The Nervous system (OB2)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
function of a nerve cell
basic structural and functional units of the nervous system- neurons.
diagram of a neuron
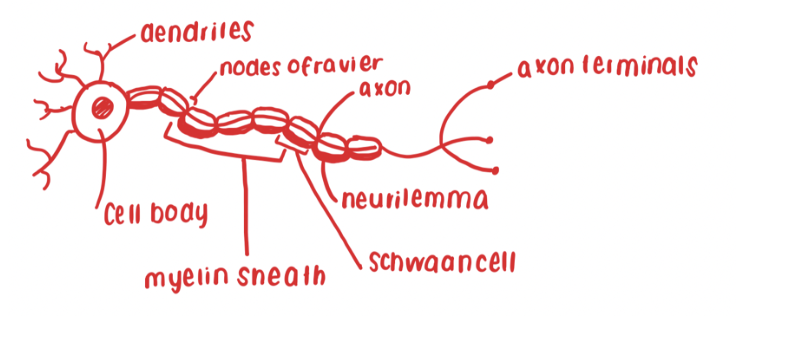
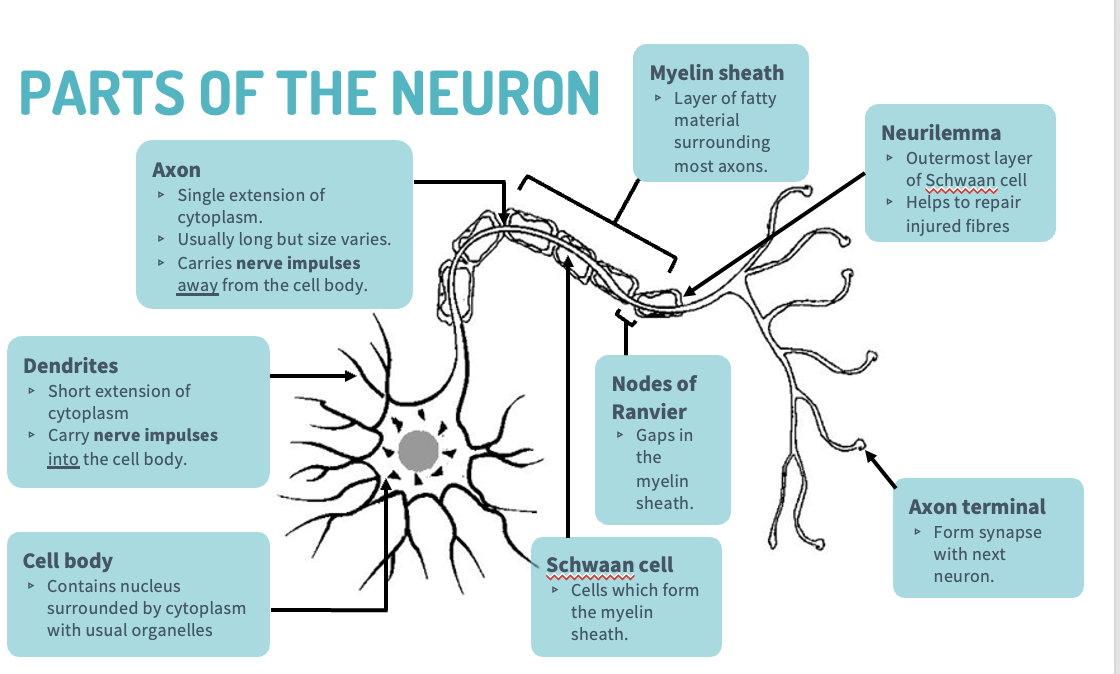
cell body
contains nucleus, surrounded by cytoplasm with usual organelles
dendrites
short extension of cytoplasm, carry nerve impulses to the cell body.
axon
single extension of cytoplasm, long but may vary in size, carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
Myelin sheath
layer of fatty material, surrounding most axons
Schwan cells
cells which may form myelin sheath
Neurilemma
outer layer of Schwan cell, helps repair injured fibres
Nodes of Ranvier
increase speed of nerve transmission
Axon terminals-
pass the nerve impulse to the next neuron, across a synapse.
functional classifications of neurons
Sensory neuron- carry messages from receptors in sense organs, or skin to CNS
Motor neurons- carry messages from CNS to the muscles and glands, the effectors.
Interneurons- link between sensory and motor neurons.
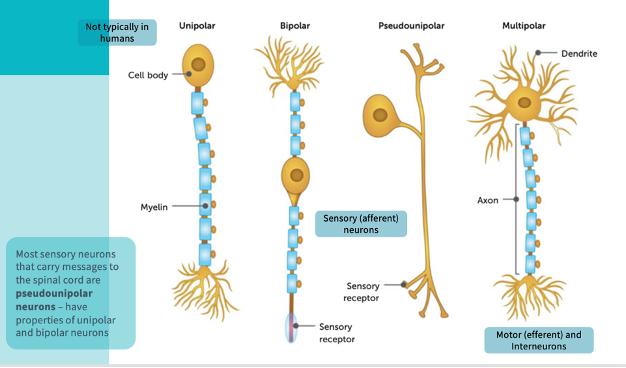
structural classifications of neurons
Multipolar neurons- one axon and multiple dendrites extending from cell body, most common, includes motor neurons and most interneurons and CNS.
Bipolar neurons- one axon and one dendrite, both have branches from the end
Occur in the eye, ear and nose, take impulses from receptors to other neurons.
Pseudo unipolar neurons- one extension only, an axon with a cell body to the side of the axon, most sensory neurons.
diagram of the different types of neurons
synapses
space between two neurons, nerve impulse is carried across it
distinguish between CNS and PNS
the CNS- made up of brain and spinal cord, incoming messages processed outgoing messages inititated
PNS- consists of nerve fibres carrying to and from CNS, 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 12 pairs of cranial nerves
The PNS- carrys nerve impulses to CNS where processed, carries outgoing messages from CNS
PNS VS CNS diagram

cranial and spinal nerves
Cranial nerves- twelve pairs which arise from the brain. Contain fibres that carry impulses into and away from brain.
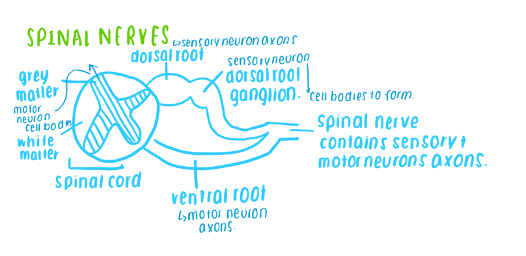
Spinal nerves- 31 pairs which arise from the spinal cord. They are all mixed nerves containing both sensory and motor fibres. Each nerve is joined to the spinal cord by two roots. The ventral root and the dorsal root.
structure of the spinal cord
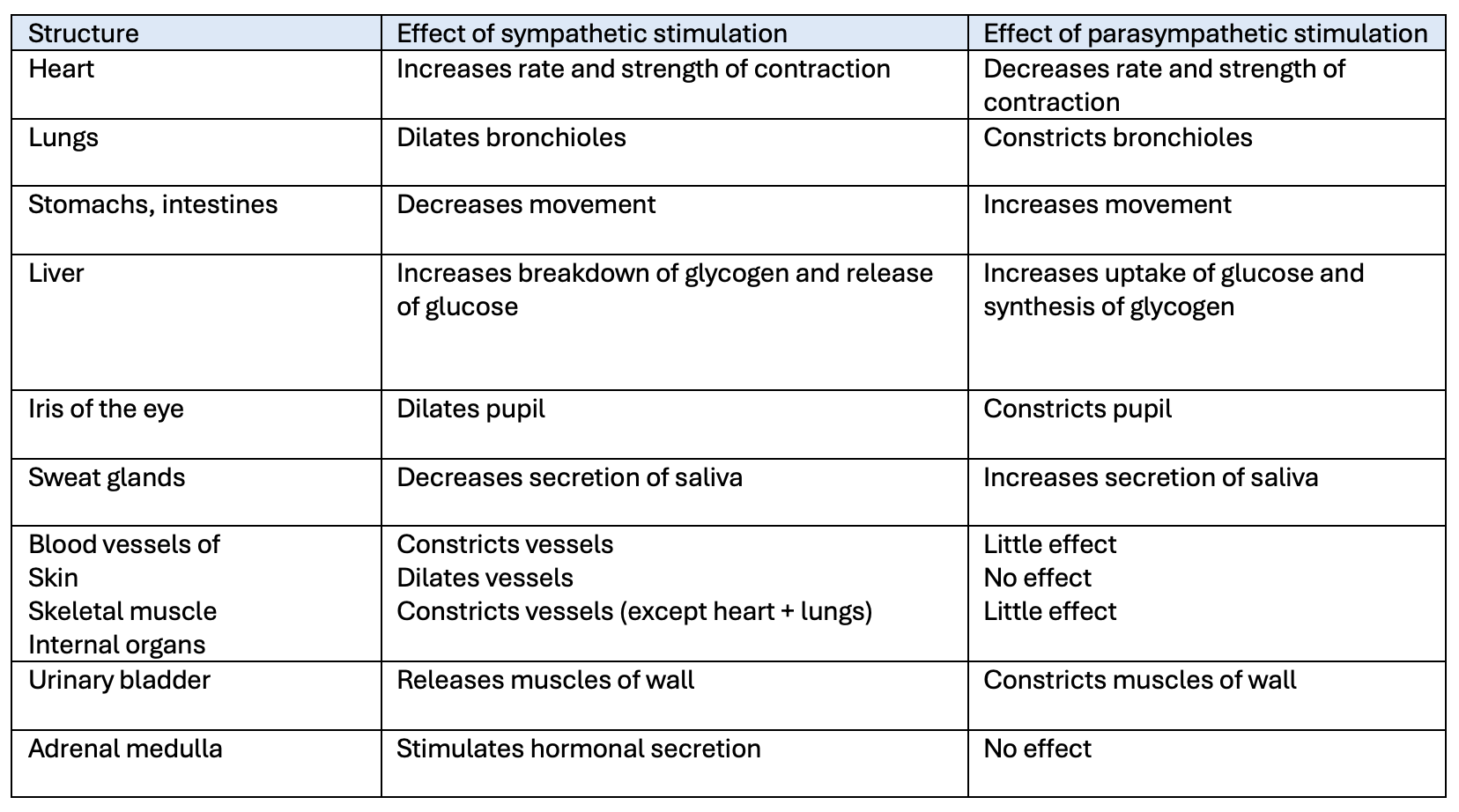
actions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system * table with stuctures
pathway the nerve impulse takes along a neuron
nerve impulse starts at the dendrites, travels to the cell body, down the axon to the axon terminal and then it goes across a synapse to the next neuron.
structure of the spinal cord
Spinal cord extends from the brain to the lower back, it is structured into different regions that coordinate sensory, motor and reflex functions
The nerve fibres are arranged into nerves, which arise from the brain and spinal cord.
ascending tracts
sensory axons that carry impulses upward, toward the brain.
descending tracts
contain motor axons that conduct impulses downward, away from the brain.
The afferent pathway of the PNS
contains sensory neurons which carry receptors away to CNS, main components- somatic sensory and visceral
somatic- neurons found in skeletal muscles and skin
visceral- neurons found in internal organs.
The efferent pathway of the PNS
motor neurons carry messages away from the CNS to effectors
divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system- takes impulse to skeletal musceles
autonomic nervous system- takes impulse to involuntary musceles + glands.
divided into
sympathetic- acts under stress, enables fight or flight response
parasympathetic- acts under rest, rest and digest responses
functions of the myelin sheath
acts as an insulator
protects axon from damage
speeds up movement of nerve impulses across axon