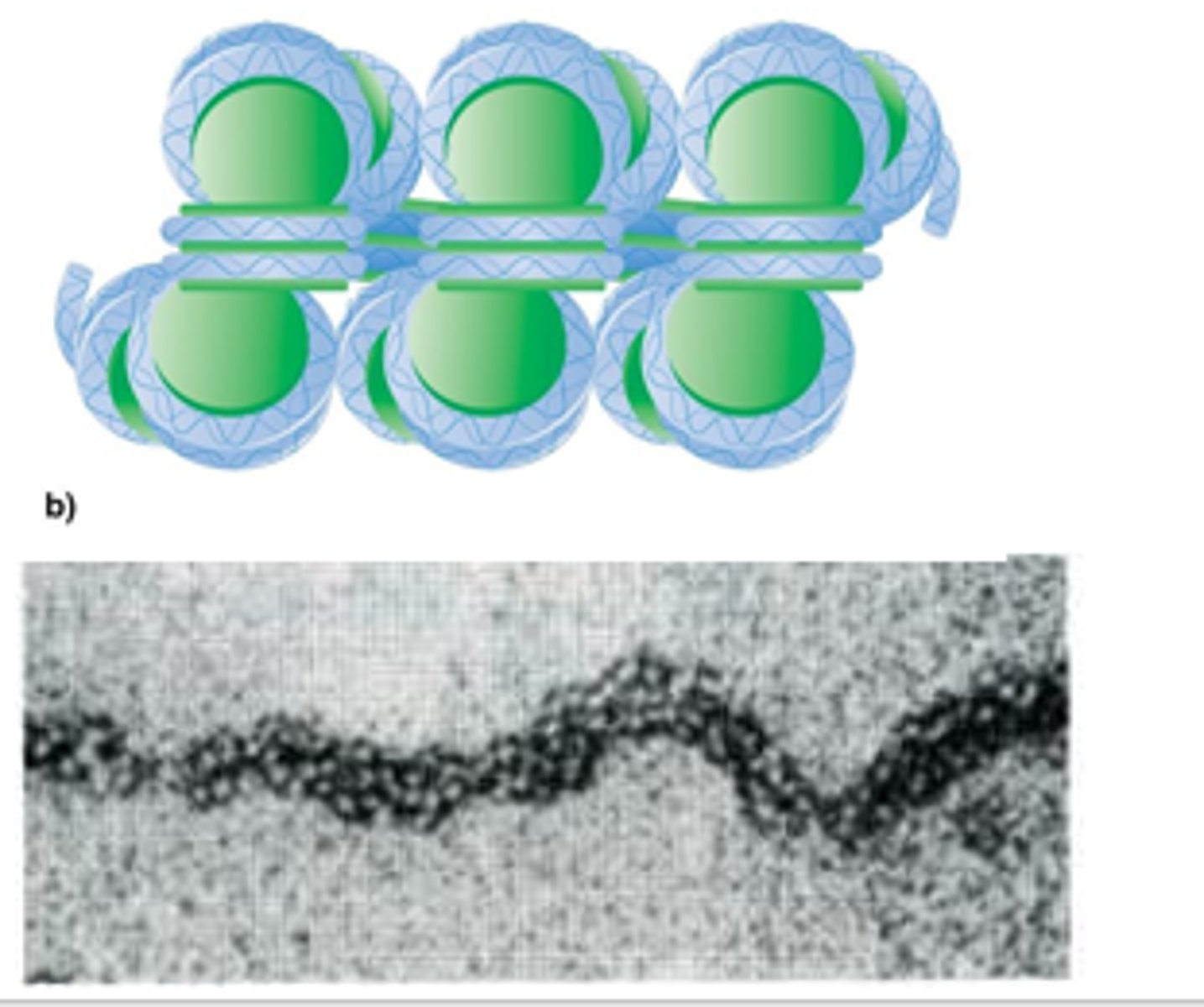
Nucleosomes can associate closer to each other and form what? This structure results from interactions between?
30 nm fiber
Adjacent histone H1 proteins
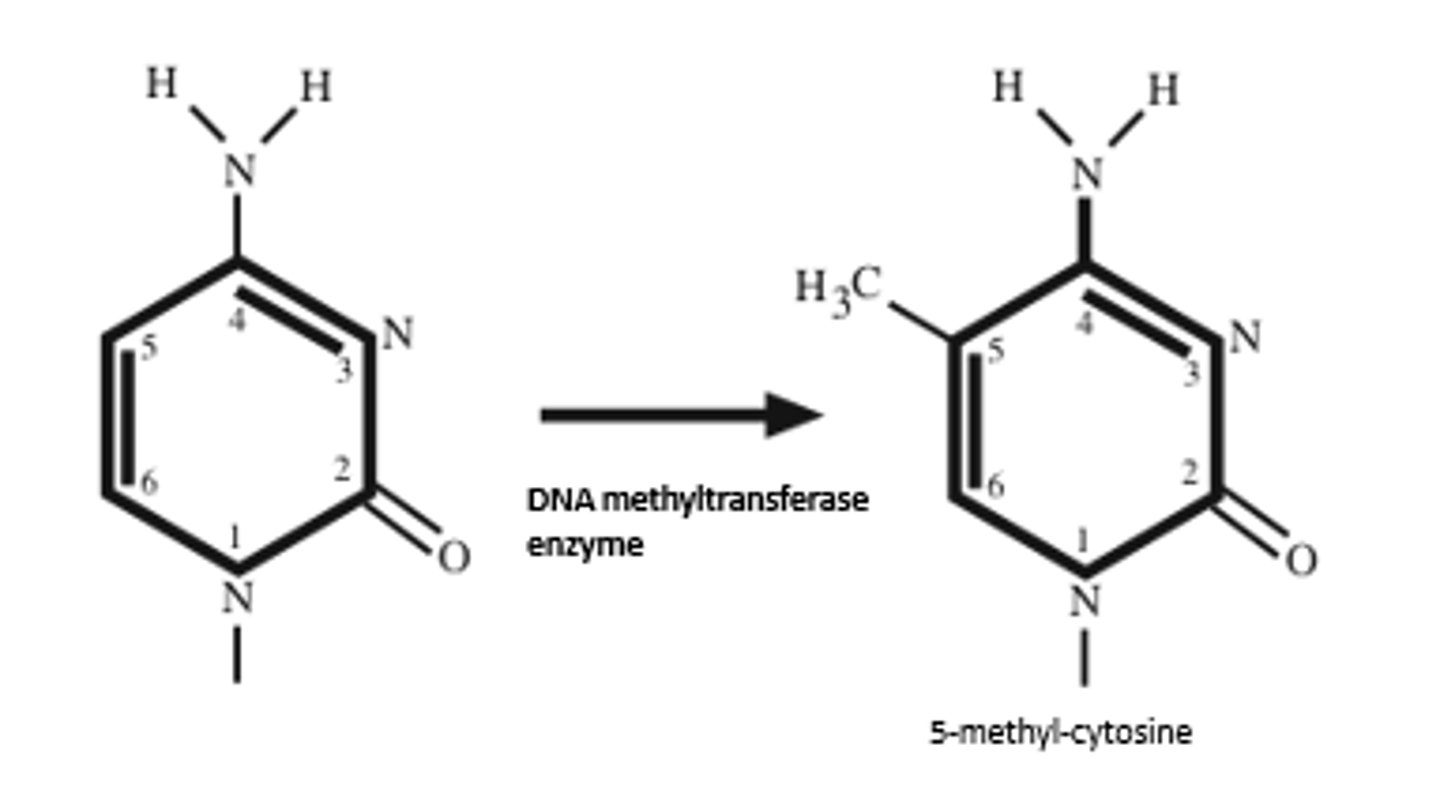
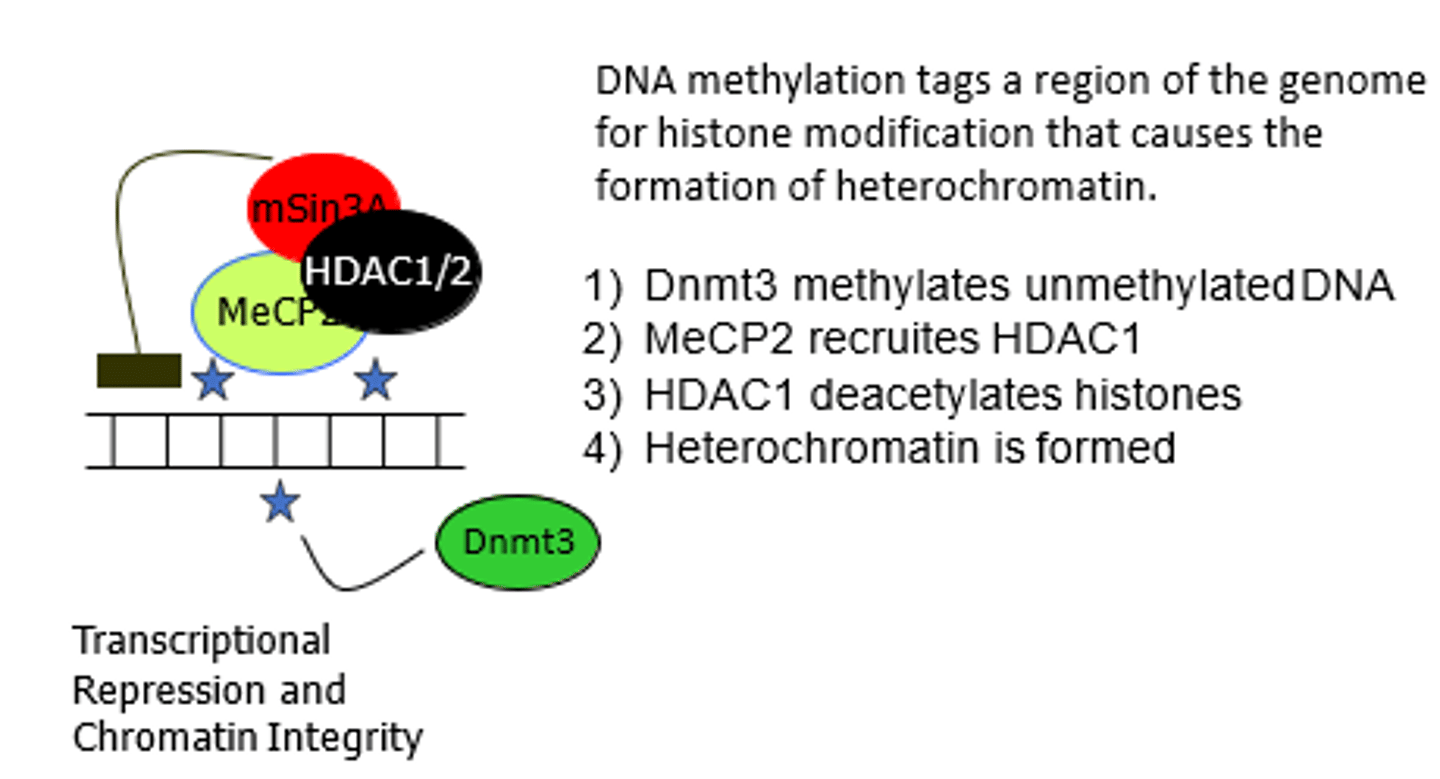
What is one of the main steps involved in formaiton of Heterochromatin?
DNA Methylation
DNA methylation tags a region of the genome for histone modification that causes the formation of heterochromatin.
What are the steps involved in the formation of Heterochromatin?
1- Dnmt3 (DNA methyltransferase) methylates (adds methyl groups) DNA
2- MeCP2 protein recruites HDAC1 enzyme complex
3- HDAC1 deacetylates histones
4- Heterochromatin is formed
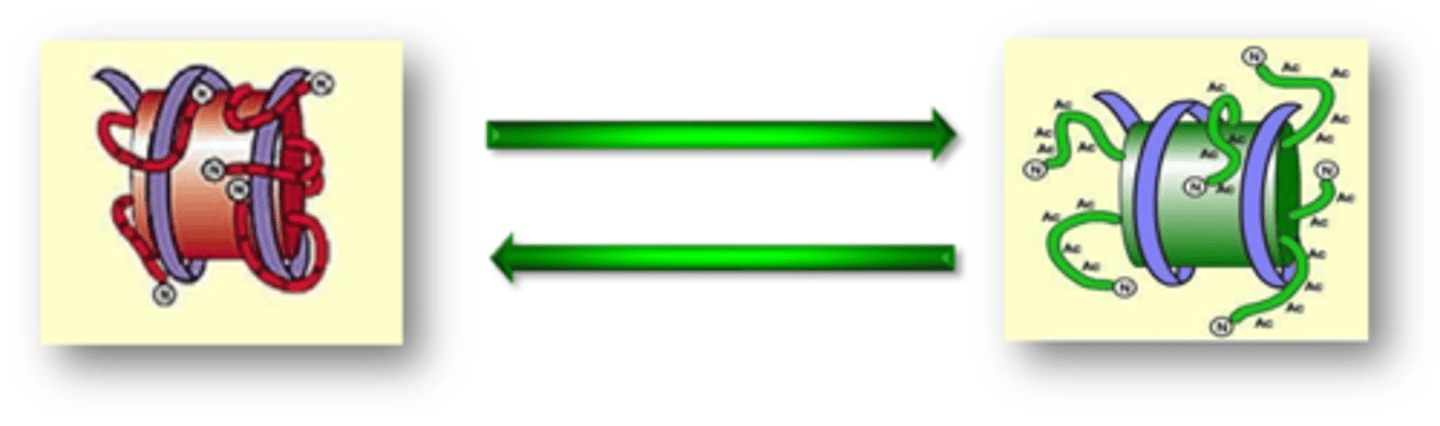
What effect does Histone Acetylation have ?
Reduces affinity between histone and DNA by removing positive charges and thus increases transcription
What is the difference between Deacetylnucleosome and Acetylated nucleosome?
Nucleosome is more tightly associated with the DNA reducing access to the DNA (heterochromatin = notranscription
A more 'open' conformation
is achieved, facilitating access
to DNA (euchromatin = potential for transcription)
What is Telomerase? Function?
An enzyme that adds bases to the ends of telomeres; abundant in young cells but eventually runs out.
What is a telomere and what is its function?
Repetitive DNA at the end of a eukaryotic chromosome
Protects the messages of the DNA from being destroyed during DNA replication.
What is Telomerase?
Enzyme responsible for maintenance of the length of telomeres by addition of guanine-rich repetitive sequences
What enzyme has the ability to synthesize DNA using RNA as a template?
Telomerase
since it has reverse transcripase (retrovirus) activity