alimentary canal
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
mesentery
attatch intestine to abdominal wall
omentum
fatty tissue insulate organs
layers
serosal
layers
muscular layers ( circular, longitudal, oblique)
layers
submucosal
layers
mucosal
parastalsis
involuntary movement of food through tract
sm intestine function
absorb nutrient/ digest
colon function
water/ electrolyte absorption
produce vitamin k by flora
polyp pathology
overgrowth of mucosal tissue internal
diverticulum
pouching out of lumen
zenkers diverticula
esophagus
meckels diverticula
intestine
ulcer
wearing away of protective mucosa
perforation
a hole in alimentary canal spillage of contents into peritoneal cavity
intossuseption, which group is common to it
telescopic/ slipping intestines
common in infants
GIA stapler
two double rows and cuts between
side to side anastamosis
EEA stapler
end to end anastamosis
circular double row, circular blade
creatae new lumen
dilation of a stricture
dilate with bougie dilators
EGD
esophagus, stomach, upper portion of duodenum
used for diagnostic procedures
EGD/W endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
uses an extension allowing to view into the billiary ducts
used to treat/view
gallbladder, bile duct, pancreas
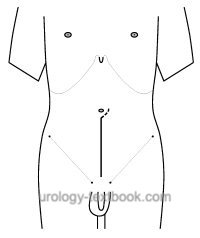
midline incision
laporotomy/ abdominal surgery
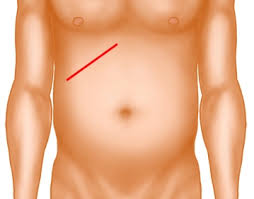
kocher’s incision
open cholesyectomy
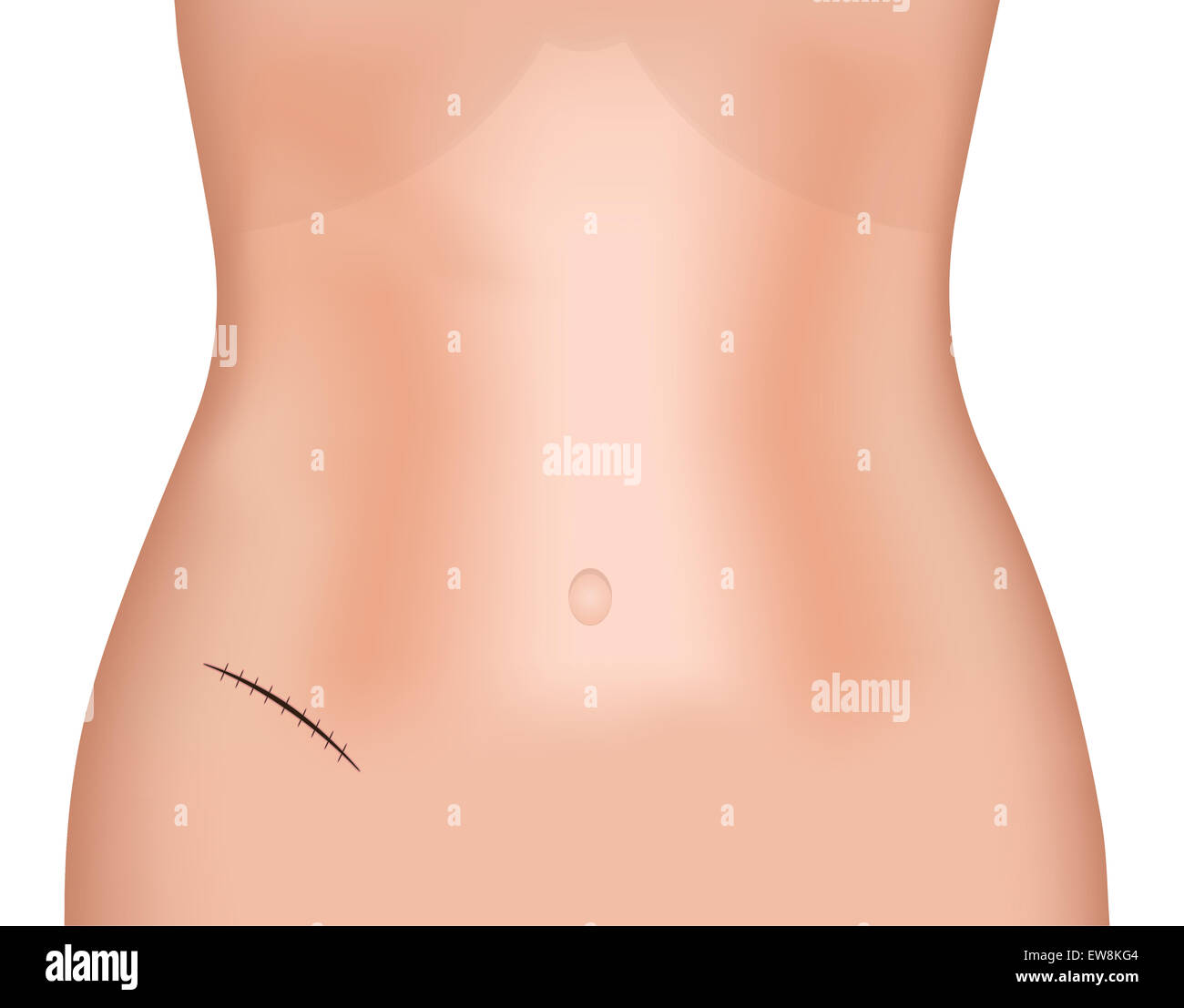
McBerney
used for appendectomy
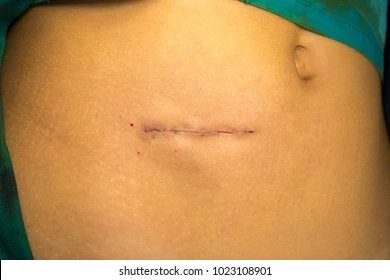
lanz incision
preform appendectomy
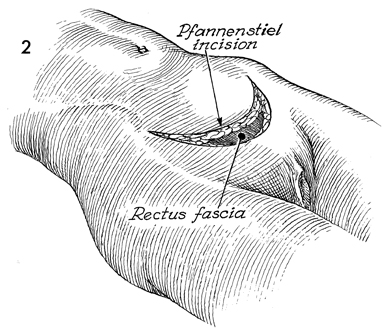
pfannenstiel incision
c section/ hysterectomy

rutherford morrison incision
r/l colonic resection, sigmoid colostomy
gastrostomy tube
gastric mucosa opening into the skin ( feeding tube, decompress/ drain stomach)
PEG
percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
feeding tube inserted through abdominal wall into stomach with aid of an endoscope
gastrectomy
partial- weight loss, ulcer
total- malignancy, uncontrol bleeding
total gastrectomy
esophagojejunostomy- end to end anastamosis
roux en y
end to side jejuno-jejunostomy
if thoracoabdominal incision was made what is needed
chest tube, must connest to pleur evac
subtotal gastrectomy ( billroth 1)
gastroduodenostomy
pylorus removal, remaining stomach anastamos to duodenum
Billiroth 2
gastrojejunostomy
pylorus removal, remaining stomach anastamos to jejunum
types of gastrectomy for bmi
sleeve gastrectomy
roux-en-y
greater than 30 BMI
what causes stomach ulcer
bacterial infection of stomach
excessive release of HCI acid
ulcer treatment
partial gastectomy/ vagotomy
transection of the vagus nerve of the stomach, reduces gastric secretions
pylorotomy
treats pyloric stenosis, thickened pylorus causes projectile vomiting
spleen
filter blood, produce immunity, production of wbc
LAR
tumor near rectum MORE than 5cm from internal rectal sphincter
APR
rectal tumor LESS than 5 cm away from internal rectal sphincter
colonostomy
colon is brought outside abdominal wall to create a stoma
pilondial cyst
in sacrococcygeal area full of skin debris, hair usually 2-5cm
hemorrhoids
swollen vericose veins of rectum and anus
can be internal/ ecternal
aka piles
hemorrhoids high lithotomy
anestesia choice, closer to external orfice
hemorrhoids
prone ( kraske)
most common for deep internal hemorrhoids
anal fistula
infected tunnel between the skin and anus
anal fistulotomy
fistula drained wound will heal inside out, seaton a loop of suture to keep pathway open
recal abscess
a collection of of pus around the anus and rectum, caused by ecoli
anal sphincter injury
occurs in childbirth