Solar system exam 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Keplers 1st law of planetary motion
each planet moves in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one focus of the ellipse
what is inertia?
resistance in changes in motion
Because radio waves have very ______ wavelengths, radio telescopes generally have ______ resolution
long, bad
which law does eccentricity relate to
kepler’s 1st law
the further away a planet is, the (more/less) eccentric the ellipse is? The closer they are, the (more/less) eccentric the ellipse is? An ellipse whose focal points are both at the center is a _______.
more, less, circle
Keplers second law of planetary motion
the lines from the sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas of space in equal time intervals
At what point in their orbits do objects move the fastest?
closer to the perihelion, when they are closer to the sun
at what point in their orbits do objects move the slowest?
closer to the aphelion, when they are farther from the sun
kepplers 3rd law of planetary motion
P2=a3
for kepplers 3rd law, if a is smaller then P is______. If a is larger then P is _____.
smaller, larger
what is the semi major axis? what is major axis?
distance from far side of orbit to center, distance from one side of orbit to the other
what did galileo observe about the moon?
not perfect, there’s blemishes and craters
proof of heliocentric model
possible for venus to be found on the other side of the sun from the earth. in this case, a full range of moon phases can be observed
what did galileo do (what was his experiment and what did he learn?)
drop 2 objects off side of leaning tower and learned that objects fall at the same rate
newtons first law
an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an opposing force (law of inertia)
Newtons second law
F=ma
Newton’s third law
every action exerts an equal and opposite reaction
what does your weight depend on?
your mass, planets mass, distance
The gravitational acceleration all objects feel towards earth depends only on….
properties of the earth
Newton’s law of universal gravitation
gravitational force depends on the mass of both objects and every object exerts a force on every other object
Determining weight on another planet
Use the gravity equation to calculate your weight on that planet
apparent weightlessness
If an object moves fast enough, it can escape earth’s gravitational pull and be in a constant free fall around the earth, causing an orbit
newton’s modified version of Kepler’s 3rd law
(m1+m2)P²=a³
Tidal force relationship
F=m/r³
what causes tides
differences in gravitational forces across an object of size
For tides, the side closer to the object feels a _________ force while the side farther feels a ______ force. As a result, compared to the average force on the earth, the closer side is being pulled _____ while the farther side is being pulled _____. This causes the closer side to ______ _____ the object while the farther side ____ _____ ___ the object.
greater, lesser, more, less, bulge towards, bulge away from
The tidal strength of the sun is only ______ as strong as the tidal force of the moon
1/2
how many high tides are there a day? how many low tides are there a day?
2 high, 2 low
how often do high tides occur? When do low tides occur
every 12 hours, in between high tides
Since moon moves around the Earth over time, we actually experience 2 high tides every…
24 hours and 50 minutes
what are spring tides?
when the sun and moon exert tidal forces in the same direction, we experience our highest high tides and our lowest low tides
what are neap tides?
when the sun and moon exert tidal forces in opposite directions, we experience our lowest high tides and our highest low tides
during what moon phases do spring tides occur
new or full
during what moon phases do neap tides occur
1st and 3rd quater
how often do spring tides occur? how often do neap tides occur?
twice a month
What is light also known as?
electromagnetic radiation
what is electromagnetic radiation composed of?
oscillating electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to the travel of motion
what is wavelength
the length over which the wave repeats its pattern
what is frequency?
how often the wave repeats itself
what is a photon
light particle
what is the energy of a photon?
E=hf
what is the visible light range?
400nm-750nm
order of e&m spectrum from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength
radio, micro, infared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma
what is spectroscopy
the study of light by spreading it out to see the various wavelengths being emitted
what is a continous spectra?
from hot, dense objects
what is an emission spectra?
emitted from excited, low density gases
what is an absorption spectra?
continuous emission passes through low-density gases, which absorb their favorite wavelengths and let everything else pass through
how do astronomers restrict observations for spectroscopic observations?
they restrict their observations to narrow slits
what is a blackbody object?
objects that absorb any radiation which hits them, then re-radiate the absorbed energy
what is blackbody radiation?
the spectrum of energy given off by a blackbody object
stefan-boltzmann law
the hotter the object the higher the intensity, the more it radiates energy
wien’s law formula (type the word wavelength for lambda)
wavelength~1/T
Wein’s law states
The hotter the object, the shorter its peak wavelength
in an electron shell, its orbital level is equal to its
energy levels
when an electron jumps up, it _________ energy. When an electron jumps down, it _____ energy
absorbs, releases
what is ionization?
when the electron completely frees itself from the magnetic pull of the nucleus
discrete energy levels
an electron at a particular distance from the nucleaus will have a particular amount of energy
what does the number of protons in an atom tell us?
what element it is
what does the number of neutrons in an atom tell us?
what isotope the element is
shorter wavelength= ______ electron jump, longer wavelength= _______ electron jump
larger, smaller
what are the 4 reasons why the movement of electrons around the nucleus cause an atom to absorb/emit energy?
opposites attract, discrete levels, descrete energy levels, ionization
what do the dips in sprecal lines represent on the solar spectrum
absorption lines
what type of spectra does the sun give off
absorption spectra
radial vs. transverse motion, which one does the doppler effect give you?
radial is towards and away from us, transverse is across our line of sight, radial
the faster the radial motion, the ________ the doppler shift
greater
how do astronomers detect a doppler shift?
look at spectrum of the light being emitted from objects in space
what is a reflecting telescopes
use mirrors to focus light onto an image
what is a refracting telescope?
use lenses to focus light onto an image
what is chromatic aberration?
different colors focus at different points on a telescope
why is a larger telescope better?
the larger the opening, the more light it will gather in a given amount of time
what is angular resolution?
ability to observe two closely spaced objects as 2 different objects
what two factors effect angular resolution? what is the formula?
size of telescope and wavelength of light angle=wavelength/diameter
she larger the telescope, the ______ the angular resolution. The shorter the wavelength, the _______ the angular resolution
better, better
is a small or large angular resolution better?
smaller
opaque
blocks or prevents the passage of a specified form of radiation
transparent
allows the passage of a specified form of radiation
seeing
a measurement of the sharpness of a telescopic image
what is a CCD?
collection of cells on a computer chip that collect light and convert it into electric harge
what produces good seeing? what produces poor seeing?
a calm atmosphere, a turbelent atmosphere
what wavelengths is the earth’s atmosphere transparent to?
visual and radio wavelengths
what wavelengths is the earth partially opaque to?
ultraviolet and infared
what wavelengths is the earth completely opaque to?
x-rays and gamma rays
A comet, with a highly elliptical orbit, will spend most of its time
A. moving away from the Sun.
B. moving towards the Sun.
C. far away from the Sun.
D. very close to the Sun.
C. far away from the sun
Planets closer to the Sun than Earth take _____ to complete one orbit.
A. more time
B. less time
C. the same amount of time
B. less time
The Earth takes one year to orbit once around the Sun (the Earth’s period equals one year). A fictional planet orbits twice as far away from the Sun as Earth. How long does it take this fictional planet to orbit once around the Sun (i.e., what is the planet’s period)?
A. less than half a year
B. exactly half a year
C. exactly one year
D. exactly two years
E. greater than two years
E. greater than two years
When dropped from the same height, when will a lead weight hit the ground compared to a less
dense wood ball?
A. much sooner
B. much later
C. the same time
A. much sooner
A man pushes on a box, but it remains at rest.
What is the net force acting on the box? (the man is to the right of the box pushing to the left)
A. The net force is to the left.
B. The net force is to the right.
C. The net force is zero.
A. The net force is to the left
When the tablecloth is pulled out from underneath the place setting, why does the place setting not
move?
A. Gravity pulls down on it forcefully enough to keep it in place.
B. While the tablecloth exerts a force on the place setting, the place setting also exerts a force on the tablecloth, and the two forces cancel out.
C. The place setting is not heavy enough to move.
D. Since no force is exerted on the place setting, it does not move.
B. While the tablecloth exerts a force on the place setting, the place setting also exerts a force on the tablecloth, and the two forces cancel out.
If there is a spring tide today, approximately how long will it be until there is another spring tide?
A. one week
B. two weeks
C. one month
D. two months
E. six months
B. two weeks
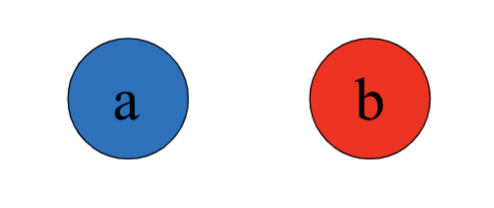
Below are two stove-top burners, their colors indicate how hot they are. You place identical pots of water on each burner at the same time (the pots being as large as the bigger burner). In each case, which burner will boil the water quicker? If you cannot tell, choose option (c)
A
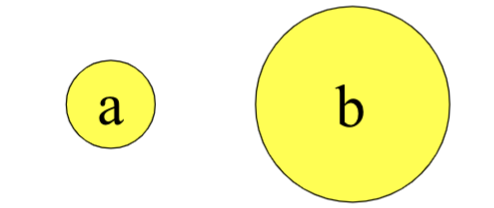
Below are two stove-top burners, their colors indicate how hot they are. You place identical pots of water on each burner at the same time (the pots being as large as the bigger burner). In each case, which burner will boil the water quicker? If you cannot tell, choose option (c)
b
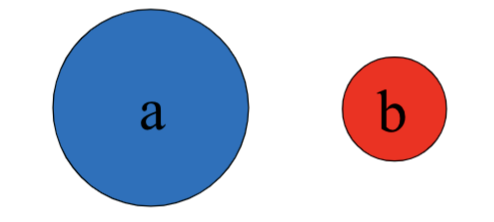
Below are two stove-top burners, their colors indicate how hot they are. You place identical pots of water on each burner at the same time (the pots being as large as the bigger burner). In each case, which burner will boil the water quicker? If you cannot tell, choose option (c)
a
The Sun is a hot dense source, surrounded by a low-density atmosphere. What type of spectrum do we observe from the Sun?
A. a continuous spectrum
B. an emission spectrum
C. an absorption spectrum
D. a Hydrogen spectrum
E. a diffuse spectrum
C. an absorption spectrum
If you excite hydrogen gas in a glass tube by running an electric current through it, the three strongest lines in its emission spectrum will have wavelengths of 656 nm, 486 nm, and 434 nm. Suppose this gas tube was moving away from you really quickly while you were measuring the wavelengths of these three emission lines. What wavelengths might you observe?
A. 668 nm, 496 nm, 442 nm
B. 644 nm, 476 nm, 426 nm
C. 656 nm, 486 nm, 434 nm
D. 656 nm, 496 nm, 426 nm
E. 668 nm, 476 nm, 442 nm
A. 668 nm, 496 nm, 442 nm
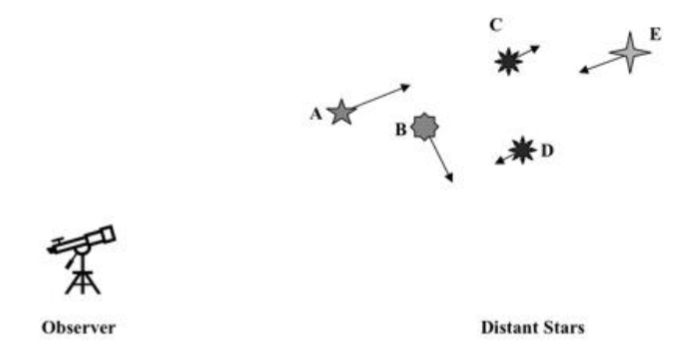
The figure below shows the motion of five distant stars (A - E) relative to a stationary observer (telescope). The speed and direction of each star is indicated by the length and direction of the arrows shown. Rank the Doppler shift of the light observed from each star (A – E) from greatest “blueshift”, through no shift, to greatest “redshift”.
A. B < D < C < E < A
B. A < B < D < C < E
C. D < C < E < B < A
D. E < D < B < C < A
E. A = B = C = D = E
D. E < D < B < C < A
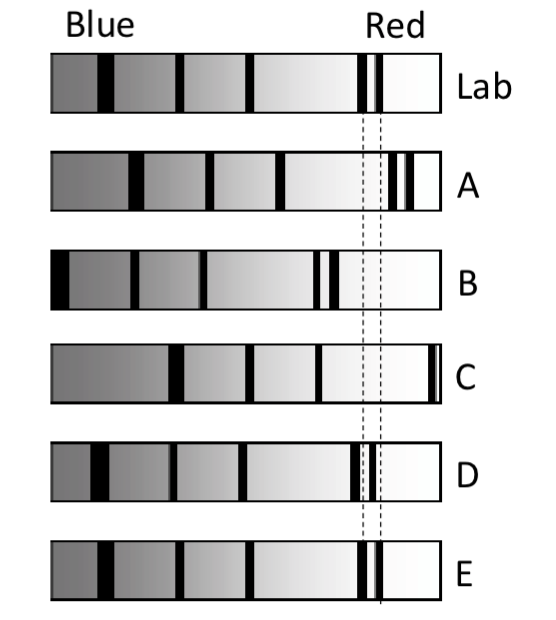

The first spectra shown below is of an element as it appears in a laboratory here on Earth. In addition, the spectra of five stars (A - E) as seen from Earth are shown. Rank the size of the Doppler shift (from largest to smallest) for the light from each star (A – E).
A. C > B > A > D > E
B. C > A > E > D > B
C. E > D > A > B > C
D. B > D > E > A > C
A. C > B > A > D > E
Compared to a 5-m telescope, a 10-m telescope gathers _____ light in the same amount of time.
A. the same amount of
B. twice as much
C. four times as much
D. eight times as much
C. four times as much
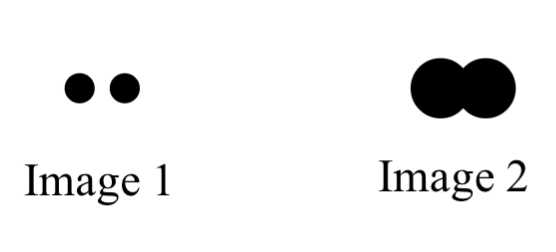
Below are two images of the same pair of stars. Both were observed over the same wavelength range for the same amount of time. One was taken with the 1-m telescope while the other was taken with the 2-m telescope. Which image was taken with the 2-m telescope?
A. Image 1
B. Image 2
C. There is insufficient information
A. image 1
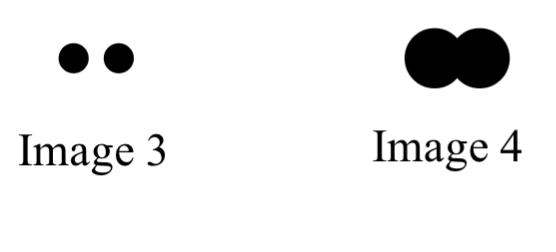
Below are two images of the same pair of stars. Both were observed with the same telescope for the same amount of time. One was observed with a red filter while the other was observed with a blue filter. Which image was taken with the red filter? (Note: The stars give off the same amount of light in both colors.)
A. Image 3
B. Image 4
C. There is insufficient information.
B. image 4
Most ground based telescope observe in the visible and radio wavelengths because
A. People are best suited to see in the visible wavelengths and hear in the radio wavelengths.
B. It is easiest to build telescopes which observe at these wavelengths.
C. All of the really cool objects emit light at these wavelengths.
D. Most other wavelengths cannot penetrate through the Earth’s atmosphere.
E. The Earth radiates too much energy in the other wavelengths, interfering with their detection.
D. Most other wavelengths cannot penetrate through the Earth’s atmosphere.