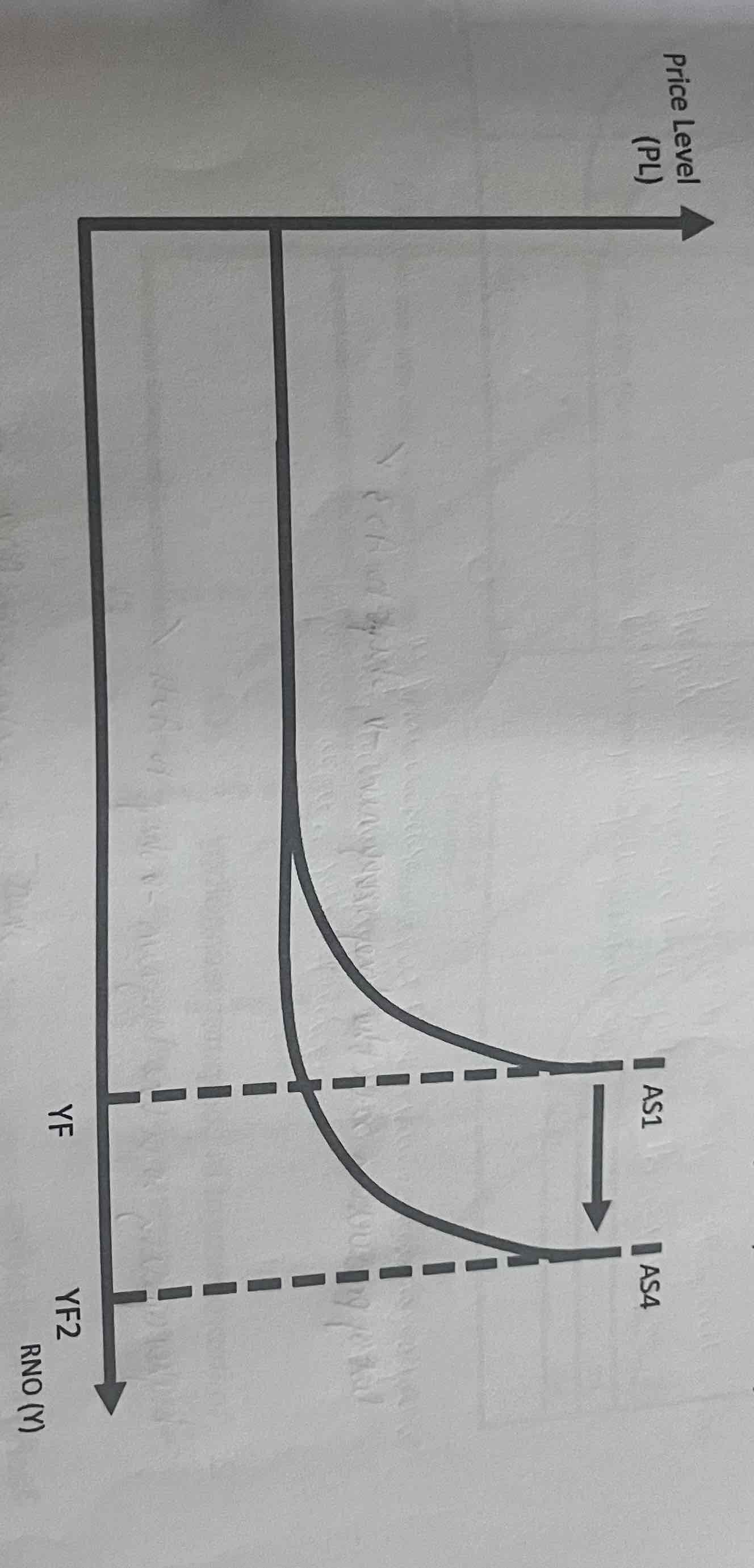
Aggregate supply curve
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
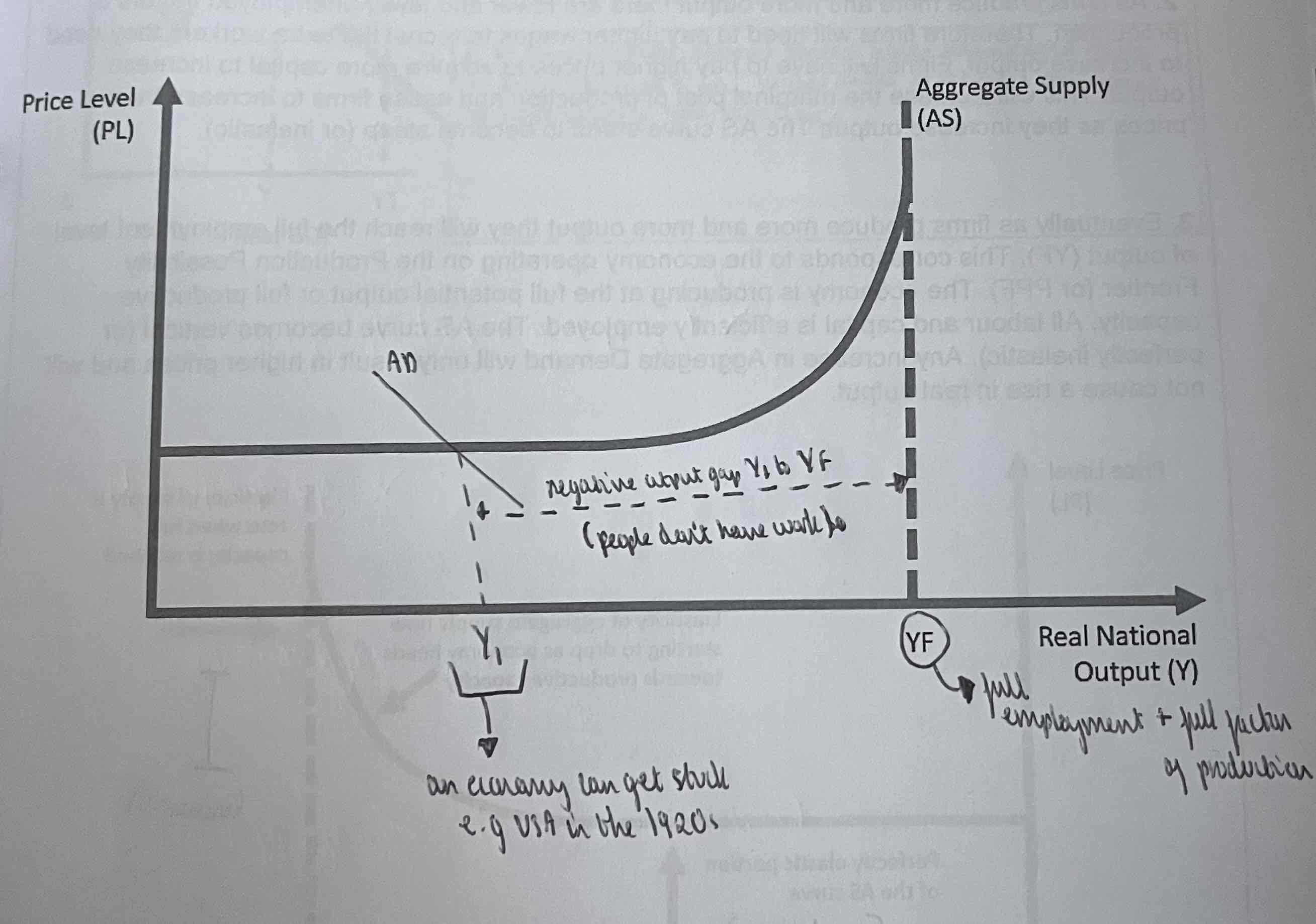
What does the AS curve show?
The total quantity of goods and services firms are willing and able to produce at each price level.
What does the Keynesian AS curve look like?
What is a movement along the AS curve due to?
changes in the price level alone.
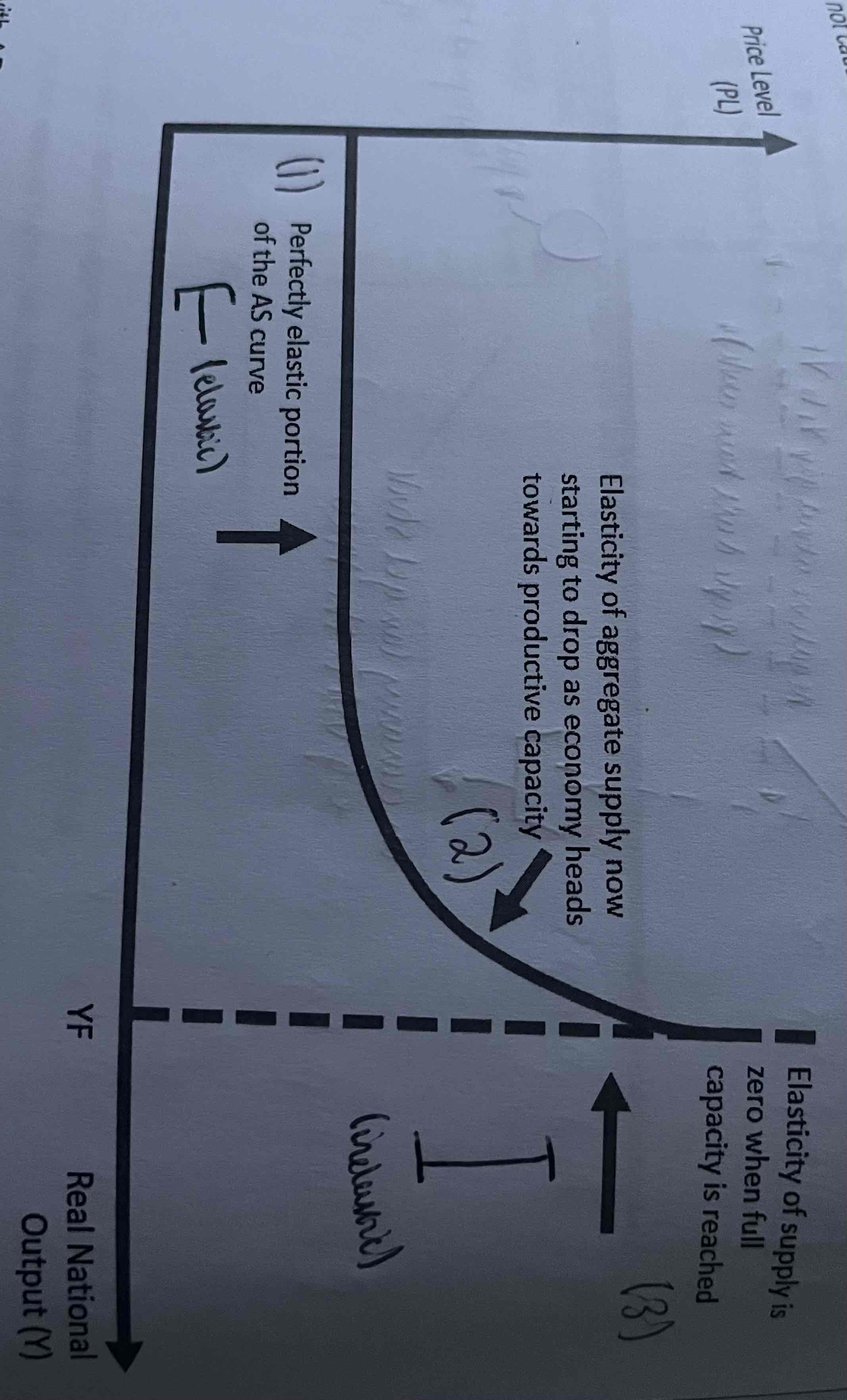
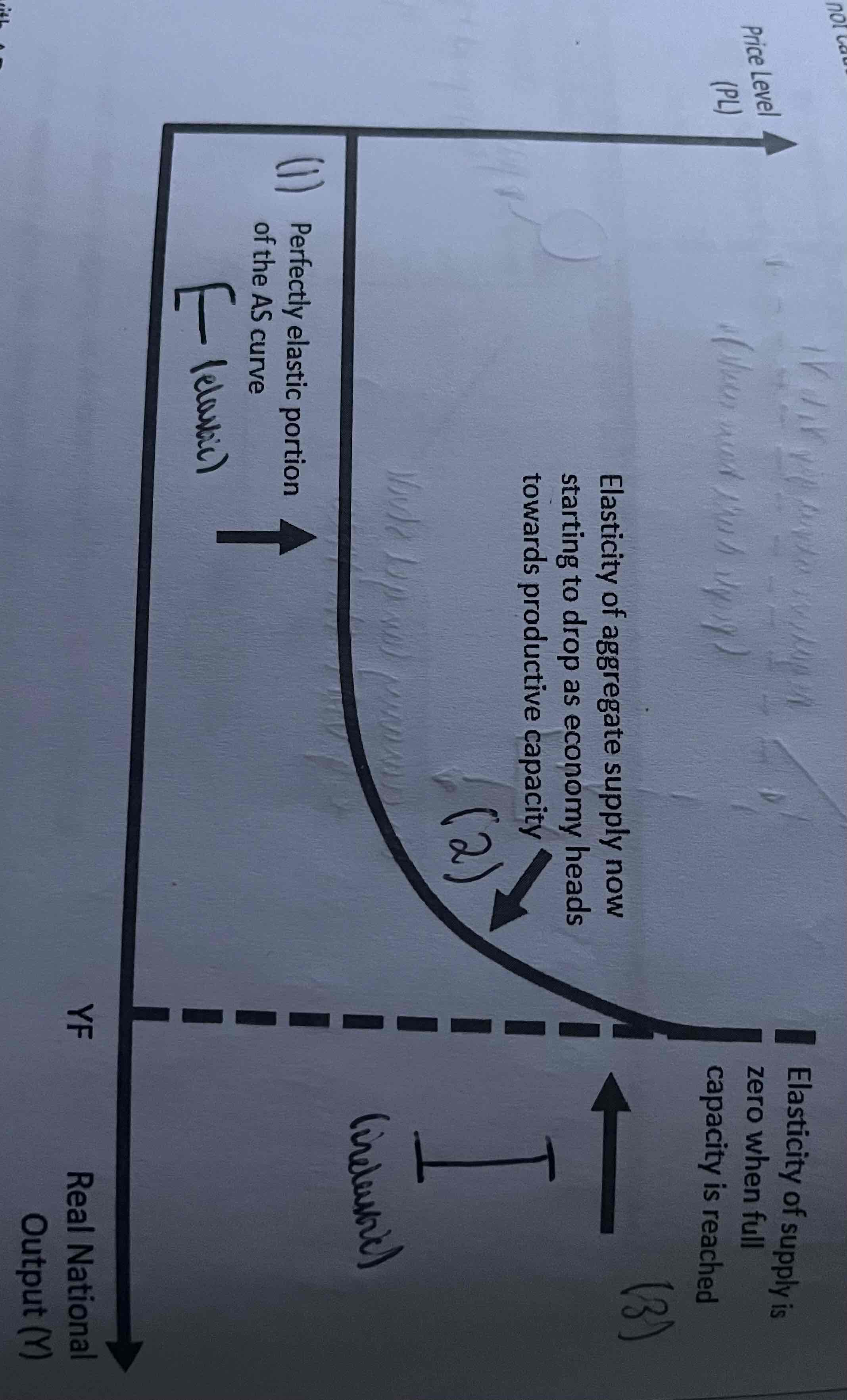
What is the summary of the Keynesian AS (first phase)?
Keynes believed that at low levels of output (e.g recession) there would be lots of unemployed labour and capital in the economy. Therefore firms could easily increase output by hiring unemployed workers and using idle capital. Firms would not need to raise wages to recruit the extra workers they need if there is high unemployment. It would be relatively easy for firms to increase output without there being a significant increase in the marginal cost of production. The reforms firms wouldn’t n need to raise their prices very much to increase output. The AS curve is flat (perfectly elastic.
What is the summary of the Keynesian AS (second phase)?
As firms price more output there are fewer unemployed factors of production. Therefore firms will need to pay higher wages to recruit the extra workers they need to increased output. Firms will have to pay higher prices to acquire more capital to increase output. This will increase the marginal cost of production and cause firms to increase their prices as they increase output. The AS curve starts to become steep (or inelastic)
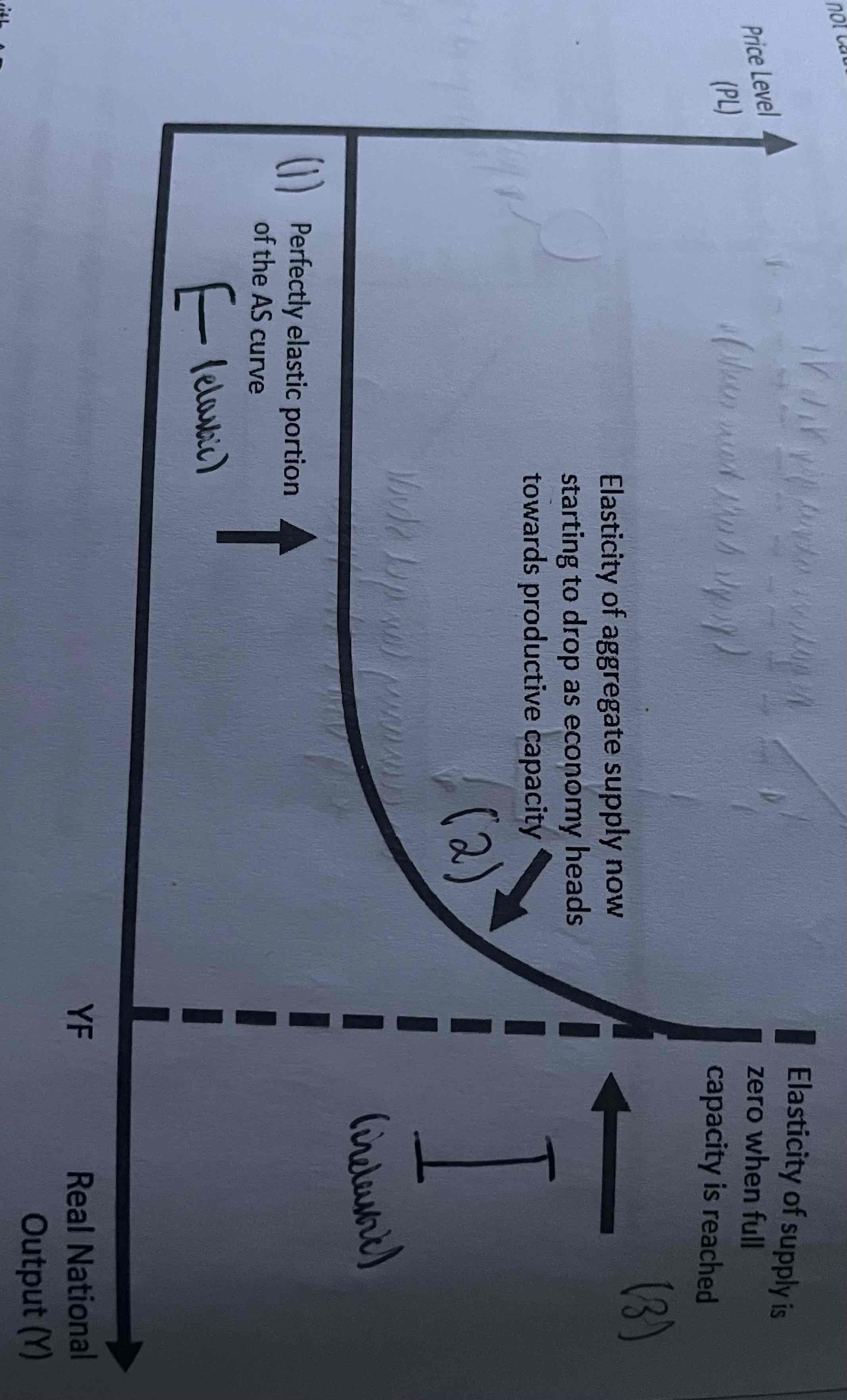
What is the summary of the Keynesian AS (third phase)?
Eventually as firms produce more output they will reach the full employment level output(YF). This corresponds to the economy operating on the PPF. The economy is producing at the full potential output of full production capacity. All labour and capital is efficiently employed. The AS curve becomes vertical (perfectly inelastic). Any increase in AD will result in higher prices and not cause a rise in real output.
What is the marginal cost of production?
The cost of producing an extra unit of ouput
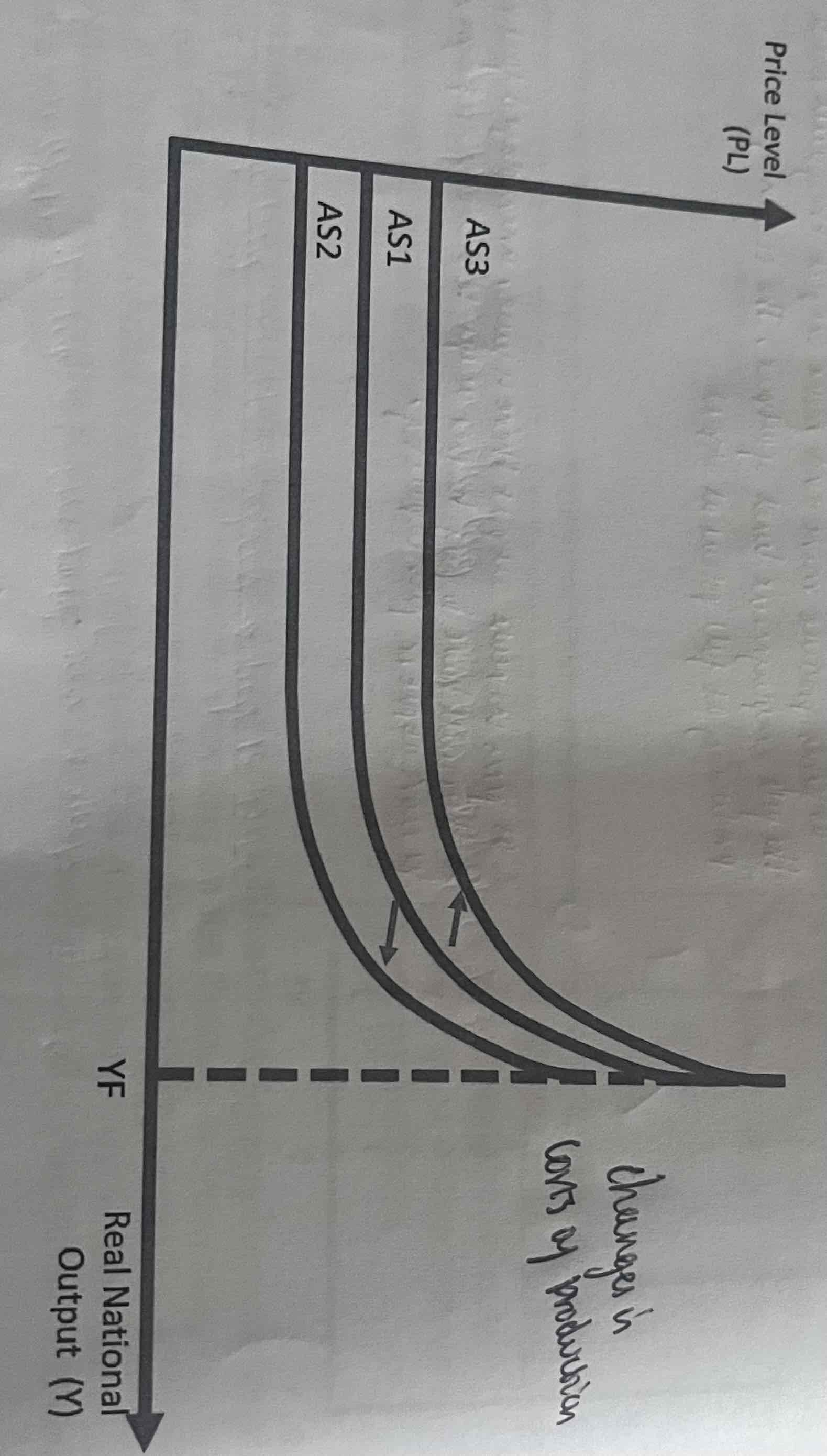
What does a rise in AS cause the AS curve to do?
Shift to the right as there is more output at any given price level. (AS2)
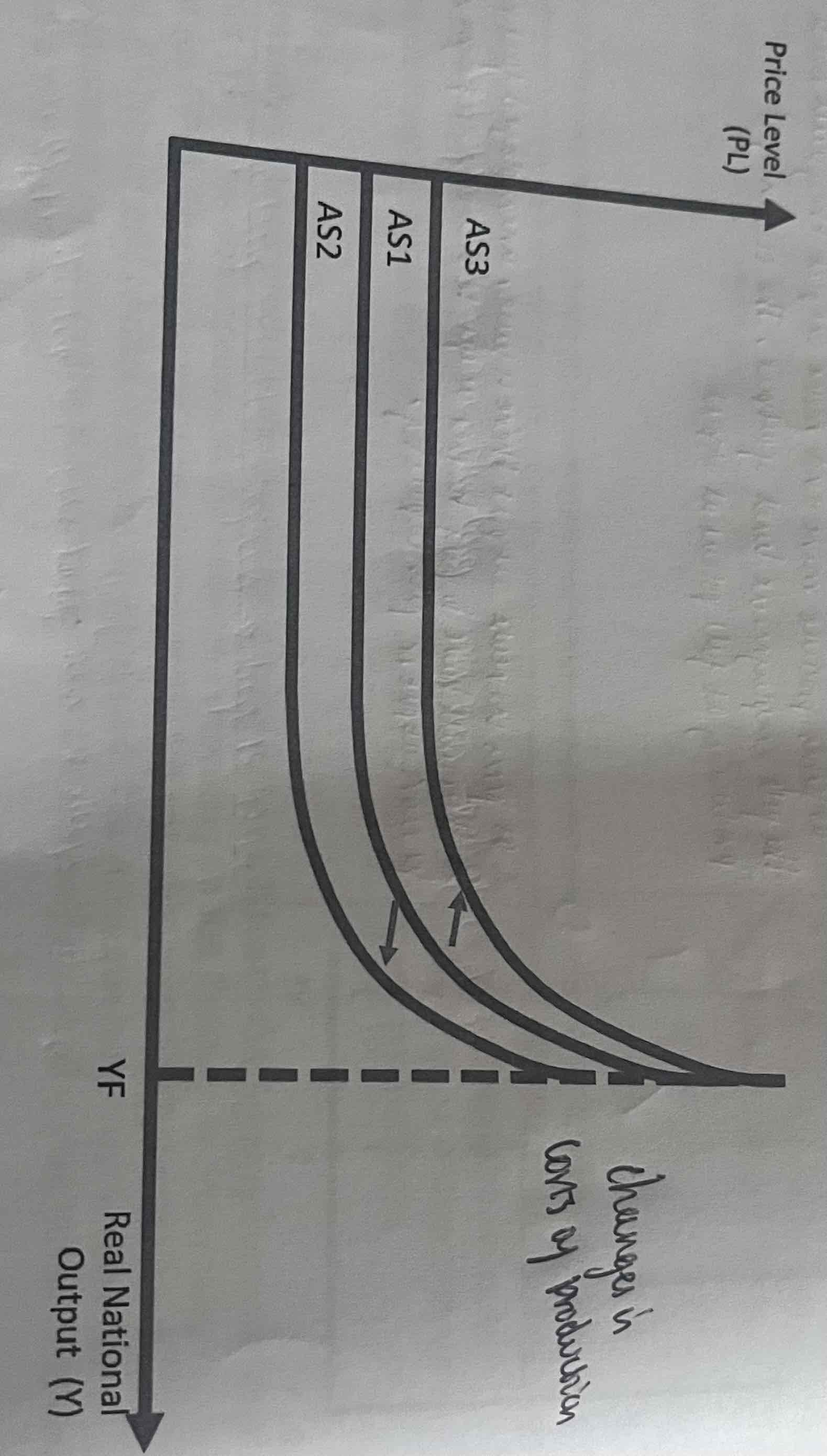
What will a fall in AS cause the curve to do?
Shift to the left as there is less output at any given price level. (AS3)
What is the short run about?
Changes in production
In the long run, what causes the AS curve to shift due to?
Changes in the potential output or productive capacity in an economy
What are the factors that cause an outward shift on the AS curve?
The same that causes an outward shift in the PPF: advancements in technology, increase size of work population (immigration), improving transportation infrastructure to widen pool of people to choice from.