Week 2 - Body Systems I
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
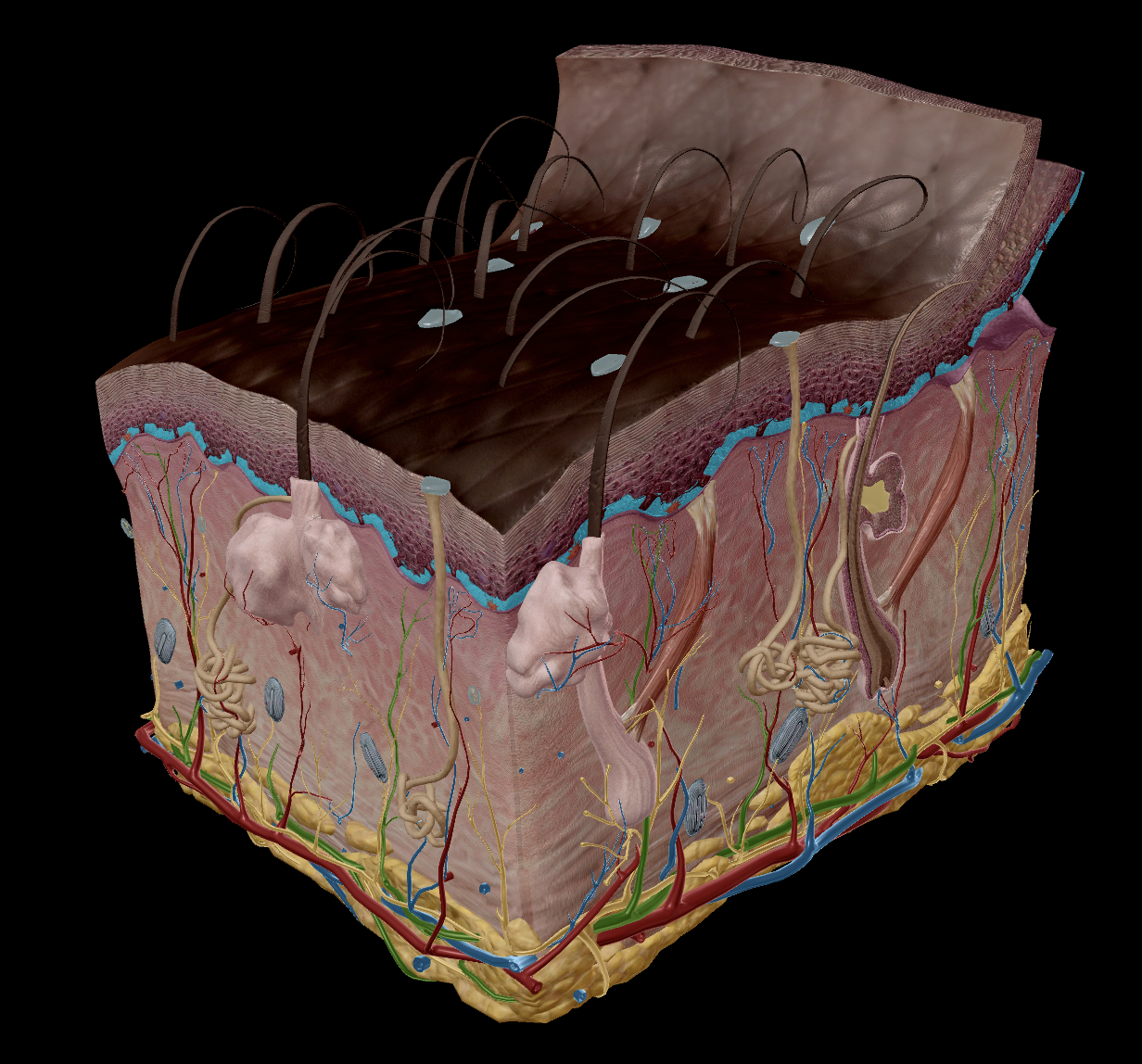
Integumentary system
Integumen: “Covering or a shield” - Latin
Contains - hair, skin, nails, sweat glands, etc.
All skin shares the same structure - Main difference lies in differing in melanin composition
Function:
Protection - barrier between the inner and outer environments
Temperature Regulation
Sensation
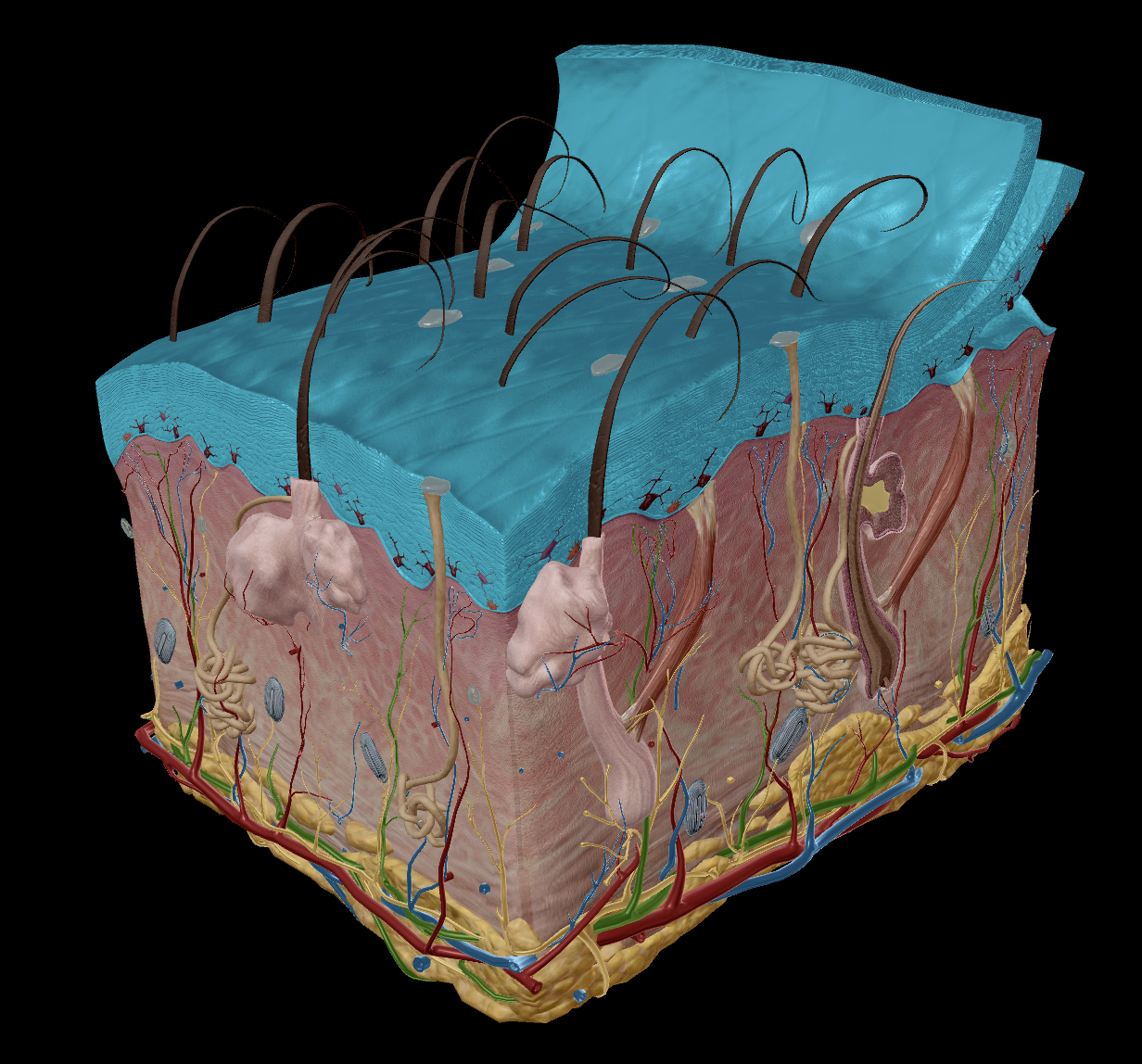
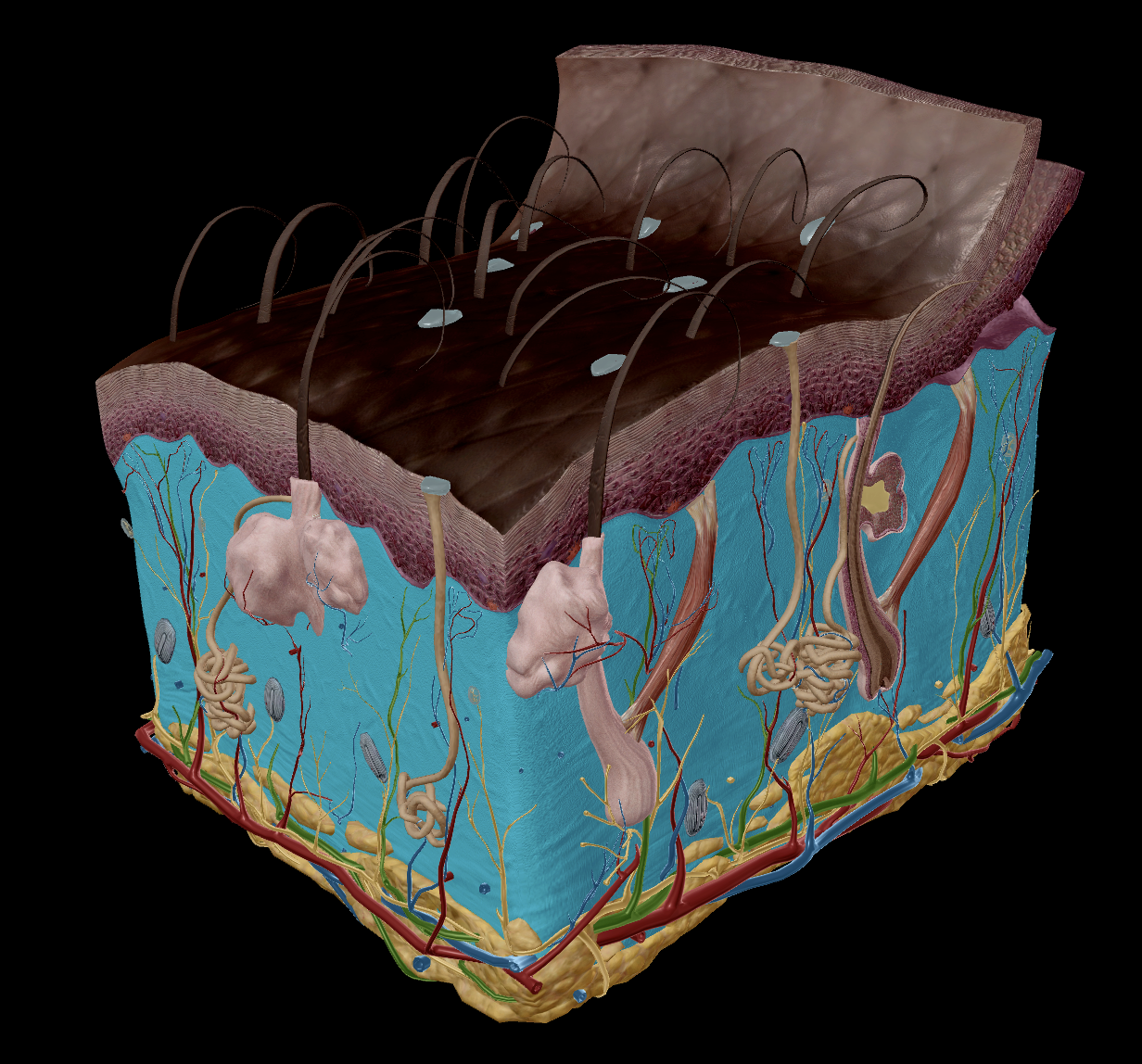
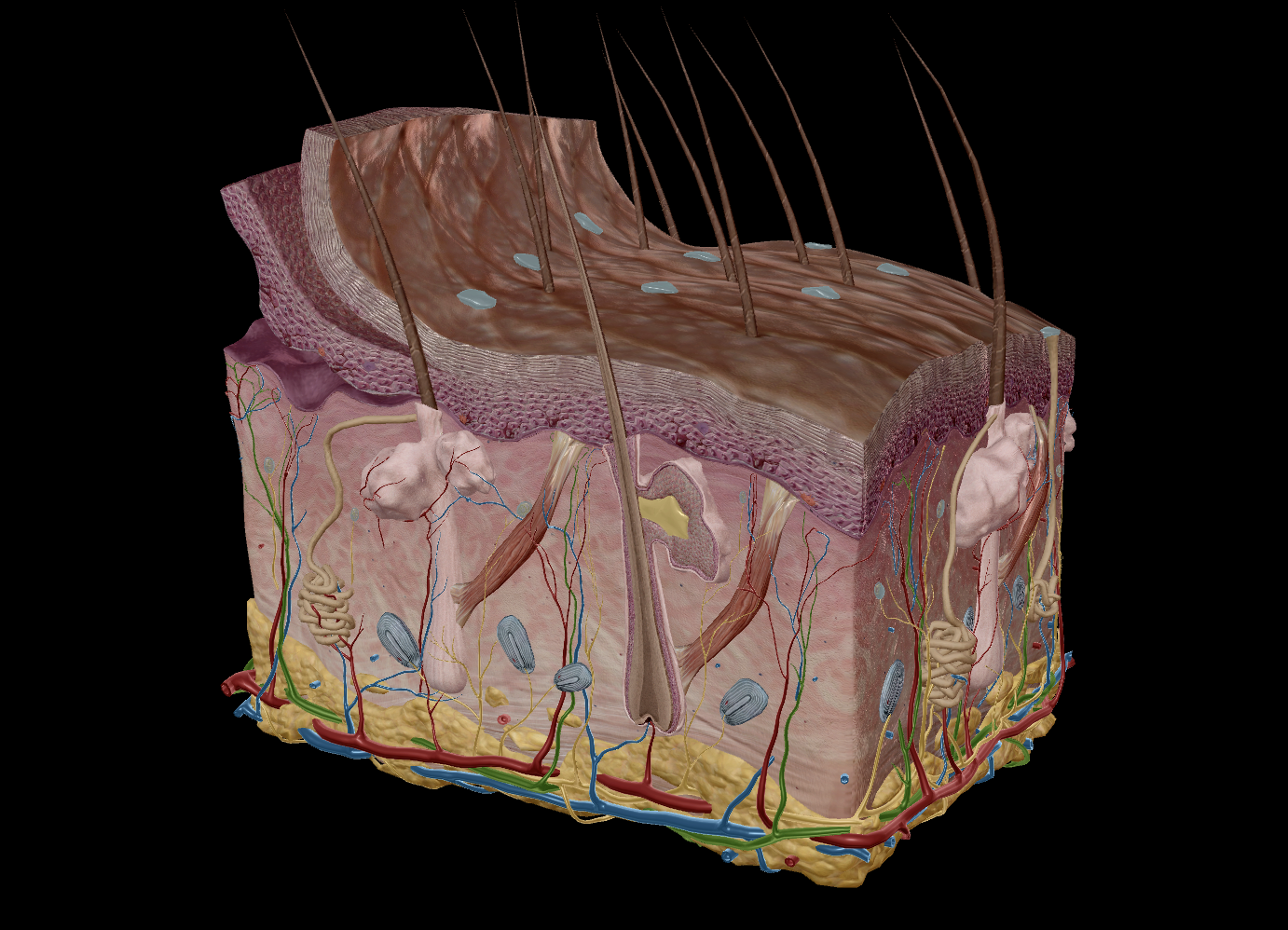
Integumentary system
Skin
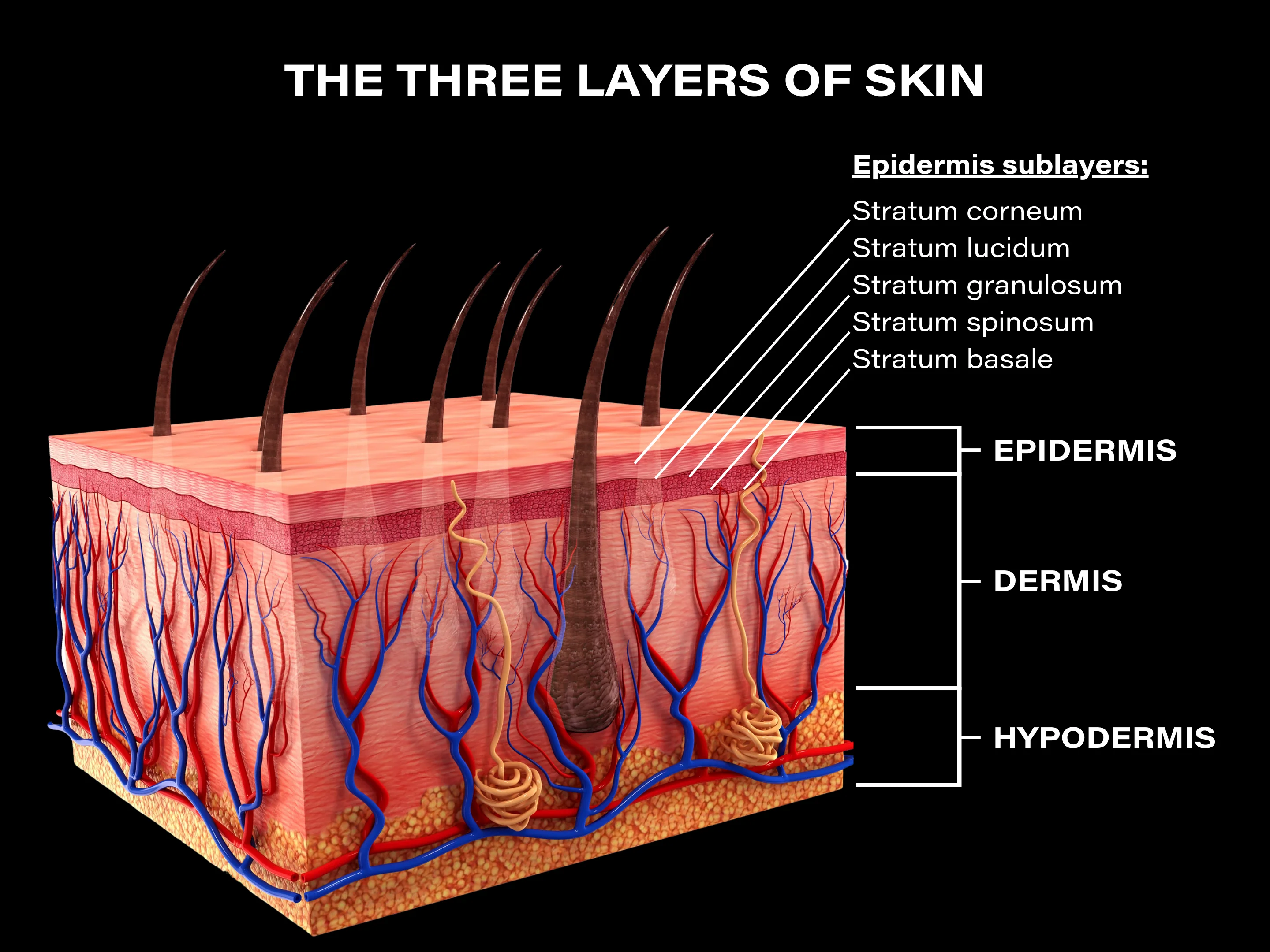
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Two sections:
Epidermis - The outer layer that serves to protect
Epithelial tissue
Dermis - serves to provide nutrients
Dense irregular connective tissue
collagen & elastin fibres
nourish the deeper layers of the epidermis
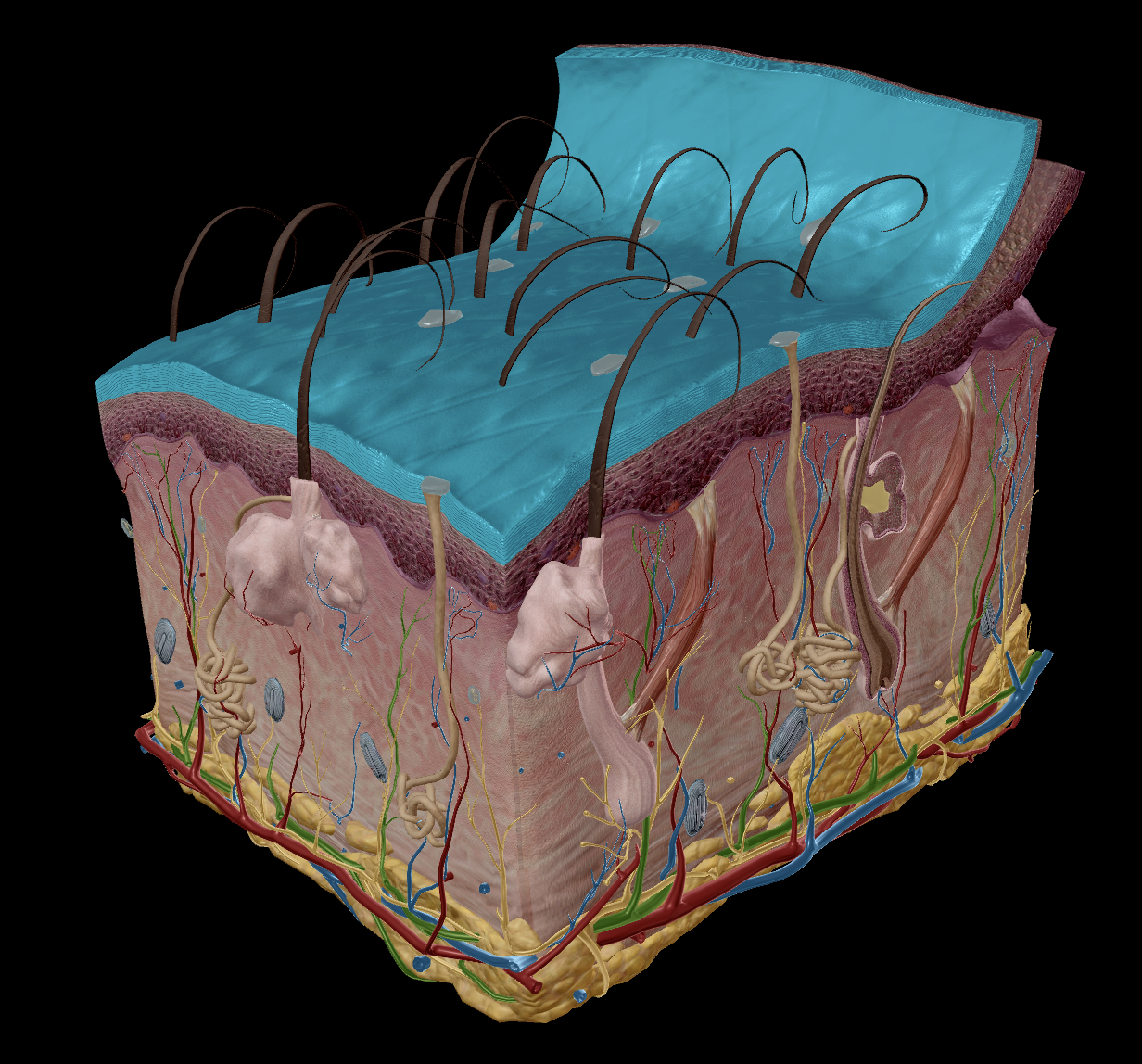
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Extremely thin - max 1mm
‘epi’ - means “on top of”
‘Stratum’ - means a “cover”
Two layers of the epidermis:
Stratum corneum - Superficial layer
‘Corneum’ - means “hardened”
Stratum basale - Deeper Layer
‘Basale’ - means “base”
Contains ONE LAYER of actively dividing cells - keratinocytes
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Basale’ - means “base”
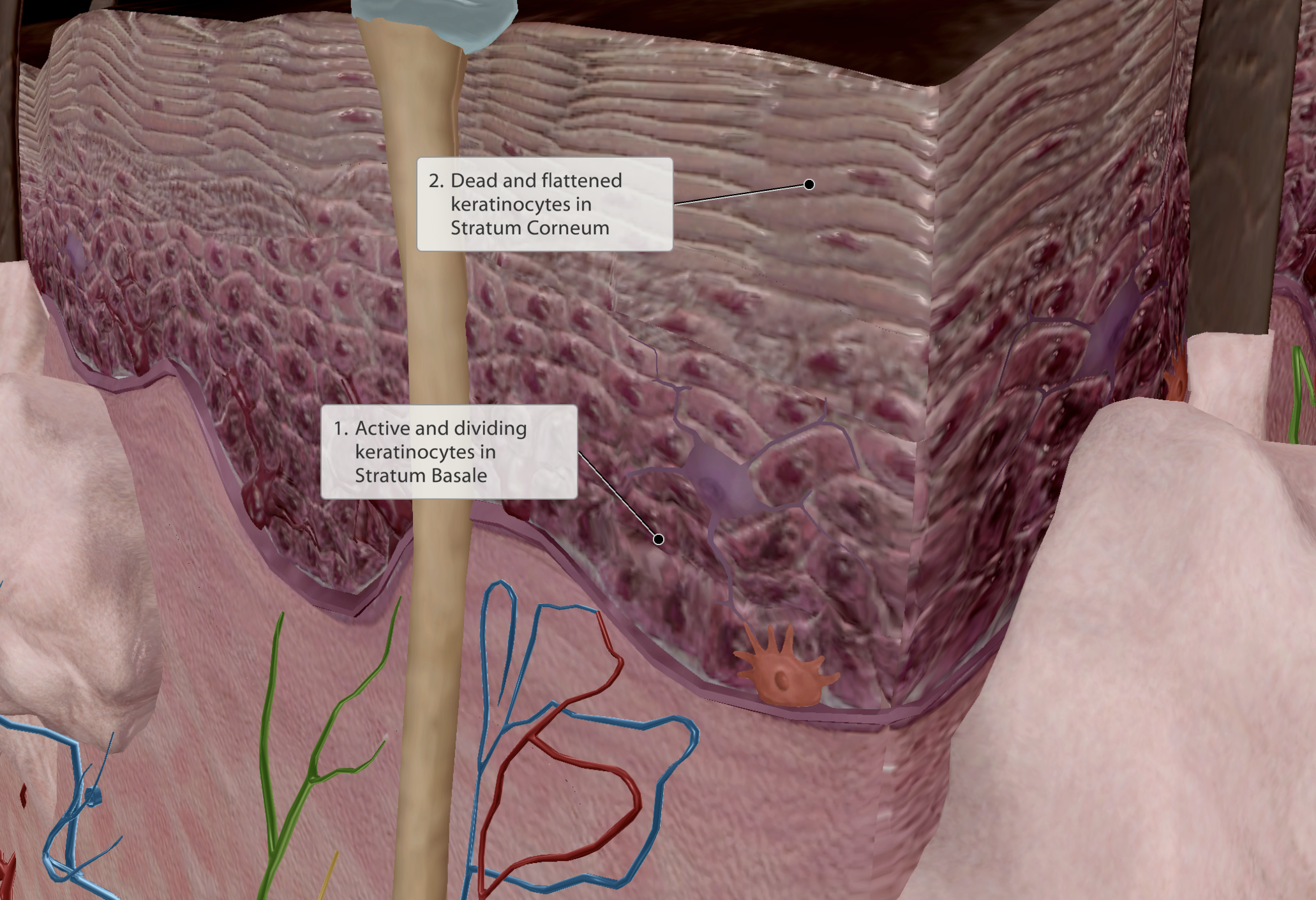
Contains actively dividing cells - keratinocytes
One Keratinocyte will split into two daughter cells.
One of the daughter keratinocytes is pushed further up, while the other stays to become a new dividing cell.
As the daughter cell moves through the layers up to the stratum corneum, they change their function.
Epidermis is avascular
No blood supply, but vessels present adjacent provide nutrients to the deepest layer of the stratum basale for keratinocyte division
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
‘Corneum’ - means “hardened”
20-30 layers of dead keratinocytes, flat, dead cells
Once keratinocytes reach the stratum corneum, they no longer receive blood supply, eventually dying and hardening into the outer layer.
Provides the skin keratin, contributing to the hard texture.
Millions of dead cells shed every day
e.g dandruff
Epidermis is avascular, stratum corneum receives no nurtrients.
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis - Keratinocytes
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Are epithelial cells, form epithelial tissue of the epidermis.
Most abundant call in epidermis
Chock full of keratin
Keratin helps absorb vitamin D from sunlight
Packed together
Dense packing helps limit the passage of substances (e.g water) into and out of the body
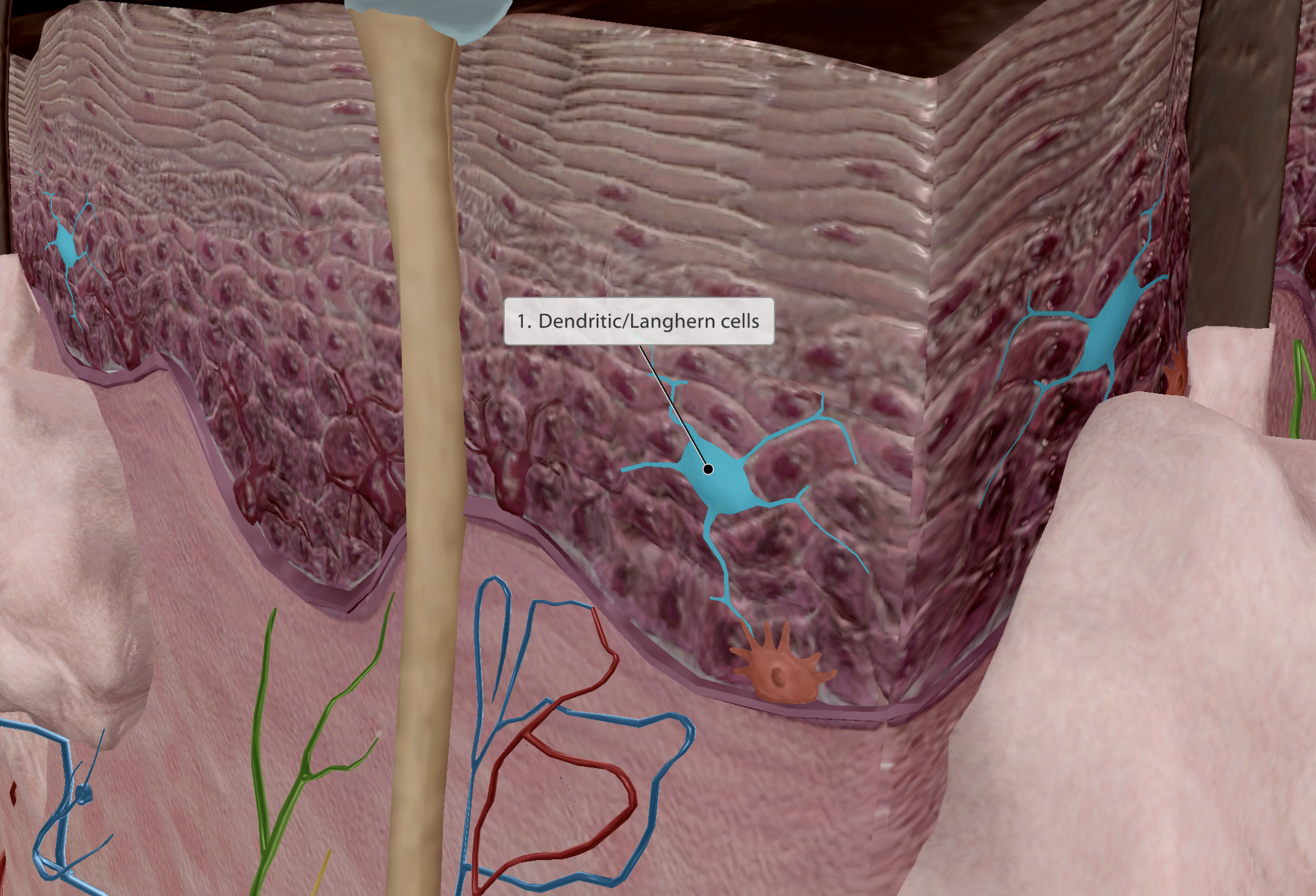
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis - Dendritic/Langhern cells
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Dendritic - Name given due to spider-like shape
Aids digesting foreign substances
Activators of the immune system
Integumentary system
Skin
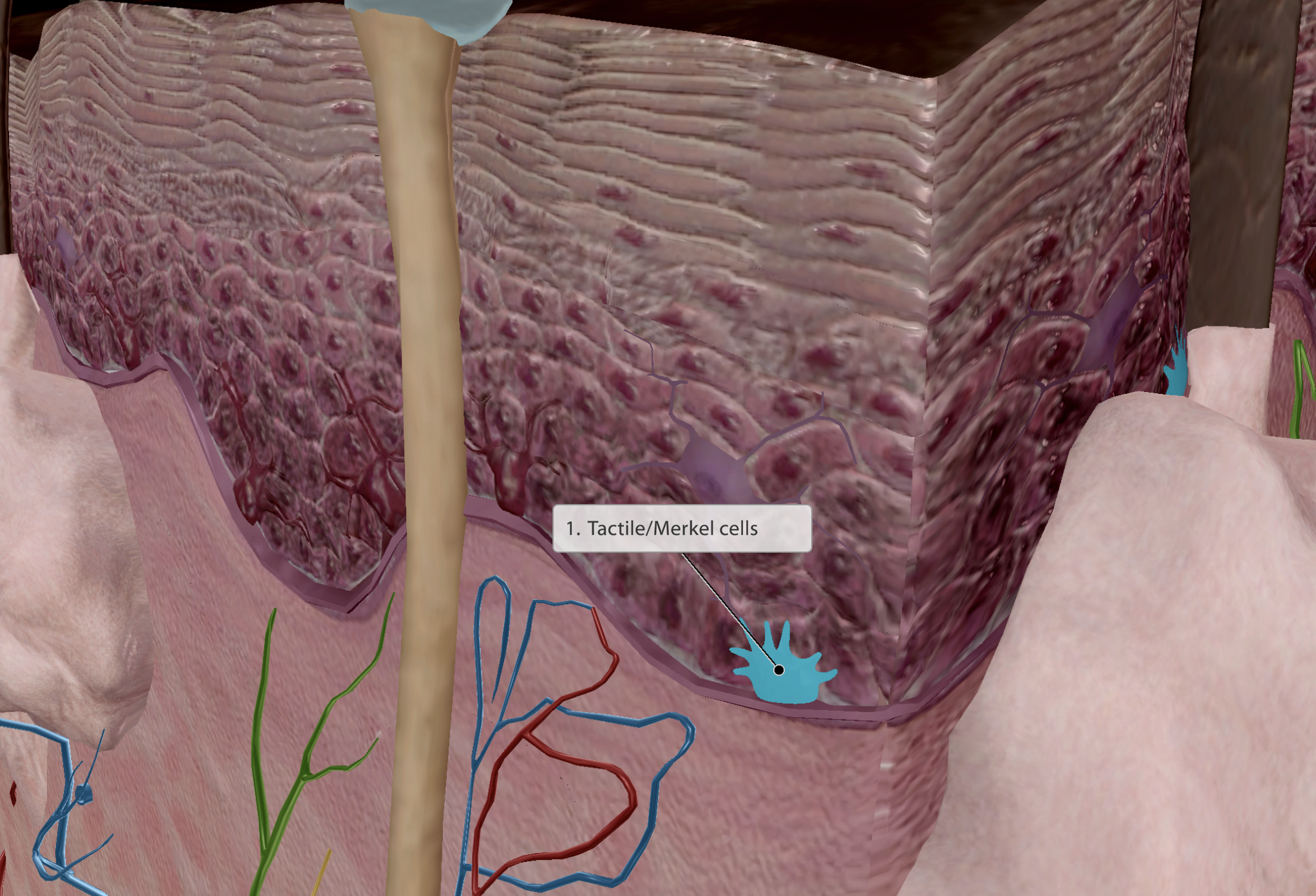
Epidermis - Tactile/Merkel cells
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Found at the border of the epidermis & dermis.
Disc like-structures
Connected to sensory nerve endings/tactile receptors for touch
Integumentary system
Skin
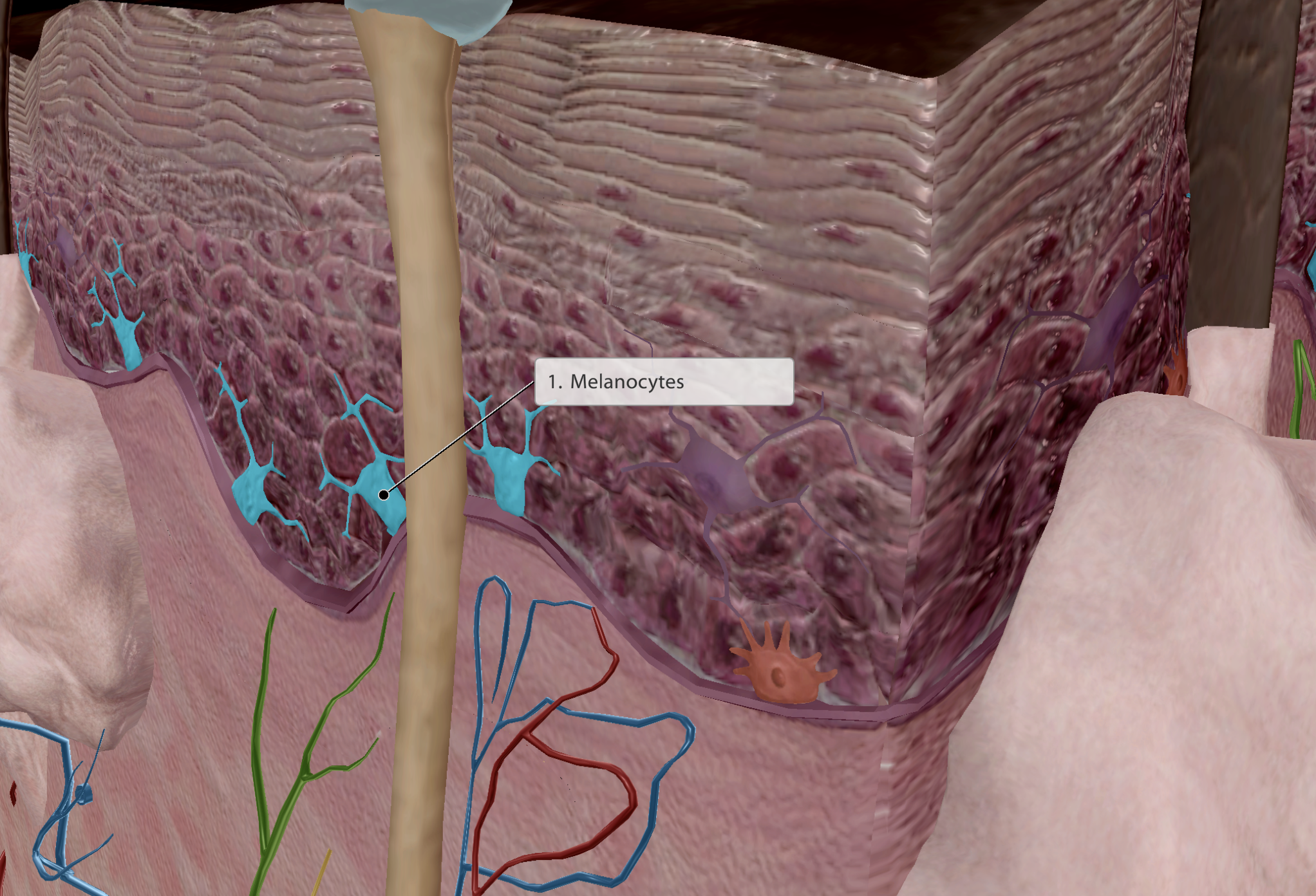
Epidermis - Melanocytes
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Produces melanin - pigmentation
The darker the skin, the greater melanin/melanosomes present. But no. menalocytes is constant across all skin types
Melanin then wraps around keratinocytes, trapping and cupping their nucleus
This protects keratinocytes from UV rays when absorbing Vitamin D from the sunlight
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Dermis - serves to provide nutrients
Dense irregular connective tissue
Collagen & elastin fibre
Tissue becomes strong (collagen) but flexible (elastin) in structure
Vasculated & Innervated
Nourishes the deeper layers of the epidermis (Stratum Basale)
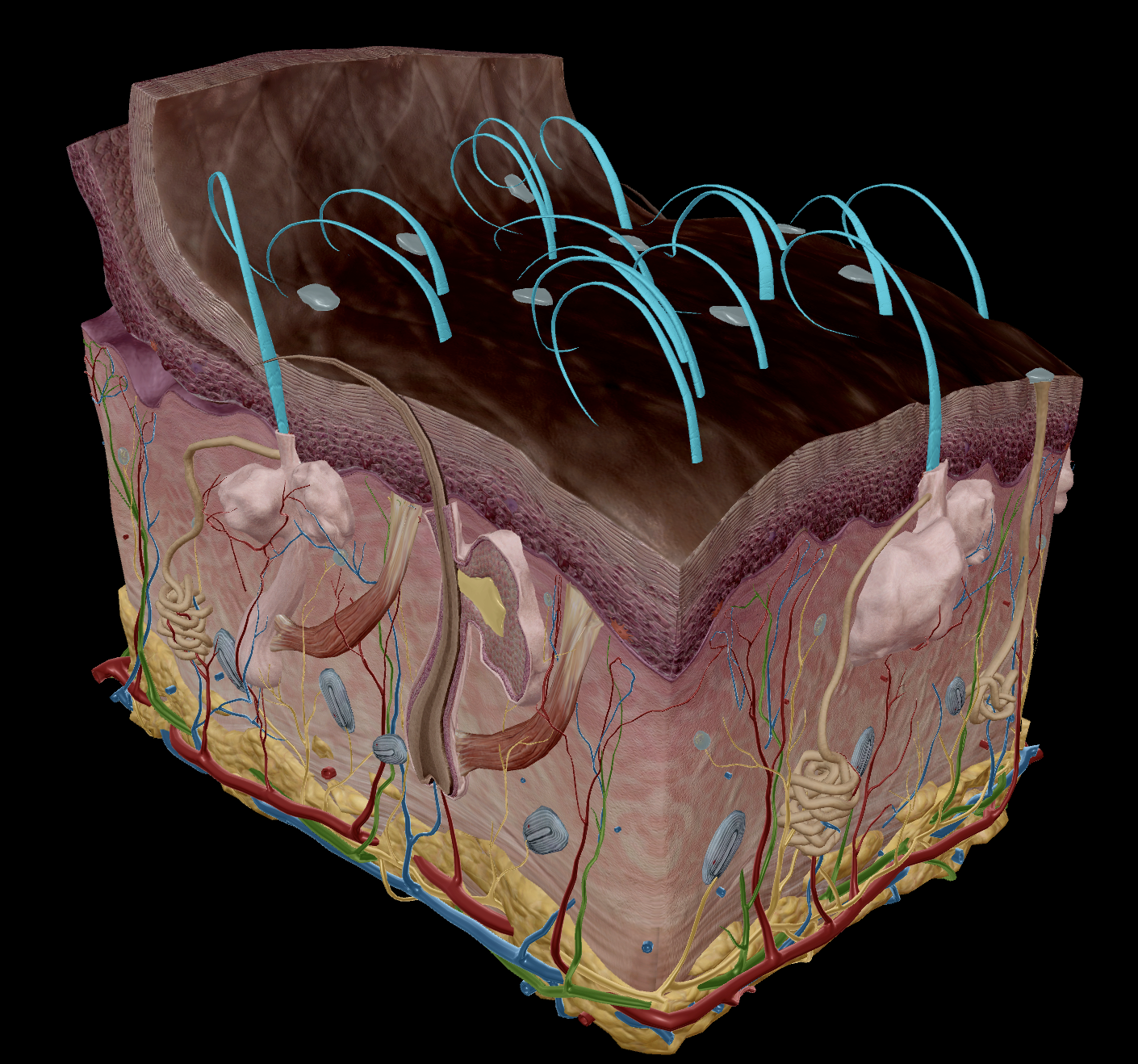
Contains appendages such as:
Hair follicles
Sweat glands
Sebaceous glands
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Formed by Keratin
Found almost everywhere (sans palms, soles, lips, etc.)
Helps detect sensation (crawling insects)
Keeps warmth/prevents heat loss
Protects head from trauma
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Formed of myoepithelial cells (Muscle epithelial cells)
Muscular - Are able to contract to eject sweat out of glands
Stimulated by sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)
Produces sweat:
Temperature regulation
Kills microbes on skin
Has low pH
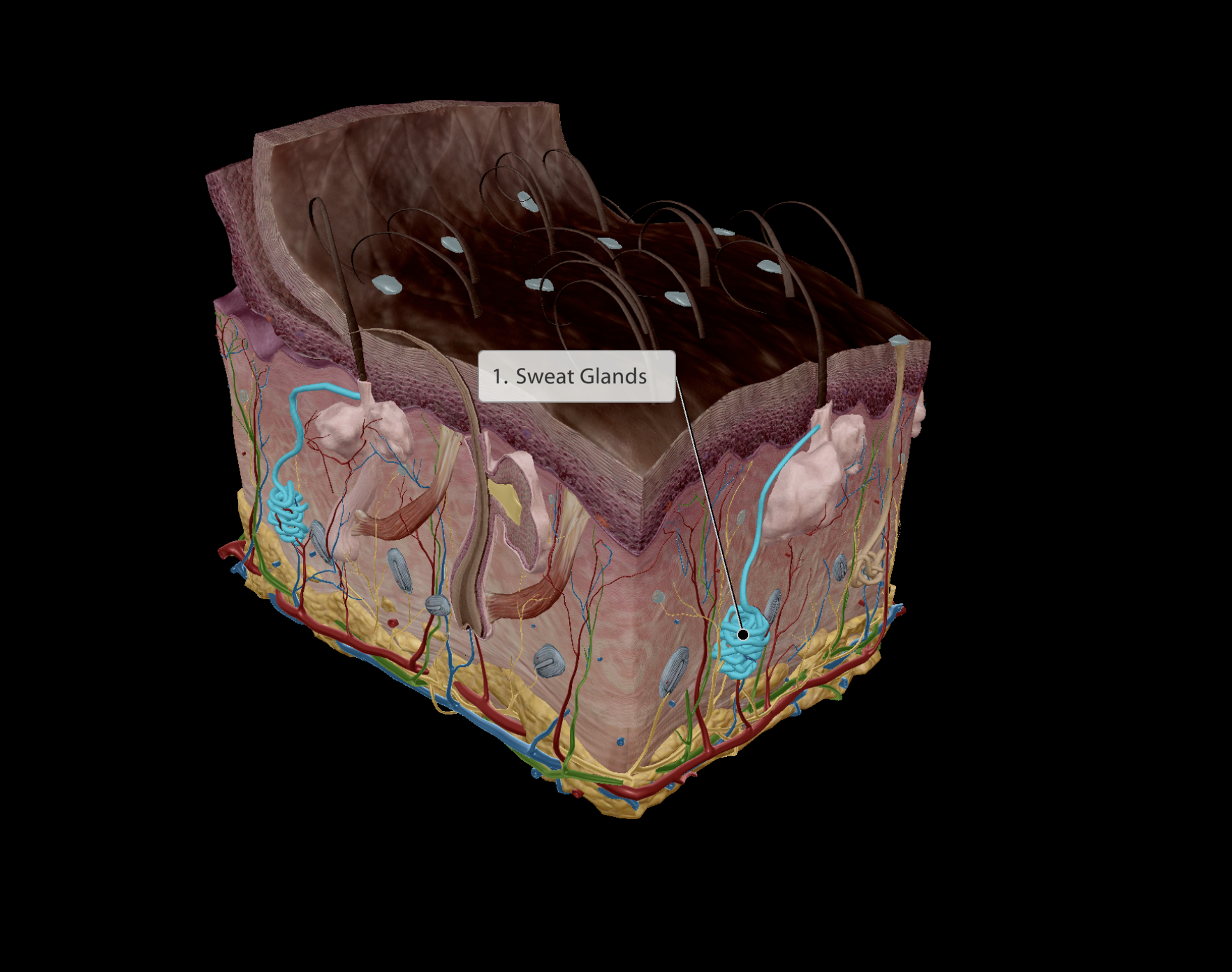
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Produces sebum:
Sebum is oily
Lubricates hair and skin
Contains bactericide (like pesticide wards of bacterial infection)
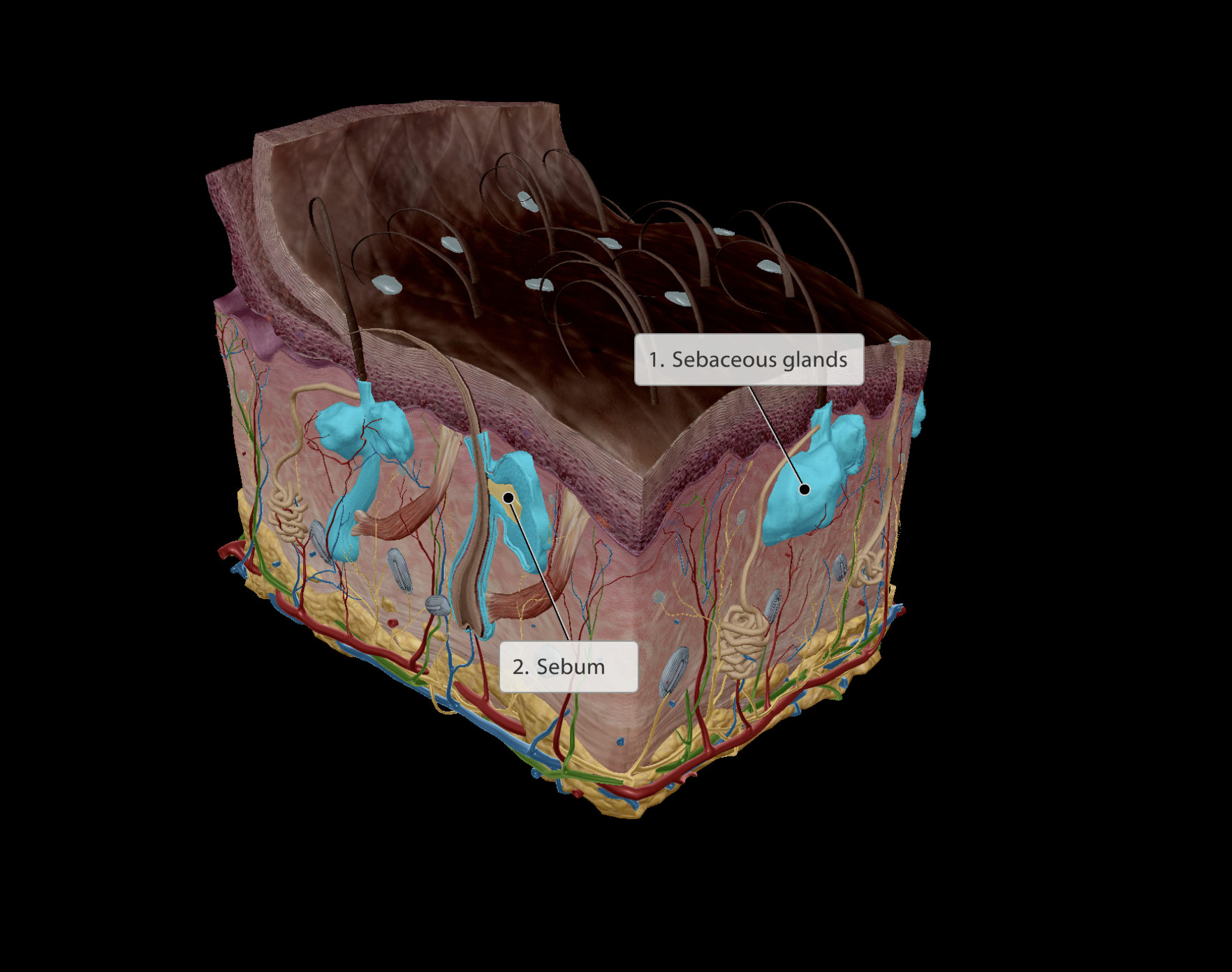
Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Basale
Dermis
Appendages:
Hair
Sweat Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Formed of keratin
Protection
Fine dexterity
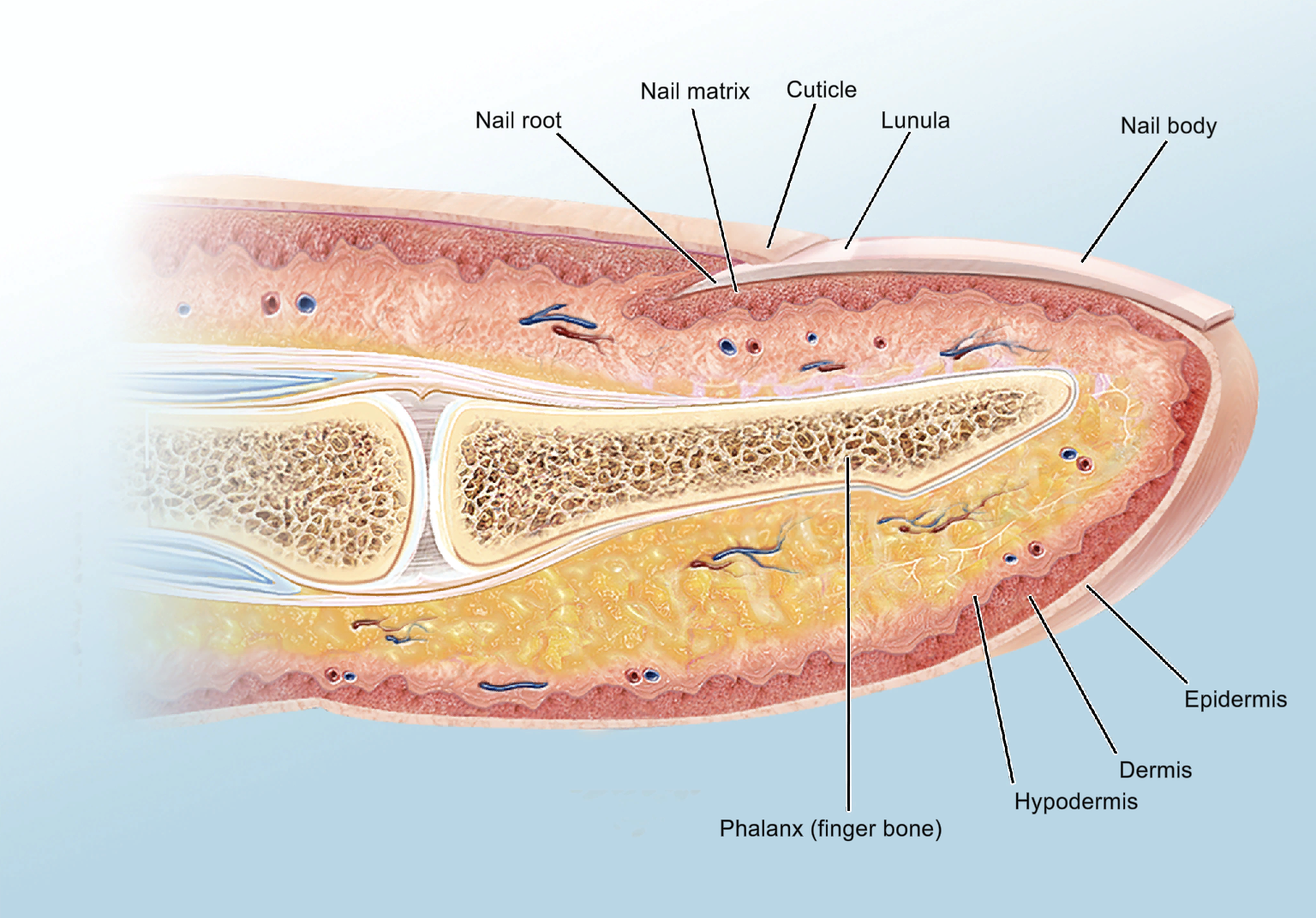
Pseudo-Integumentary system
Skin
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
Contains loose connective tissue - adipose tissue
Deeper to the dermis
Attaches dermis to deep fascia
Vasculated & innervated
Adipose tissue (fat):
Stores energy as fat
Provides insulation, thus helps retains heat
Shock absorption
Enables the skin to slide around slightly without tearing muscles
Not actually part of the integumentary system
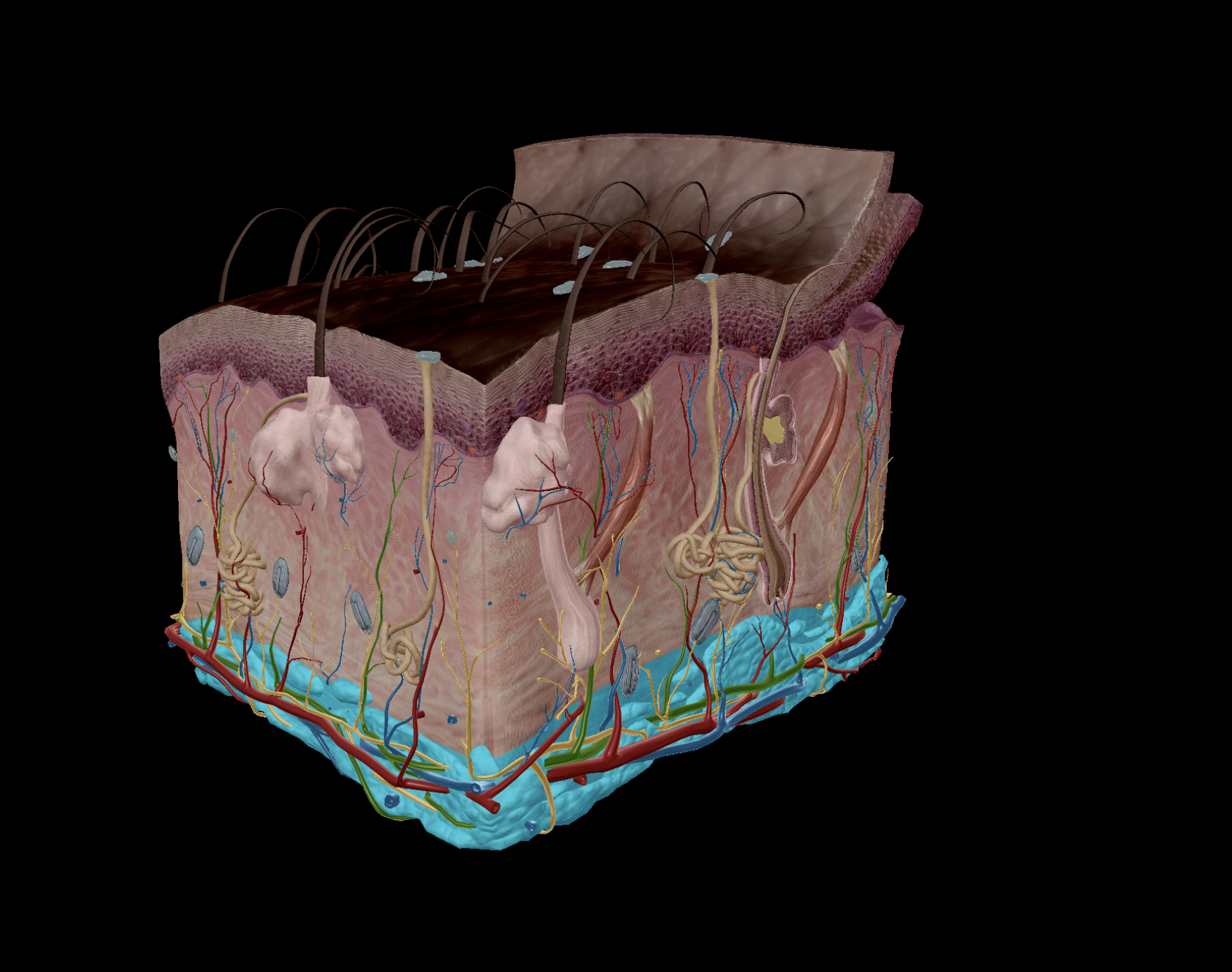
FUNCTIONS - Integumentary system
Protective barriers
Physical
Keratinocytes blocking foreign substances with tight packing
Melanin from melanocytes blocking UV ray absorption
Chemical
Sweat lowers pH to make is difficult for bacteria to survive
bactericide from sebum
Biological
Dendritic cells digesting foreign substances/initiating immune responses
Sensation
Touch, pressure, pain (noiciception) and temperature
Temperature regulation
Regulating blood flow to the skin, to radiate heat from blood
Heat loss through sweating
Vitamin D absorption/production
Keratinocytes
Skeletal System
Contains - Bones, ligaments & cartilage
Function:
Provides the base structure of the body
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline/articular
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
Support
provides a base frame for other body systems to attach and be supported by
Anchorage
Skeletal muscles connect to bones via tendons, pulling the bones to facilitate movement
Protection
The rigidity of bones allow them to protect other soft tissue/organs. (e.g skull protects bone, ribs protect heart & lungs)
Mineral storage
Calcium & phosphate is stored within bones (calcium hydroxyapatite), which can be released when needed by other organs (Ca2+ & PO43- ions)
Muscles and neurons use calcium to contract/propagate action
DNA requires phosphate ion (phosphodiester bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone)
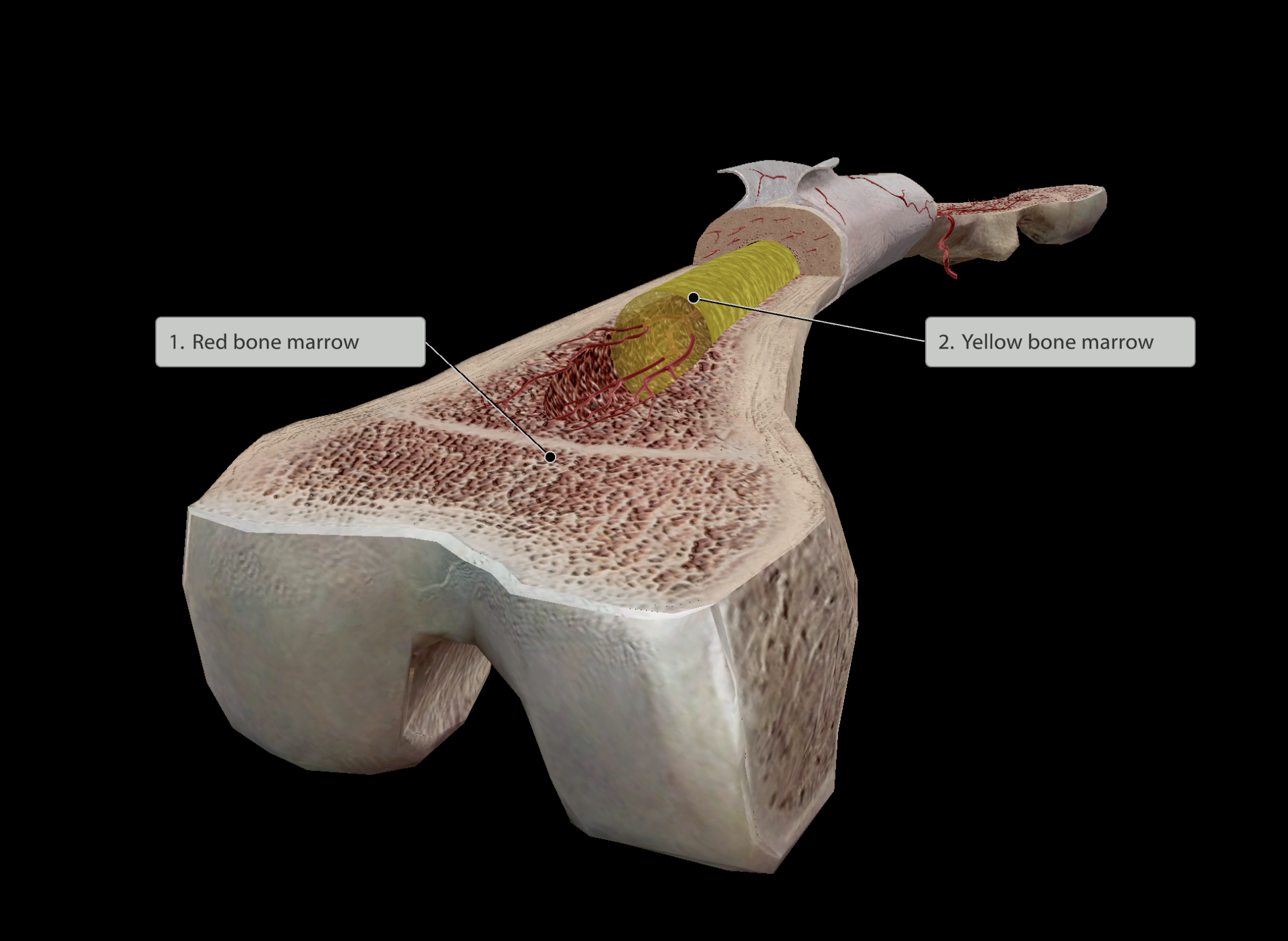
Hematopoiesis
‘hemato’ - blood
‘poiesis’ - Greek for “to make”
Red bone marrow stored within the spongy bone is the cite of blood cell formation
Usually occurs at the end of long bones
Fat storage
Yellow bone marrow
Stored usually in the middle shaft of bones
Hormone: osteocalcin
Produced in bone
Hormones aids with glucose homeostasis
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline/articular
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
Softer than bones
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline/articular
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
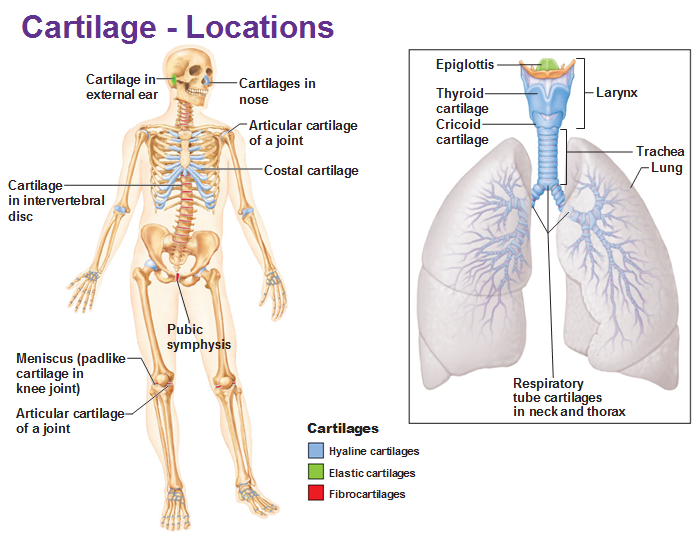
Provides flexibility and smoother surfaces at joints, lowering friction.
Most abundant cartilage type
‘hyaline’ - Greek/latin for glassy
Found at the end of bones meeting at a joint.
Also found in growth plates on bones
Cartilage of nose and rib to sternum connection
Also found making up trachea, bronchi and larynx
Arthritis can arise with the breakdown of hyaline cartilage
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline/articular
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
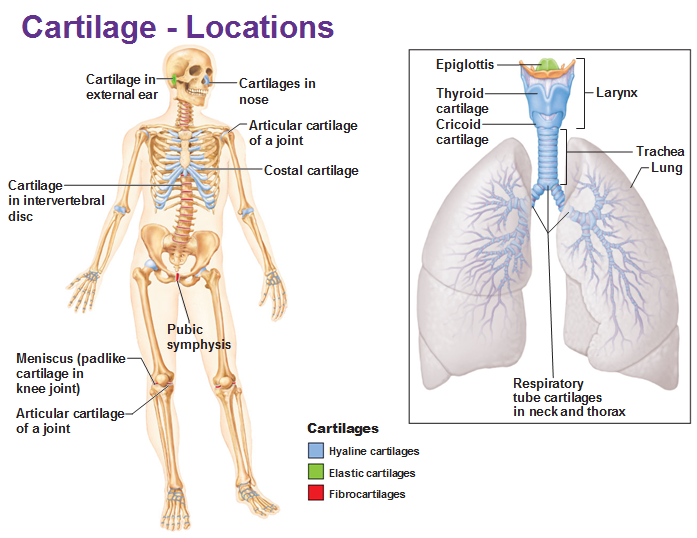
Contains much more elastin compared to other cartilage
enables it to maintain original shape after being manipulated
Found in:
Ear
Eppiglottis
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline/articular
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
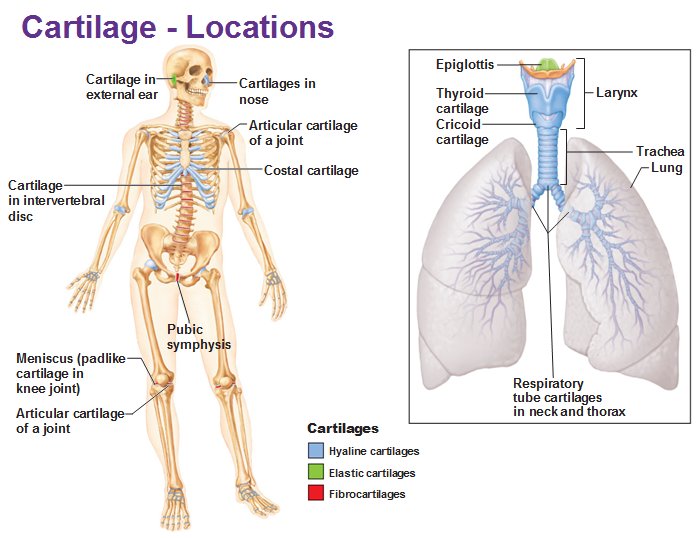
Withstands much compressive & tensile force
tensile force - pulling
Found at:
sites of pressure & stretch
Intervertebral discs
pair of meniscus at knee
pubic symphysis
helps bear the weight of the pelvis while also withstaning the pulling apart occuring during childbirth
Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilage
Hyaline
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Ligaments
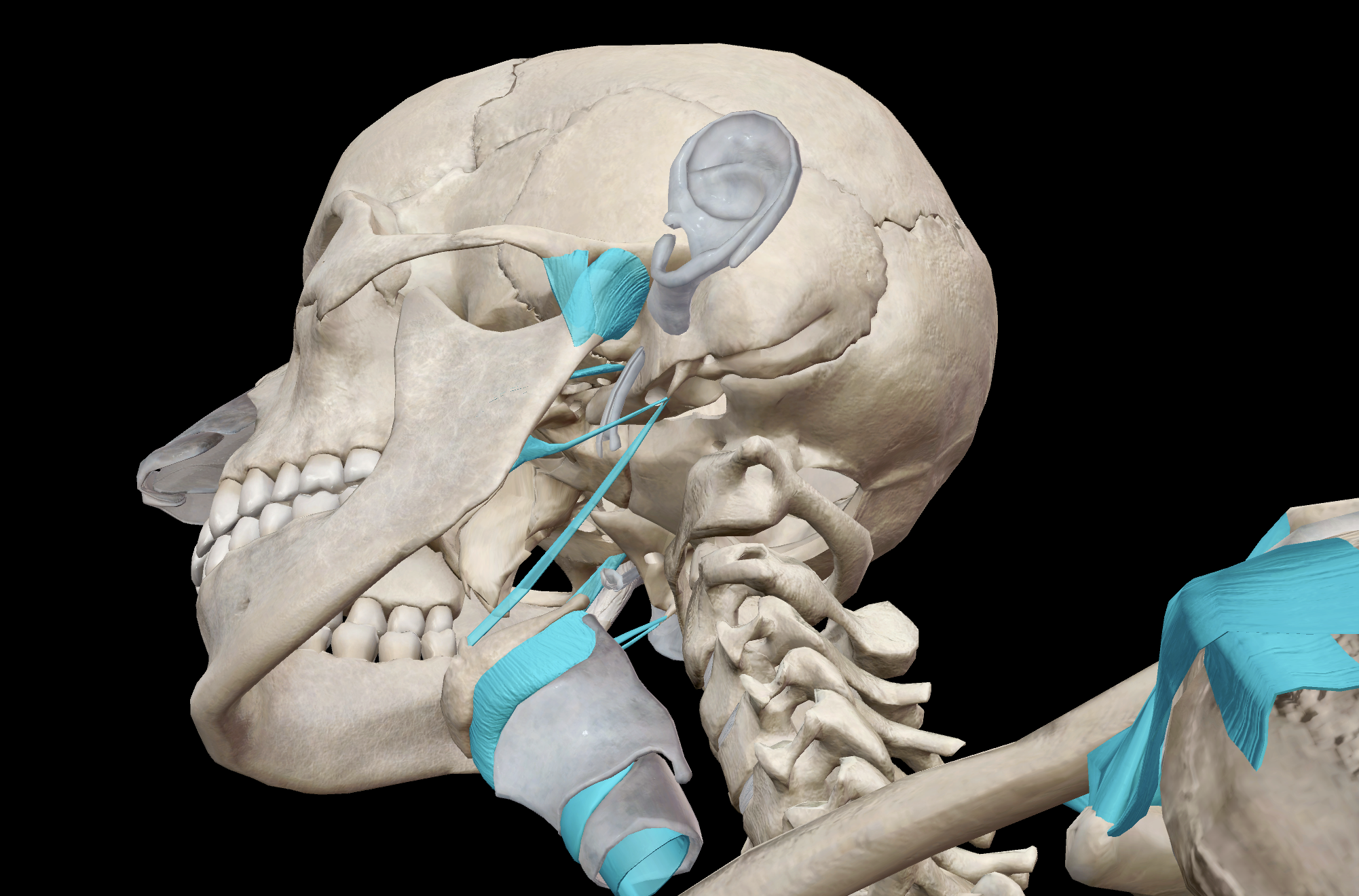
Dense, regular connective tissue
Extremely fibrous
Connects bone to bone, stabilising joints
fibres run in one direction
Thus is able to withsitand tensile forces in the direction, preventing bones from being pulled apart easily
Muscular system
Responsible for movement!
Made of:
Muscular tissue
Connective Tissue
Innervated nervous tissue
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
Most of the muscular system:
Responsible for movement
Movement occurs with cells containing myofilaments (actin & myosin) that slide over one another to create a contraction
Highly vascularised & innervated
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle - GI Tract
Cardiac muscle
Connective Tissue - GI Tract
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
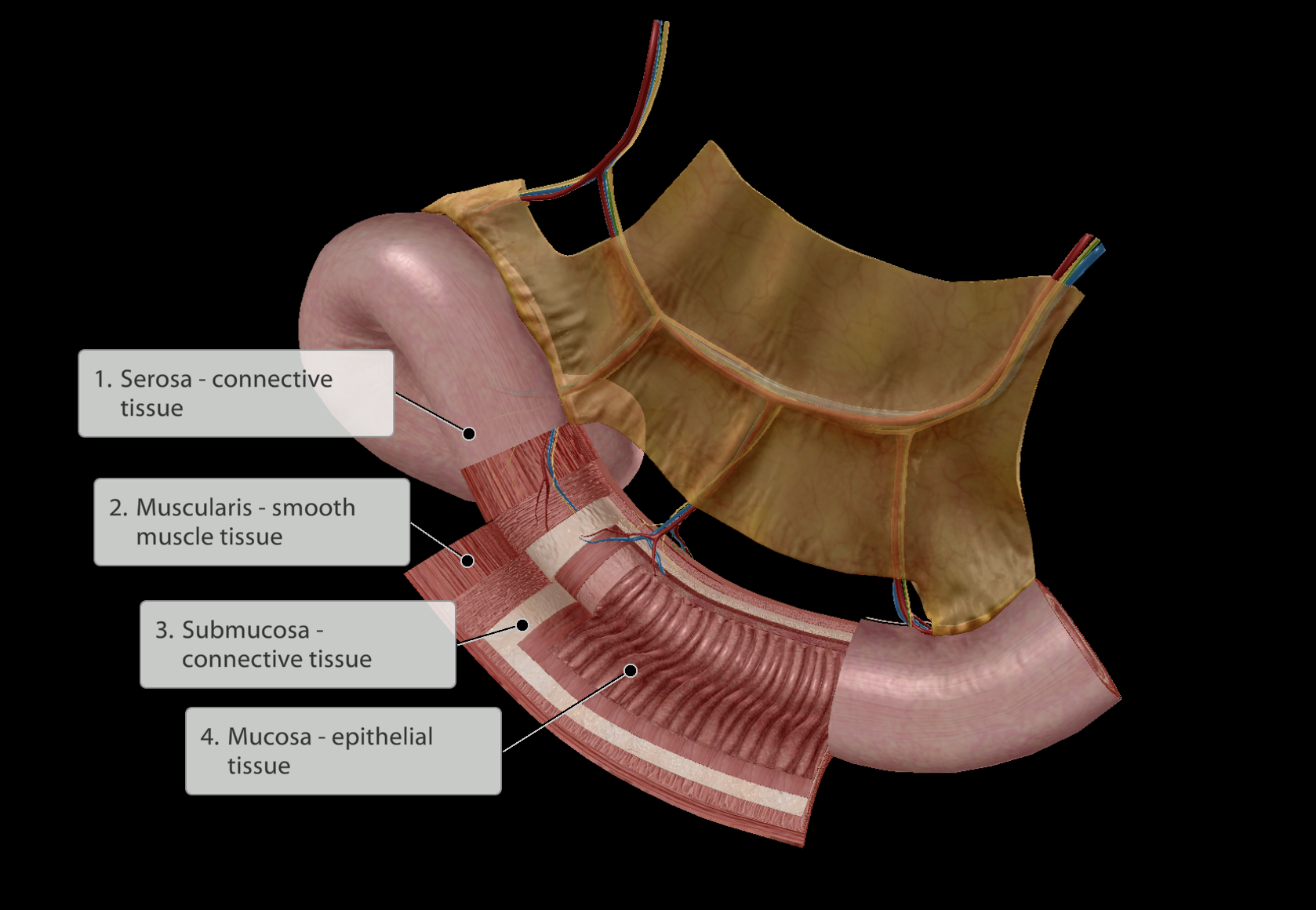
4 Layers:
Serosa layer - Outer layer of connective tissue
a. Membrane surrounding the GI tract
Muscularis layer - Next inner layer of smooth muscle cells
Submucosa layer - Next inner layer of connective tissue
Mucosa - Inner layer of epithelial tissue
a. Simple epithelium to maximise ability to absorb nutrients from food
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle - Blood vessels
Cardiac muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
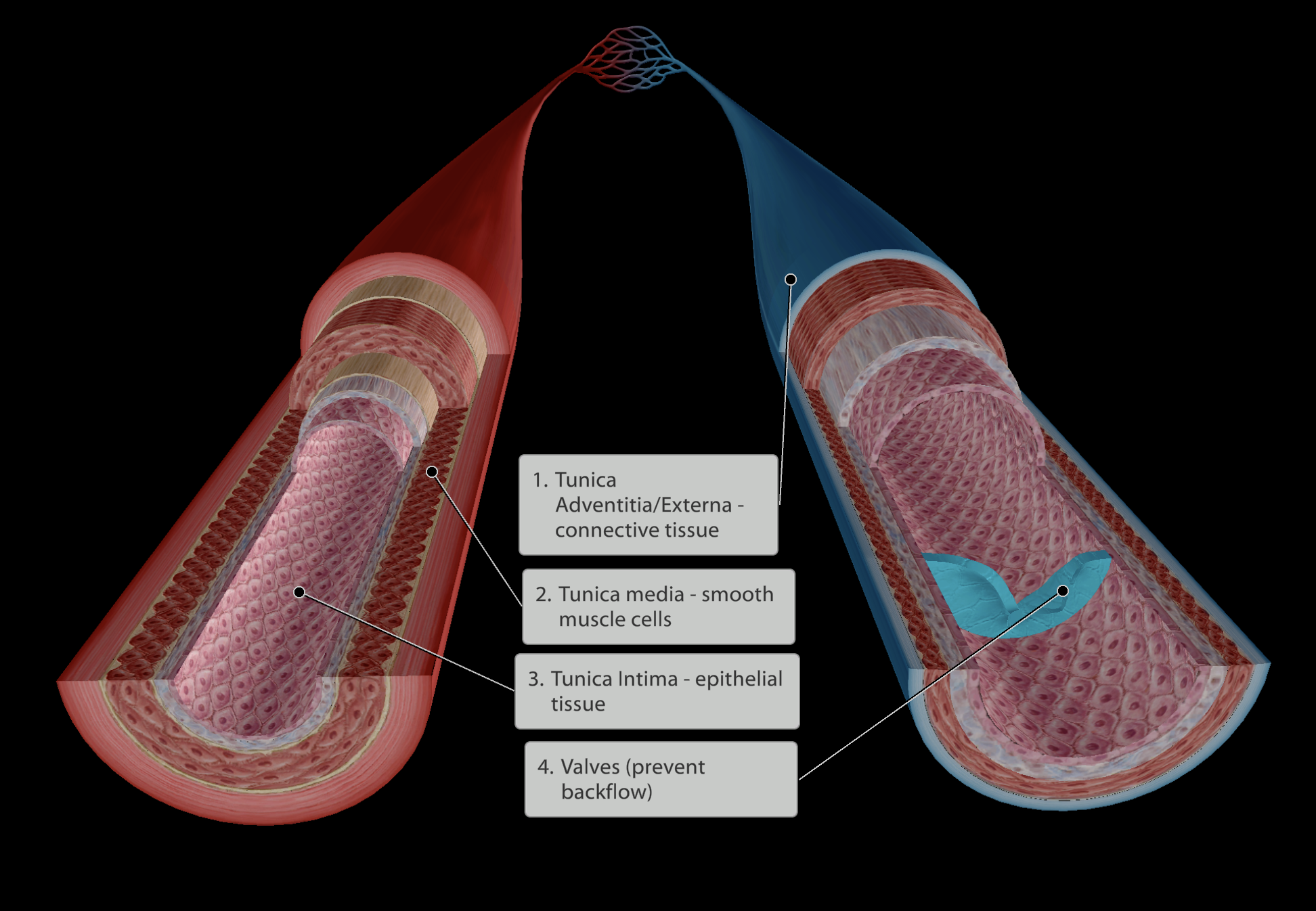
4 Layers:
Tunica Adventitia/Externa - Outer layer of connective tissue
a. ‘tunica’ - means “coating”
Tunica media - Next layer of smooth muscle cells
a. thicker layer in arteries compared to veins
Tunica Intima - Inner layer of epithelial tissue
a. Simple epithelium to maximise gas exchange/nutrient and waste exchange
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
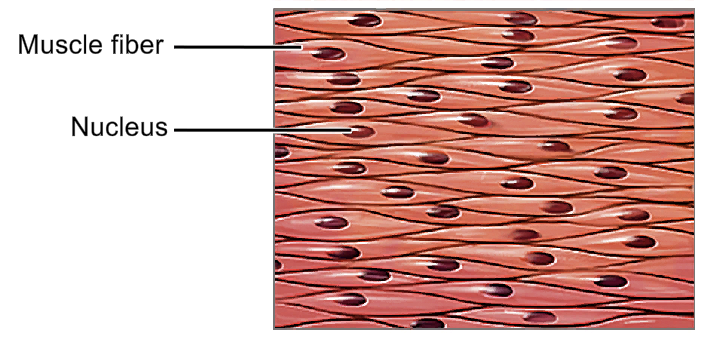
Smooth Muscle - Smooth muscle cells
Cardiac muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
Involuntary control
Not striated, can compress and stretch in any direction
Single nucleus
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac muscle - Heart
Connective Tissue - Heart
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
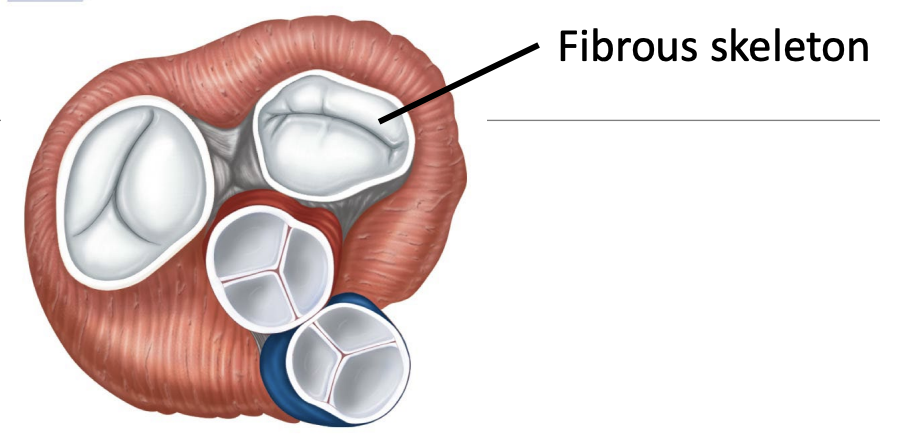
Heart has a fibrous skeleton
This fibrous skeleton supports entryways and exits of the heart
3 Layers:
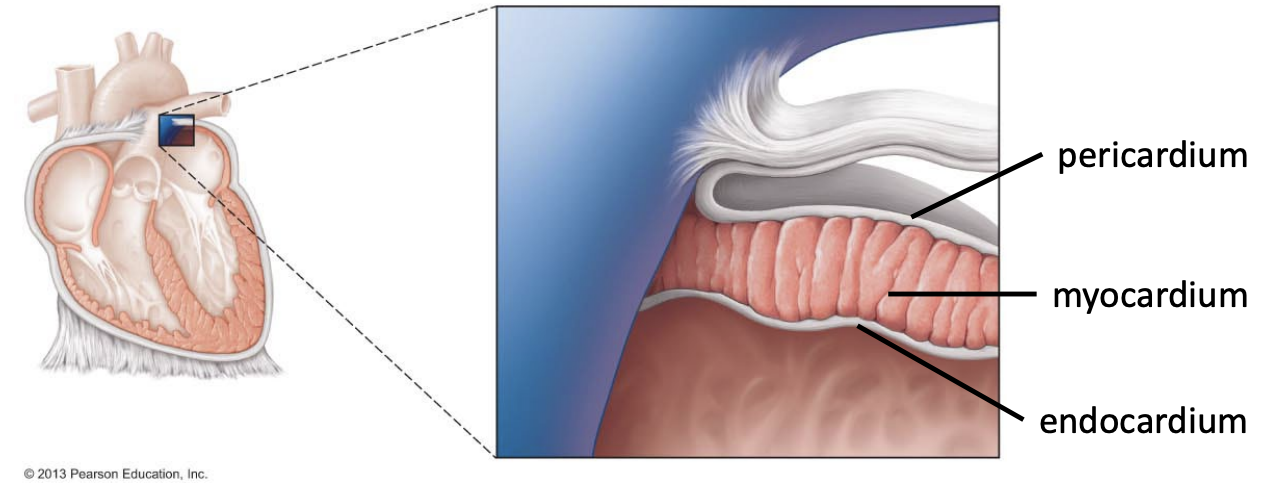
Pericardium - Connective tissue
a. Membrane surrounding the heart
Myocardium - Cardiac muscle tissue
Endocardium - Epithelial tissue
a. In contact with blood, hence epithelial tissue
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac muscle - Myocardial cells
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
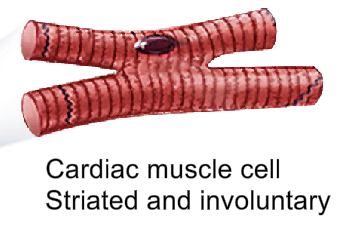
Makes up the heart’s muscle
Single nucleus
Involuntary contraction
Striated
Cells connected via intercalated discs.
When one myocardial cell contracts, it pulls the neighbouring cell to initiate its contraction. Thus, there is a synchronous contraction occurring throughout the heart, a heartbeat.
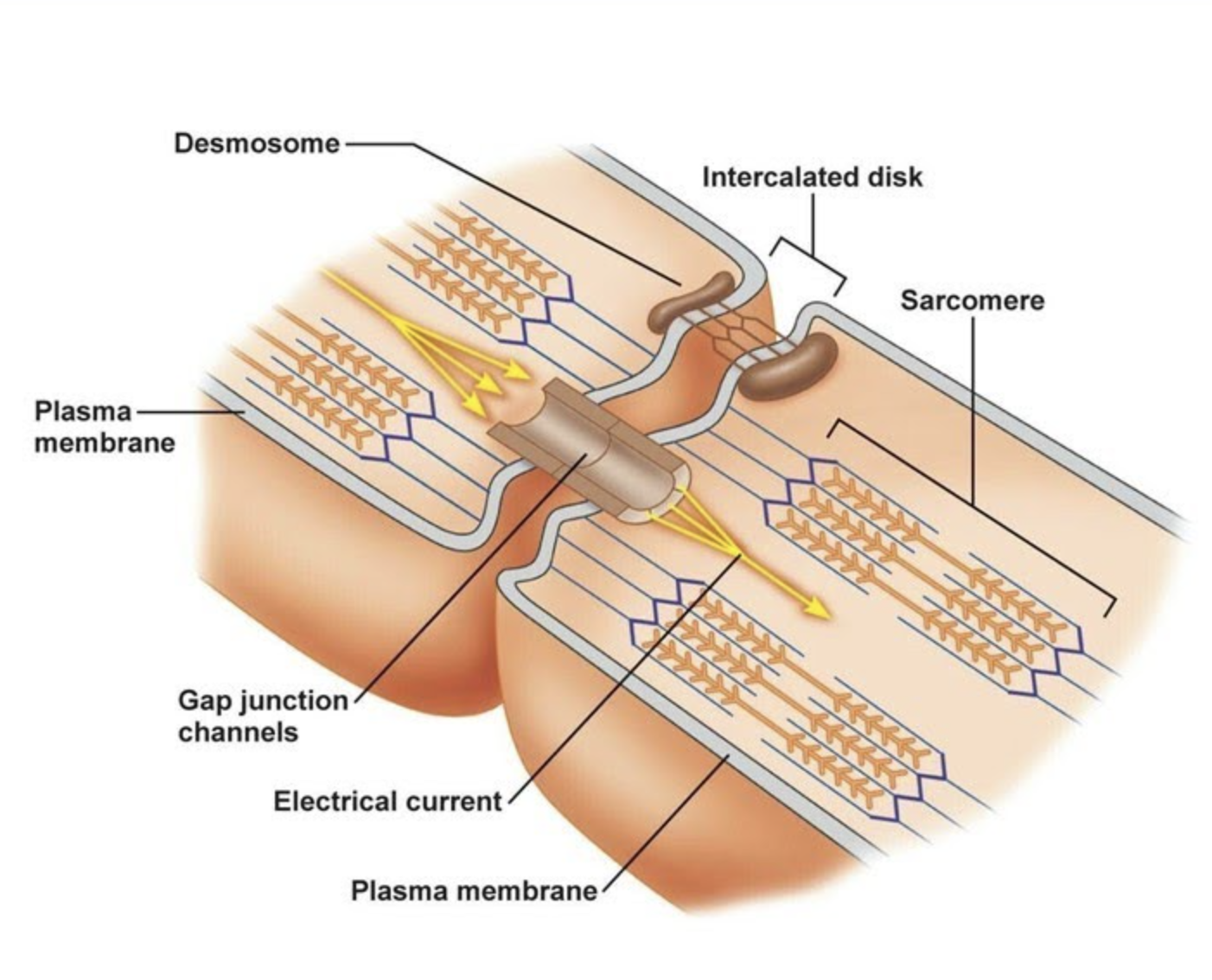
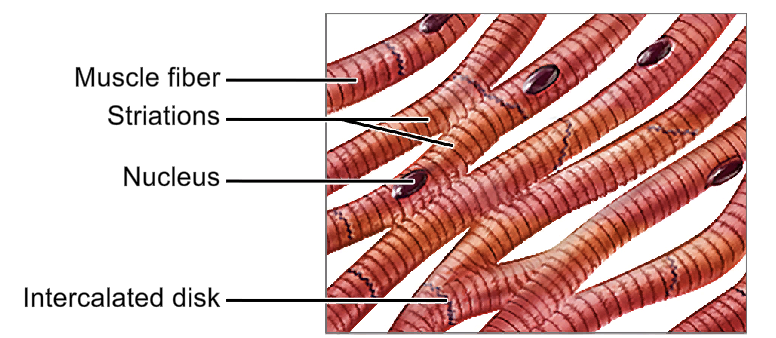
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscles
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
Levels of the Muscle Belly (Inner to Outer):
Actin & Myosin myofilaments within skeletal muscle cell
Skeletal Muscle cell
Endomysium - Connective tissue surrounding skeletal muscle cell
Fascicle - Groups of skeletal muscle cells each wrapped in endomysium
Perimysium - Connective tissue surrounding each fascicle
Epimysium - Connective tissue surrounding all fascicles in muscle belly
Tendon - Joining point of all inner connective tissue (endomysium, perimysium, epimysium) that links muscle to bone.
a. Dense fibrous regular connective tissue.
b. Links muscle directly into bone
All muscle is highly vascularised, however the tendons at the end of muscles have less blood supply.
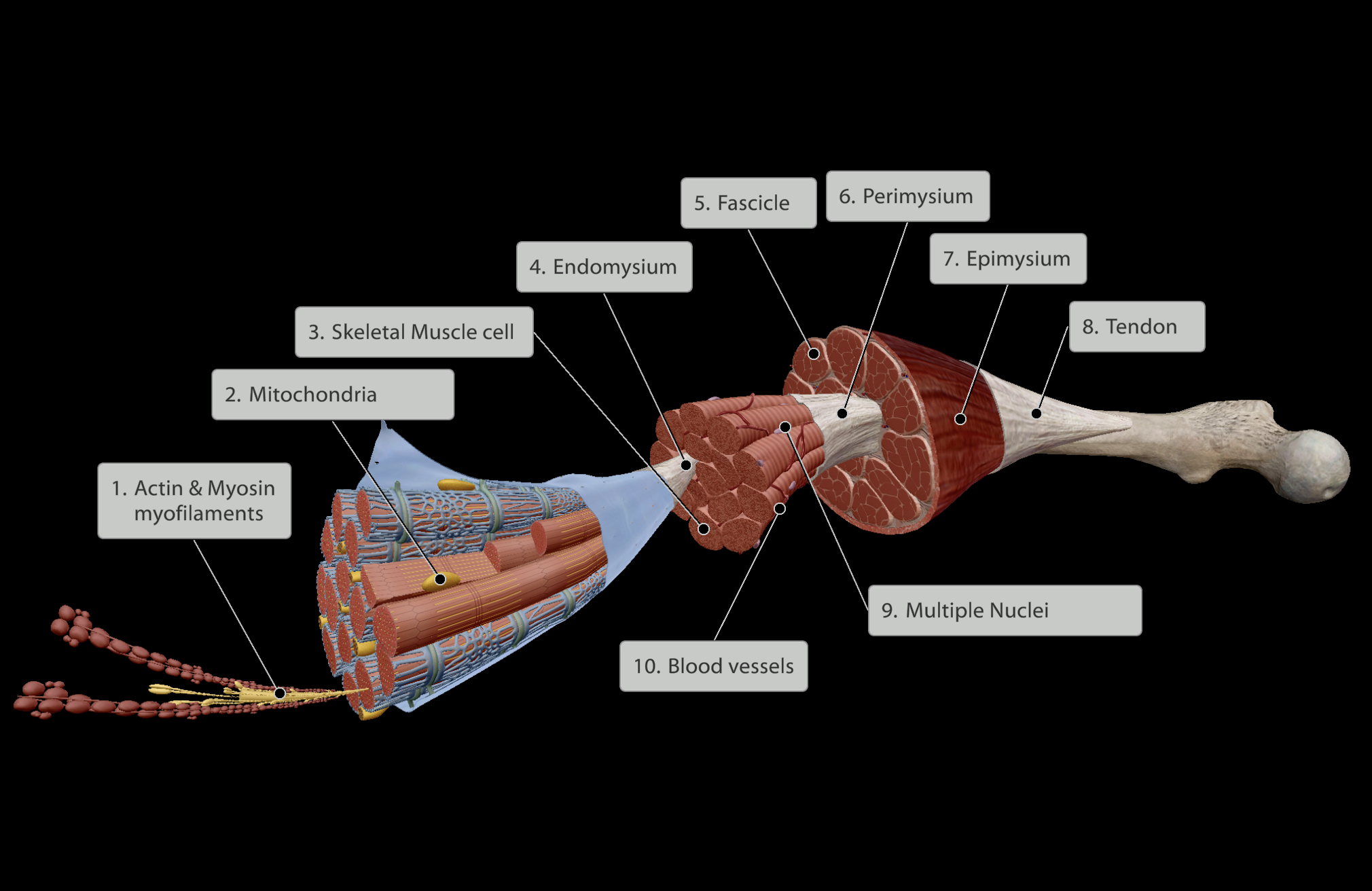
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle - skeletel muscle cells
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
Voluntary
Multi-nucleated
Striated
Always has an attachment to bone (tendon)
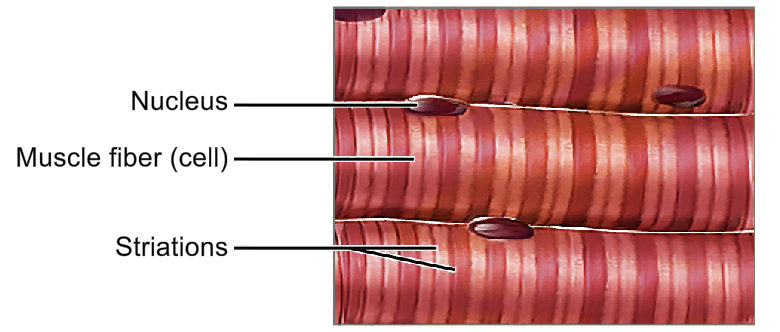
Muscular system
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Connective Tissue
Innervated Nervous tissue
Deep fascia
Dense irregular connective tissue.
enables the fascia to change shape without tearing as muscles grow/shrink with age
contains elastin fibres to help it recoil as the muscle relaxes
Wraps tightly around muscles
Dividing muscle and connecting to adjacent bones
Compartmentalises muscles in limbs
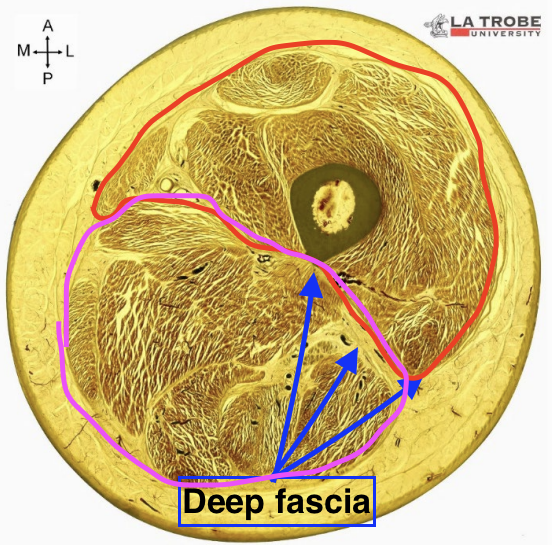
Nervous system
Functions as control system in tandem with endocrine system
Rapid activation and deactivation
Short term control - muscles and glands can react in milliseconds
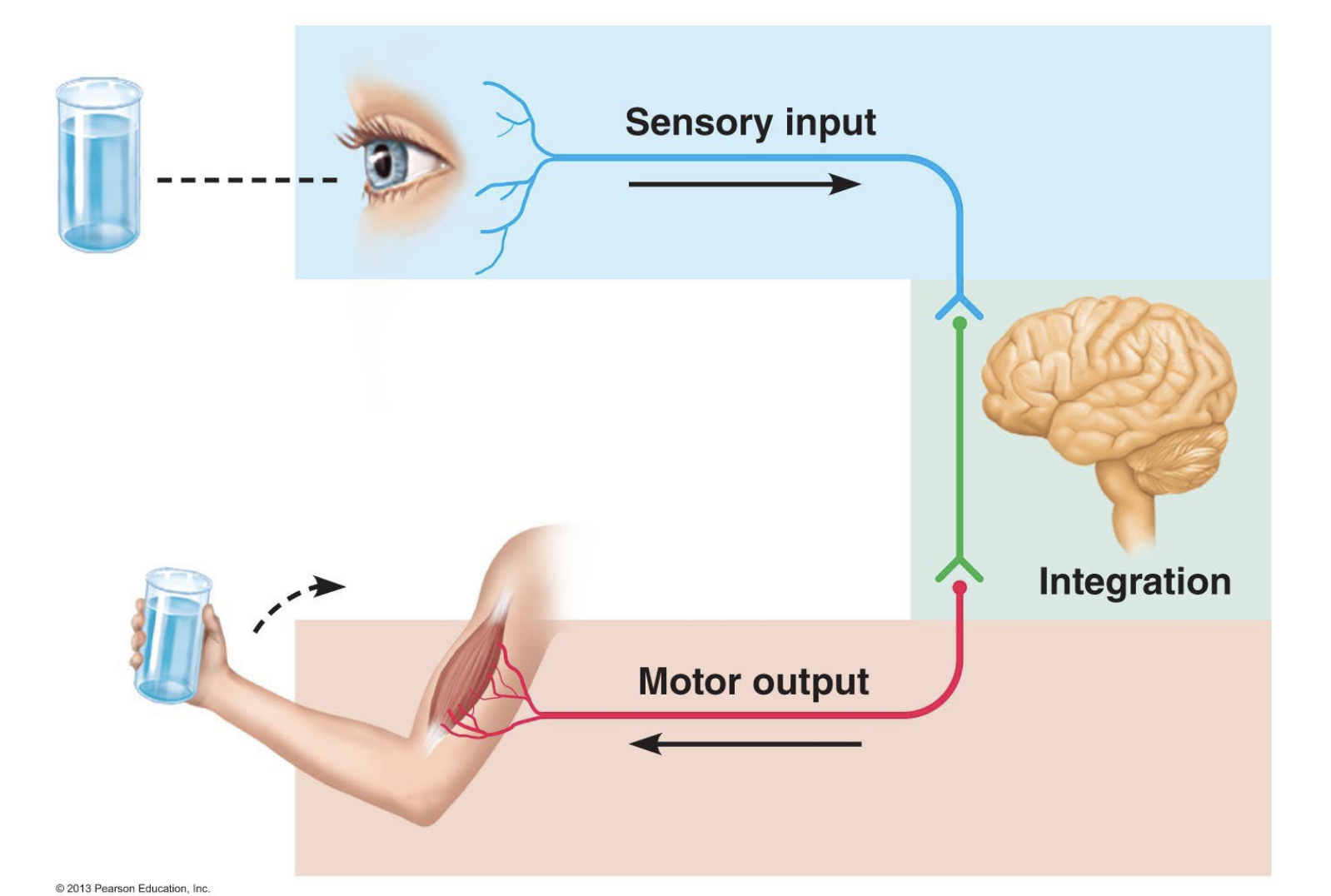
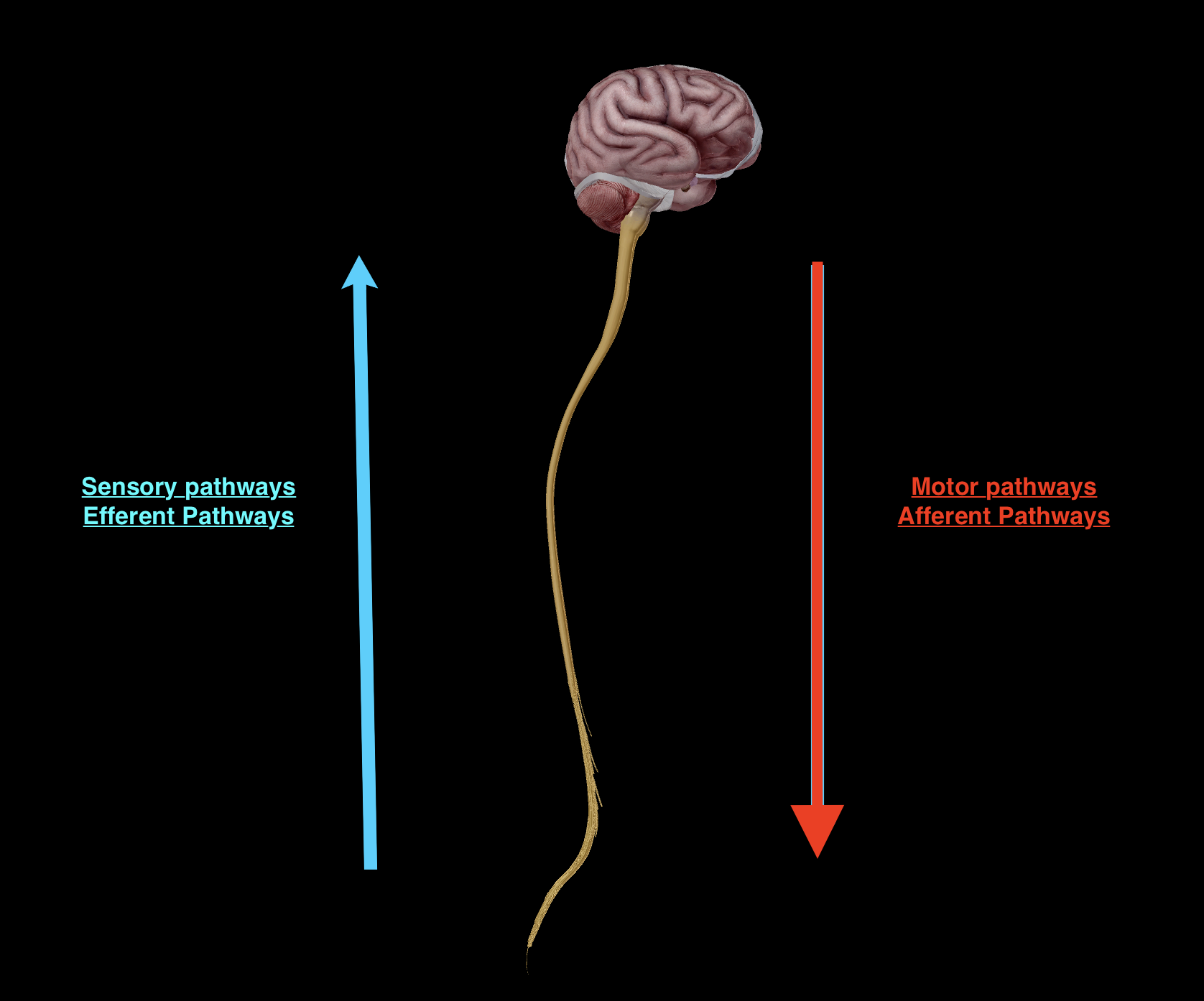
Sensory input (perception)
Sensory division - afferent pathway
Integration
Within the brain
Motor output (response)
Motor division - efferent pathway
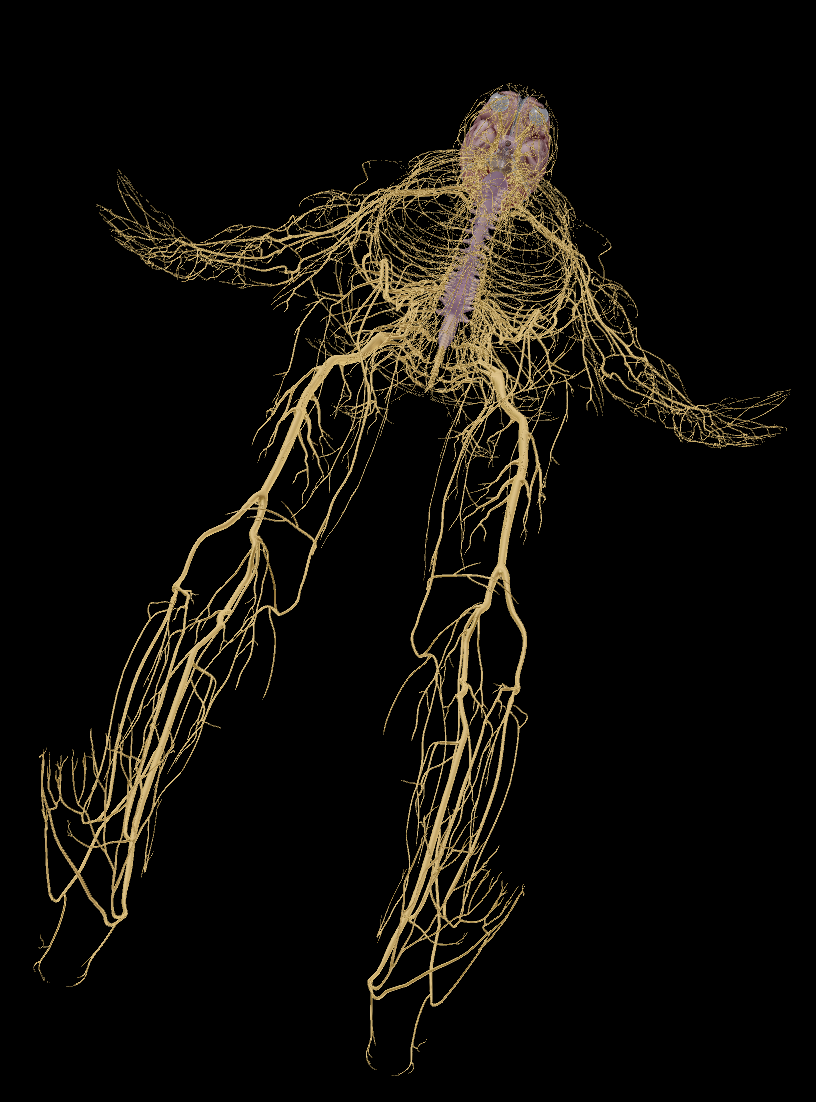
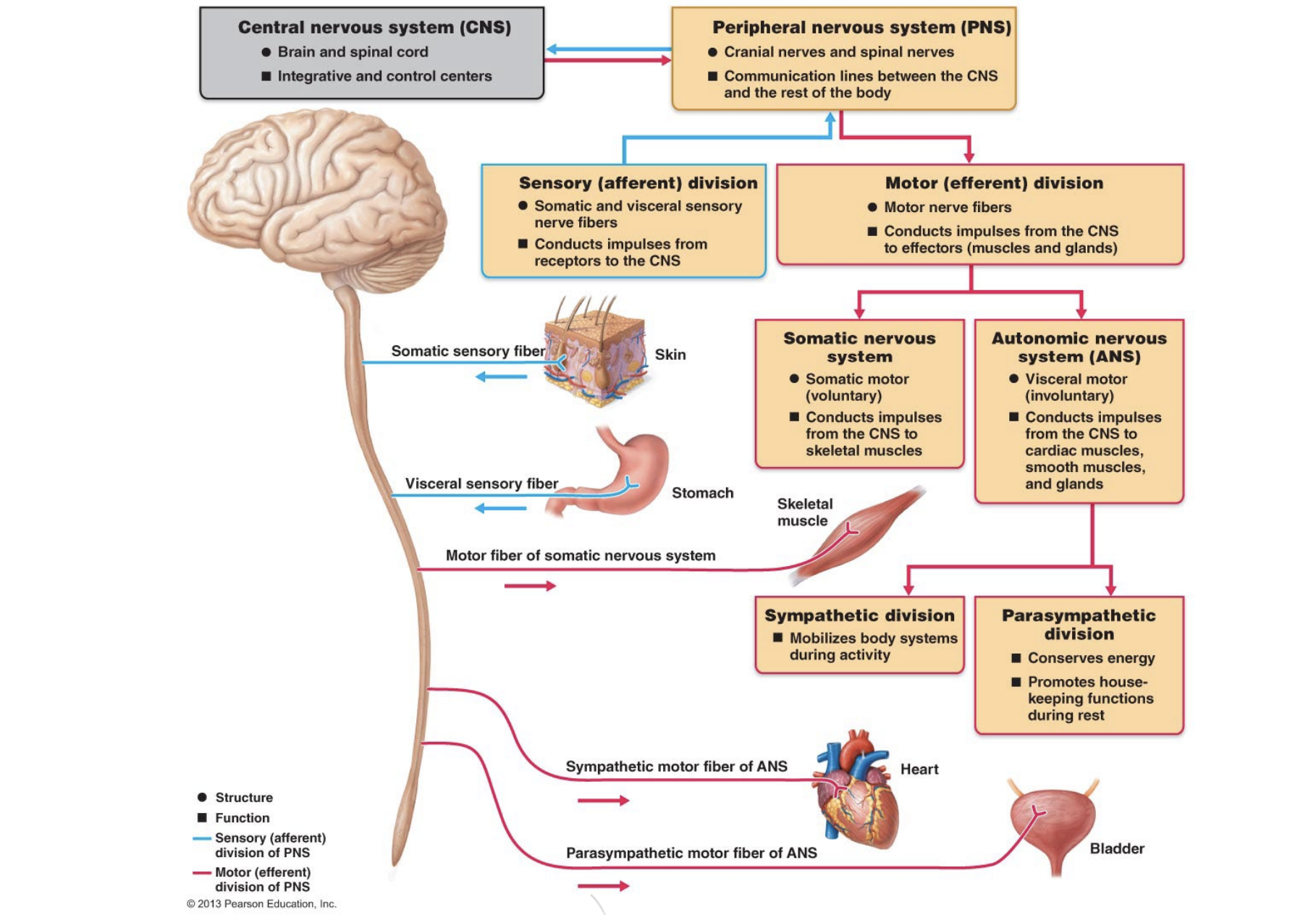
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS) - Brain
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Interprets and provides meaning to any sensation.
Sends information out to inititiate movement
Grey Matter: Cell bodies of brain neurons
White Matter: Fatty, axons that connect and facilitate communication between brain neurons, the wiring of the brain.
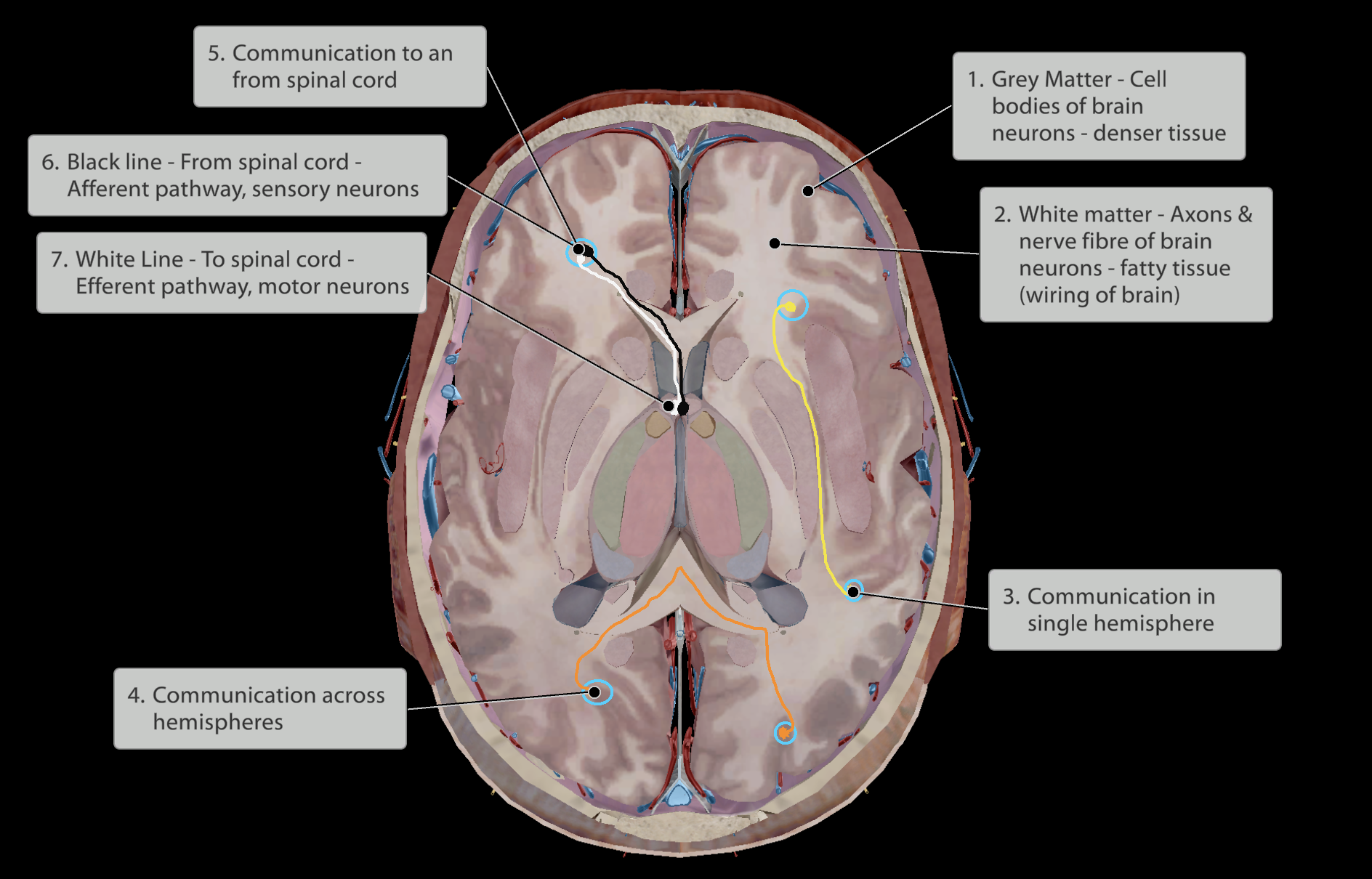
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS) - Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Constructed of:
afferent (sensory) pathways, going up
efferent (motor) pathways, going down
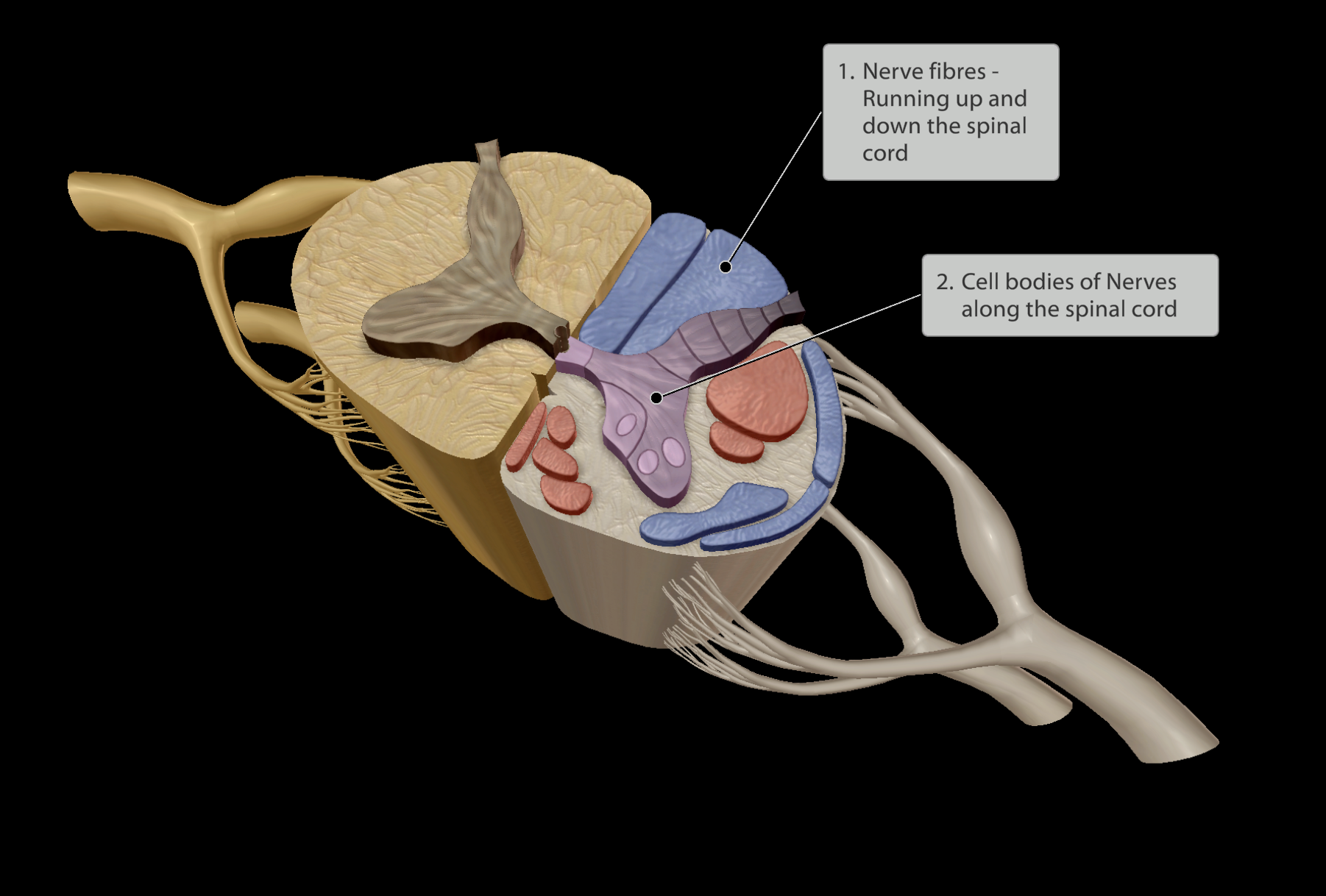
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Nerves directing exiting and entering the spinal cord.

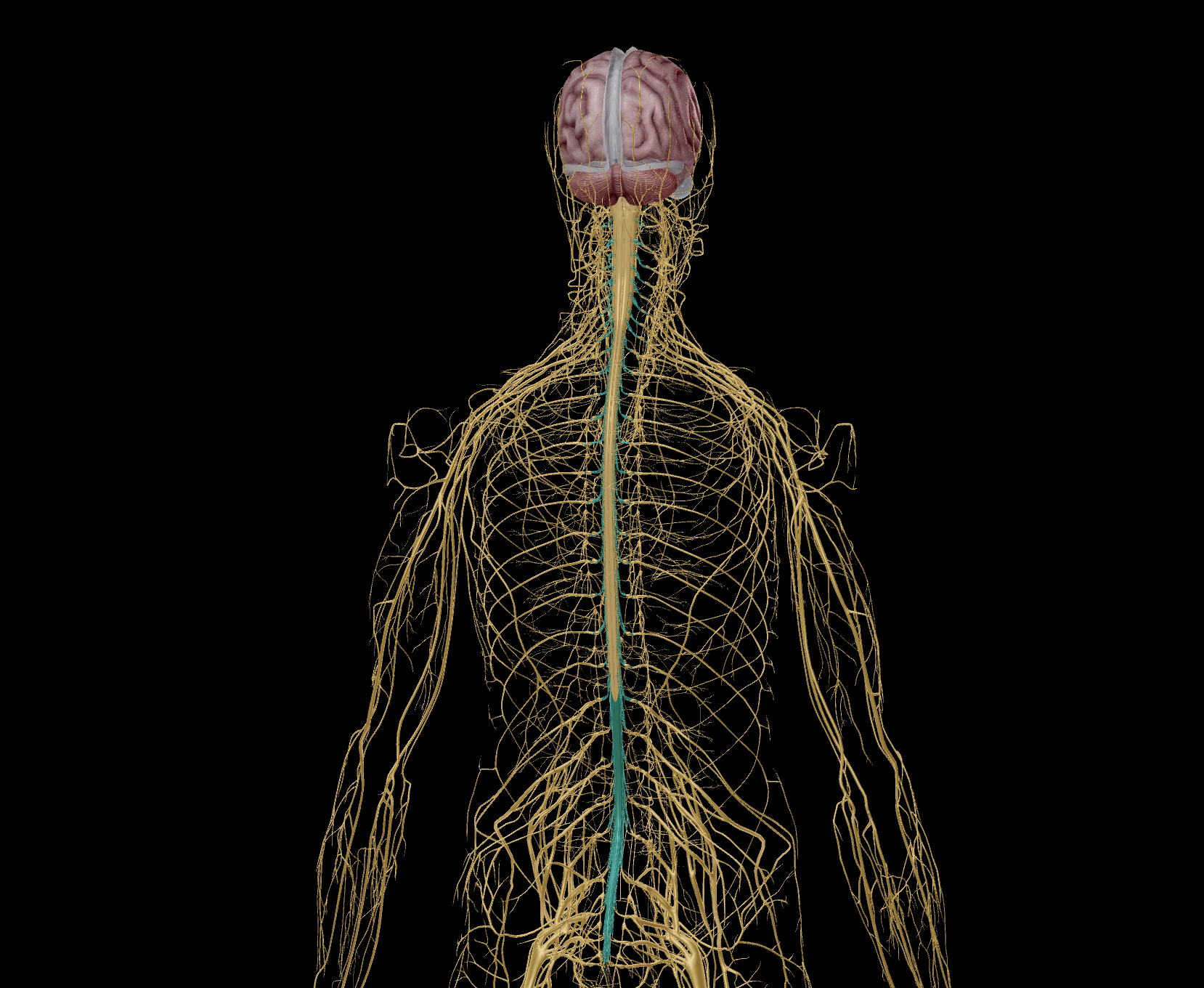
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Nerves directing exiting and entering the brain stem or brain.
There are 12 cranial nerves
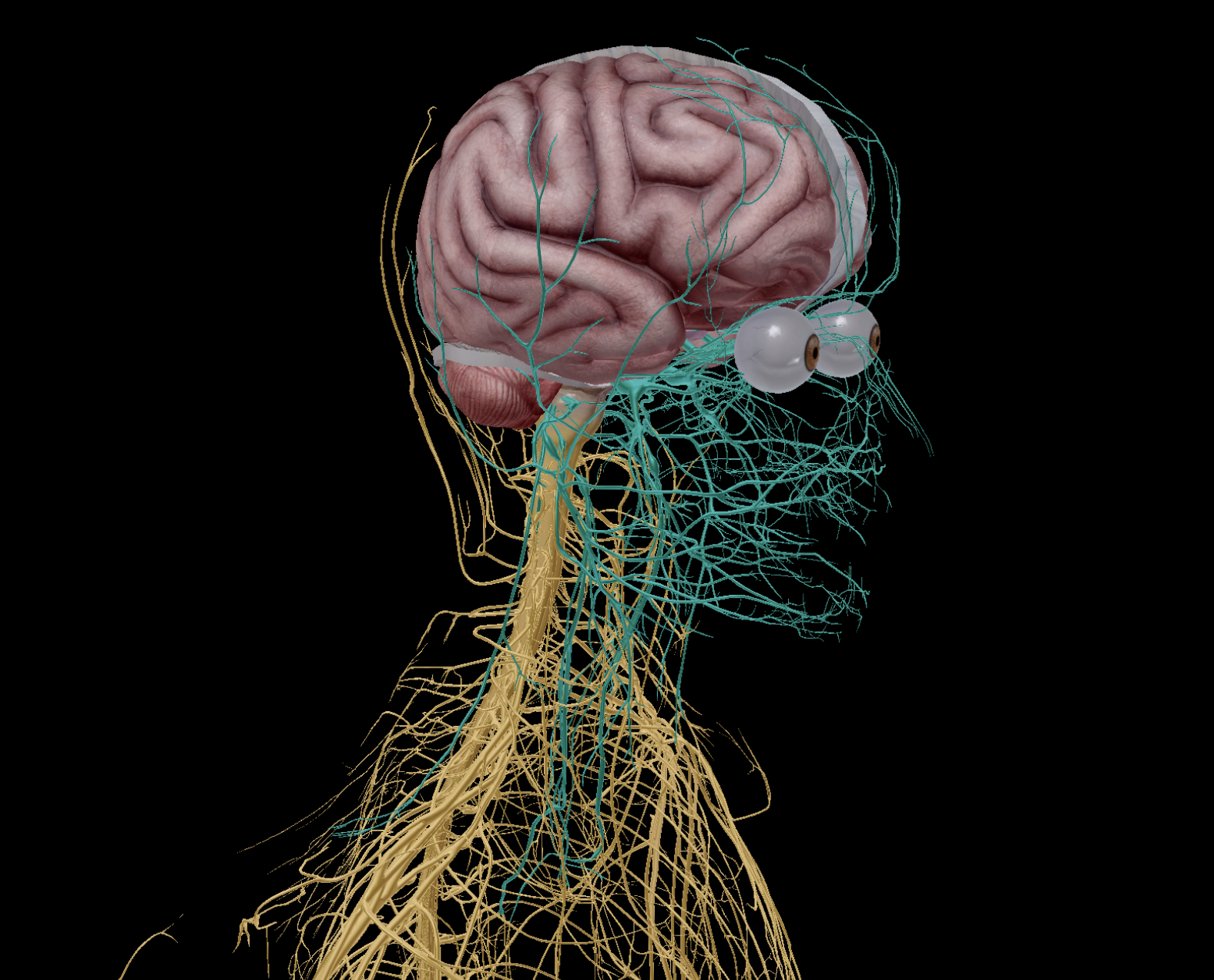
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Levels of the Nerve (Inner to Outer):
Axons - send sensory information towards the spinal cord (afferent pathways) or motor information away from the spinal cord (efferent pathways)
Nerve or Neuron
Endoneurium - Connective tissue surrounding a specific neuron/nerve fibre
Fascicle - Groups of neurons/nerve fibres each wrapped in endomysium
Perineurium - Connective tissue surrounding each nerve fascicle
Epineurium - Connective tissue surrounding all fascicles in a nerve
All nerves are highly vascularised.
Fat cells present around nerve fascicles for shock absorption.
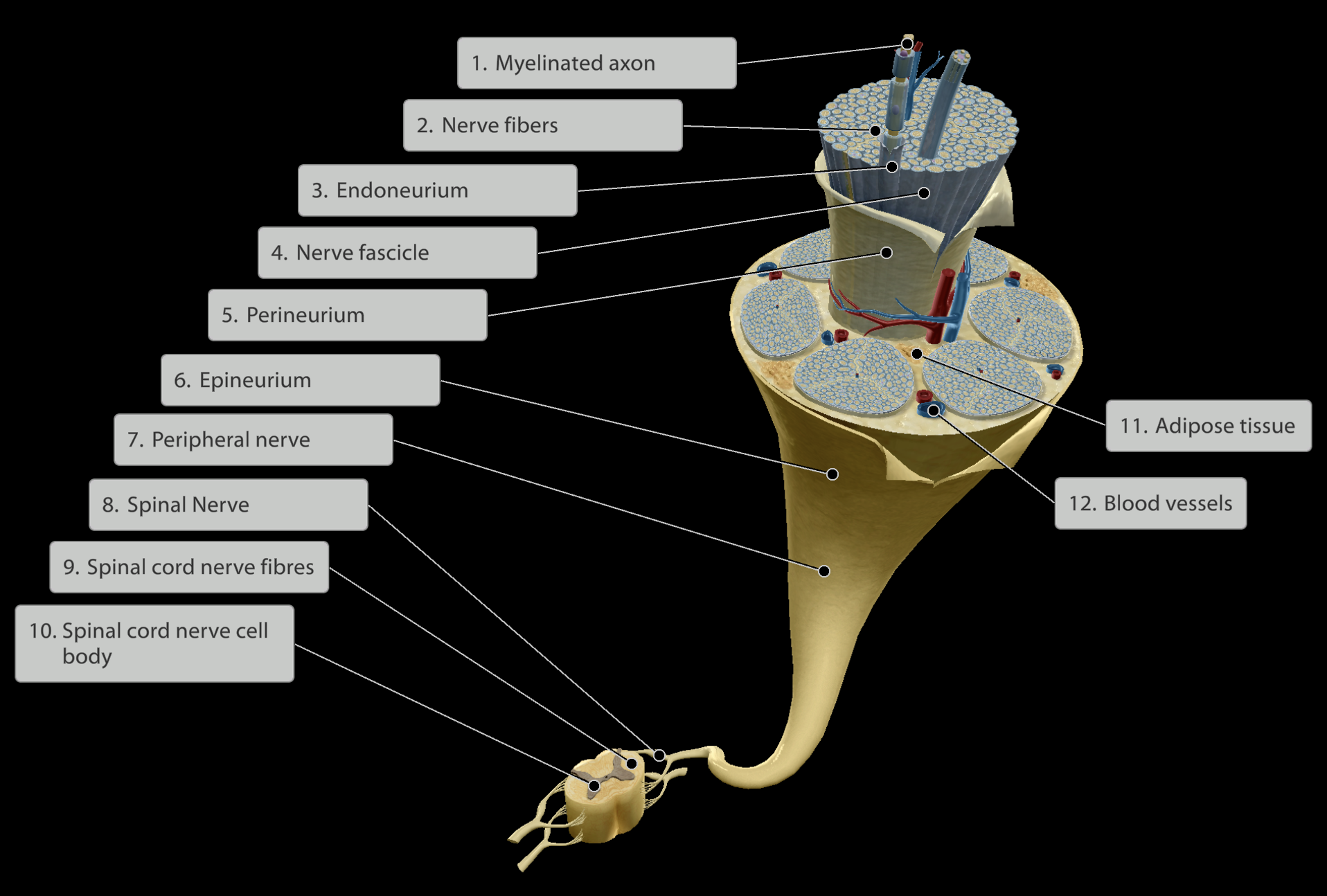
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Nerves that control voluntary muscle movement.
Skeletal muscles
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
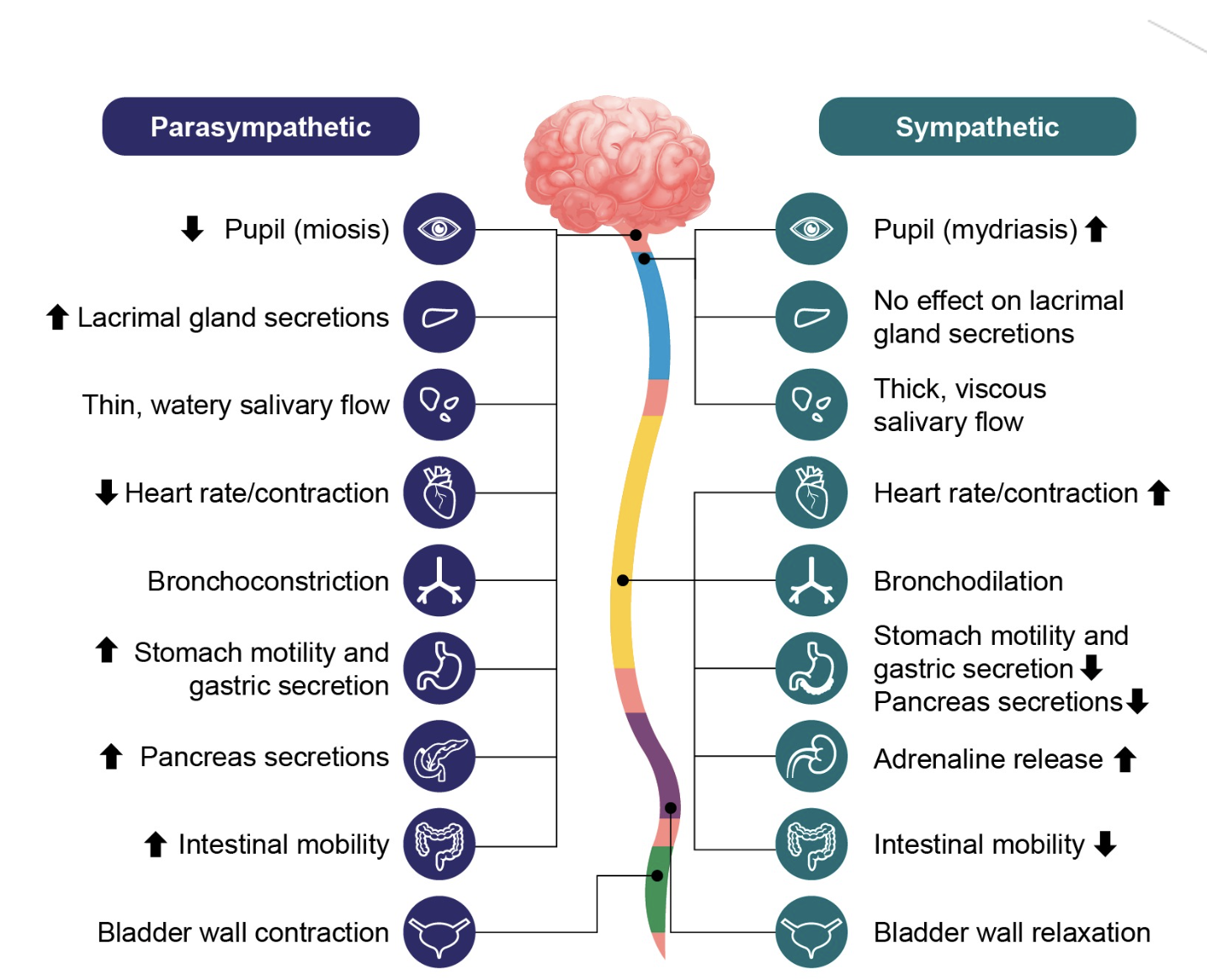
Nerves that control involuntary muscle movement.
Cardiac muscles & smooth muscle cells
Subdivided into two pathways that send, inhibitory and excitatory signals.
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Fight or flight.
Propagates excitatory responses.
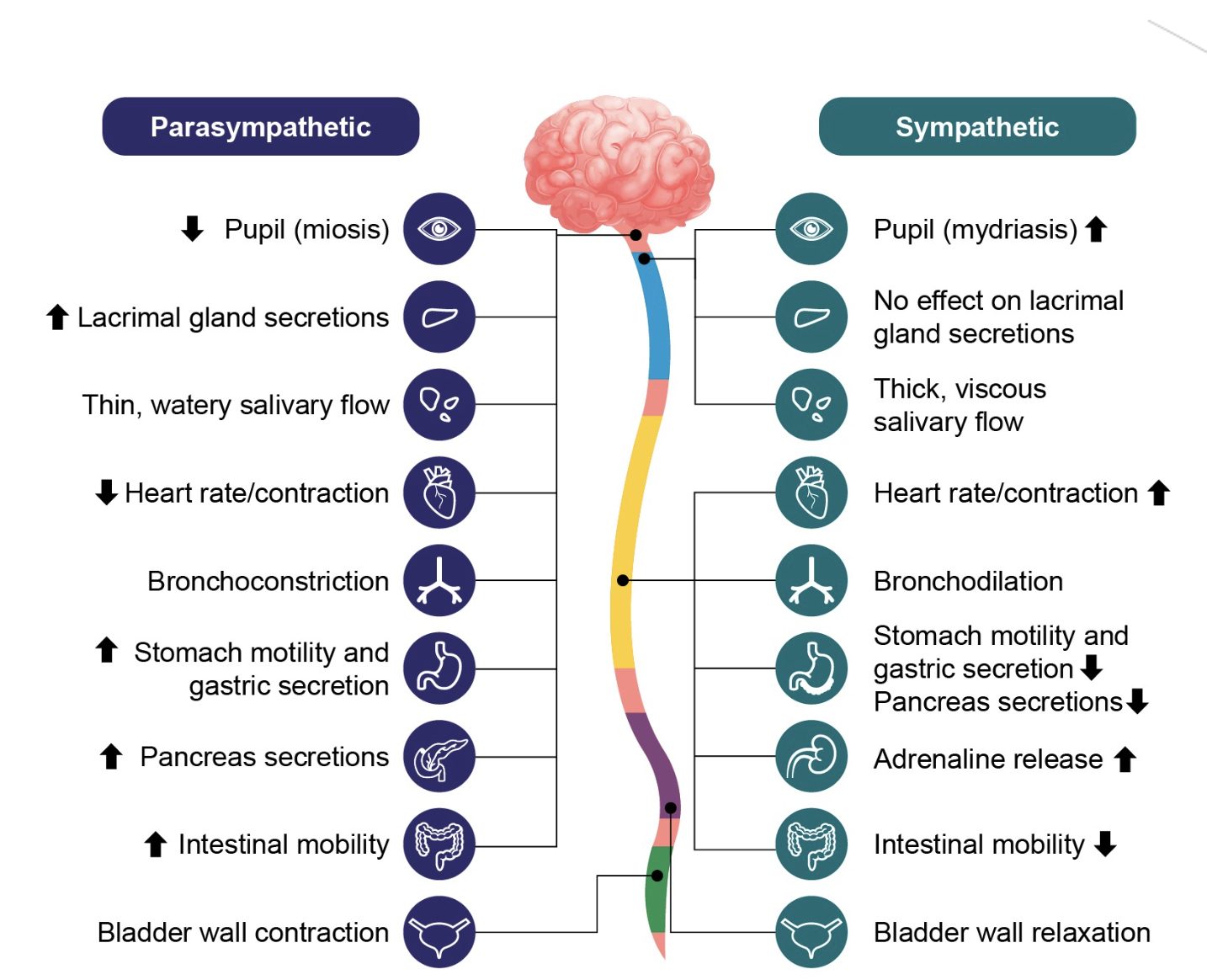
Nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves
Pathways:
Sensory division (Afferent pathway)
Motor division (Efferent pathway)
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Rest and digest.
Propagates inhibitory responses.
Endocrine system
Functions as control system in tandem with nervous system
Slow activation and deactivation
Long-term control - completed with the use of hormones in the bloodstream
Hormones travel through the bloodstream and attach to cell receptors to create changes
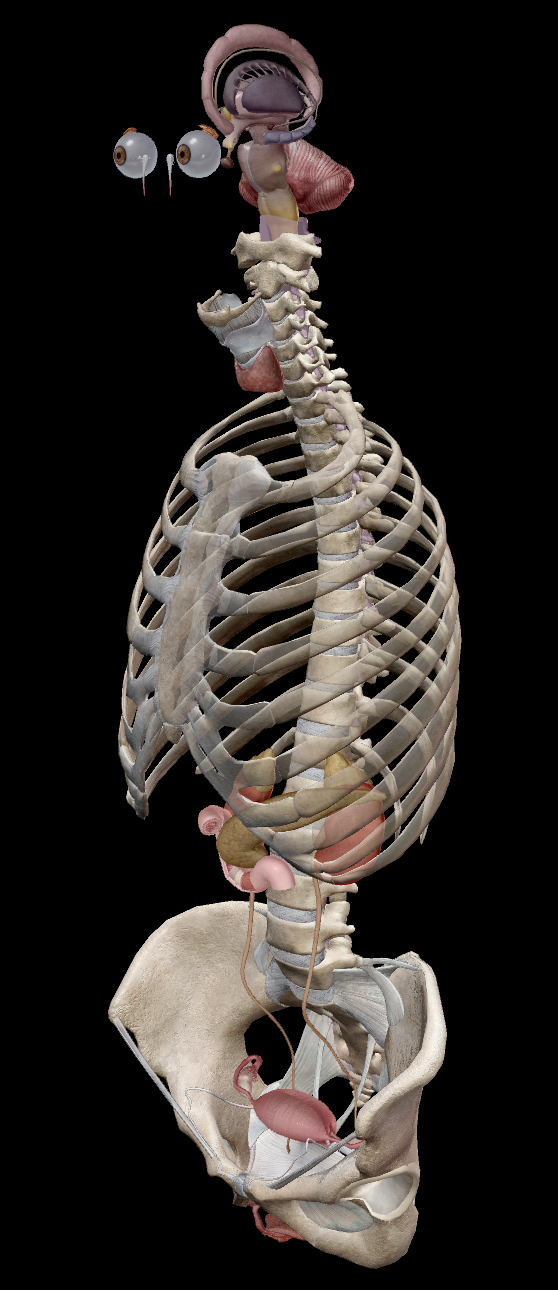
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
Some hormones released:
Oxytocin to contract the uterus during childbirth
Growth hormones
Thyroid-stimulating hormones
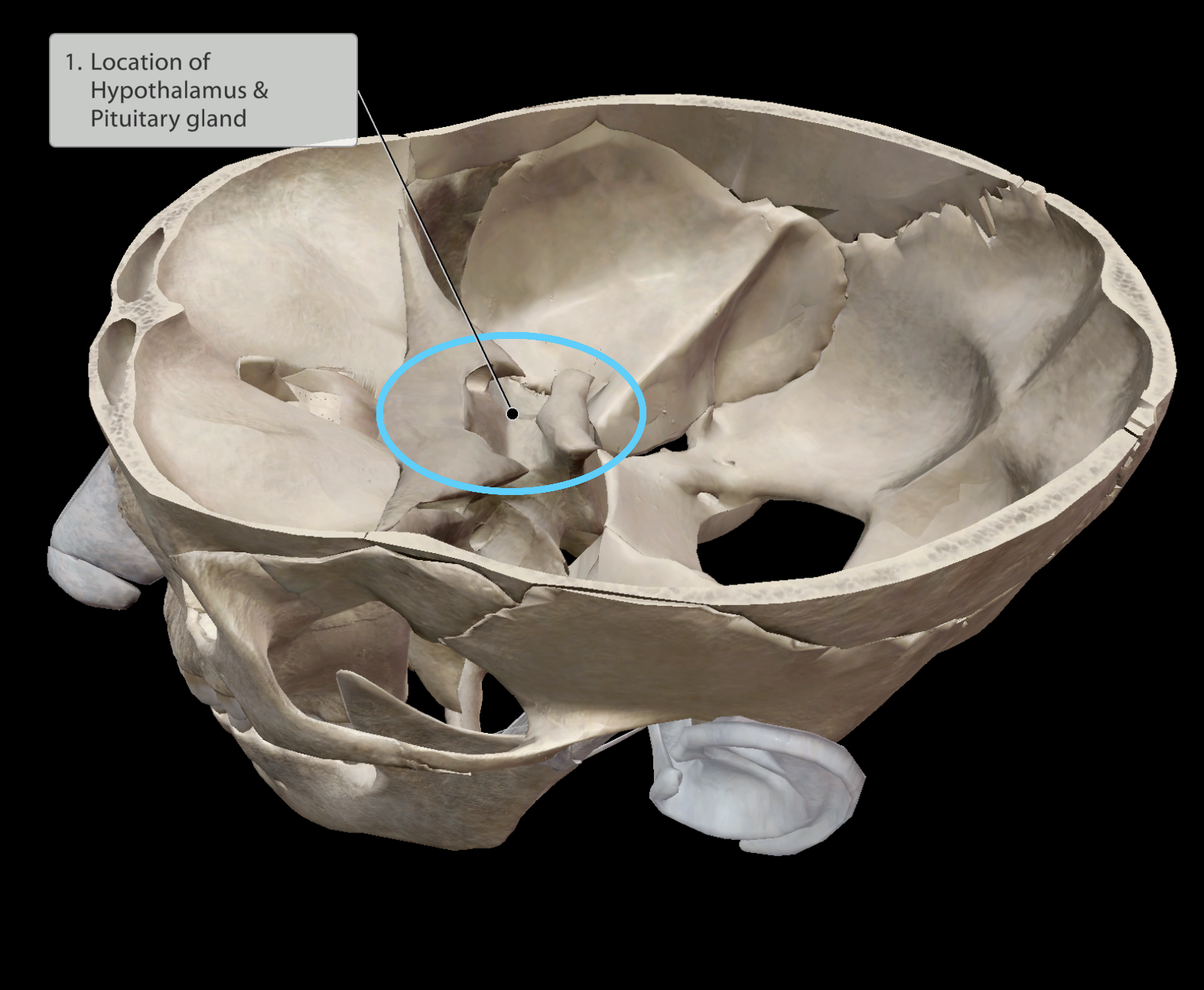
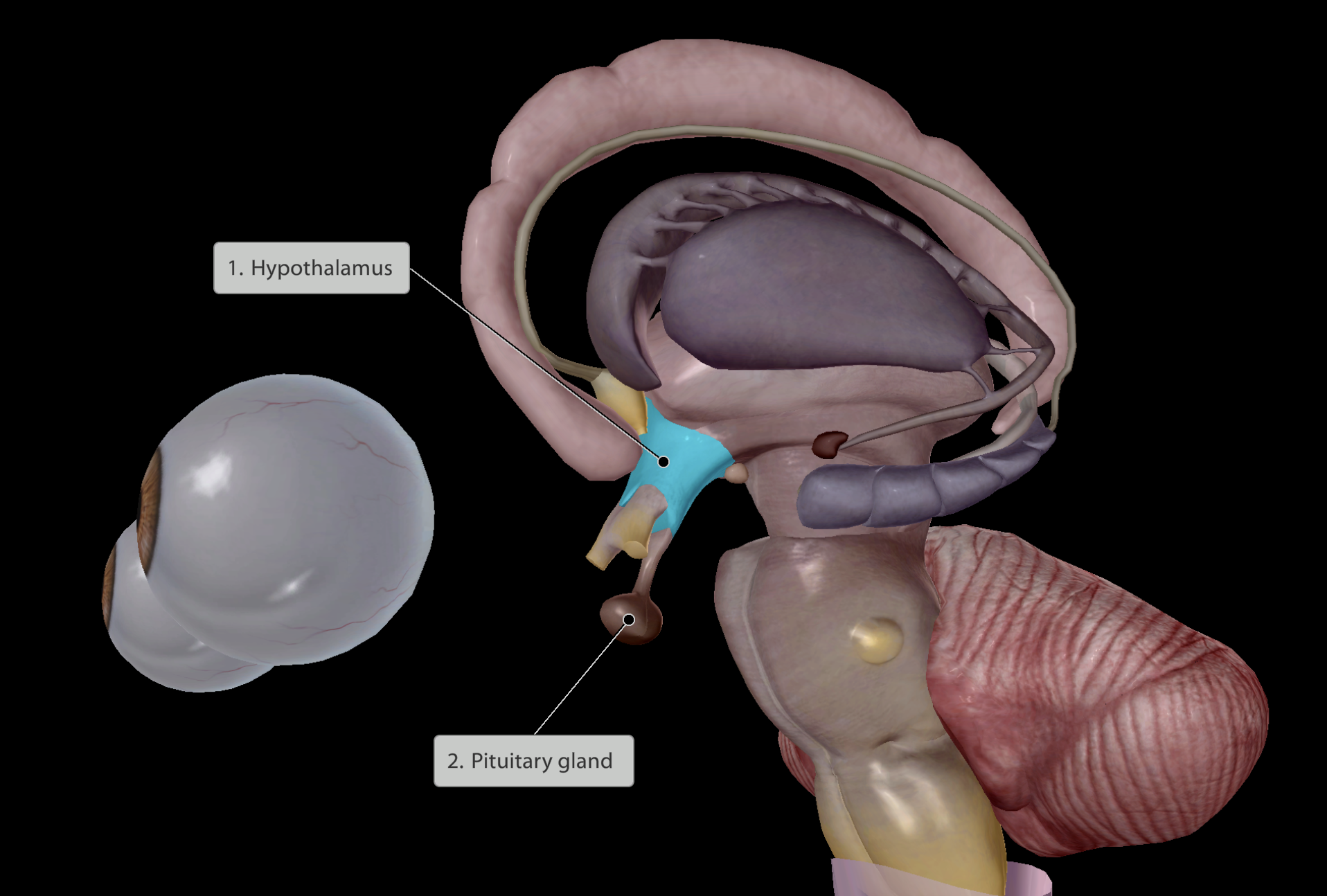
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
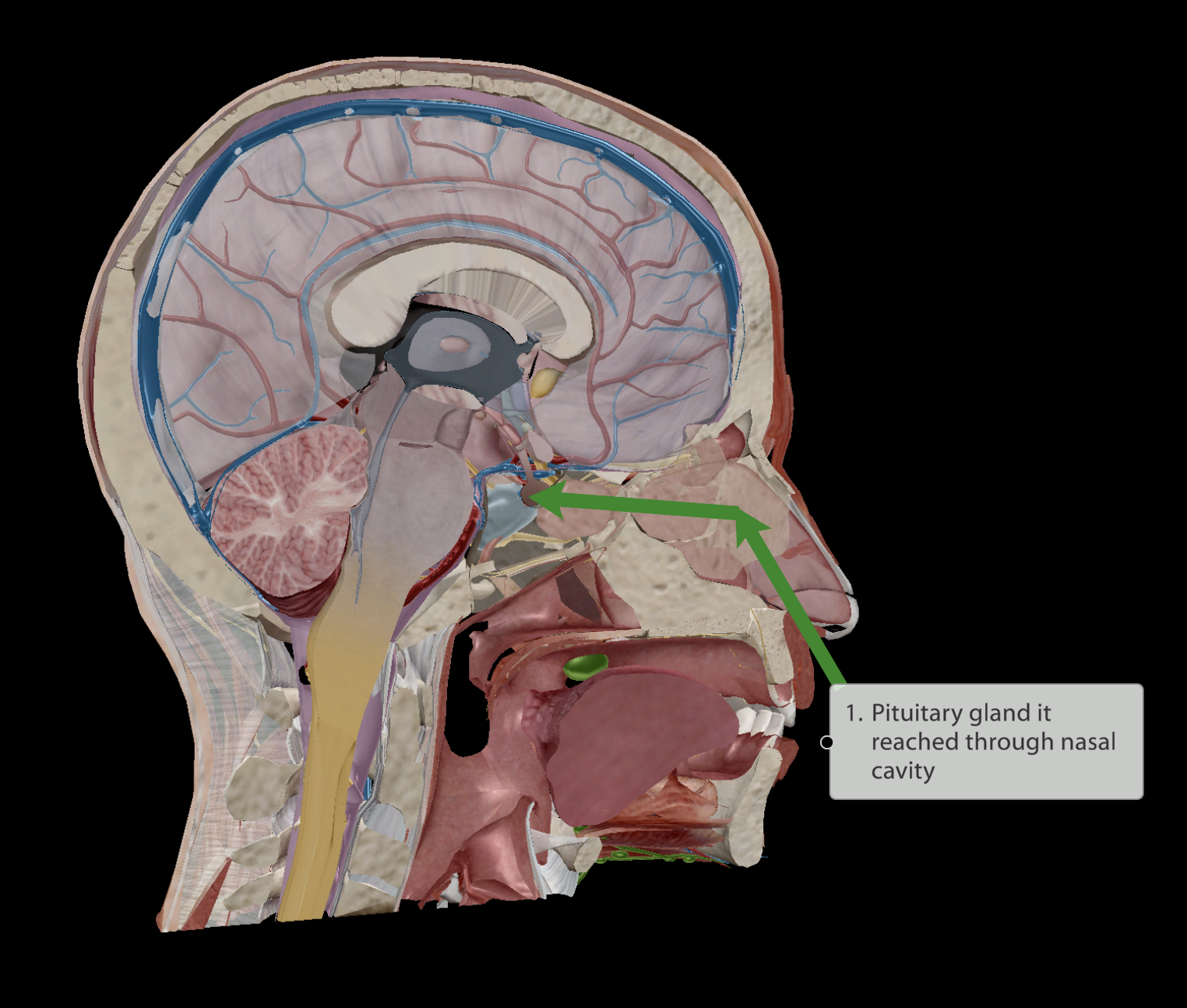
Found very deep within the brain
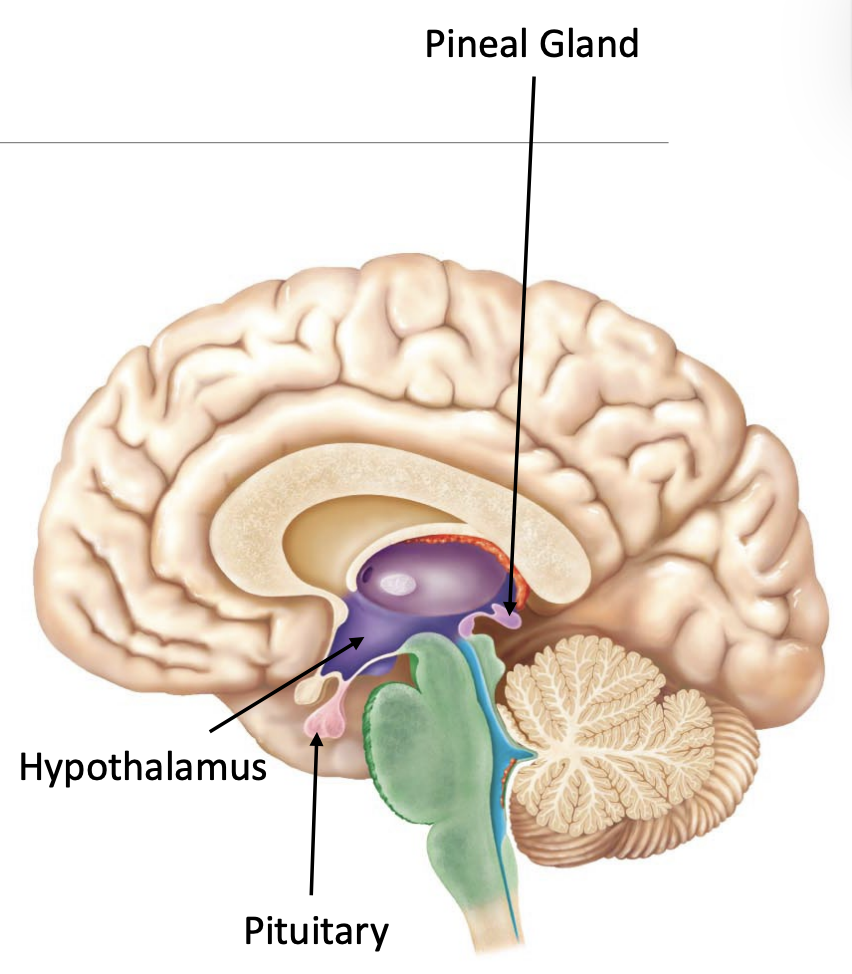
Main function:
Helps regulate circadian rhythm/sleep cycle
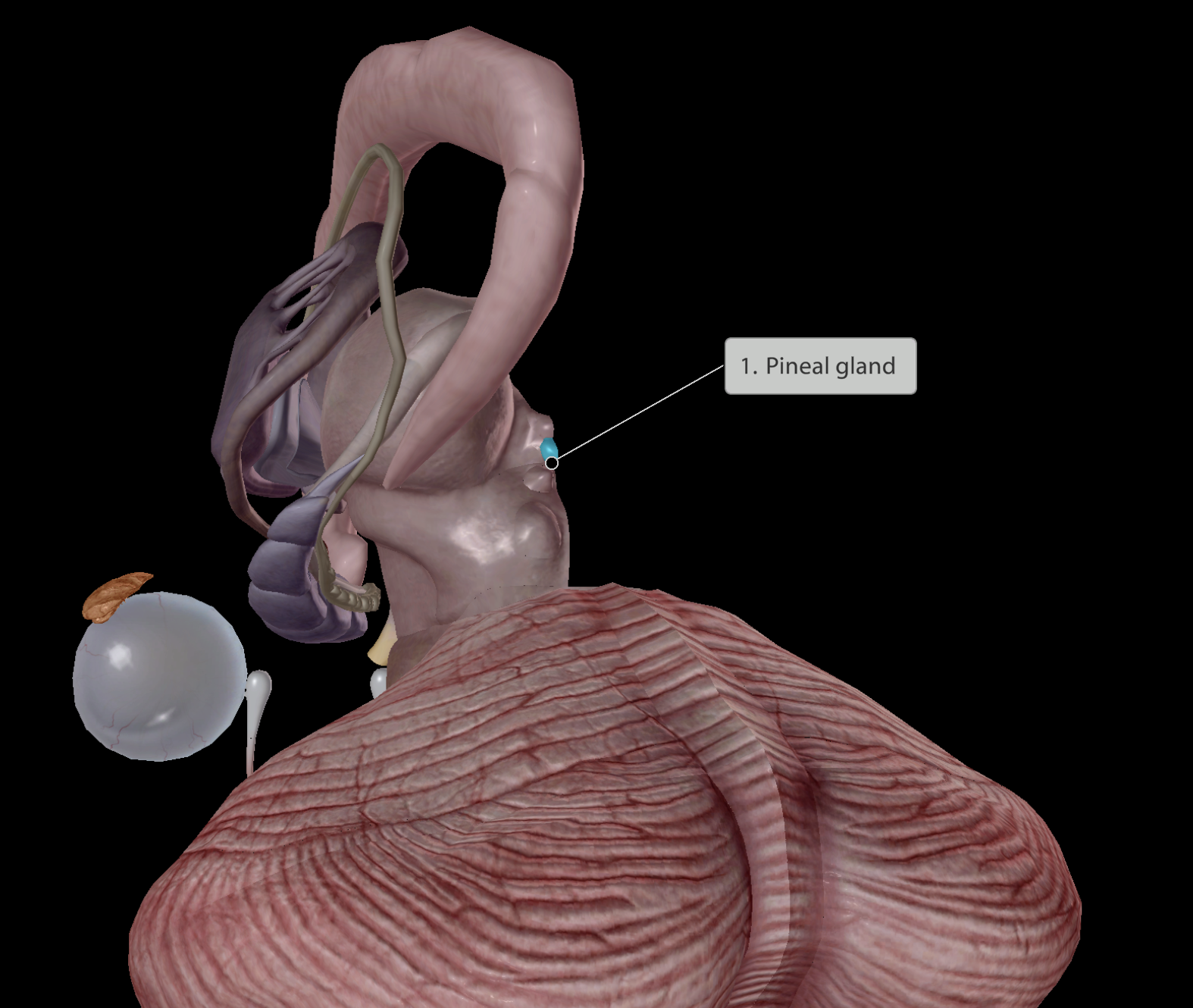
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
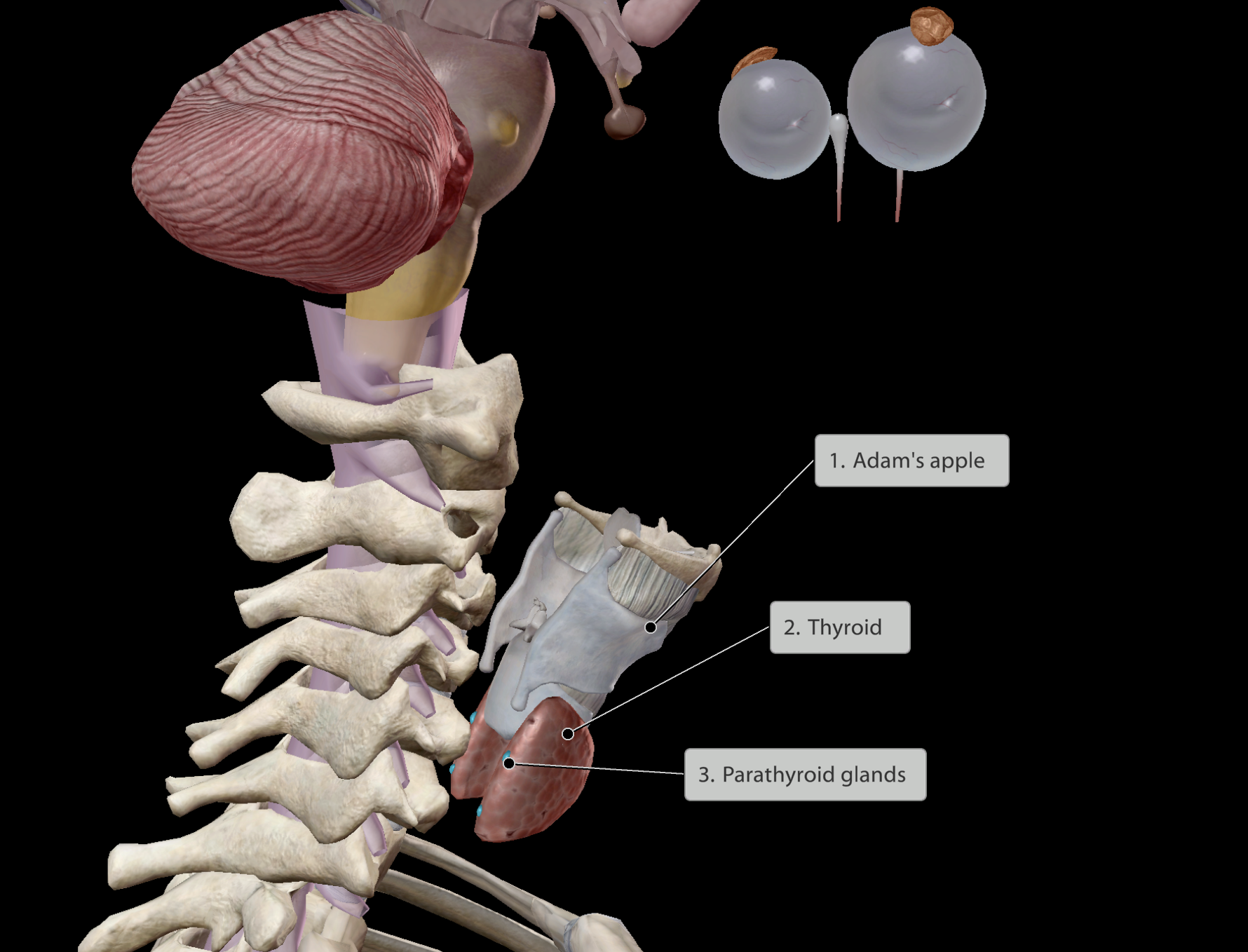
Thyroid
Some main functions:
Helps regulate:
Body temperature
Weight
Energy levels
Goiter: Condition where there is extreme enlargement of the thyroid gland
Parathyroid
Some main functions:
Helps regulate:
Calcium blood levels
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
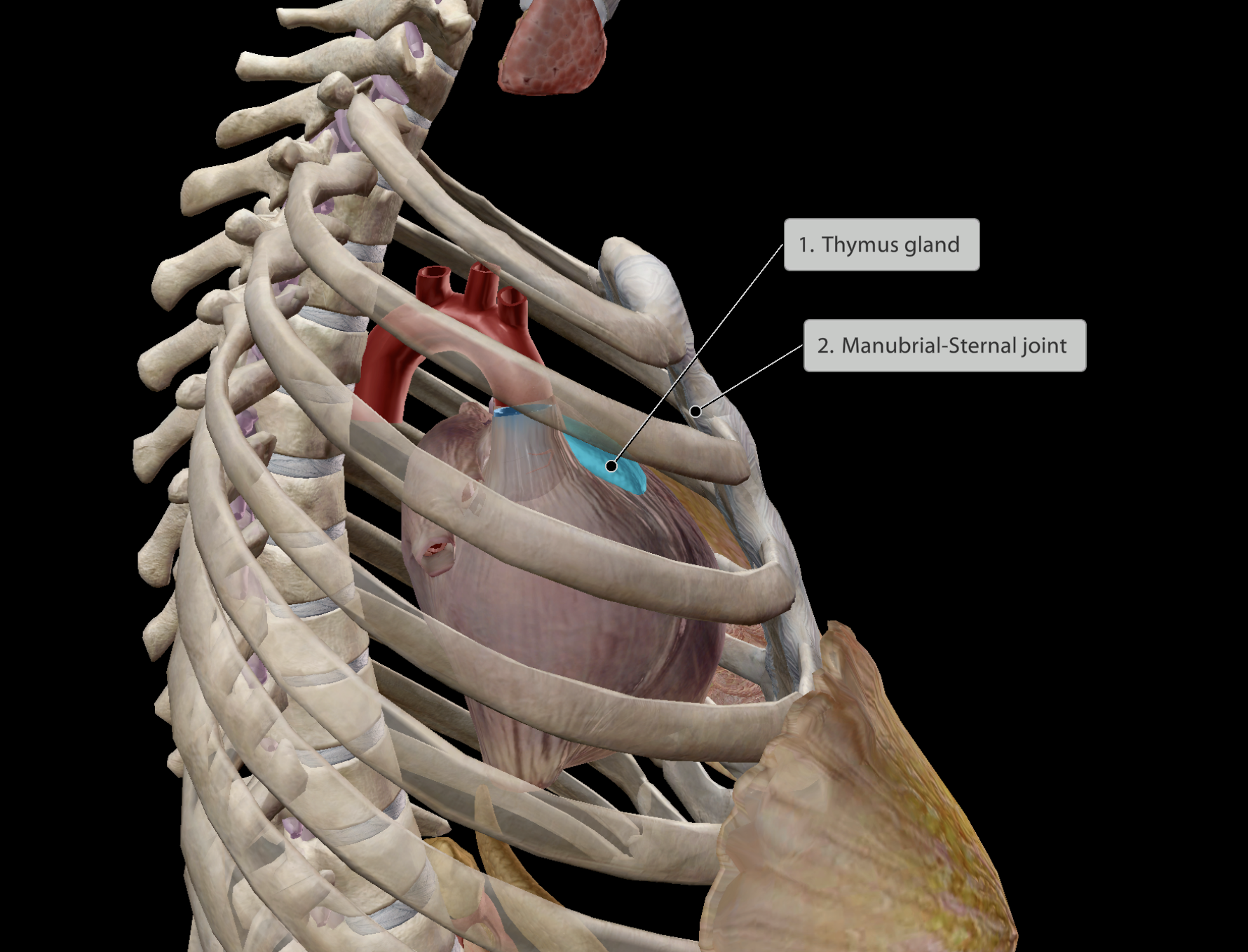
Location:
Deep to the sternum
Just posterior to the manubrial-sternal joint
Superior to the heart
Large in infants, shrinking to become fatty tissue as a person ages.
Thymus
Some main functions:
Helps regulate:
Immune cell development & function
Hence, large as an infant when developing a strong immune system, slowly shrinking and dying off in adulthood and old age, where immune system is established
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
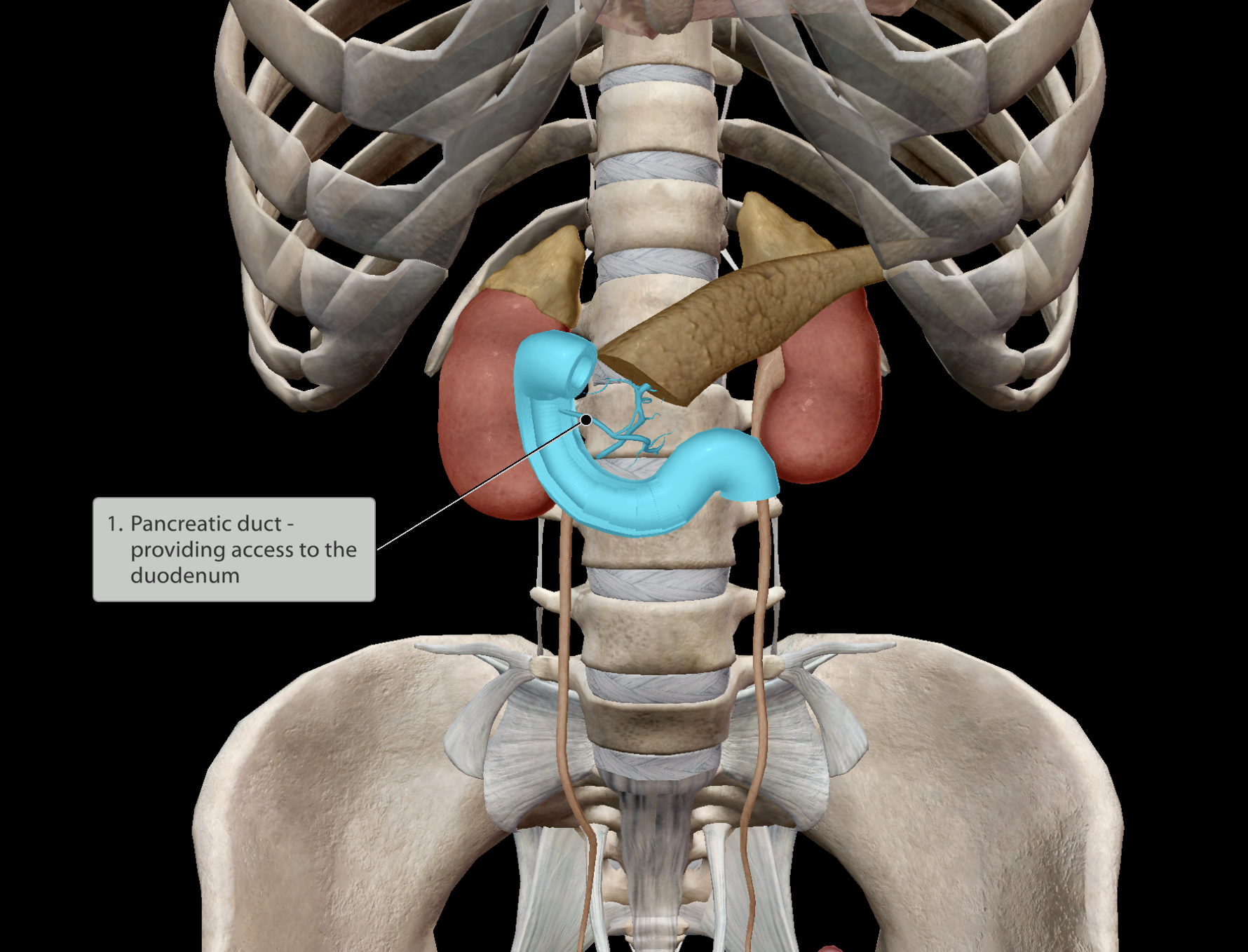
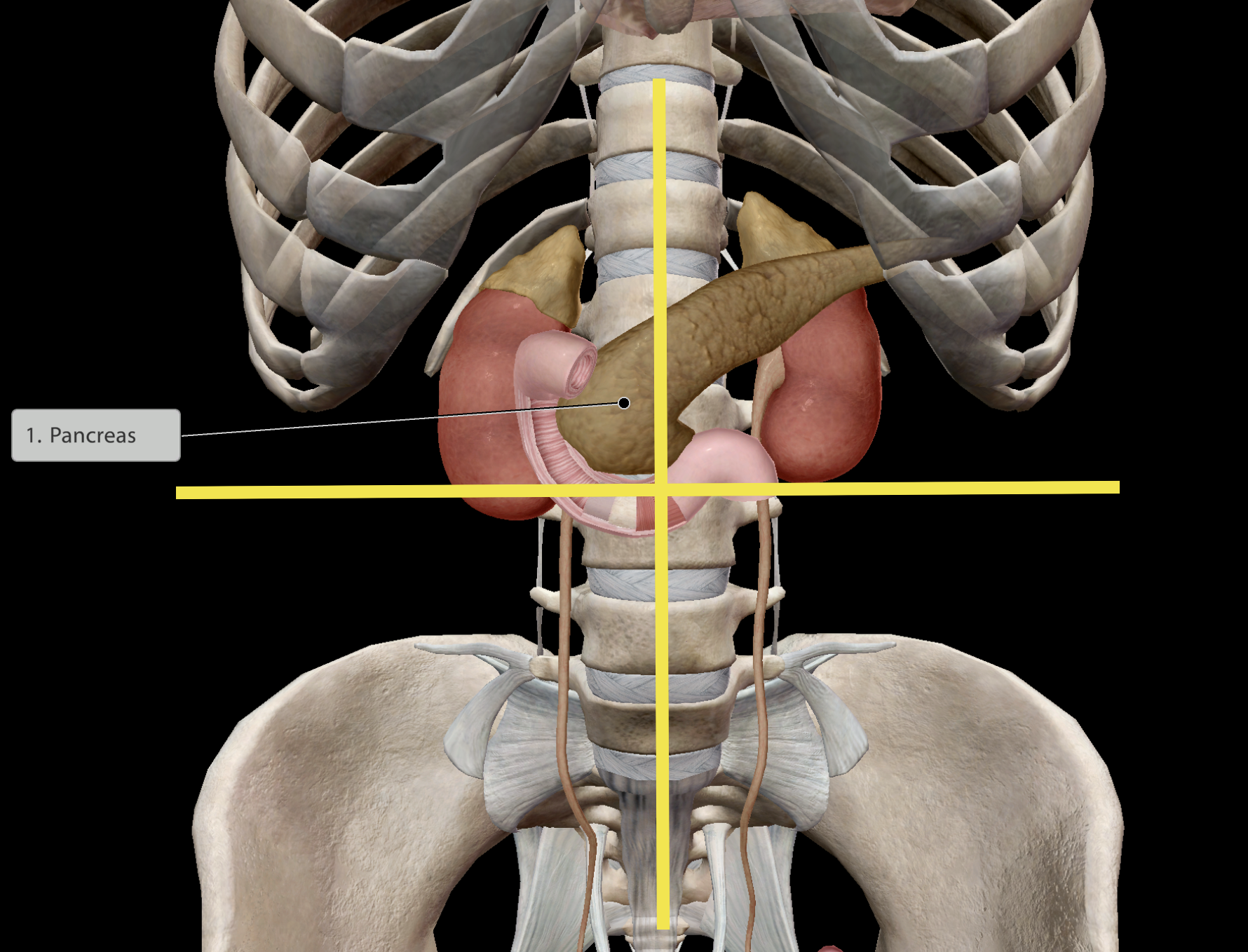
Location:
Left & right upper quadrants of the abdomen.
In close contact with the duodenum (initial section of the small intestine)
The pancreas releases enzymes into the small intestine to aid digestion
The pancreas releases ions to balance the acidic pH of chyme that has exited the stomach.
Critical in regulating glucose levels.
Inability leads to diabetes
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
Location:
Directly superior to the kidneys.
Separately situated in left & right upper quadrants of the abdomen. Close to the posterior wall of the abdomen
Produces hormone adrenaline (supplies sympathetic nervous system)
Paired organ
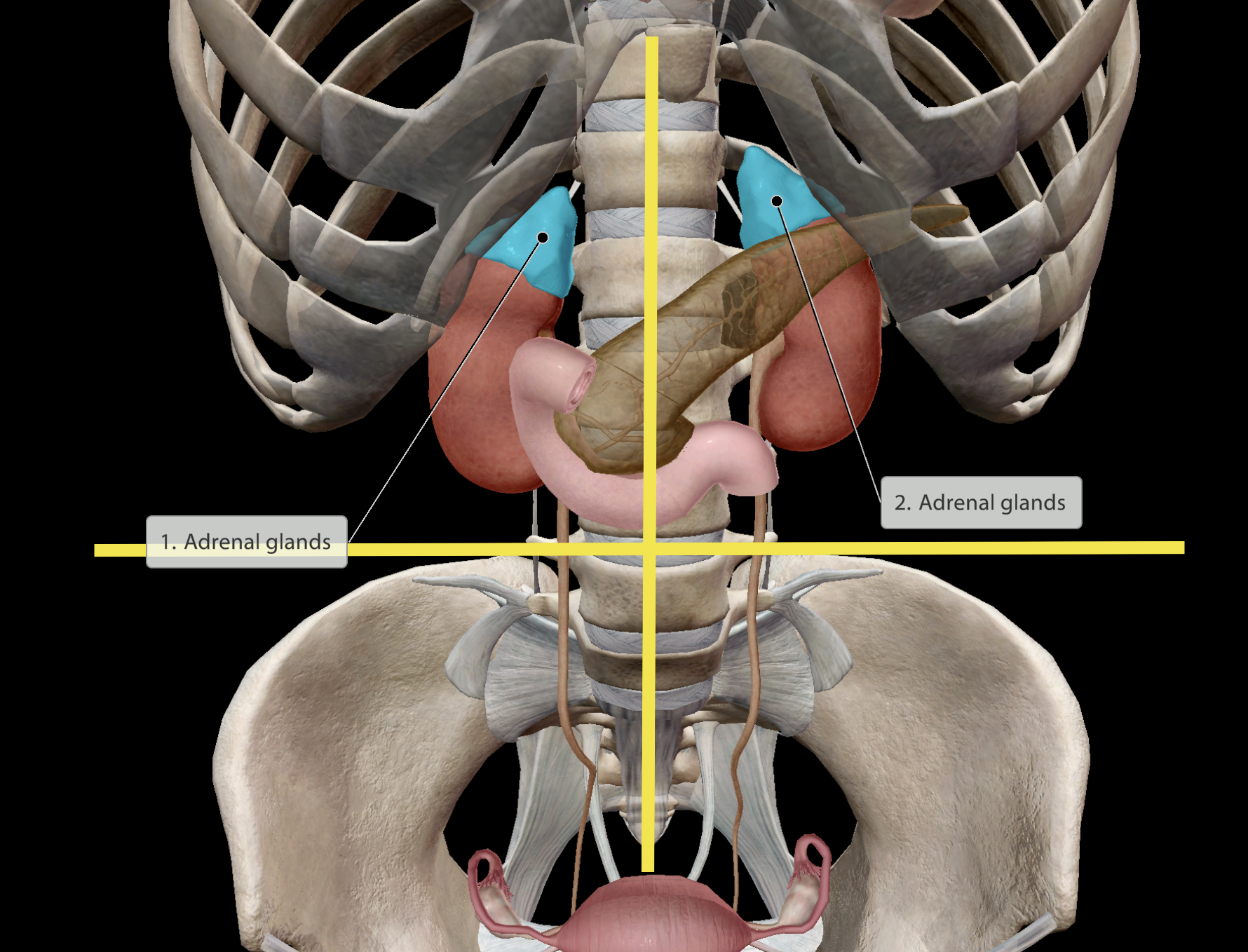
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
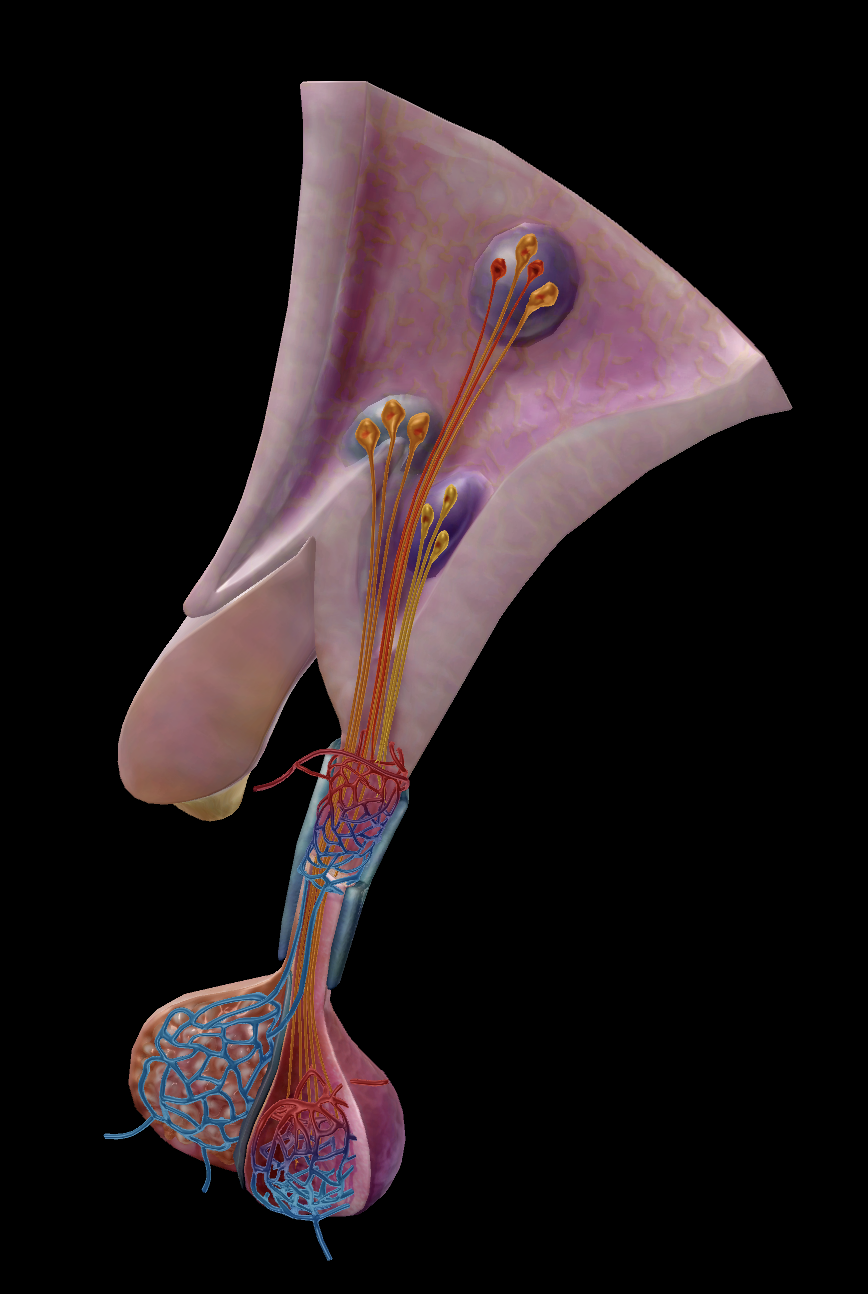
Location:
Deep within the pelvis, lateral to the uterus.
Some main functions:
Helps regulate:
Ovulation
Menstrual cycle
Zygote conception
etc.
Paired organ
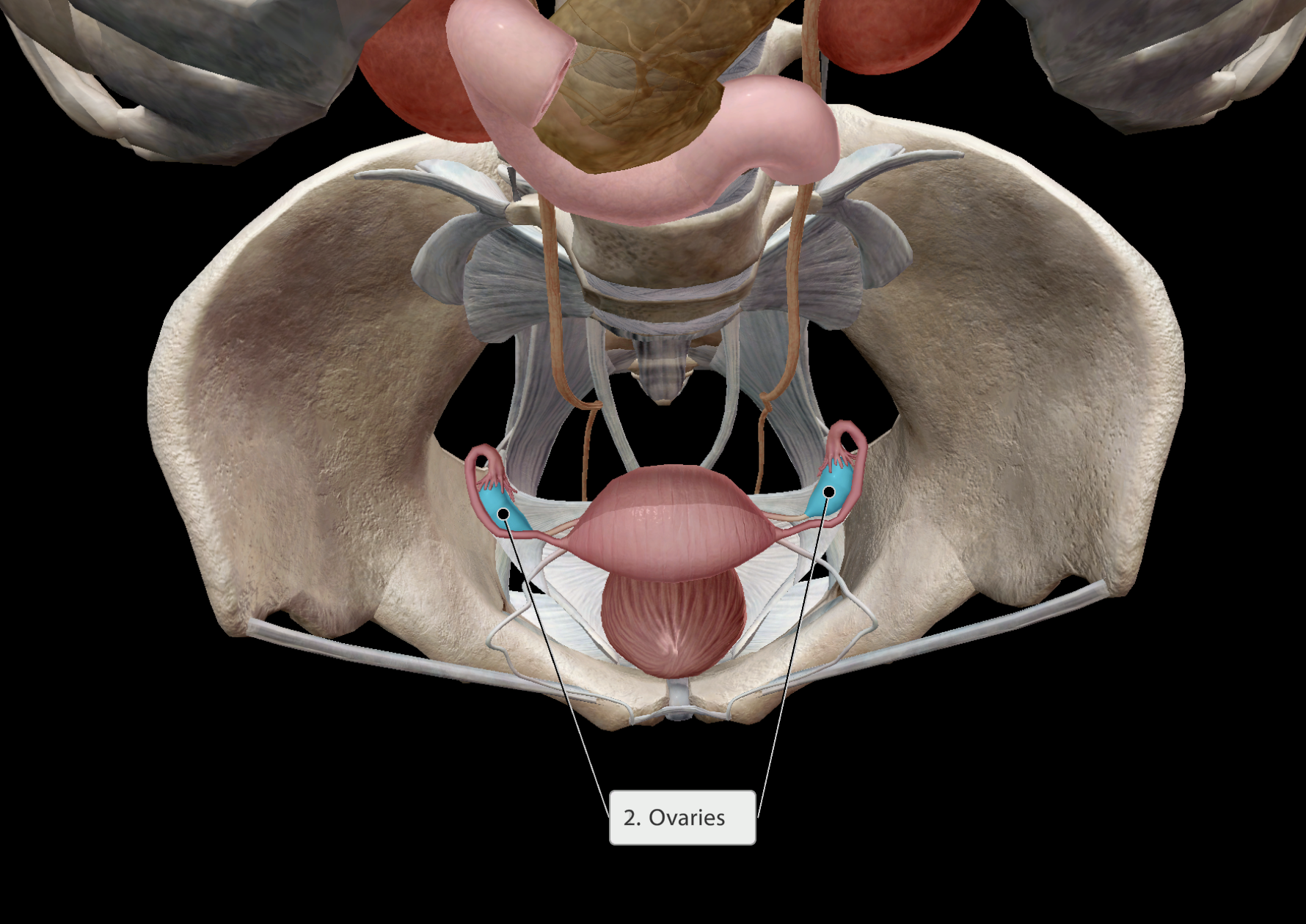
Endocrine system
Brain
Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Neck
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thorax
Thymus gland
Abdomen
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pelvic region
Ovaries
Testicles
Location:
External to the pelvis, just inferior to the pubic bones.
Some main functions:
Helps regulate:
Sperm containment
Male puberty
Paired organ
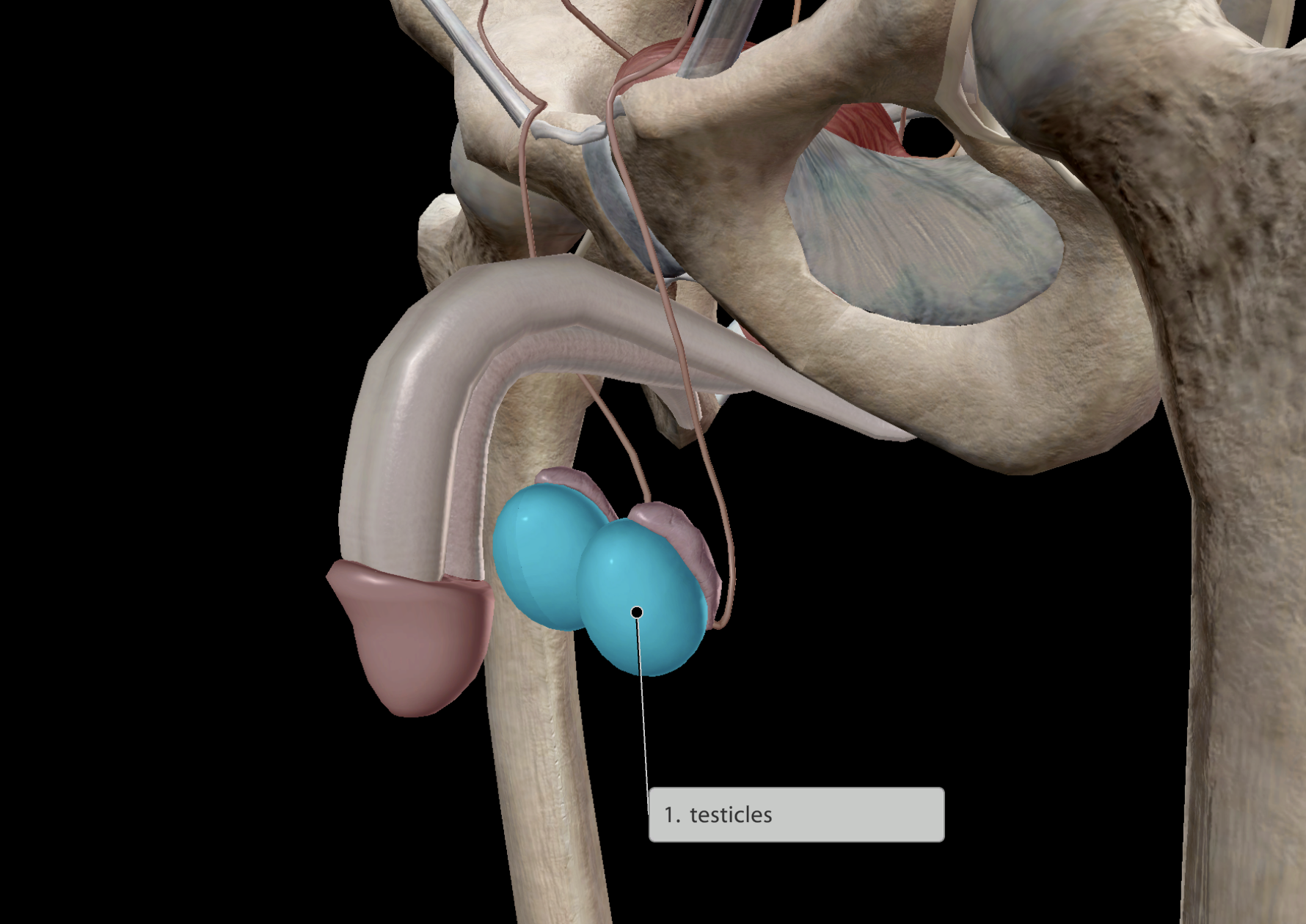
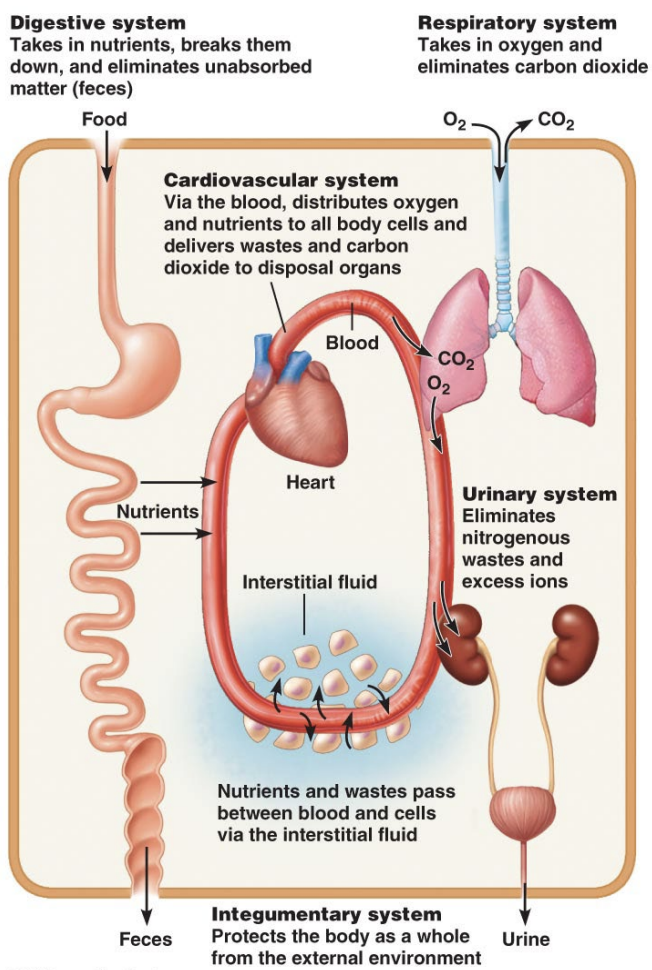
Cardiovascular System
Cardio-: “Heart”
-vascular: “blood vessels”
Plumps blood around the body
Circulating nutrients, oxygen & waste products (CO2)
Bloodflow occurs in one direction
Blood pressure ensures one-way flow
Valves in veins prevent backflow
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
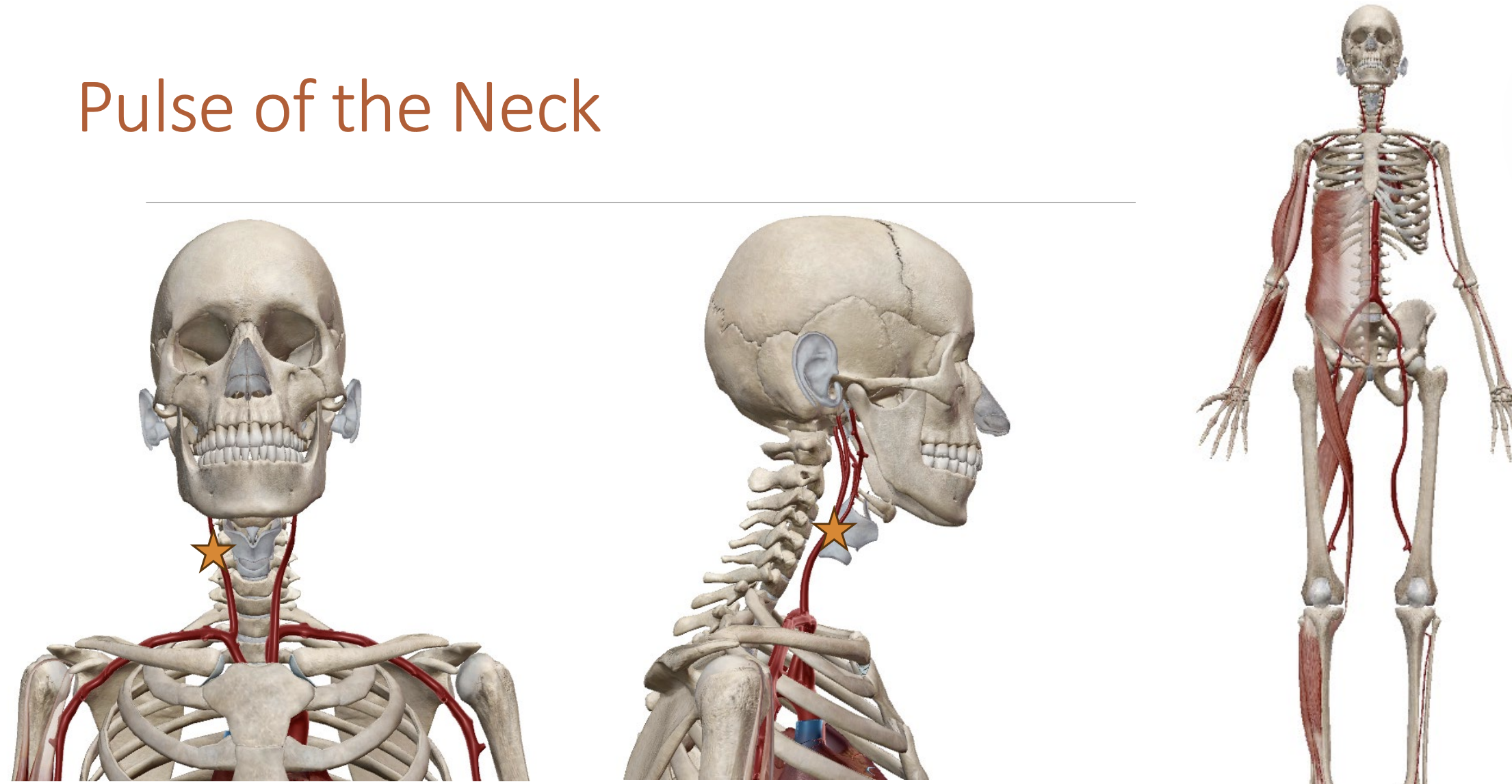
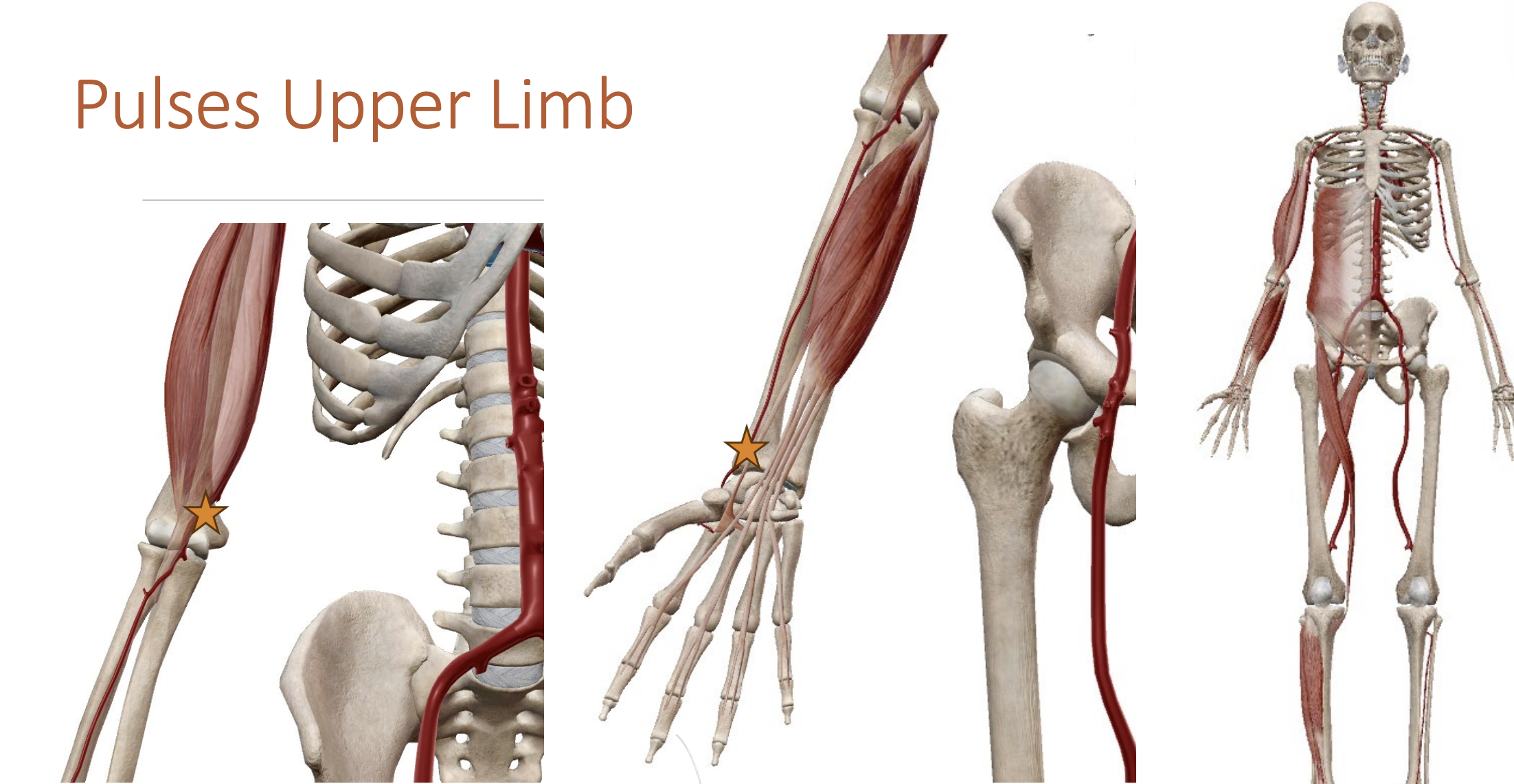
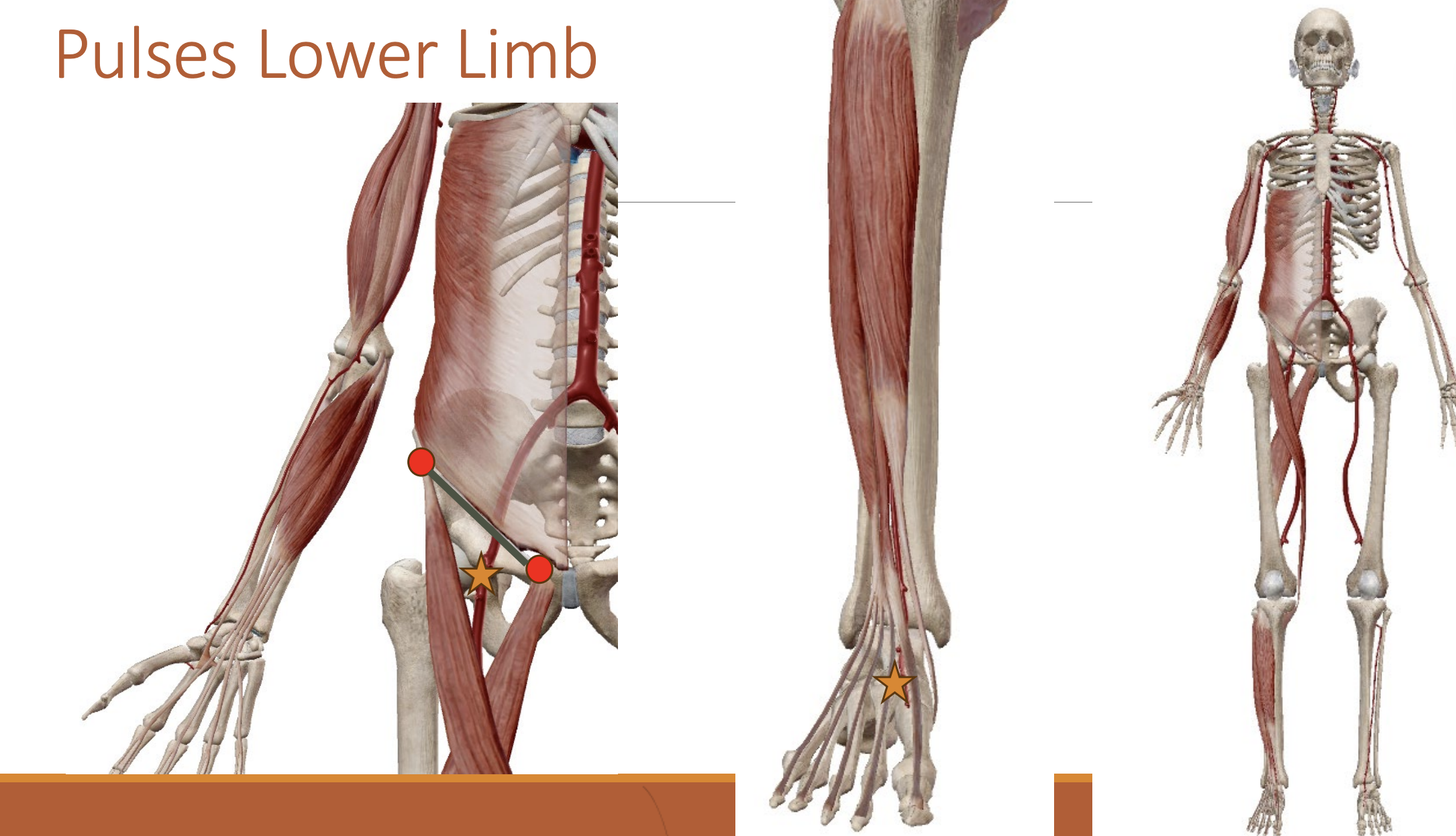
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
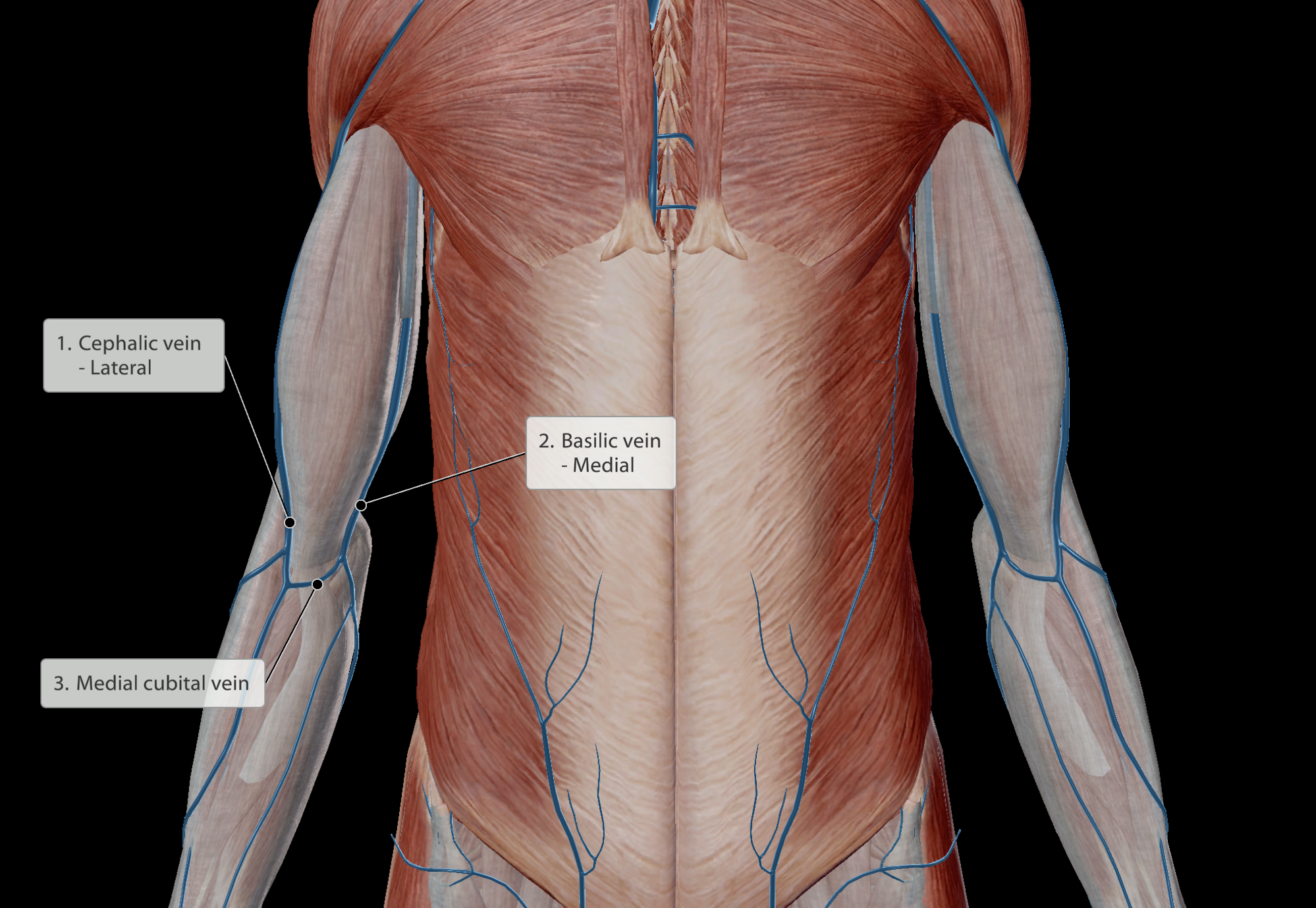
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
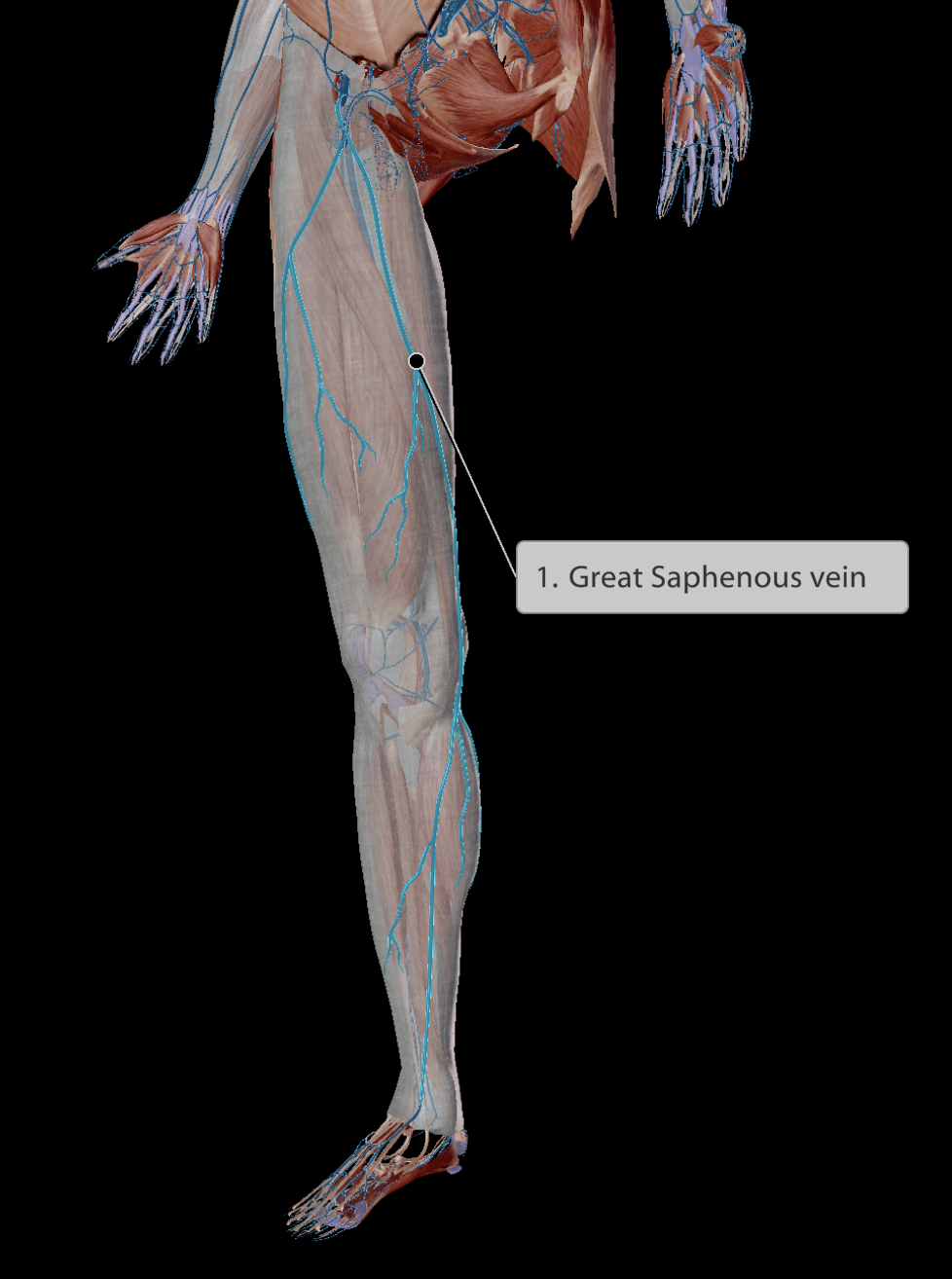
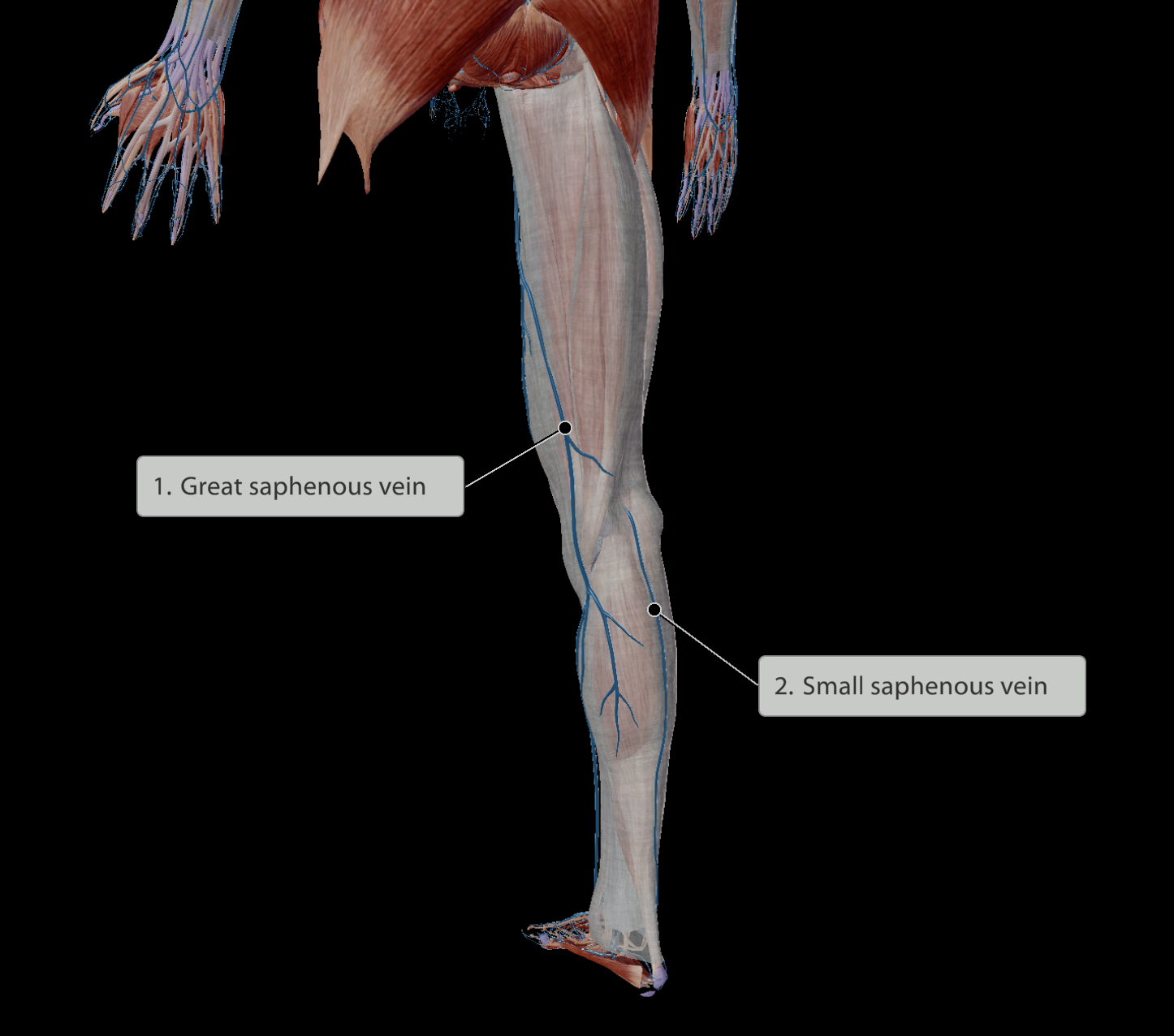
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
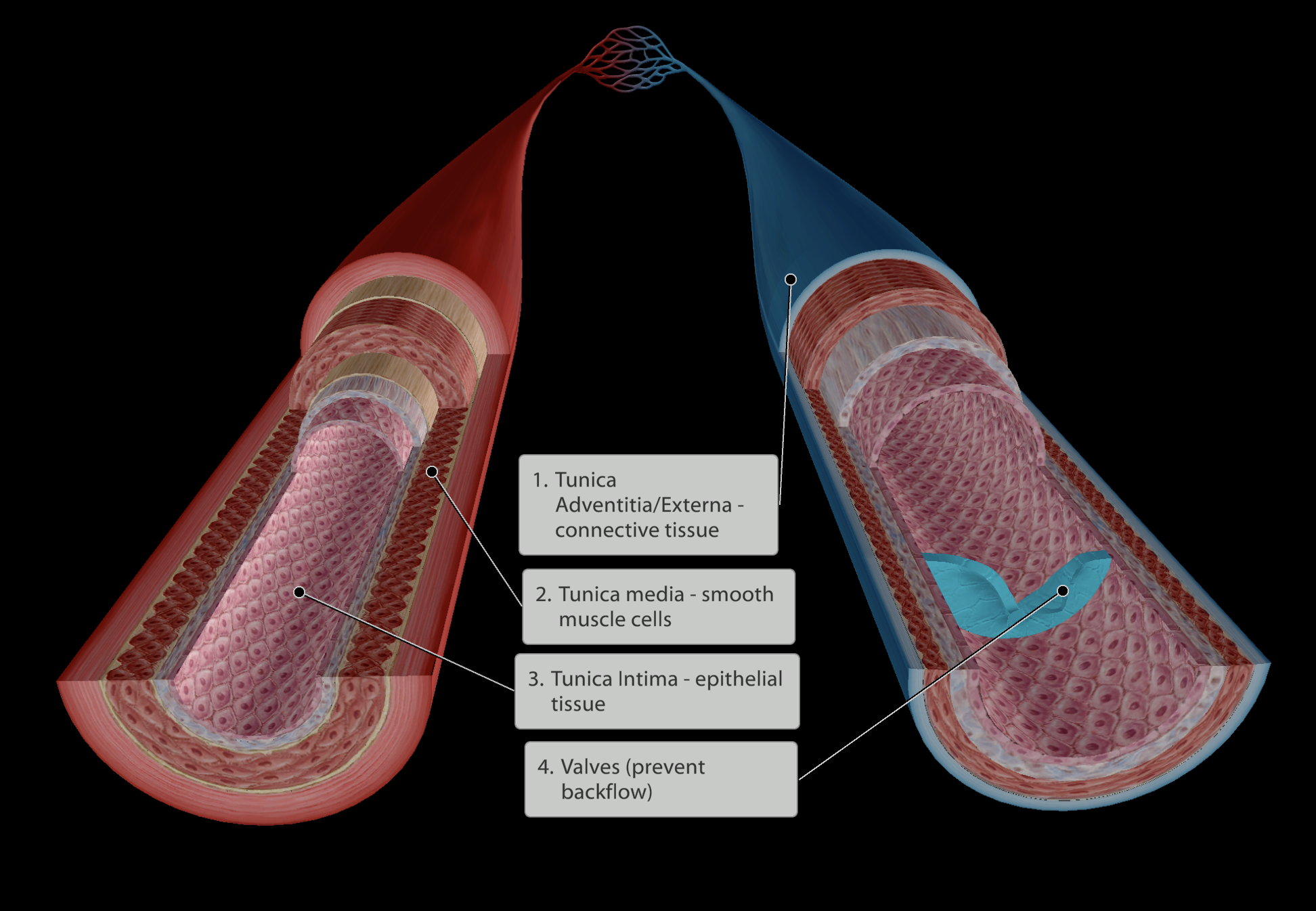
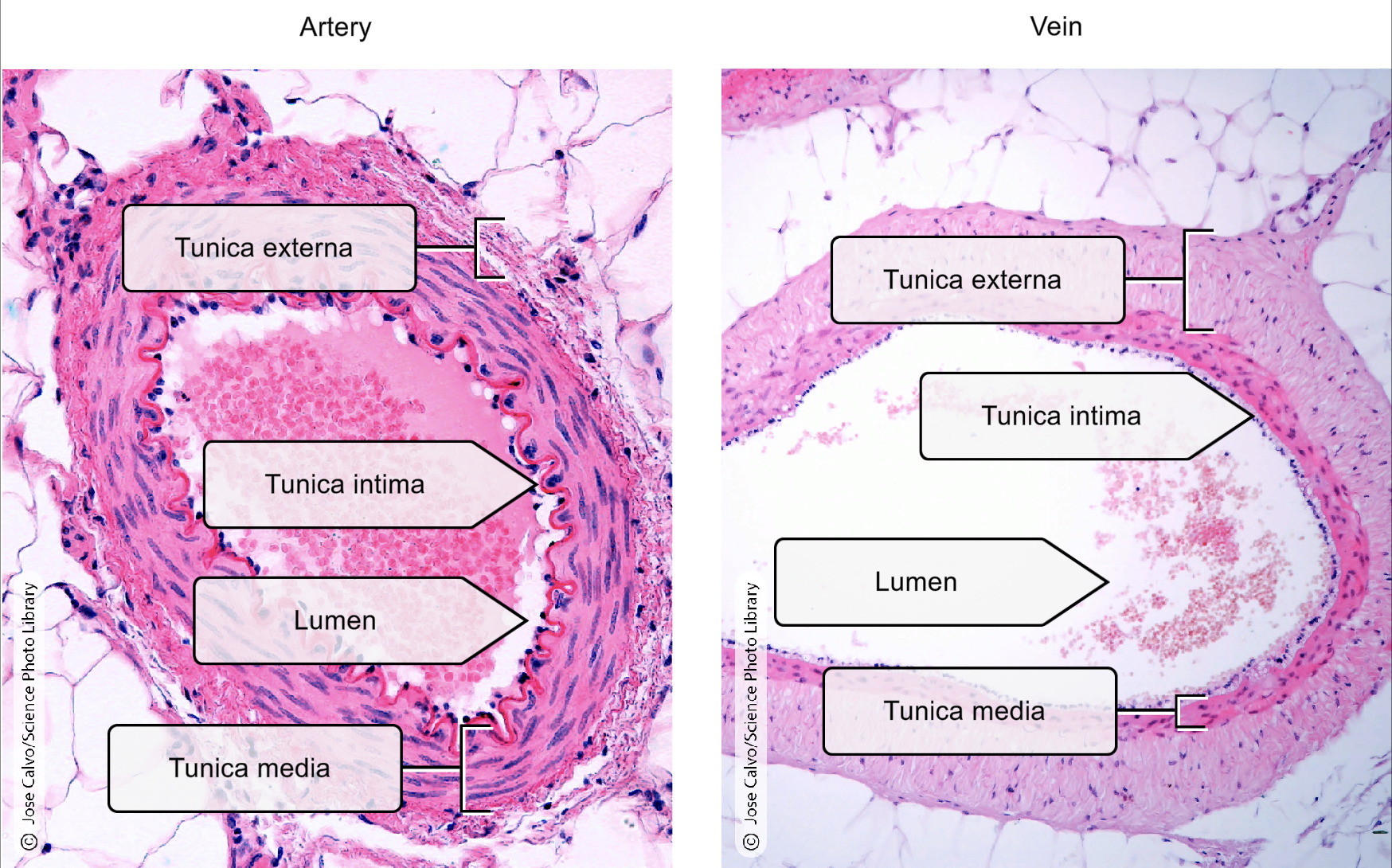
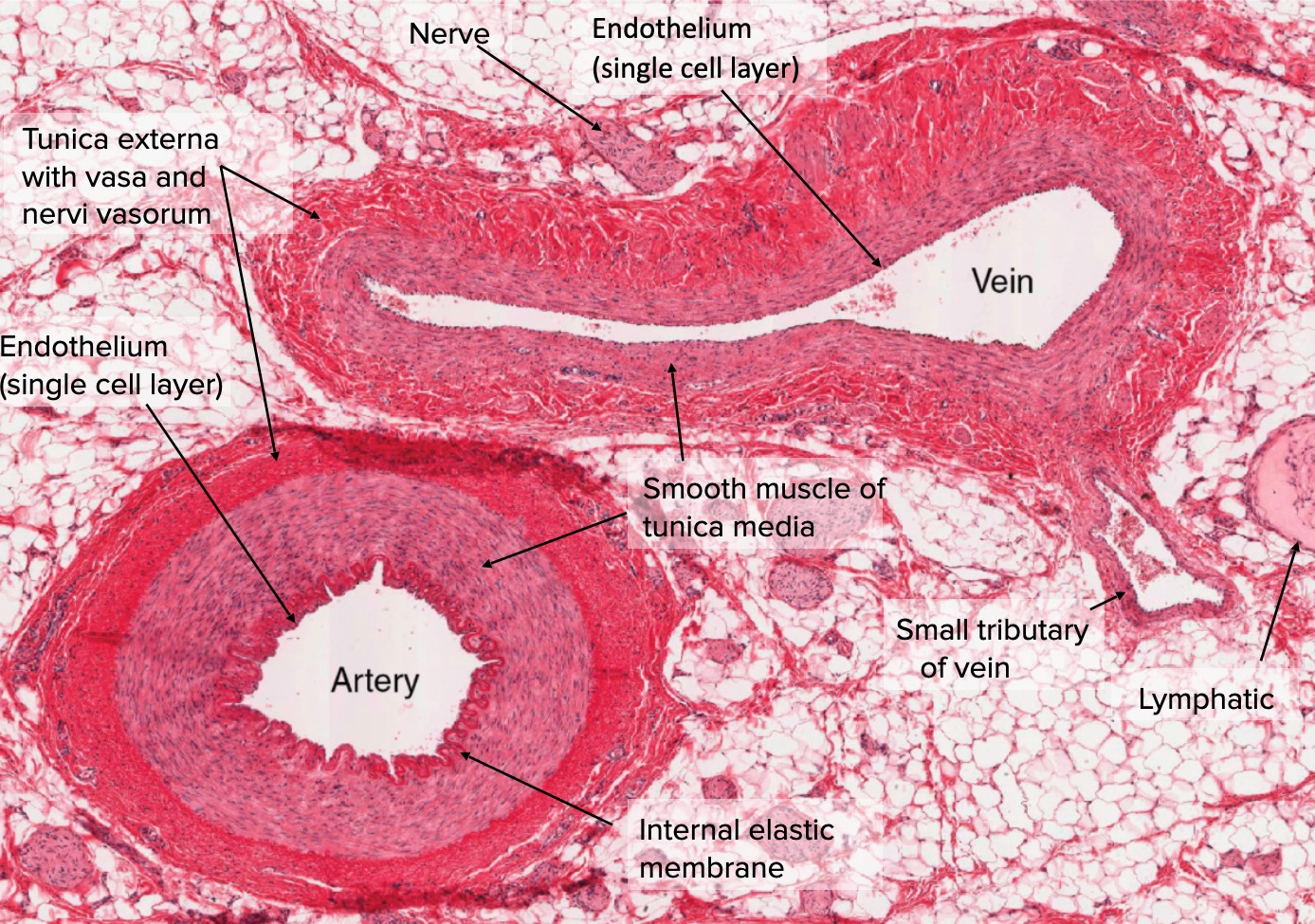
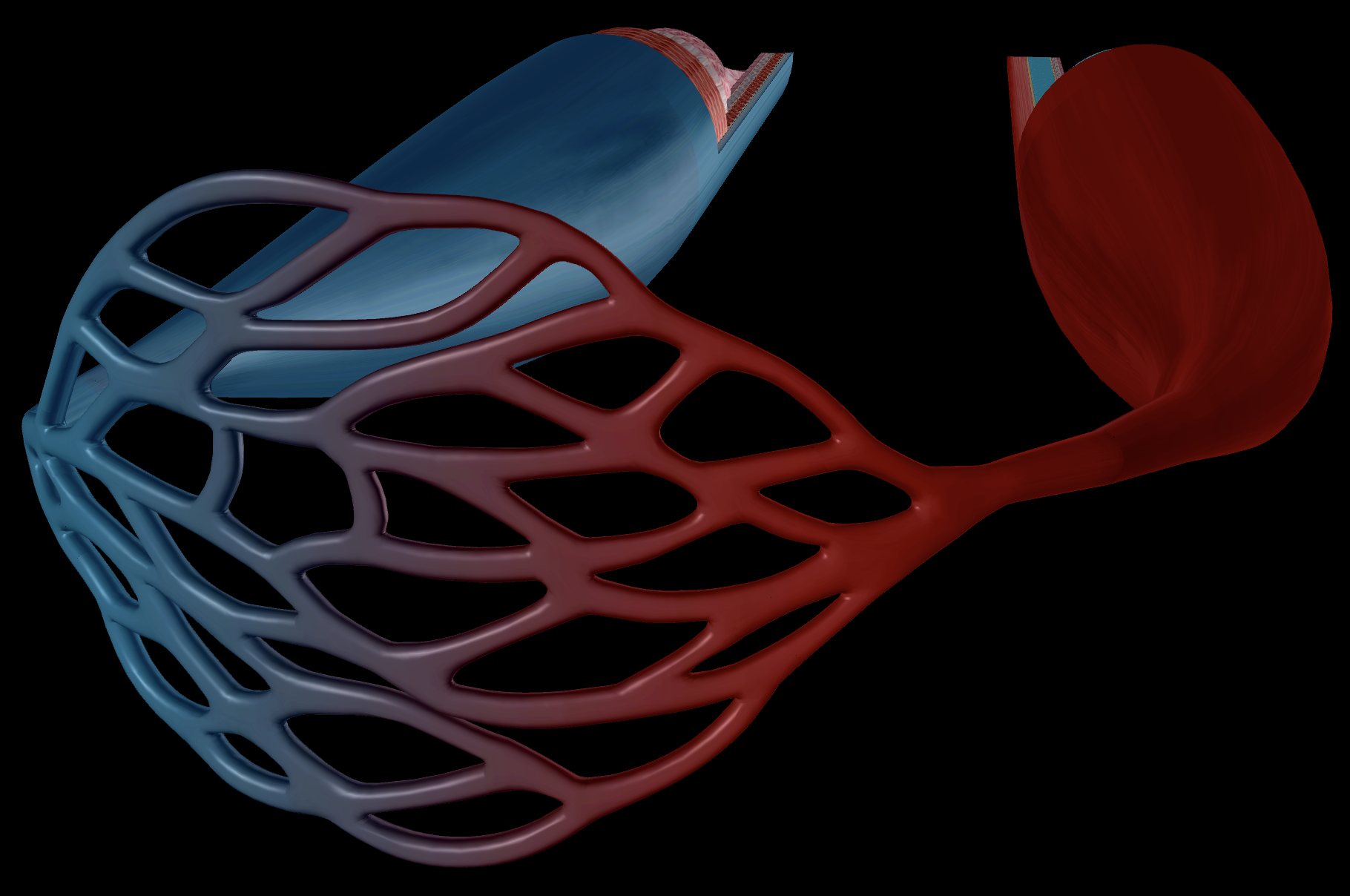
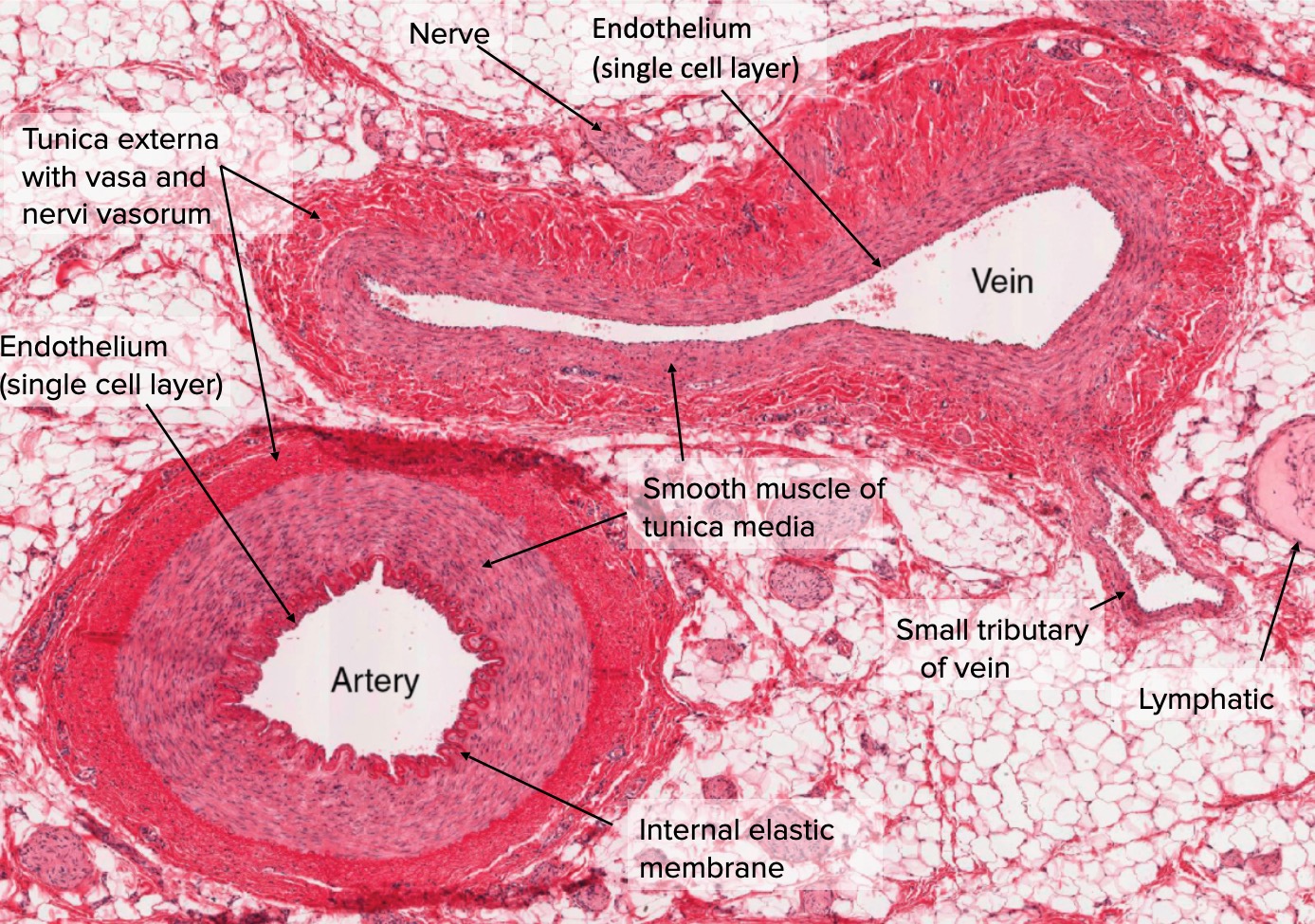
Moves blood away from the heart
Oxygenated Blood
Thick, muscular wall
Muscle ensures the arteries do not burst due to the high blood pressure.
Muscles allow vasodilation and vasoconstriction to redirect bloodflow
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Nutrient & gas exchange.
Diameter is one-cell thick, making the vessels very fragile.
Thus, blood must have low pressure to not rupture vessels
Bloodflow is slow, under low pressure
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Moves blood back to the heart
Deoxygenated Blood
Extremely low blood pressure
Capillaries already have low blood pressure, so the blood entering the veins has even lower pressure (to follow the pressure gradient from high to low)
Thin, valved vessel walls
Little muscle is needed to strengthen the vein walls as blood pressure is so low


Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Skeletal muscle pump
When moving skeletal muscles, the muscle bellies push against veins and push blood back towards the heart.
Valves
Veins are lined with one-way valves
When skeletal muscles push against veins, blood is squeezed in both directions
One-way valve ensures blood does not travel backwards
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Found in arteries, as they have high blood pressure in sync with the heart.
Deeper within the tissue, due to being protected with muscles, so can be difficult to find
Some areas, the artery must travel more superficially to access an area of the body
If there is a nearby solid structure (i.e bone), then pulse can be palpated
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Identifiable veins.
Found superficial
e.g Superficial to deep fascia
Used to draw blood
low pressure means less risk of bleeding out
Used to insert IV drips
Enables nutrients to travel back to the heart and be pumped out to the rest of the body
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubital vein - connects cephalic and basilic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Skeletal muscle pump
Valves
Characteristics:
Pulses
Carotid artery - Neck
Radial artery - Wrist
Brachial artery - Elbow
Femoral artery - Thigh
Dorsalis Pedis Artery - Foot
Identifiable veins
Cephalic vein - Lateral to biceps
Medial cubitan vein - connects cephalic and basiclic veins
Basilic vein - Medial to biceps
Great saphenous vein - Medial to thigh
Small saphenous vein - Begins lateral to foot, travelling posteriorly up to the knee
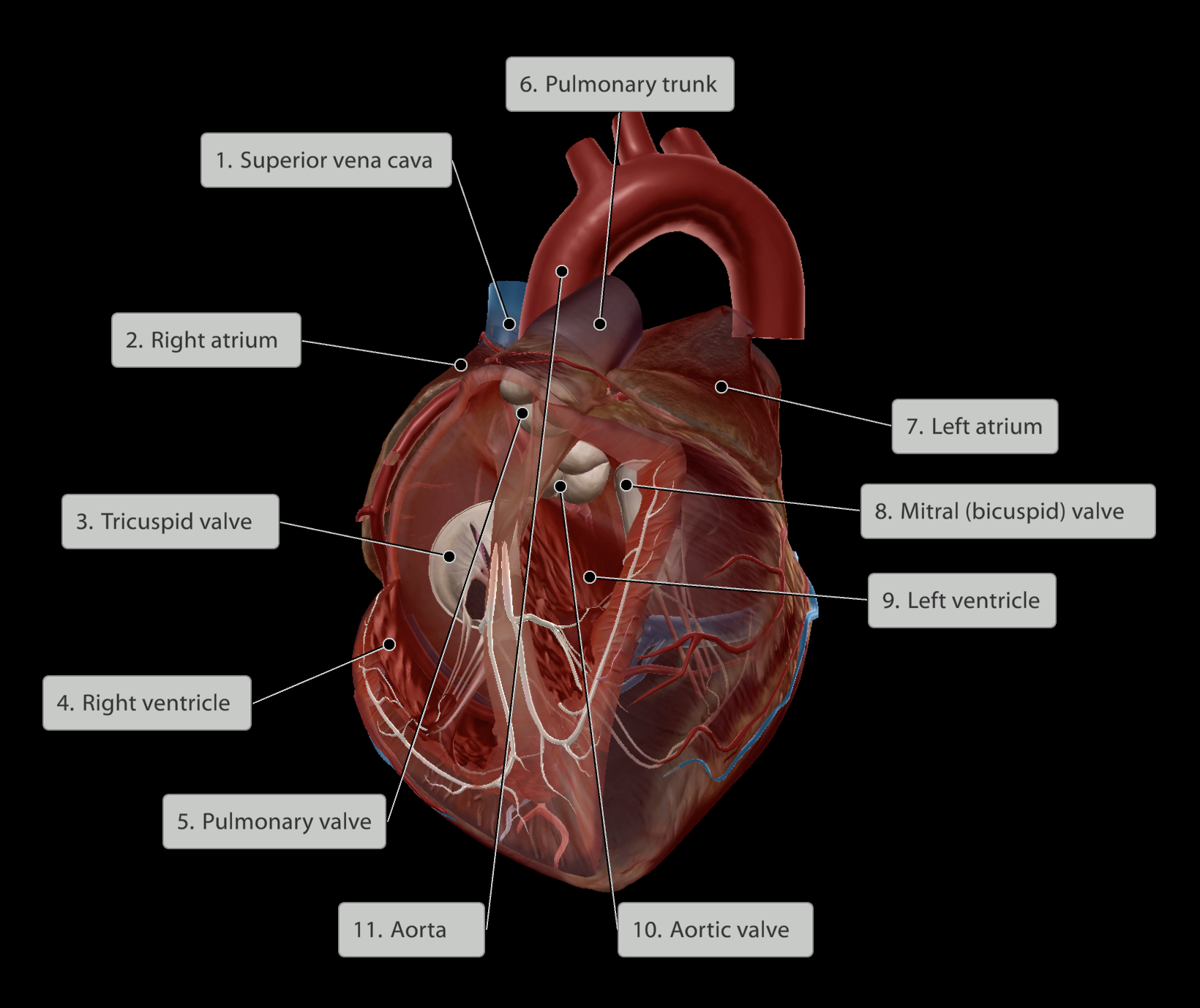
Upper chambers: Atria
Lower chambers: Ventricles
Valves present between chambers/exit and entry points to ensure one-way flow
Blood travels:
Right atrium
Past tricuspid valve
Into right ventricle
Past the pulmonary valve
Out through the pulmonary trunk
Into the pulmonary arteries and oxygenated in lungs
Back to heart through pulmonary veins
Into the left atrium
Past the bicuspid/mitral valve
Into left ventricle
Pumped out past the aortic valve
Into aorta to be distributed around the body
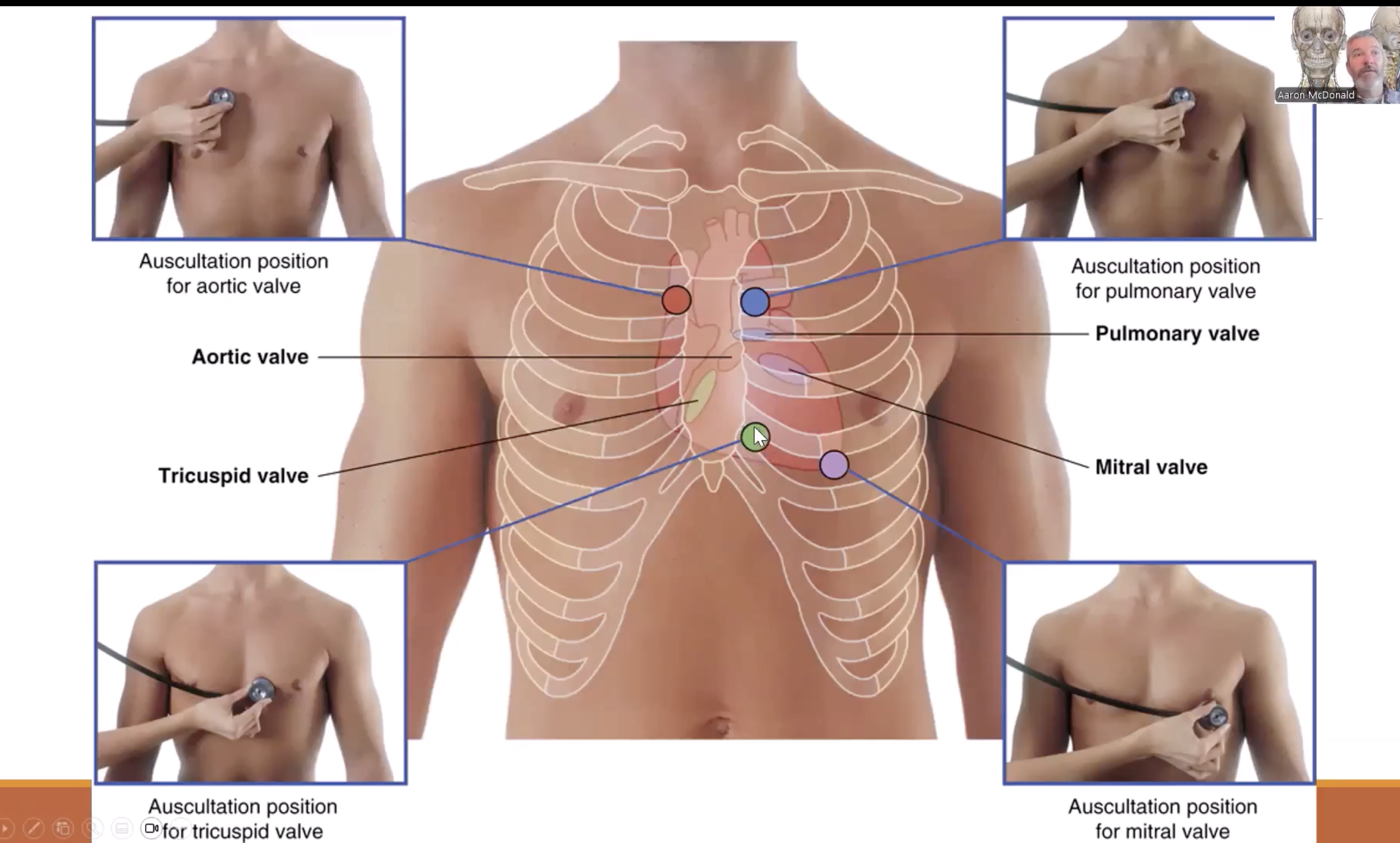
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Auscultation
Auscultation:
To hear the heart with a stethoscope
Heartbeat:
Sound is created when blood rushes against closed valves
Ensures valves are working accordingly and blood is rushing in the correct direction