Transportation and Respiration - Part 2: The Heart and Lungs
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
The Anatomy of the Heart
The septum is a thick wall of muscle that separates the left and right ventricles.
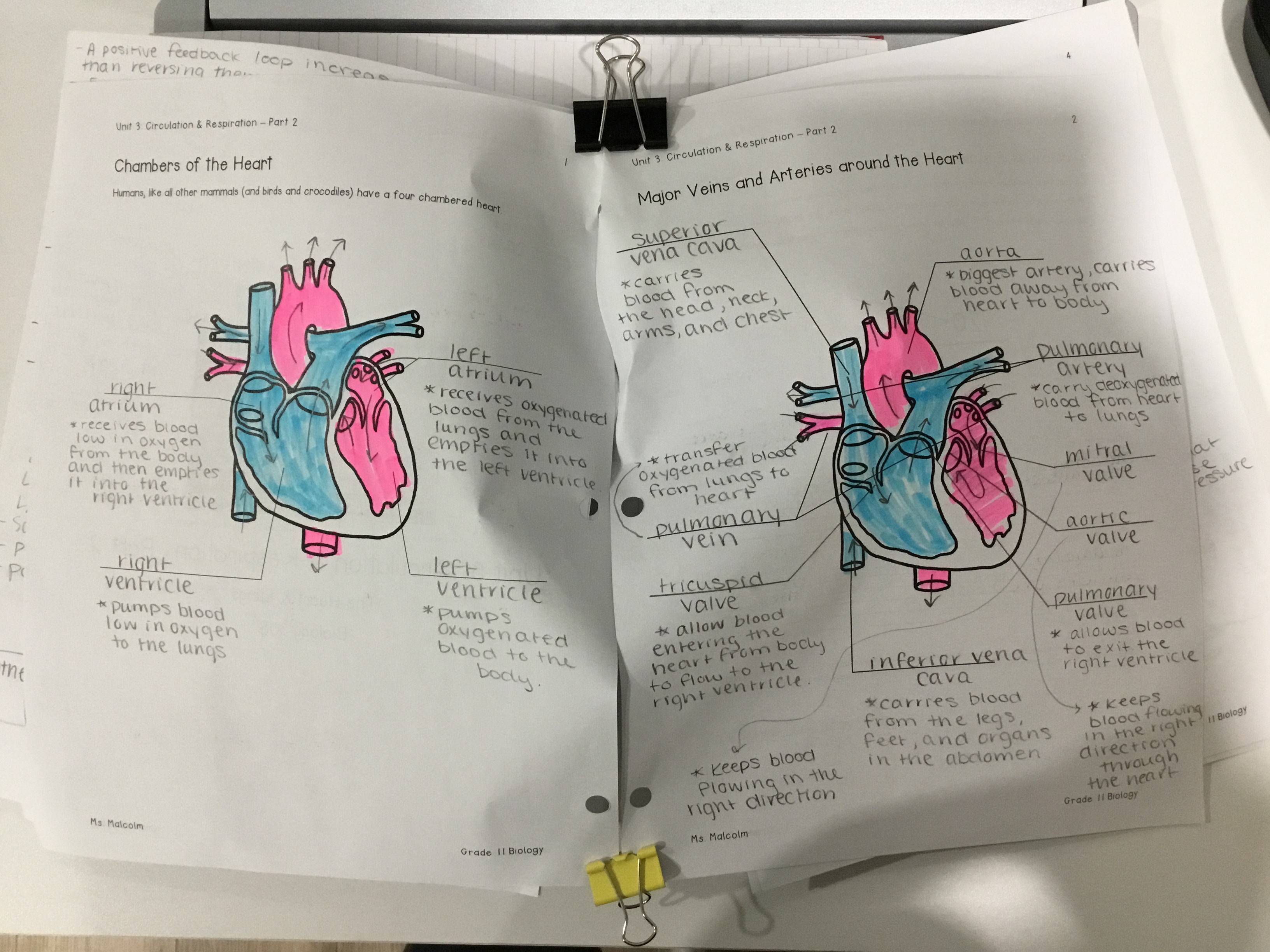
2
New cards
How is blood pressure measured?
Blood pressure is read as a relationship between two numbers: systolic (top) and diastolic (bottom) pressure. The units for blood pressure are mmHg, which stands for “millimeters mercury.”
3
New cards
Diastolic Pressure Definition
The amount of pressure the blood exerts on the walls of the arteries when the ventricles are relaxed.
4
New cards
Systolic Pressure Definition
The amount of pressure the blood exerts on the walls of the arteries when the ventricles contract.
5
New cards
What are some causes of high blood pressure?
Obesity / being overweight, genetic factors, not enough physical activity, age, and a diet high in salt.
6
New cards
What are some causes of low blood pressure?
Pregnancy, heart conditions, dehydration, blood loss, tobacco use, and too much alcohol.
7
New cards
Hypertension Definition
High blood pressure.
8
New cards
Hypotension Definition
Low blood pressure.
9
New cards
What is a stroke / what causes a stroke?
Strokes happen when __blood flow (oxygen supply) is cut off to an area of the brain__, causing it to become damaged or cause brain cell death in that area.
This can either happen if __a clot forms in a capillary in the brain__ or __moves to a capillary in the brain__ from another area of the body, or if a __capillary bursts in the brain__.
This can either happen if __a clot forms in a capillary in the brain__ or __moves to a capillary in the brain__ from another area of the body, or if a __capillary bursts in the brain__.
10
New cards
What stroke risk factors can you control?
Things that cause strokes but you can change are high blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, birth control, alcohol, and weight.
11
New cards
What stroke risk factors are out of your control?
Age, gender, ethnic origin, family history, and prior strokes / mini strokes.
12
New cards
What is moved around your body by the circulatory system?
Oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the cells.
Carbon dioxide, nitrogenous wastes, and hormones away from the cells.
Carbon dioxide, nitrogenous wastes, and hormones away from the cells.
13
New cards
How does the circulatory system maintain homeostasis?
By carrying __nutrients to cells__, carrying __wastes away from cells__, carrying __hormones from cells in one part of the body to the target tissues__, __distributing heat__ throughout the body, __maintaining body fluid levels__, and __providing defense__ against invading organisms.
14
New cards
What is bloodletting / phlebotomy?
Bloodletting is a process where __“bad blood” is removed from a person’s body to cure illnesses__ like fevers, coughs, headaches, inflammations, and hemorrhages.
Doctors thought that the drained blood could be replaced within a few hours by new, healthy blood.
Doctors thought that the drained blood could be replaced within a few hours by new, healthy blood.
15
New cards
Why is bloodletting bad?
It drops blood volume, which lowers blood pressure. The low blood pressure messes up transport systems and homeostasis because your body will not be able to transport things like nutrients, oxygen, etc. to the parts of the body that need it, which can cause death.
16
New cards
The Anatomy of the Lungs
\
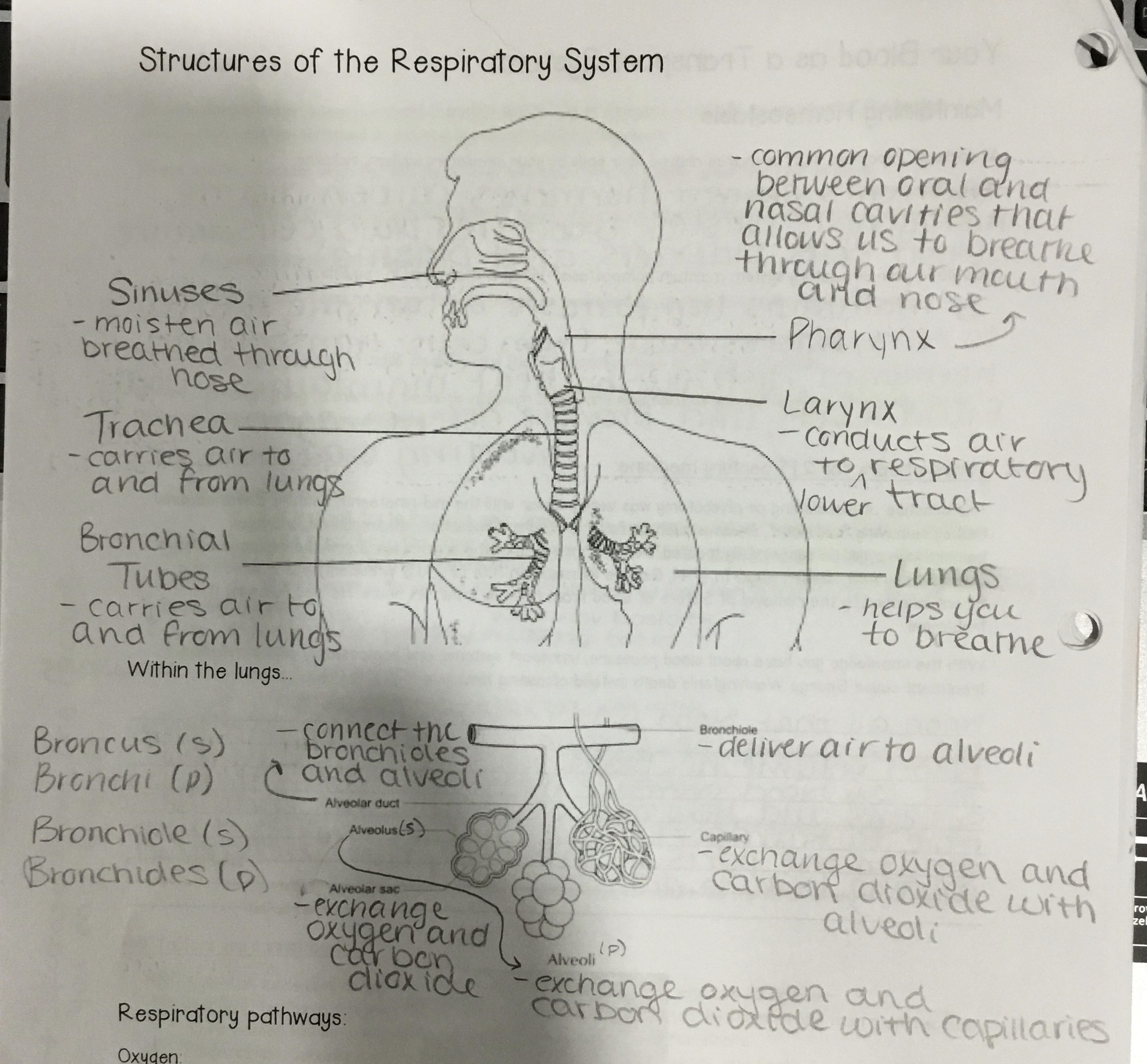
17
New cards
Respiratory Pathways for Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
\

18
New cards
Why do we need to breathe?
Your cells need oxygen to create energy. This energy is used to complete all sorts of vital functions in your body.
19
New cards
How does oxygen get into body cells?
The capillaries take oxygen from the alveoli in the lungs, and it is transported to the heart, then sent out to all parts of the body, where the capillaries pass it to the cells through diffusion.
20
New cards
How is carbon dioxide removed from the lungs?
The capillaries pick up carbon dioxide from cells throughout the body, which passes through the heart and into the lungs. Capillaries in the lungs pass carbon dioxide to the alveoli and you breathe it out.
21
New cards
External Respiration Definition
__Breathing__: When oxygen is taken from the external environment and carbon dioxide is returned to the external environment. Includes the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide into/out of the bloodstream with the alveoli.
22
New cards
External Respiration Word Equation
carbon dioxide ⟺ oxygen
23
New cards
External Respiration Chemical Equation
CO2 ⟺ O2
24
New cards
Internal Respiration Definition
__Gas Exchange__: The process of transferring oxygen from the blood to the cells of the body and carbon dioxide back into the blood. It occurs between the capillaries and cells of the body and involves diffusion.
25
New cards
Internal Respiration Word Equation
carbon dioxide ⟺ oxygen
26
New cards
Internal Respiration Chemical Equation
CO2 ⟺ O2
27
New cards
Cellular Respiration Definition
__Aerobic Respiration__: The process in cells that uses glucose and oxygen to create energy that is used to complete functions in the body. Carbon dioxide is a waste product of this process.
28
New cards
Cellular Respiration Word Equation
glucose + oxygen ⇒ carbon dioxide + water + ATP
29
New cards
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation
C6H12O6 + O2 ⇒ CO2 + H2O + ATP
30
New cards
Diagram of External, Internal, and Cellular Respiration
\
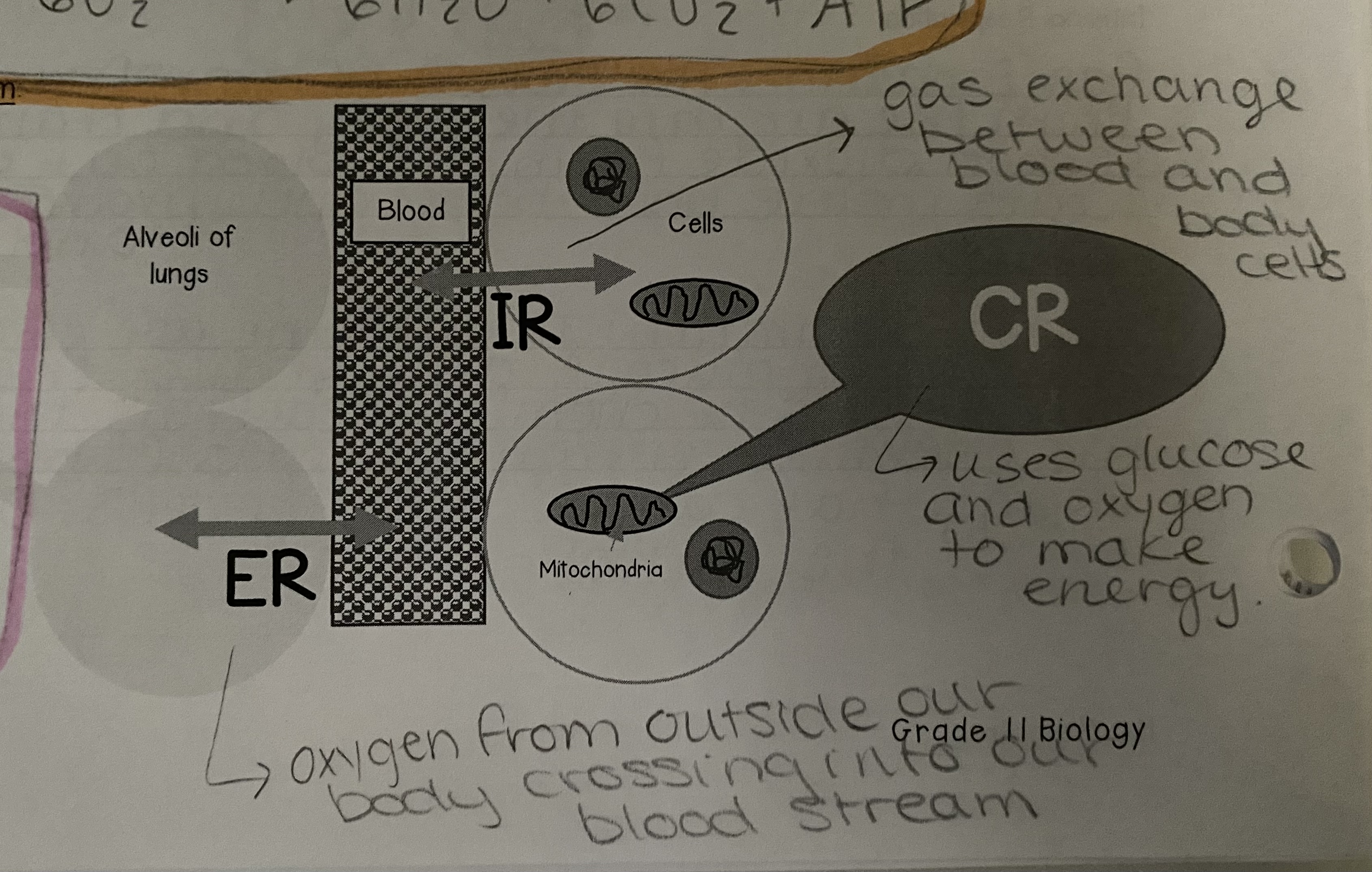
31
New cards
What is negative pressure?
Negative pressure is when the diaphragm contracts, increasing the volume of the chest cavity. This increase of volume lowers the air pressure in the lungs to below atmospheric pressure, creating a vacuum (inhalation).
32
New cards
What is inspiration?
When your diaphragm contracts, and at the same time the intercostal muscles contract to move your ribs up and out. This pulls at your lungs, forcing them to expand, and creating a negative pressure inside of them, which sucks in air from the outside.
33
New cards
What is expiration?
When your diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, your chest cavity shrinks, squishing the air out of your lungs and expelling it through your oral and nasal cavities.
34
New cards
Diagram of Inspiration and Expiration
\
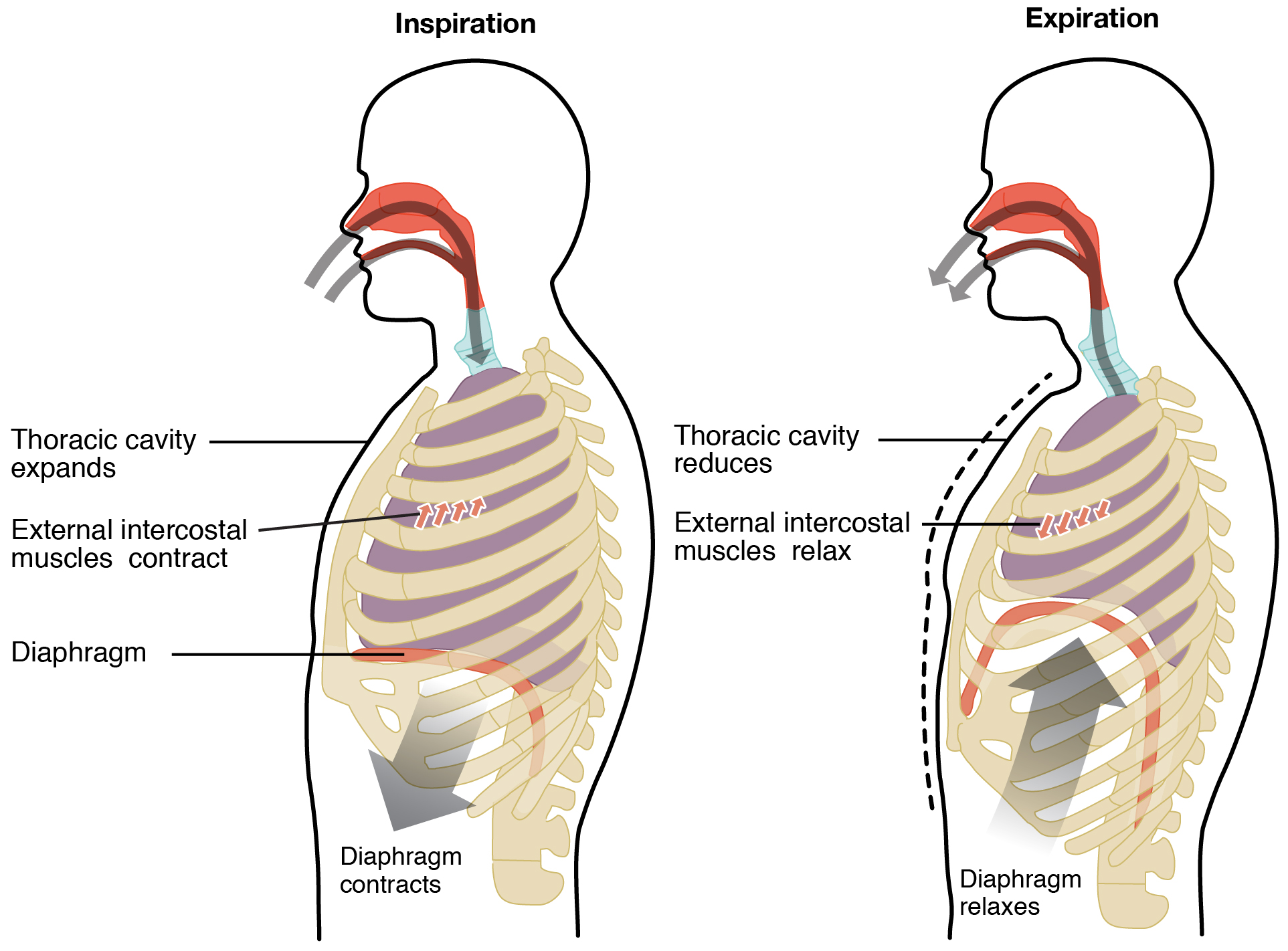
35
New cards
What is your diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a dome shaped muscle that contacts when you inhale.
36
New cards
Breathing Negative Feedback Loop
\
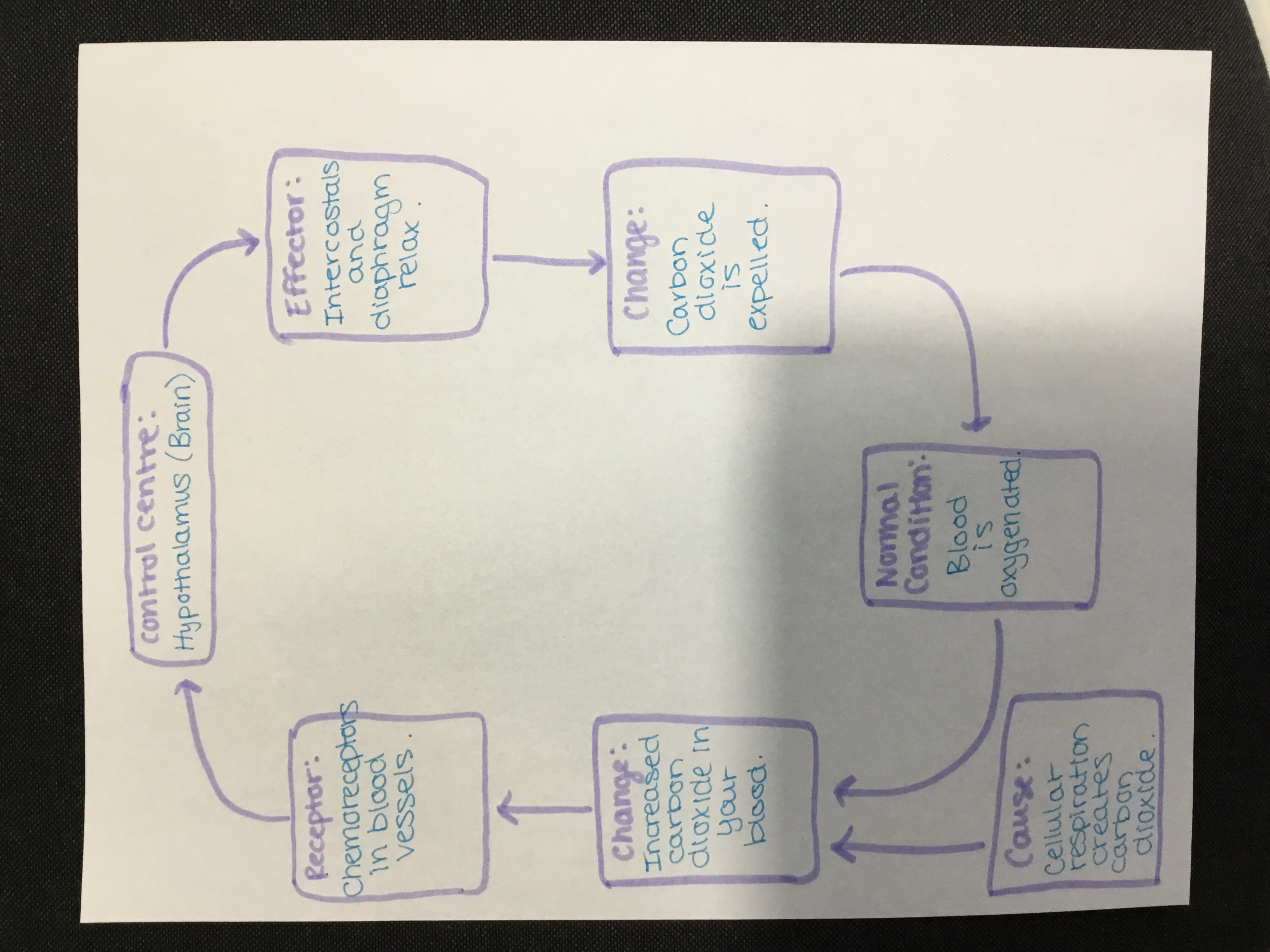
37
New cards
Where in the cell does cellular respiration happen?
The mitochondria.
38
New cards
What is the normal range for blood pressure?
Between 120/80mmHg and 140/90mmHg.
39
New cards
What device measures blood pressure?
A sphygmomanometer.
40
New cards
Where in your body is your blood pressure the highest?
In the __aorta__ (the left ventricle in the heart has a higher pressure, but blood pressure is defined as the pressure on the arteries, so it is not included).
41
New cards
Why is it important to know your blood pressure?
Because __high blood pressure__ greatly increases your risk of heart disease and stroke.
On the contrary, even __moderate forms of low blood pressure__ can cause dizziness, weakness, fainting, and an increased risk of injury.
__Severely low blood pressure__ can deprive your body of enough oxygen to carry out its normal functions, leading to damage to your heart and brain.
On the contrary, even __moderate forms of low blood pressure__ can cause dizziness, weakness, fainting, and an increased risk of injury.
__Severely low blood pressure__ can deprive your body of enough oxygen to carry out its normal functions, leading to damage to your heart and brain.
42
New cards
Capillaries, Veins, and Arteries Flow Chart
\

43
New cards
Aorta Definition
The largest artery in the body.
44
New cards
Pleura Definition
A membrane that envelops each lobe of the lungs.
45
New cards
Intercostal Muscles Definition
The muscles between the ribs that help with breathing.
46
New cards
Blood Pressure Definition
The amount of pressure exerted on the walls of your arteries by your blood.
47
New cards
Homeostasis Definition
The maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions even though external conditions constantly change; __balance__.
48
New cards
Negative Feedback Definition
Any change or deviation from the normal range of function is opposed or resisted.
49
New cards
Positive Feedback Definition
A system that does not regulate itself and instead builds upon itself, increasing the current condition.
50
New cards
Aerobic Definition
Uses oxygen.
51
New cards
Anerobic Definition
Does not use oxygen.
52
New cards
Respiration Definition
A process that takes place in all living cells of an organism where they produce energy by intake of oxygen and liberation of carbon dioxide. Therefore, __anything that has cells respires__.
53
New cards
Thorax Definition
The part of the body between the neck and the abdomen; the chest.
54
New cards
Interpleural Fluid Function
Reduces the friction between the lungs and the thoracic wall during breathing.
55
New cards
What colour is deoxygenated and oxygenated blood?
__Deoxygenated blood is a dark red / deep rust colour__. It only looks blue in your veins because your skin has a yellow tint.
__Oxygenated blood is a brighter red colour.__
__Oxygenated blood is a brighter red colour.__
56
New cards
How thick are the membranes of the alveoli and capillaries?
__One cell__. This is to allow for gas exchange (diffusion).
57
New cards
What triggers you to take a breath?
When the chemoreceptors in your body sense that __your blood pH level is too low (acidic) because you have too much carbonic acid in your blood__ and you need to get rid of it.
58
New cards
What is your trachea made of and why?
Your trachea is made of __cartilage__. This is because __it needs to be flexible__ so it does not break and puncture your lungs or heart, __but also strong__ so you do not suffocate when you lay down or go underwater.