Bio 132 - Urinary System Part 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
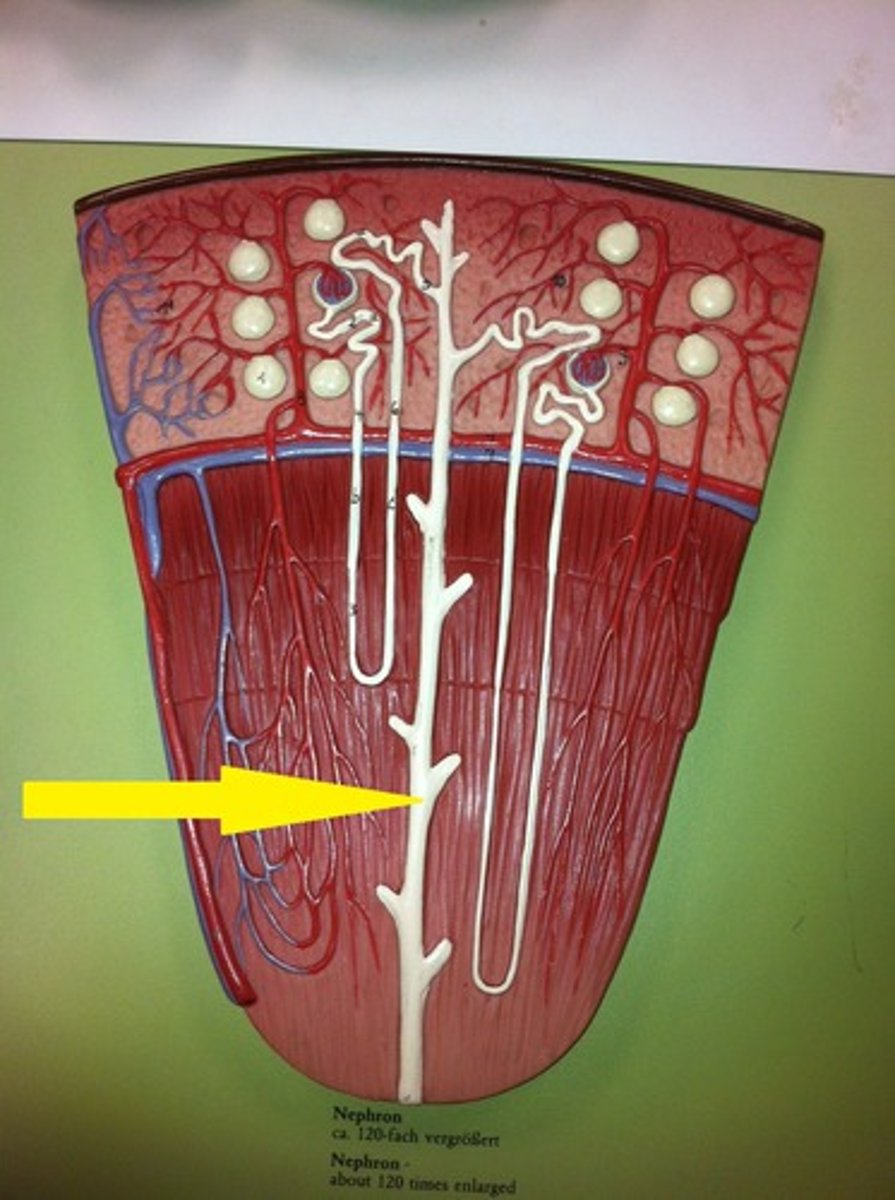
Nephron
- Consists of renal tubule and renal corpuscle
- > 1 million per kidney
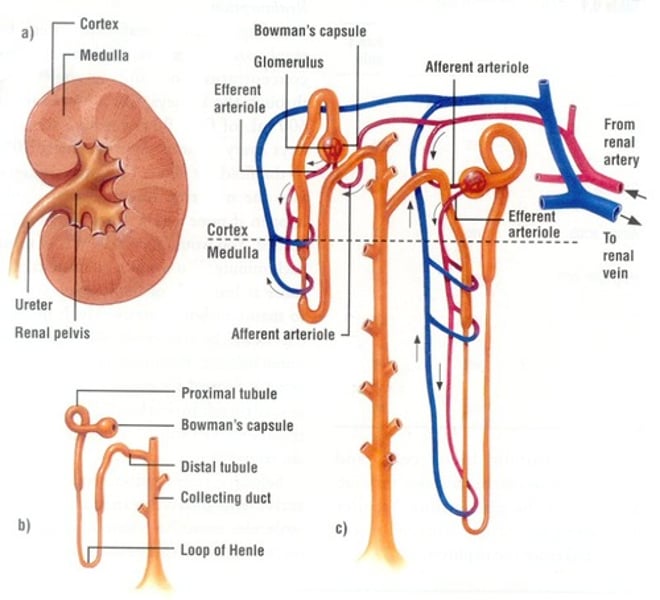
Renal Tubule
-Long tubular passageway
-Begins at renal corpuscle
Renal Corpuscle consists of
-Bowman's (Glomerular) capsule
-cup-shaped chamber
-capillary network (glomerulus)
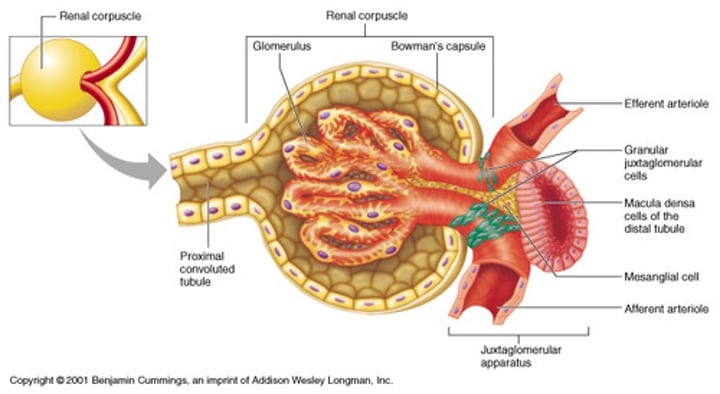
Glomerulus consists of
50 intertwining fenestrated, highly porous capillaries
Glomerulus blood is delivered via
afferent arteriole
Glomerulus blood leaves in
efferent arteriole:
-flows into peritubular capillaries
-which drain into small venules
-and return blood to venous system
Filtration occurs in the
renal corpuscle
Filtration: blood pressure forces
water and dissolved solutes out of glomerular capillaries into capsular space
Filtration: blood pressure produces
protein-free solution (filtrate) similar to blood plasma
3 Functions of Renal Tubule
1.Reabsorb useful organic nutrients that enter filtrate
2.Reabsorb more than 90% of water in filtrate
3.Secrete waste products that failed to enter renal corpuscle through filtration at glomerulus
Segments of Renal Tubule located in the cortex
-Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
-Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Segments of Renal Tubule separated by loop of Henle (nephron loop)
-U-shaped tube
-extends at least partially into medulla
3 Processes of the DCT
1.Active secretion of ions, acids, drugs, and toxins
2.Selective reabsorption of sodium and calcium ions from tubular fluid
3.Selective reabsorption of water: concentrates tubular fluid
Traveling along tubule
filtrate (tubular fluid) gradually changes composition
Each Nephron empties into the
collecting system
Collecting System
A series of tubes that carries tubular fluid away from nephron
Collecting ducts
receive fluid from many nephrons
Each collecting duct
-begins in cortex
-descends into medulla
-carries fluid to papillary duct that drains into a minor calyx
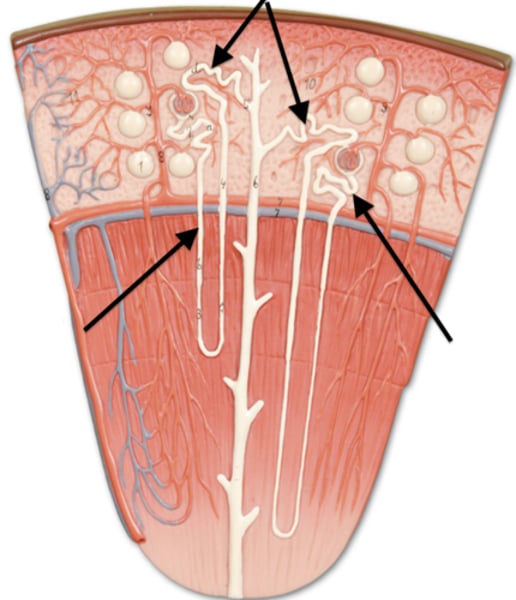
2 types of Nephrons
-cortical nephron
-juxtamedullary nephron
Cortical Nephrons
-85% of all nephrons
-Located mostly within superficial cortex of kidney
-Loop of Henle (Nephron loop) is relatively short
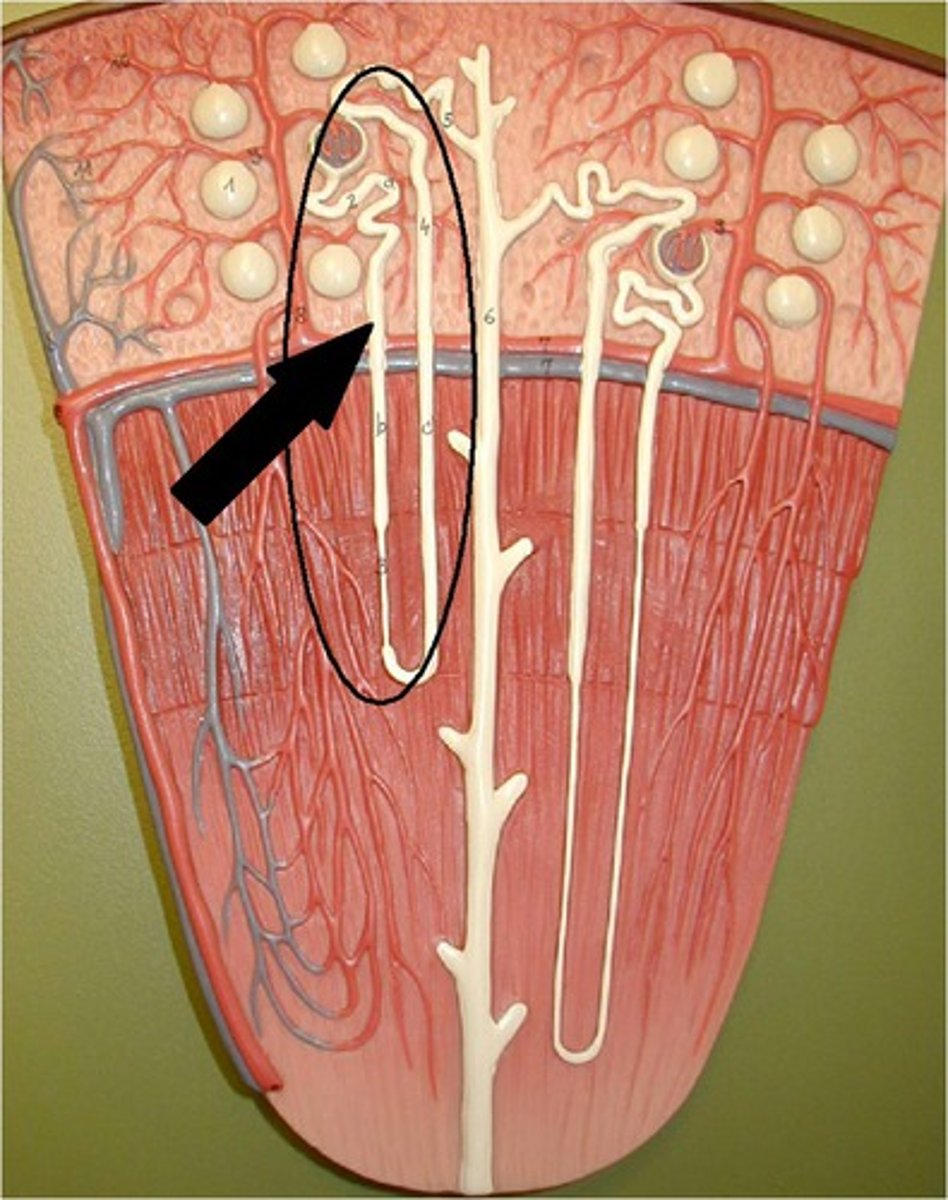
In Cortical Nephrons efferent arteriole delivers
blood to a network of peritubular capillaries:
-which surround entire renal tubule
-Low-pressure, porous capillaries adapted for absorption of
water and solutes
Cortical Nephrons perform most of the
reabsorptive and secretory functions of the kidney
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
-15% of nephrons
-Have long loops of Henle that extend deep into medulla
Juxtamedullary Nephrons have capillaries connected to
vasa recta:
-long, straight capillaries parallel with loop of Henle
Juxtamedullary Nephrons function
making concentrated urine
Each renal corpuscle
-is 150-250 µm in diameter
-includes Bowman's capsule and glomerulus
Bowman's Capsules
-Is connected to initial segment of renal tubule
-Forms outer wall of renal corpuscle
-Encapsulates glomerular capillaries
Bowman's (Glomerular) Capsule outer wall is lined by
simple squamous parietal epithelium:
-Continuous with visceral epithelium which covers glomerular capillaries
Bowman's Capsule Parietal & Visceral Epithelial
-Separated by capsular space
-Continuous where glomerular capillaries connect to afferent and efferent arterioles
Visceral Epithelium consists of
large cells (podocytes):
-with complex foot processes (pedicels) that wrap around specialized lamina densa of glomerular capillaries
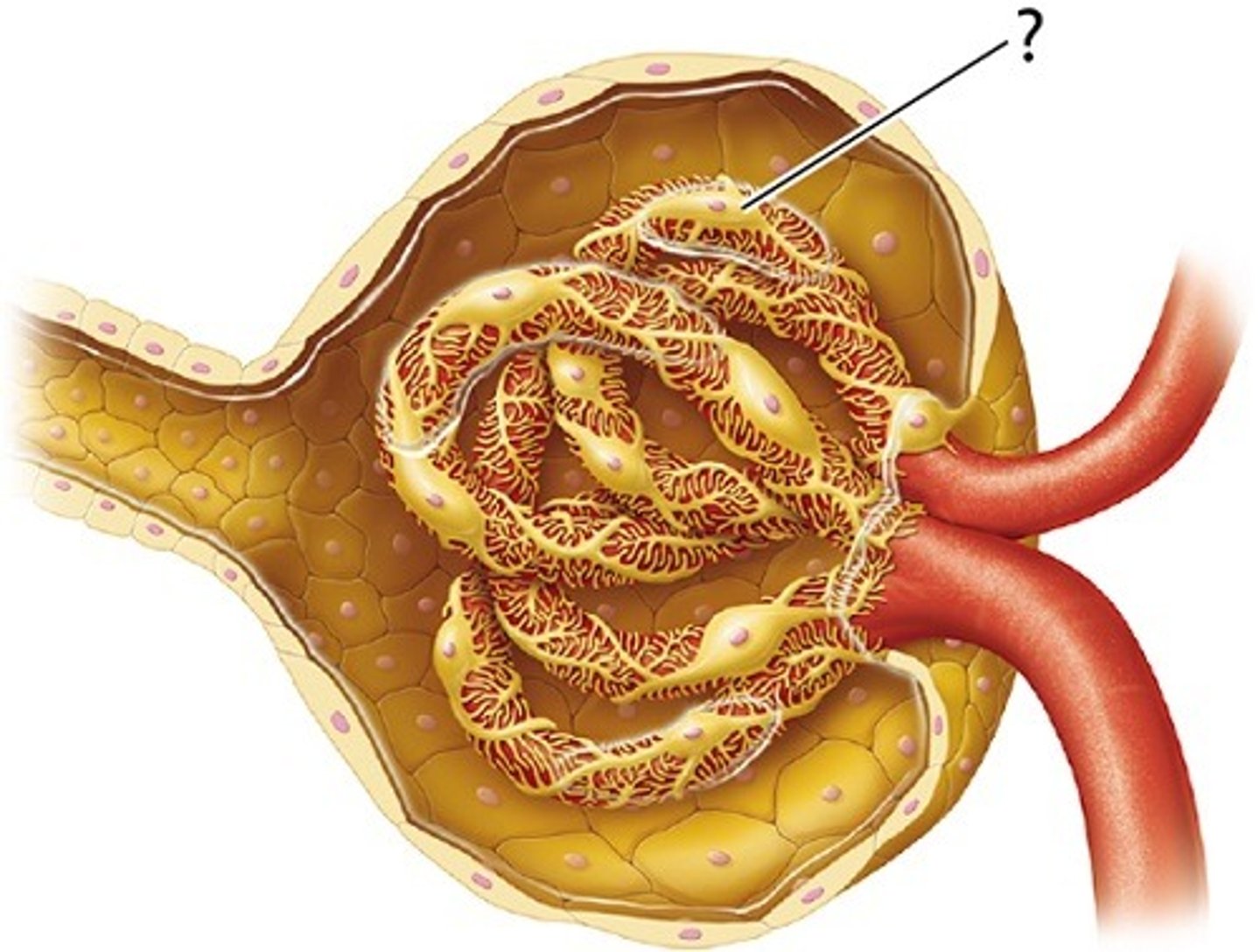
Filtration Slits
-Are narrow gaps between adjacent pedicels
-Materials passing out of blood at glomerulus:
~ must be small enough to pass between filtration slits
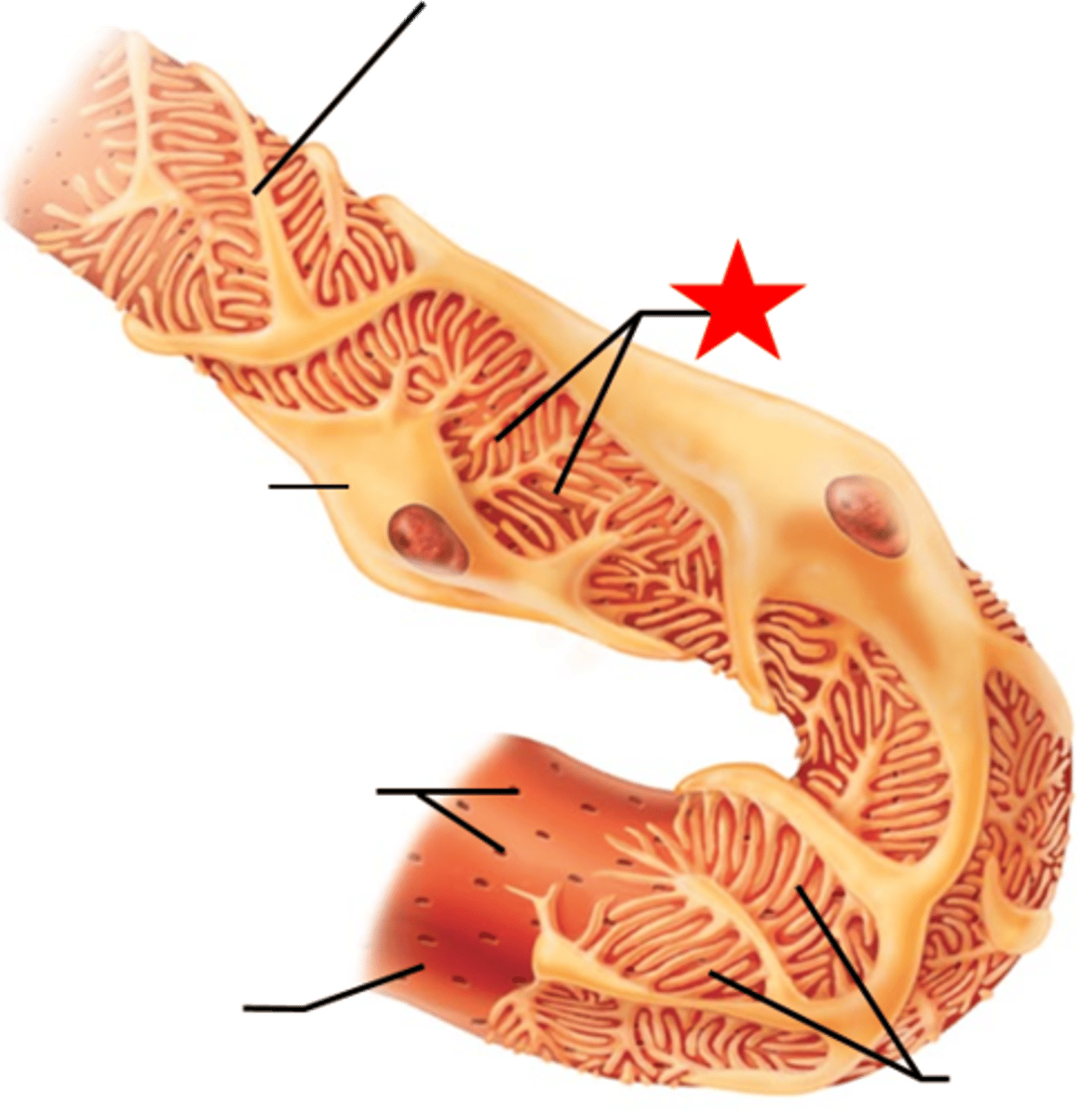
Glomerular Capillaries are
fenestrated capillaries:
-endothelium contains large-diameter pores
Lamina Densa
May encircle more than 1 capillary
Special supporting (Mesangial) cells of Bowman's Capsule
-between adjacent capillaries
-control diameter and rate of capillary blood flow
-Angiotensin II will cause contraction
Filtration Membrane consists of
-fenestrated endothelium
-lamina densa
-filtration slits
Fenestration (pore) of glomerular endothelial cell
prevents filtration of blood cells but allows all components of blood plasma to pass through
Basal lamina of glomerulus
prevents filtration of larger proteins
Slit membrane between pedicels
prevents filtration of medium-sized proteins
Filtration: blood pressure forces
water and small solutes across the membrane into capsular space
Glomerular filtration
larger solutes, including all but the smallest plasma proteins, are excluded
Filtration at Renal Corpuscle
-Is passive
-Solutes enter capsular space
Solutes that enter capsular space
-metabolic wastes and excess ions
-glucose, free fatty acids, amino acids, and vitamins
Reabsorption
process where useful materials are recaptured before filtrate leaves kidneys
Reabsorption occurs in
proximal convoluted tubule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
-Is the first segment of renal tubule
-Entrance to PCT lies opposite the point of connection of afferent and efferent arterioles with glomerulus
Epithelial Lining of PCT
-Is simple cuboidal
-Has microvilli on apical surfaces (brush boarder)
-Functions in reabsorption
-Secretes substances into lumen
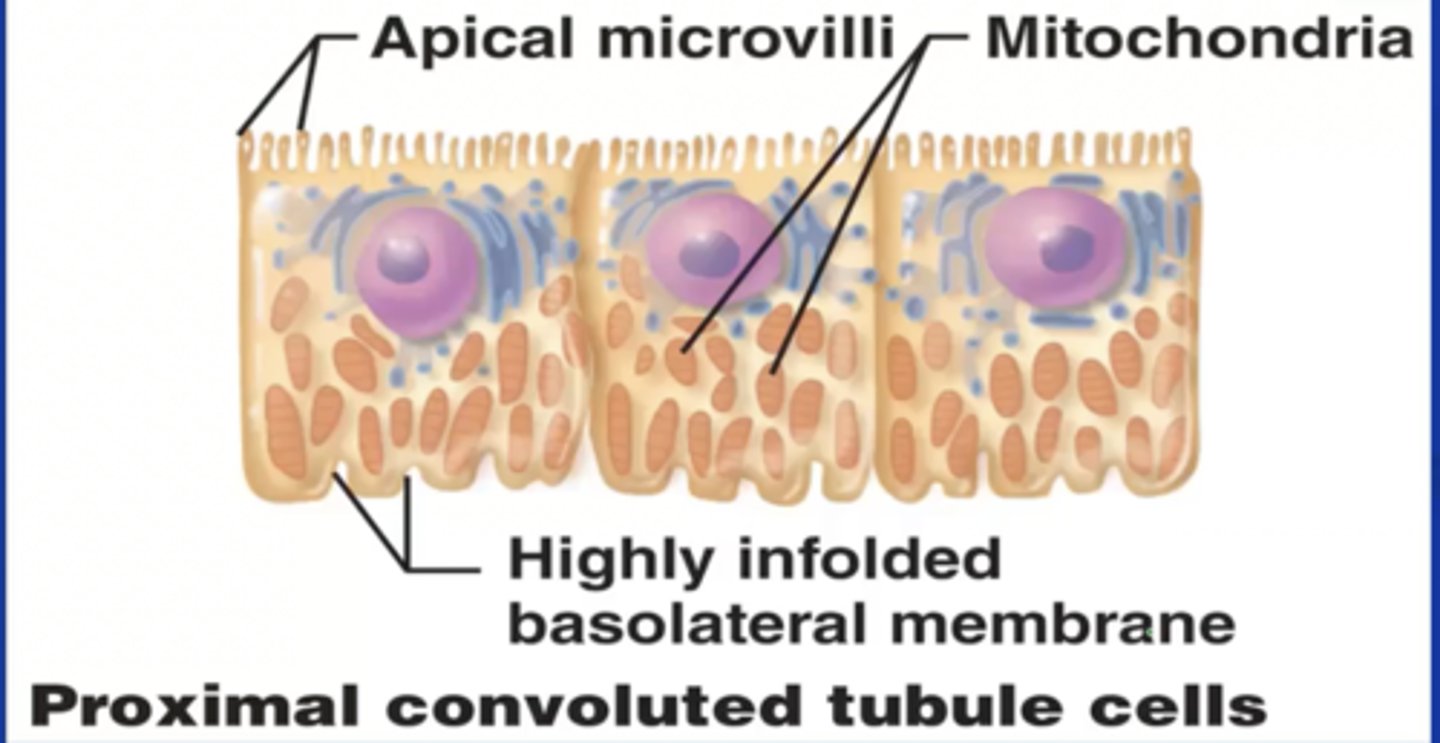
Tubular Cells
-Absorb organic nutrients, ions, water, and plasma proteins from tubular fluid
-Release them into peritubular fluid (interstitial fluid around renal tubule)
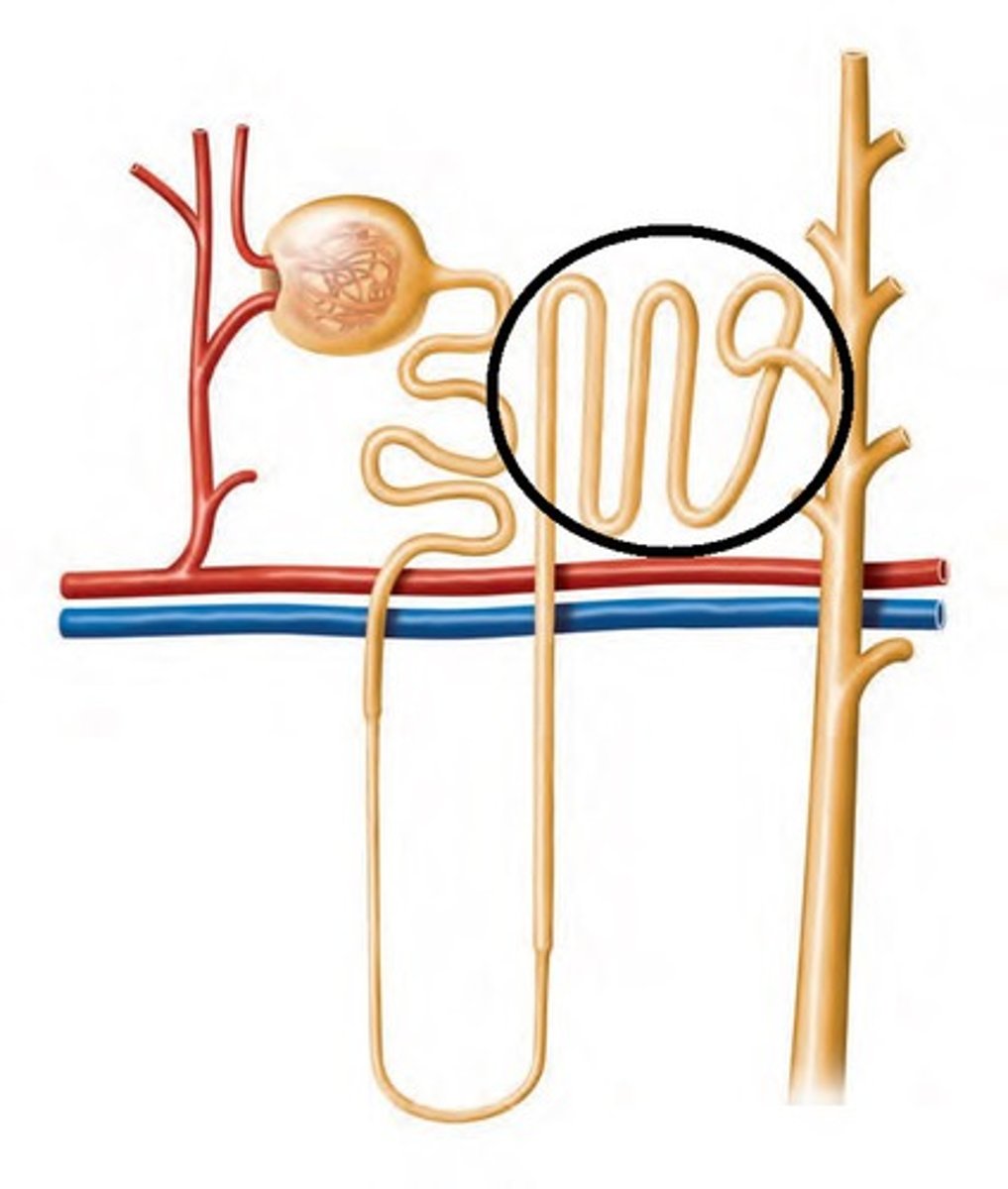
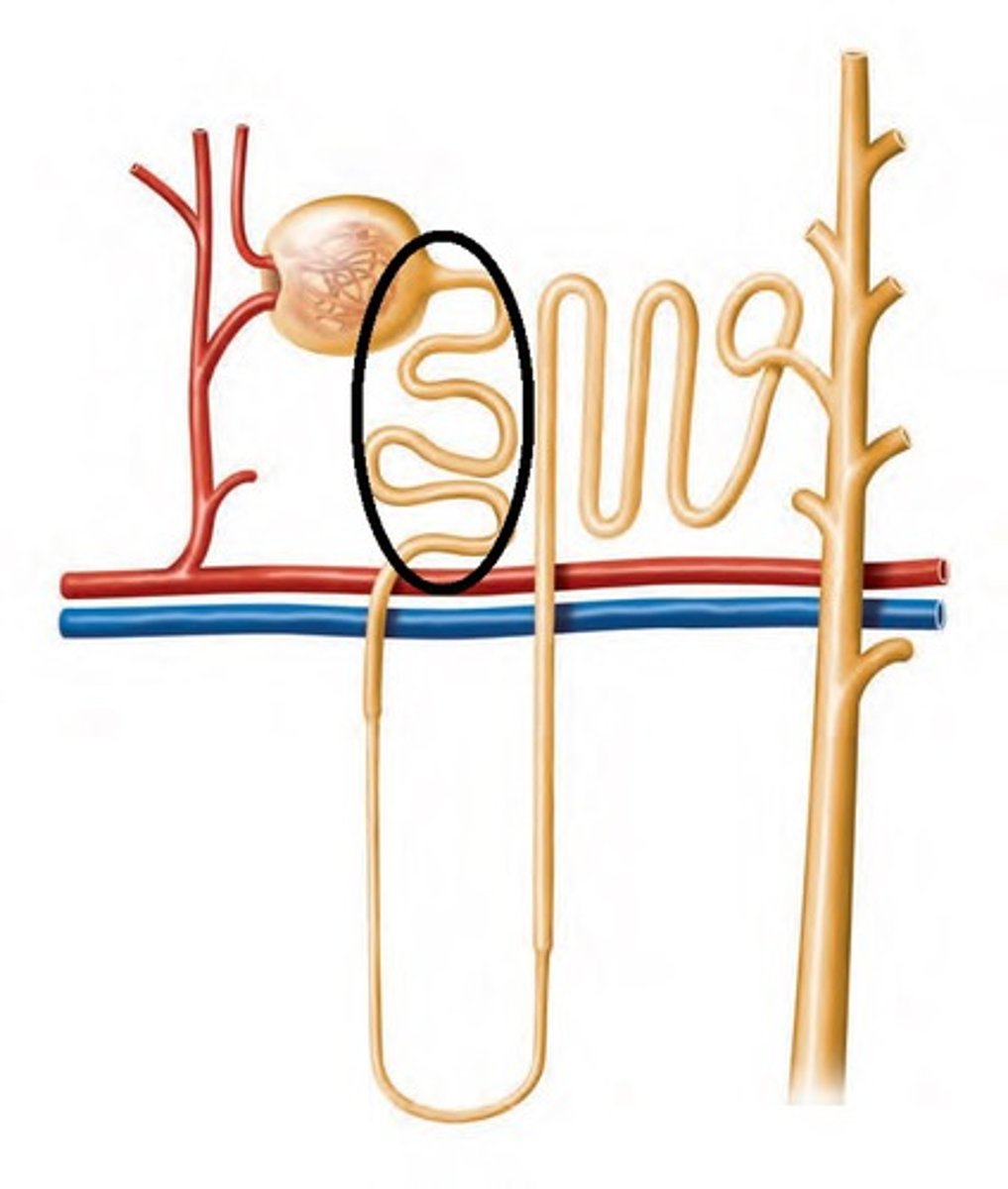
Loop of Henle is also known as
nephron loop
Nephron Loop: renal tubule turns toward renal medulla leading to
the loop of Henle
Nephron Loop: Each limb contains
-thick segment
-thin segment
Thick Descending Limb
Has functions similar to PCT
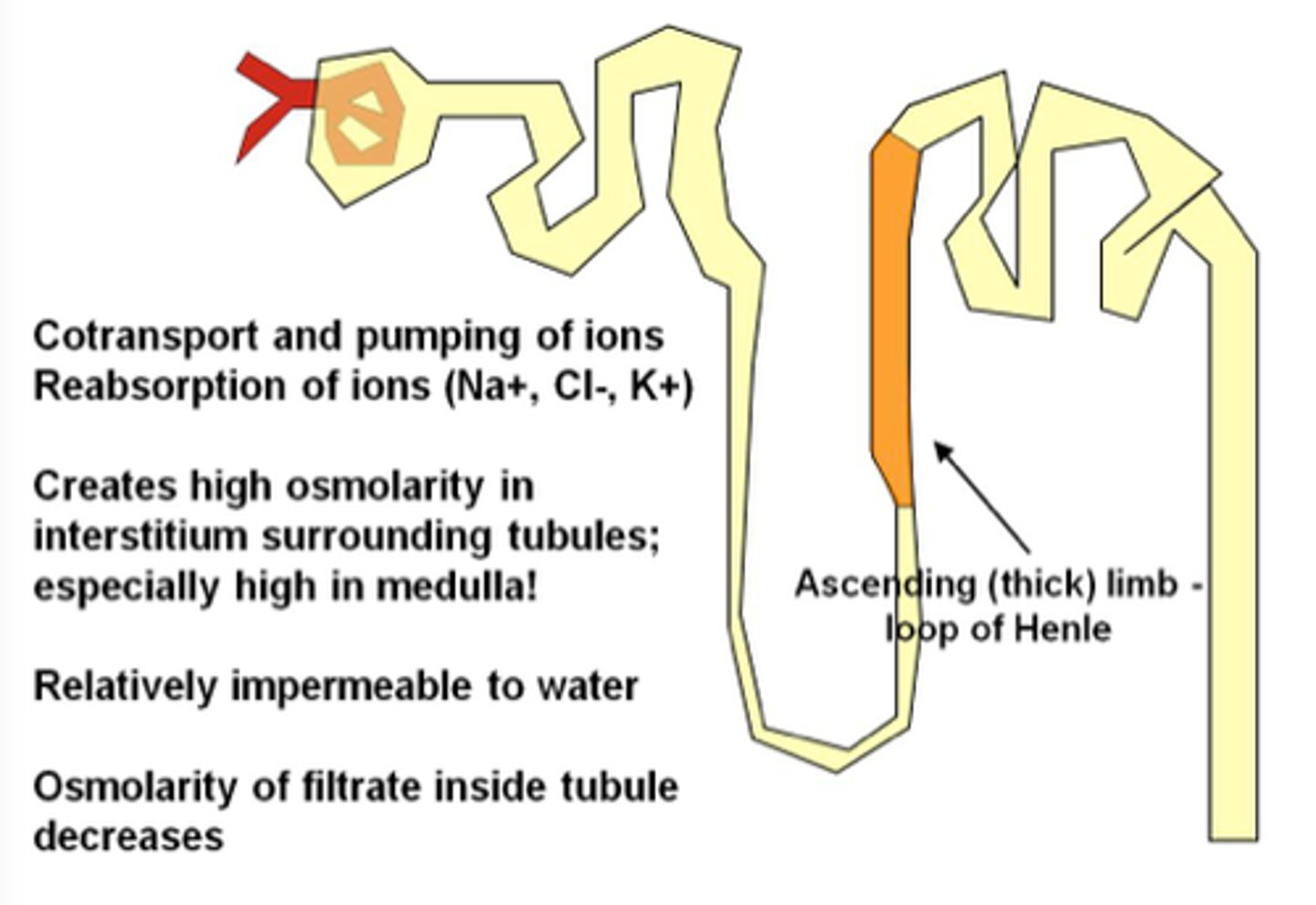
Ascending Limbs of juxtamedullary nephrons in medulla
create high solute concentrations in peritubular fluid
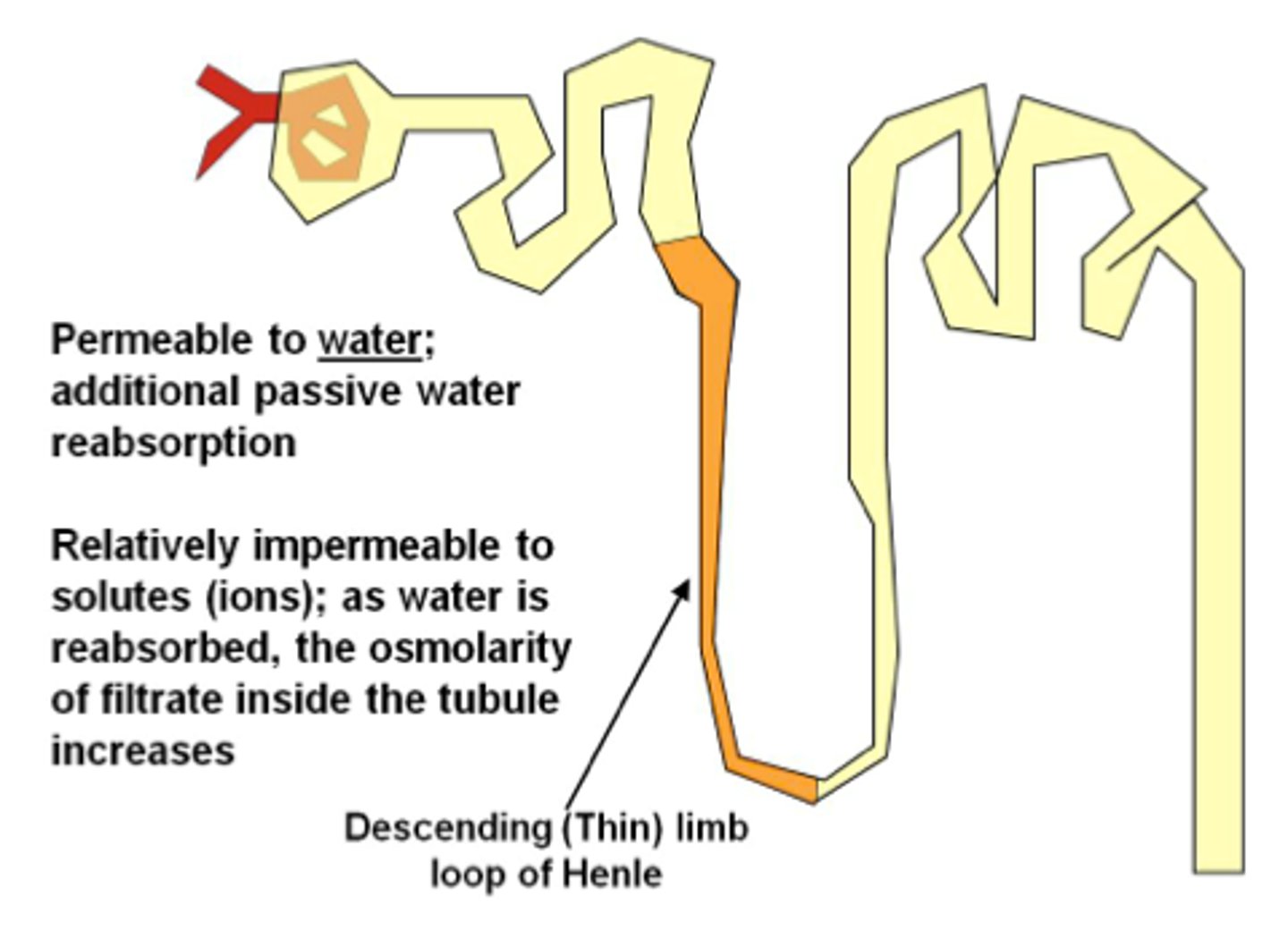
Thin Segments
-simple squamous epithelium
-Are freely permeable to water: not to solutes
-Water movement helps concentrate tubular fluid
Thick Ascending Limb
-Cuboidal to columnar cells
-Ends at a sharp angle near the renal corpuscle: where DCT begins
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
third segment of renal tubule
-Initial portion passes between afferent and efferent arterioles
-Has a smaller diameter than PCT
-Cuboidal cells with very few microvilli