AP Psych Ch. 2 Vocab
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Biological psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes (applied by studying how brain damage affects behavior)
Biological psychologists
scientists who study the interplay of biology and behavior/mind
Neuron
a nerve cell; building block of the body’s neural information system, transmits messages from senses to brain (neuron notification)
Dendrite
receives information and conducts it toward the cell body (dendrite detect — the listener)
Axon
passes the message through its terminal branches to other neurons, muscles, or glands (axon acts — the speaker)
Myelin sheath
layer of fatty tissue that insulates axons and speeds impulses (makes messages move faster)
Action potential
brief electrical charge that travels down an axon when neuron fires (neuron’s zap of electricity)
Refractory period
resting pause after a neuron fires when it cannot fire again (reload time)
Excitatory signal
signal that pushes a neuron’s accelerator (go)
Inhibitory signal
signal that pushes a neuron’s brake (stops)
Threshold
minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural response (amount needed to fire)
All-or-none response
neuron either fires completely or not at all
Cell body/Soma
part of neuron that contains nucleus (neuron’s control center)
Terminal branches/buttons
end of axon that releases neurotransmitters (bus terminal is at the end of the line aka axon)
Synapse
meeting point between neurons, tiny gap where neurotransmitters meet
Neurotransmitter
chemical messenger released by neurons to transmit messages (mail man — think a barbershop haircut that costs a quarter)
Reuptake
process of reabsorbing excess neurotransmitters (brain recycling system)
Endorphins
neurotransmitters that relieve pain and increase pleasure (ex: runners high)
Agonist
molecule that mimics a neurotransmitter and stimulates a response (agonists activate)
Antagonist
molecule that blocks a neurotransmitter response (antagonists attack receptors)
Substance P
neurotransmitter involved in transmitting pain signals (p for pain)
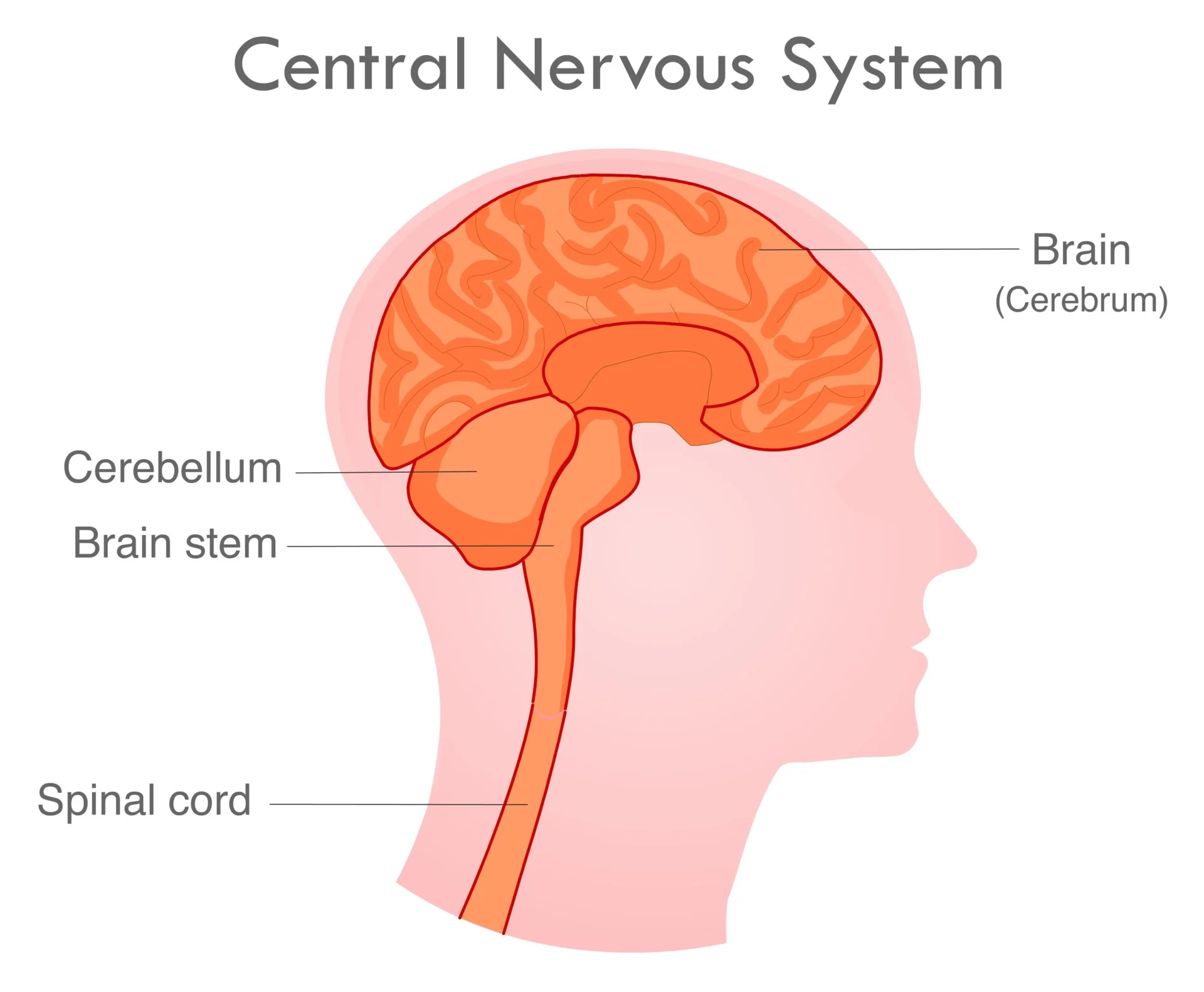
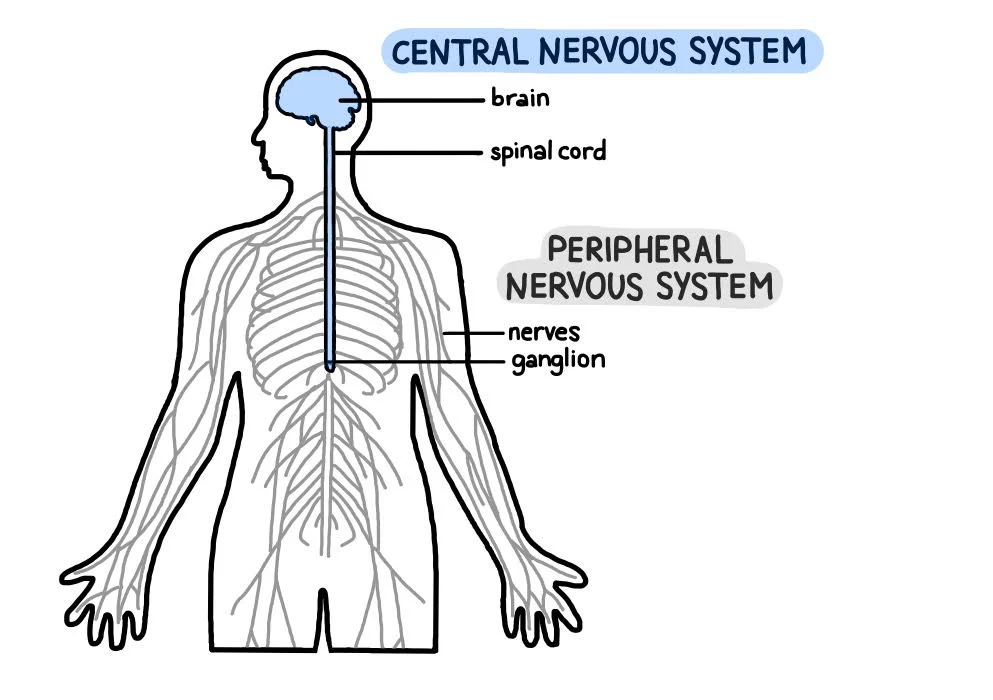
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord; decision-making center (central = command center in cord)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
sensory and motor neurons connecting CNS to body (peripheral = pathways)
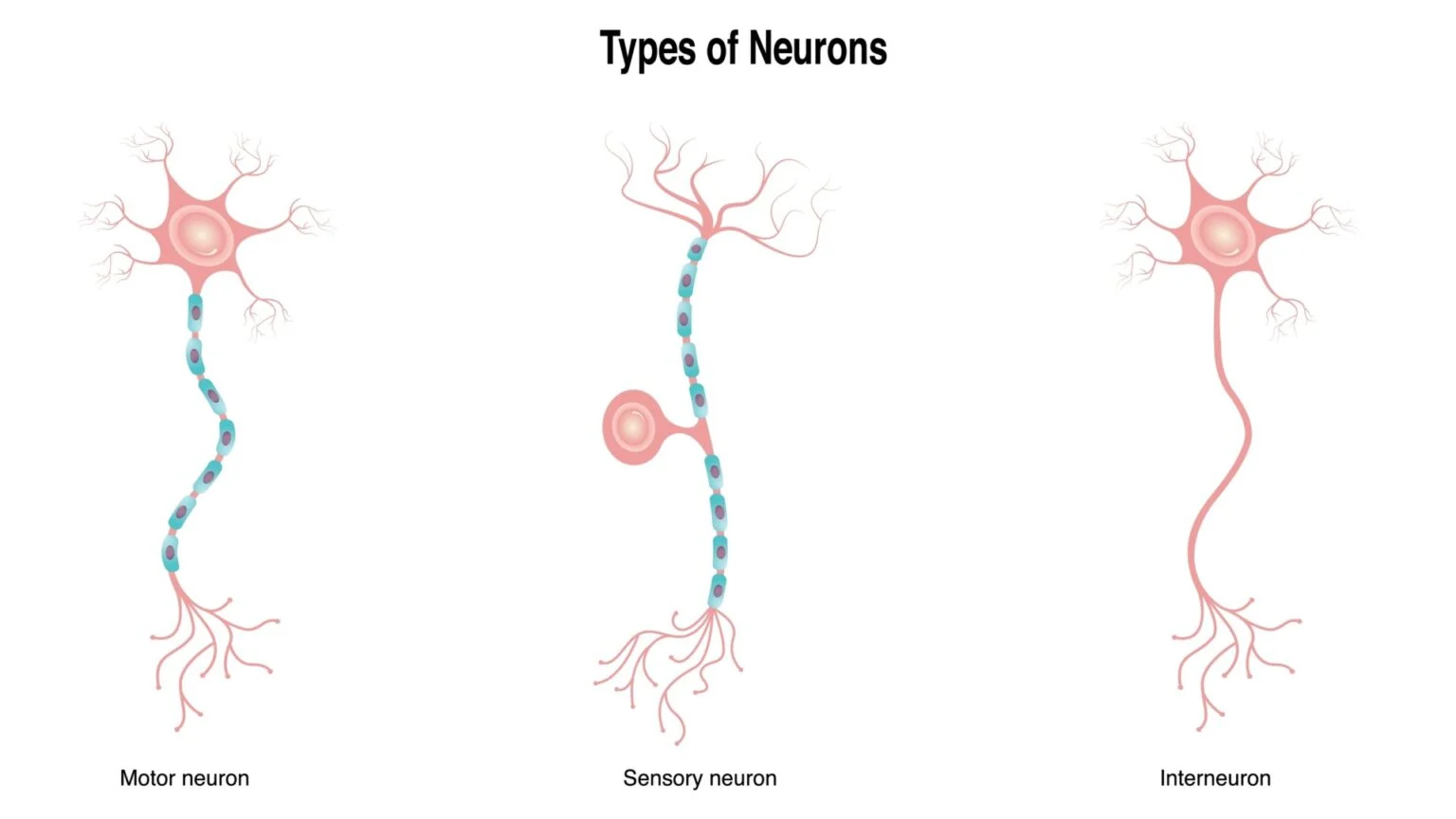
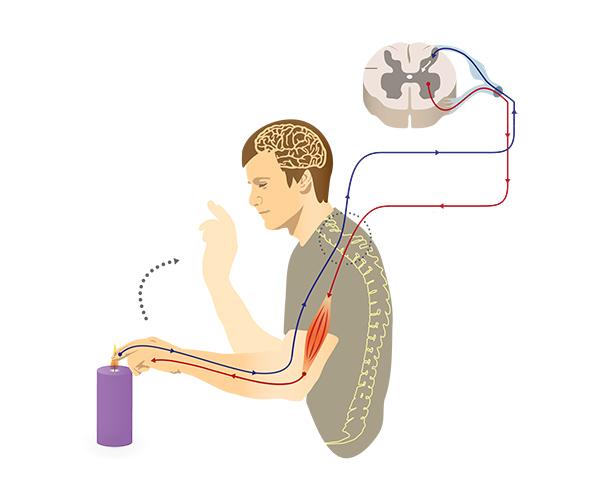
Sensory (afferent) neurons
carry incoming information from senses to brain/spinal cord aka CNS (sensory sends, affarant arrives)
Motor (efferent) neurons
carry outgoing instructions from CNS to muscles/glands (motor moves out, efferent exits)
Interneurons
neurons in CNS connecting sensory and motor neurons (internal connections)
Somatic nervous system
controls voluntary movement in PNS (SOMAtic — purposeful body control)
Autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary processes (AUTOnomic = AUTOMATIC)
Sympathetic nervous system
speeds things up, fight or flight response (yelling when seeing a spider)
Parasympathetic nervous system
calms and slows down body (rest and digest)
Reflex
automatic response to a stimulus (ex: knee jerk reflex)
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter involved in muscle movement, memory, learning. it is released by nerve endings to send signals across a synapse (ACh triggers muscles to ACH-tivate)
Endocrine system
the “slow" chemical communication system. a set of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream (exit onto hormone highway)
Hormones
chemical messengers that are mad3 by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues (snail mail of the body)
Adrenal glands
produce hormones like epinephrine/norepinephrine for stress response (ADRENALine for anxiety)
Pituitary gland
master gland controlling other endocrine glands (prominent pituary)
Melatonin
hormone that regulates sleep and increased production when dark (melatonin = mellow tone in)
Oxytocin
hormone managing reproductive behaviors, social bonding, trust, love

Lesion
tissue destruction in the brain to study function (lesion = lose function)
EEG
measures electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on scalp (brainwave listener, ELECTRODE EEG)
CT scan
X-ray images showing brain structure
PET scan
tracks brain activity via glucose consumption (PETs eat sugar)
MRI
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed brain images (MRI = magnetic map)
fMRI
tracks blood flow to show brain function and structure (f = function)
Brainstem
oldest brain region controlling automatic survival functions (stem = supports life)
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing (medusa stops medulla when turning a person to stone)
Pons
coordinates movement and controls sleep (lele pons dances and pons pillow)

Crossover point
point where nerves from each brain side connect to opposite body side
Thalamus
brain’s sensory hub (except smell) sending info to higher areas (ThalaMUST relay signals from senses)
Reticular formation
responsible for maintaining wakefulness and alertness. receives sensory signals from throughout the body and sends them to the brain cortex, which then initiates arousal (reTICKLE wake up)
Cerebellum
coordinates balance, movement, nonverbal (motor) learning (cerebelllum ballerina)

Amygdala
processes fear and aggression (amygdala anxiety and agression)

Hypothalamus
regulates hunger, thirst, body temp, sexual behavior, controls pituitary (hypo the llamas, feed water to the llamas to cool them down)

Nucleus accumbens
part of reward system linked to pleasure behaviors (accumbens award)

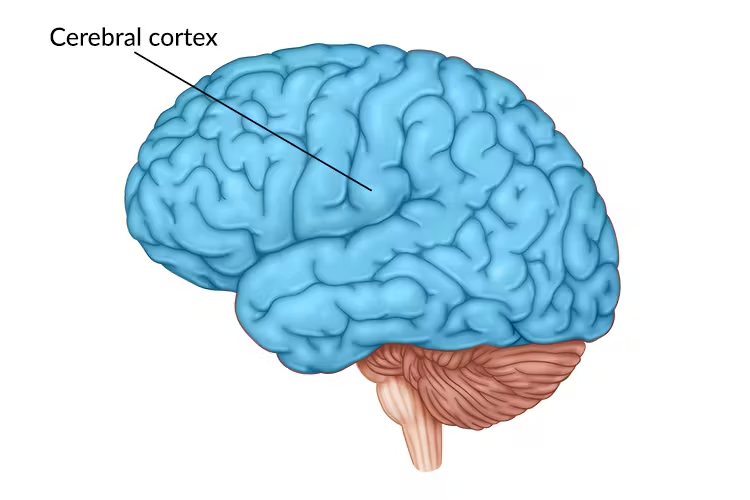
Cerebral cortex
Outer layer of brain; control & information processing center (cerebro sombrero) |
Glial cells
support, nourish, and protect neurons (glial guards of the neurons)

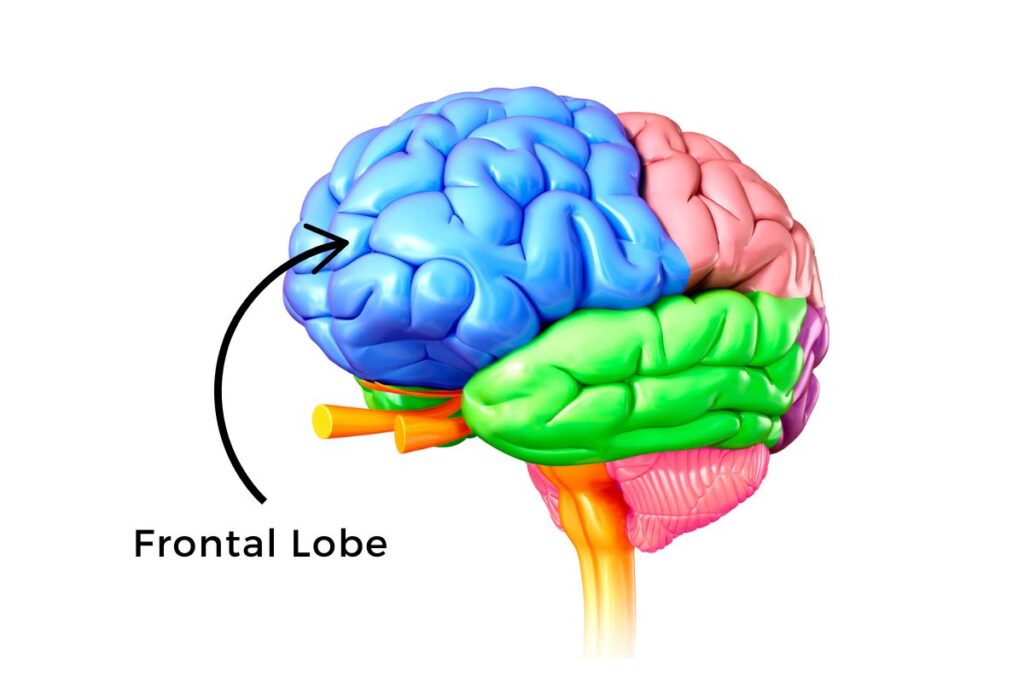
Frontal lobes
involved in speaking, muscle movement, planning, judgment (frontal lobe doesn’t develop until 25)
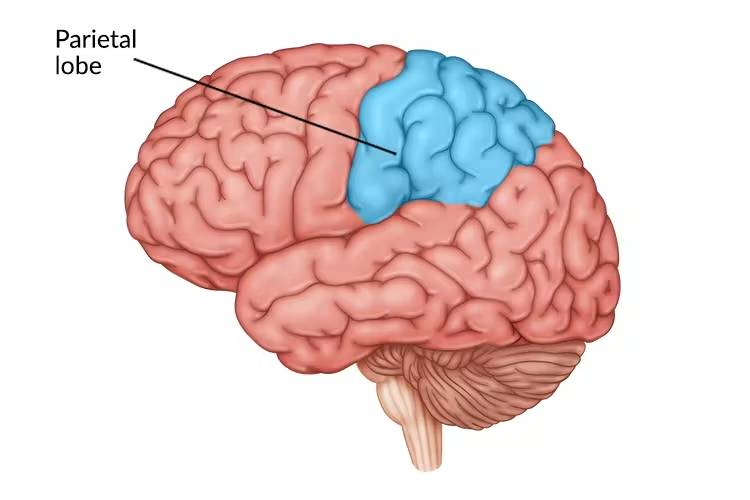
Parietal lobes
processes sensory input for TOUCH and body position (parietal pressure perception)
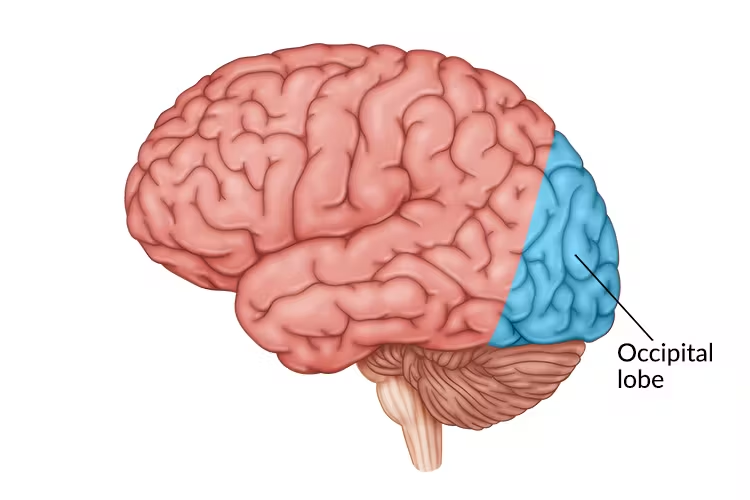
Occipital lobes
processes visual information (occipital open eyes)
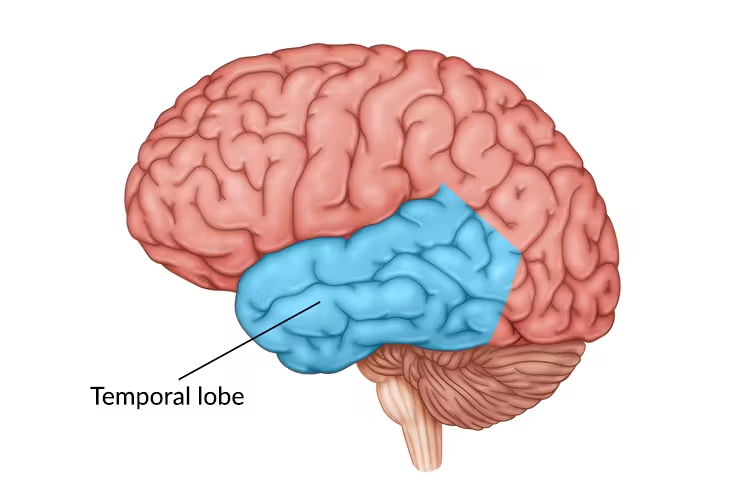
Temporal lobes
auditory processing, some memory, smell, vision (temporal temple near ears)
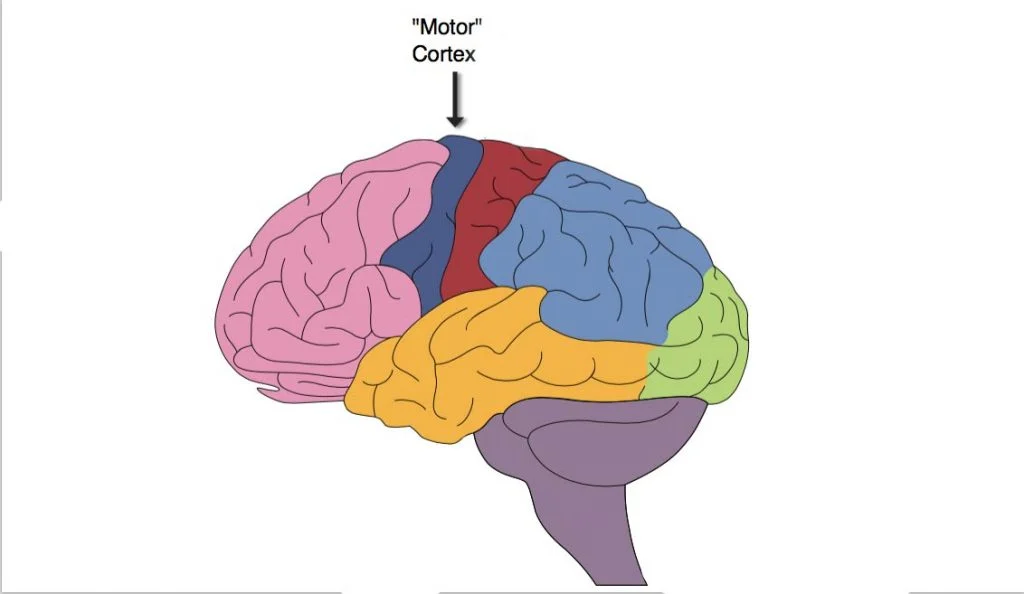
Motor cortex
plans, controls, and executes voluntary movements (motor = move)
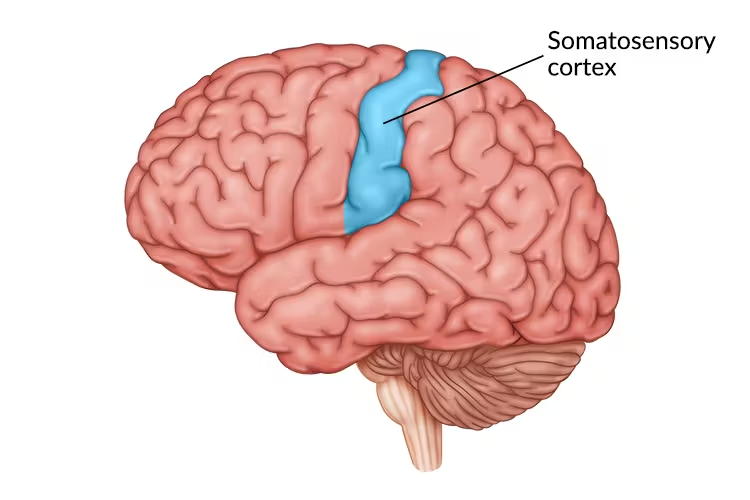
Somatosensory cortex
processes touch and movement sensations (soma = body sensory = senses)
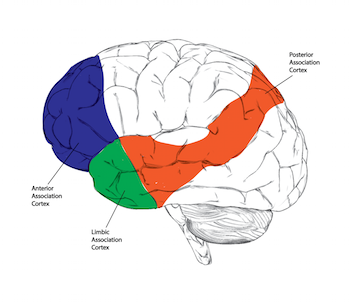
Association areas
involved in higher mental functions like learning, memory, speaking (associate ideas = higher think, in stats high association is smart)
Plasticity
brain’s ability to reorganize after damage or experience (plastic = flexible brain)

Neurogenesis
formation of new neurons (neuron generation)
Lateralization
Hemispheres have different functions. Left = language/math, Right = tone/patterns. (LATTERs = sides)
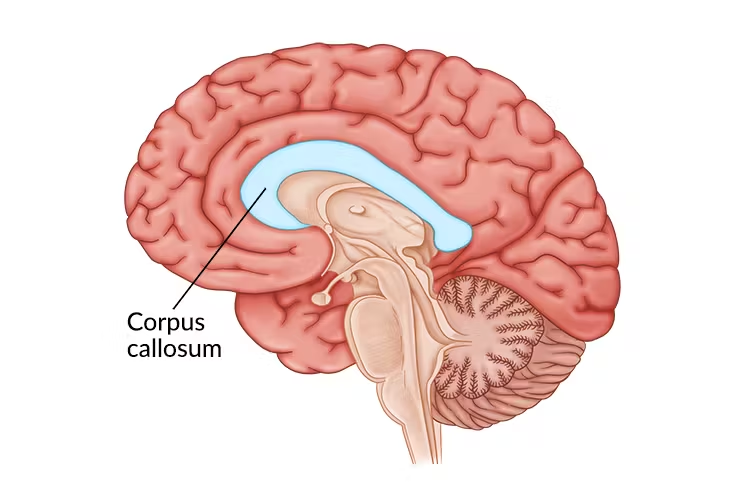
Corpus callosum
Connects left & right hemispheres (Like a bridge letting brain sides communicate)
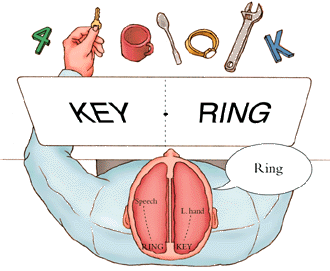
Split brain
When hemispheres are surgically separated (Left can speak, right cannot)
Blindsight
Responding to visual information without consciously seeing (Blind but avoids obstacles)
Dual processing
Brain processes information on conscious and unconscious tracks (High road = deliberate, low road = automatic)
Cognitive neuroscience
Links brain activity to mental processes (Scanning brain to see thinking)
Visual perception/action tracks
Perceiving vs. acting on objects (Look vs. reach)
Readiness potential
Brain activates before conscious decision (Hand moves before awareness)

Parallel processing
Fast, unconscious processing (driving on autopilot, driverless car = parallel parking)

Sequential processing
Slow, conscious problem-solving (writing an essay with your own brain power and NO CHAT)

Behavior geneticists
Study how genes and environment affect behavior (Scientists studying nature vs. nurture)
Environment
External influences shaping a person (Family, culture, experiences)
Chromosomes
DNA strands carrying genes; humans have 46 (Blueprint bundles)
DNA
Molecule holding genetic information (Instruction manual for body)
Genes
DNA segments that determine traits (Individual recipes in the manual)
Genome
All of an organism’s genetic material (Entire instruction manual)
Identical twins
From one egg, share 100% of genes (Clone-like siblings)
Fraternal twins
From two eggs, share ~50% of genes (Regular siblings born at same time)
Molecular genetics
Study of specific genes and traits (Zooming in on DNA instructions)
Heritability
Proportion of trait differences due to genes (How much of height/personality comes from genes)
Interact
Genes and environment influence each other (Nature and nurture “team up”)
Epigenetics
Environment can turn genes on/off (Stress or diet can switch genes)
Evolutionary psychology
Study of how natural selection shapes behavior and mind (Why behaviors exist, not should exist)
Natural selection
Traits aiding survival/reproduction get passed down (Survival of the fittest)
Mutation
Random genetic changes creating new traits (DNA “typos” that may help)
Adaptation
Trait increasing survival/reproduction (Like camouflage or fear of snakes)
Gender
Socially influenced roles/traits of males and females (Cultural expectations + biology)
Behavioral tendencies
Patterns shaped by evolutionary pressures (Fear of danger, social bonding, mate preferences)
Broca’s Area
A part of the brain, usually on the left side, that is crucial for producing speech and articulating words (SPEAKS AND PERFECTS GRAMMAR)
Wernicke’s Area
a region in the left temporal lobe of the brain that plays a crucial role in language comprehension (LISTENS AND UNDERSTANDS)