CPR1 - Clinical {1.09, 1.11, 1.15-1.16,2.06,2.08-2.09,2.12-2.13}
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is hypoplasia?
Incomplete or arrested development of an organ, below normal number of cells
What is hyperplasia?
Higher than normal number of cells
What is dysplasia?
Abnormal growth noted microscopically, not malignant
What is aplasia?
Congenital absence of an organ
What cells mediate aplastic anemia?
T cell mediated
What is the presentation of aplastic anemia?
dyspnea on exertion, fatigue, infection, bleeding, bruising, CBC: Low HGB, WBC, PLT
What is the criteria for sever aplastic anemia (SAA)?
Neutrophils <500/cmm, platelets <20,000/cmm, Reticulocytes <0-0.5%
What is the etiology of sever aplastic anemia (SAA)?
Fanconi’s anemia
What is the treatment for congenital sever aplastic anemia (SAA)?
Bone marrow transplant
What is the initial treatment of idiopathic severe aplastic anemia (SAA)?
Combination of immunosuppressive agents and bone marrow growth factors
What are some chemical causes of bone marrow aplasias?
Insecticides, benzene, high dose chemotherapy, toluene (glue), wood preservative PCP, Herbs
What infections cause bone marrow hypoplasia?
HIV, EBV, CMV, influenza, bacterial/fungal infections
What infections cause bone marrow aplasia?
Hepatitis, Parvo - RBC aplasia
What is myelophthisic anemia?
Anemia (cytopenias) due to marrow infiltration
What is myelofibrosis?
Abnormal proliferation of fibrous tissue, or even new bone formation in marrow
What is the blood count pattern of multi-lineage cytopenias/pancytopenia?
Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, suggests a primary bone marrow disorder
What is thalassemia?
Heritable, microcytic, hypochromatic anemia; genetic defects result in decreased or absent production of mRNA and globin chain synthesis
What is alpha thalassemia usually caused by?
Gene deletion
What is beta thalassemia usually caused by?
Gene mutation
What is the result of one deletions in alpha thalassemia?
Silent carrier, no clinical significance
What is the result of two deletions in alpha thalassemia?
Mild hypochromic, microcytic anemia, α thal trait
What is the result of three deletions in alpha thalassemia?
Hgb H (β4), variable severity, but less severe than beta thal major
What is the result of four deletions in alpha thalassemia?
Barts HgB (γ4), hydrops fetalis, in utero or early neonatal death
What is the MCV value of one deletion in alpha thalassemia?
Borderline low (78-80fL)
What is the MCV value of two deletions in alpha thalassemia (α thal trait/α thalassemia minor)?
70-75 fL
How does the human body respond to alpha thalassemia with three deletions?
Make hemoglobin with four beta subunits or four gamma subunits
What are the characteristics of Hgb H (β4)?
Vulnerable to oxidation, gradually precipitates to form Heinz-like bodies of denatured hemoglobin
What is Bart’s hydrops fetalis syndrome?
Four deletion alpha thalassemia, massive edema and ascites caused by accumulation of serous fluid in fetal tissues as the result of sever anemia
What is the result of beta thalassemias?
Overproduction of alpha globulin chains, which precipitate in the cells causing ineffective erythropoiesis
How is beta-thalassemia major treated?
Chronic transfusion therapy, chelation, splenectomy, HSC transplant, RBC maturation agent (Luspatercept)
What is the pathophysiology of sideroblastic anemia?
Defects involving incorporation of iron into the heme molecule despite availability of iron stores
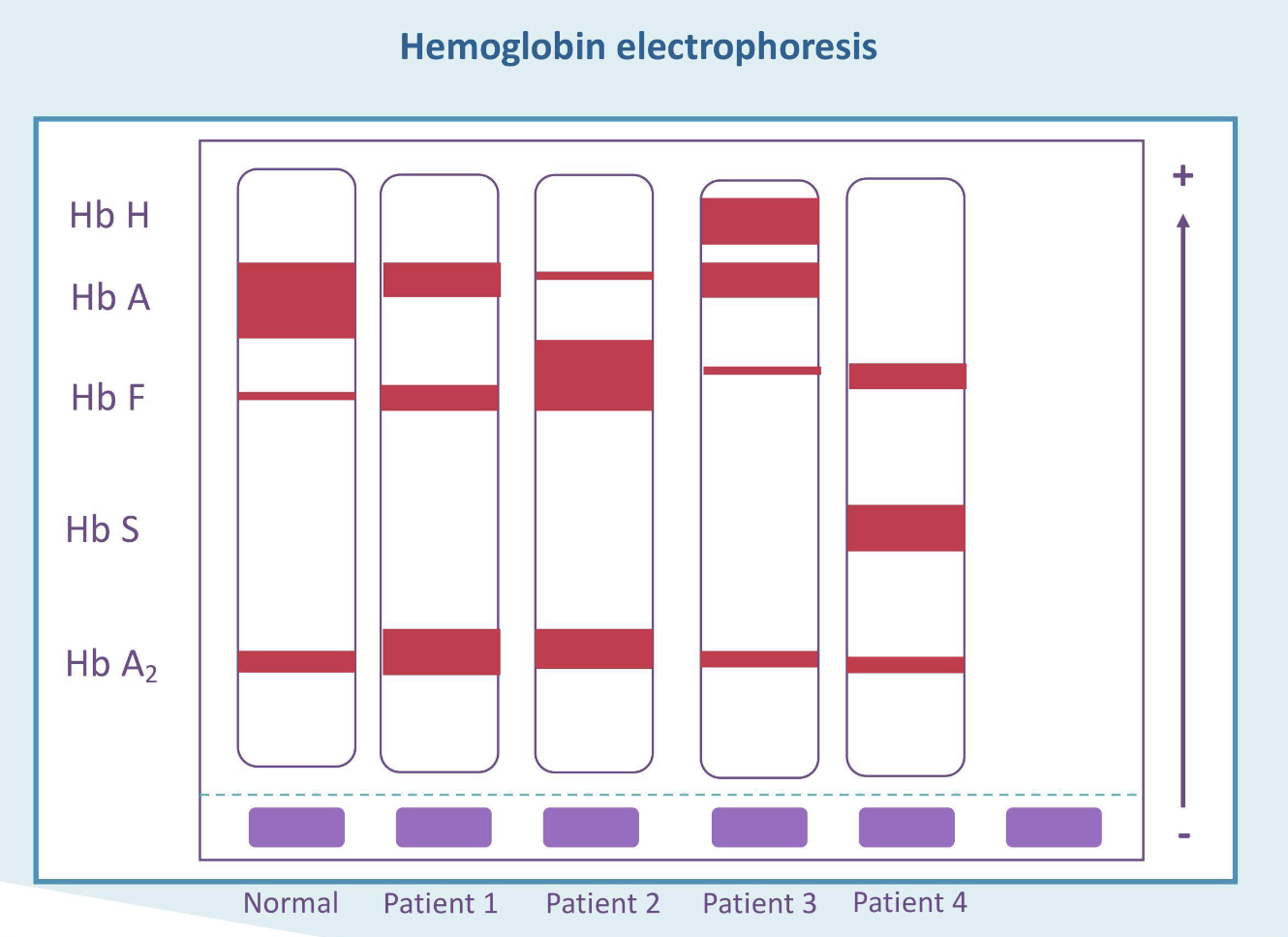
What is the most likely diagnosis for patient 1?
Beta thalassemia trait
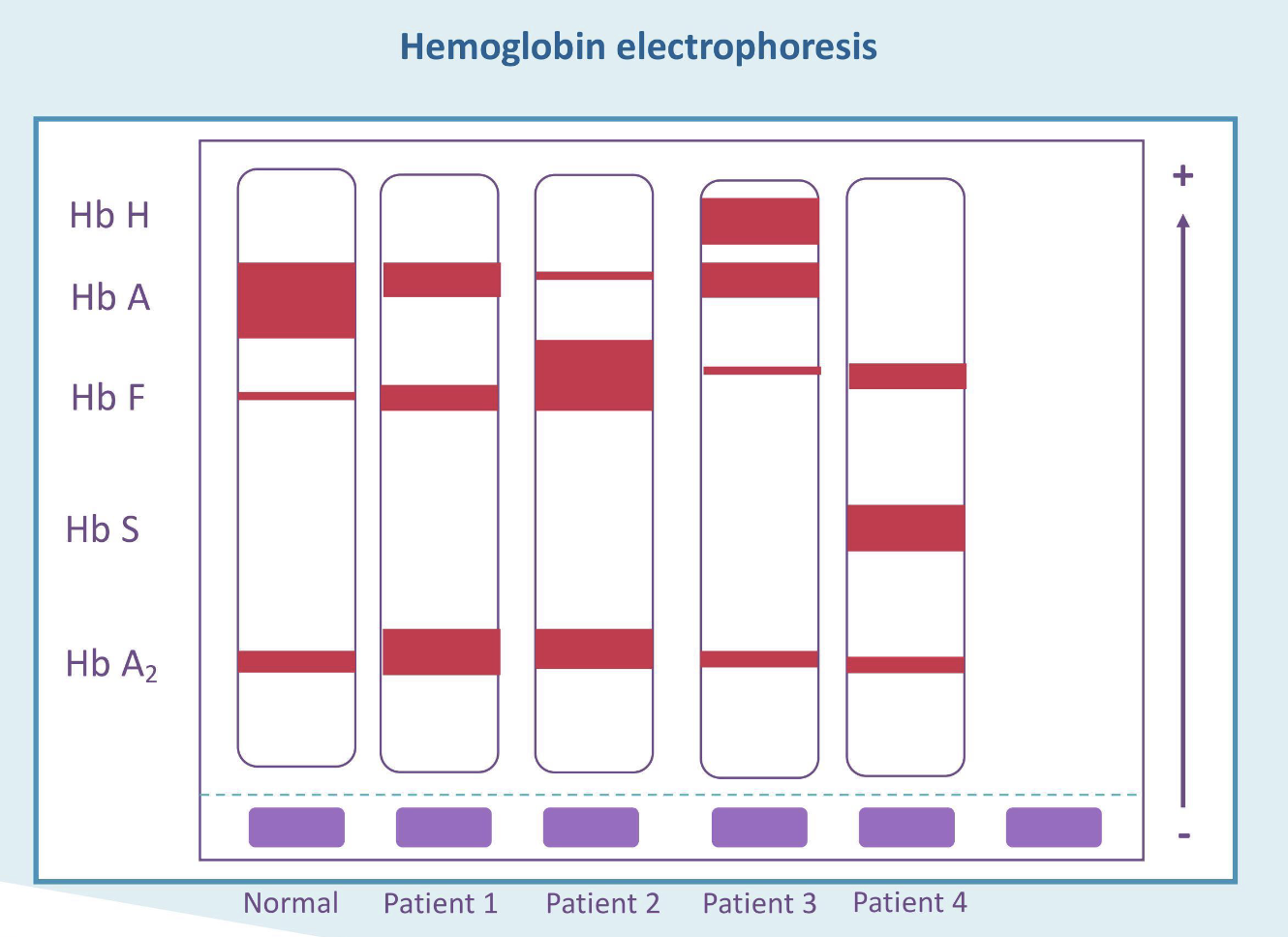
What is the most likely diagnosis for patient 2?
Beta thalassemia major
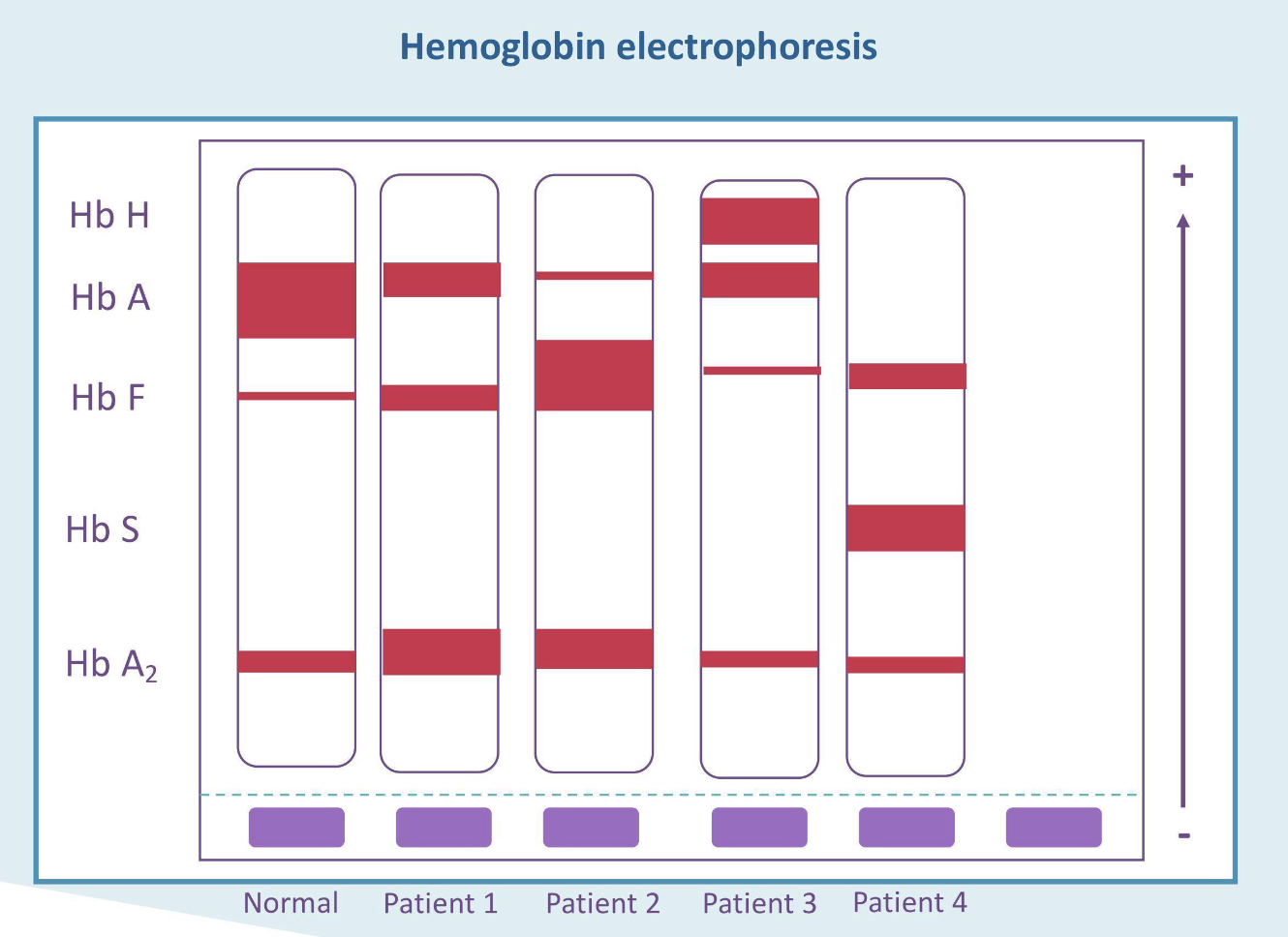
What is the most likely diagnosis for patient 3?
Hgb H disease
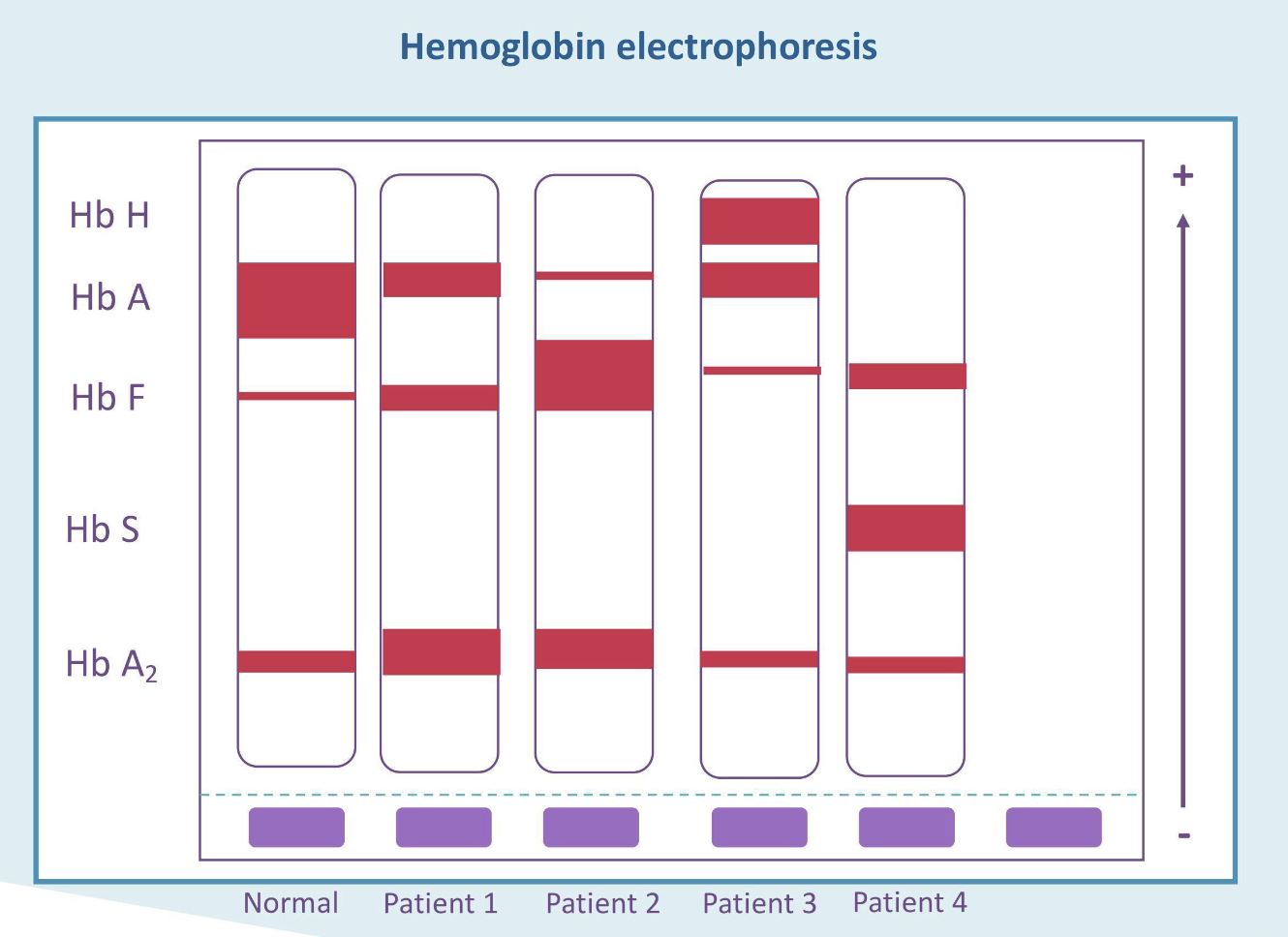
What is the most likely diagnosis for patient 4?
Sickle cell disease
When is the CBC test used?
WBC analysis, RBC analysis, platelet analysis
In an anemic patient in which bone marrow is not responding properly. The reticulocyte count will be:
Low
In an anemic patient with a ____ reticulocyte count may reflect accelerated blood cell destruction.
Higher than expected
In an anemic patient a _____ reticulocyte count reflects that bone marrow is responding to anemia.
Appropriate
What are some physical features of iron deficiency anemia?
Pallor of mucus membranes, spoon nails (koilonychia), angular cheilitis
What are some issues with laboratory evaluations in ACD?
Ferritin may be falsely high if patient has an active infection or active inflammation
What are some laboratory evaluations that should be tested when ACD is suspected?
C reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (measure of inflammation), soluble transferrin receptor levels, hepcidin levels
A patient with:
low serum iron
Elevated transferrin
Low iron saturation
Low ferritin
Elevated soluble transferrin receptors
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Iron deficiency
A patient with:
low serum iron
Reduced transferrin
Low iron saturation
High ferritin
Normal soluble transferrin receptors
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Anemia of chronic disease
What is disseminated intravascular disease (DIC)?
An acquired syndrome characterized by systemic intravascular coagulation producing both thrombosis and hemorrhage
What is the pathophysiology of DIC?
Activation of blood coagulation, suppression of physiologic anticoagulation pathways, impaired fibrinolysis, cytokines
How does suppression of physiologic anticoagulant pathways induce DIC?
Reduced ATIII levels, reduced activity of protein C and S, Insufficient regulation by TFPI
How do cytokines induce DIC?
IL-6/IL-1 mediate coagulation activity, TNF mediates dysregulation of anticoagulant pathways and fibrinolysis, IL-10 may modulate activity of coagulation
What are some clinical manifestations of DIC?
Oozing blood from wound sites, petechiae, purpura and echymosis
How do you treat DIC?
Stop the triggering process, supportive therapy (Platelets, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate)
What is Bernard-Soulier syndrome?
Defective adhesion, deficiency in GPIb/IX receptor, autosomal recessive
What is Glanzmann thromboasthenia?
Defective aggregation, dysfunction in GPIIb/IIIa, autosomal recessive
What are storage pool disorders?
Defective release of mediators (ADP, Thromboxane)
What is immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)?
Immune-mediated isolated low platelet count in absence of other etiologies
What causes immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)?
Environmental exposure (medications and toxins), Infectious agents (Helicobacter pylori)
What are the clinical features of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)?
Isolated thrombocytopenia, epistaxis, petechiae, bleeding
What are the histological features of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)?
Isolated thrombocytopenia, large and well-granulated platelets, no significant dysplasia of any lineage
What is the treatment implication of type 1 heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
Usually, no change in heparin therapy needed
What is the treatment implication of type 2 heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
Heparin must be stopped, alternative anticoagulant required
What is Evans syndrome?
Combination of immune-mediated thrombocytopenia and Coombs (+) autoimmune hemolytic anemia
What is pseudothrombocytopenia?
Physiologically normal with a true normal platelet count, in vitro laboratory artifact, anticoagulant in collection tube modifies platelet surface antigens causing antibody-mediated platelet agglutination
What anticoagulants are implicated in pseudothrombocytopenia?
EDTA, Citrate, heparin, oxalate, hirudin
What are thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMAs)?
Group of disorders caused by excessive platelet activation, formation of platelet rich thrombi in small vessels
What is the treatment for TTP?
Plasmapherisis first, platelets never
What does schistocytes, low platelets and neurologic symptoms point to?
TTP
What happens when there is an ADAMTS13 deficiency?
Ultralarge vWF multimers
What is hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)?
Acute renal failure, thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
What infection causes diarrheal/infectious hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)?
Shiga toxin-producing bacteria (e. coli O157, Shigella dysenteriae)