psych 240 exam 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
raven’s progressive matrices, working memory
______ _________ ______: a type of test where you have to identify patterns and solve problems. temporarily places information in working memory to be used later.
performance on this task predicts performance on reading comprehension and logical reasoning.
consistent with the idea that ______ ______ is important for higher cognitive task performance
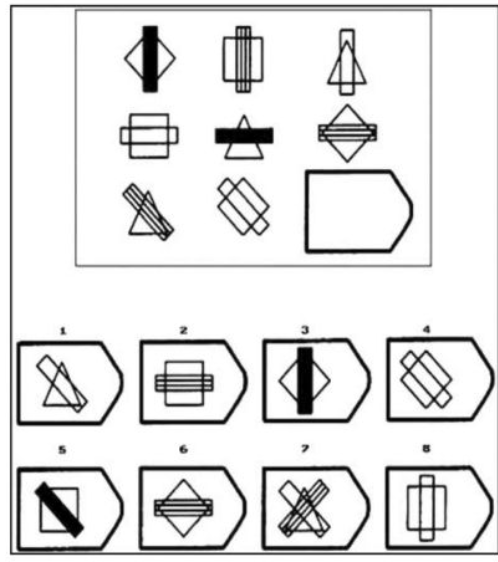
decreases, increases, decreases, similar
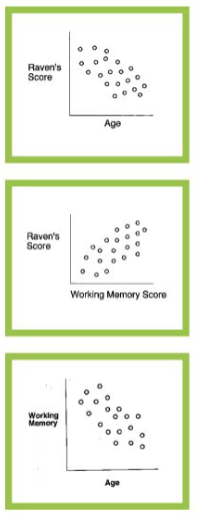
raven’s score, working memory, and age
raven’s score _____ with age
raven’s score _____ with working memory span
working memory span _____ with age
those with _____ working memory span have similar raven’s score regardless of age
mental arithmetic
solving addition problems with just your mind and working memory is called _____ ________
logical syllogisms
a _______ ________ is a form of deductive reasoning that consists of two premises and a conclusion.
the exam is either multiple-choice or short answer
the exam is not short answer
so exam is multiple choice
interference
__________ is when different cognitive tests interact with each other which can affect performance
random number generation
________ _______ _________: a task requiring you to generate a sequence of random numbers that requires cognitive effort
dissociation
working memory / long-term memory distinction
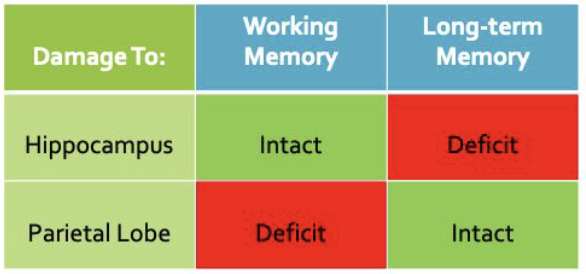
_______ shown in people with brain damage
anterograde and retrograde, hippocampus, impaired, intact
Patient H.M.
_______ and _______ amnesia
removed __________
_______ long term memory
_______ working memory
parietal, intact, impaired
Patient K.F.
______ lobe injury
______ long term memory
______ working memory
double dissociations
______ __________ are strong forms of evidence used to distinguish two systems in cognitive psychology/neuroscience
evidence from lesion studies
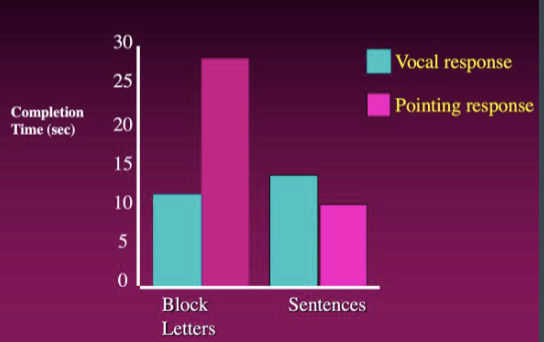
behavioral
________ double dissociation: when doing one task doesn’t affect another. they’re independent tasks and show how they’re handled by different parts of the brain.
ex) someone is good at cooking but not riding a bike (skills are separate in brain)
serial position curve, primacy, recency
______ _______ ______: the likelihood of remembering items in a list based on their position or order within that list
_______ effect: better recall of words at the beginning of the list (long-term memory)
_______ effect: better recall of words at the end of the list (working memory)
modal model (Baddeley article)
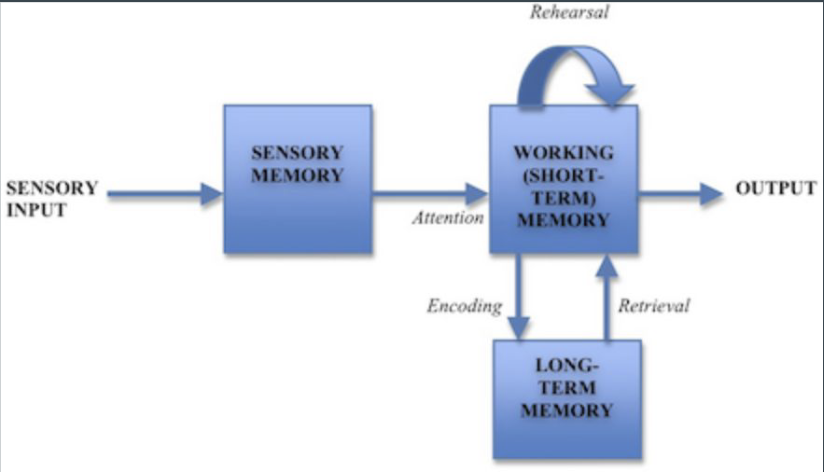
baddeley tripartite model working memory
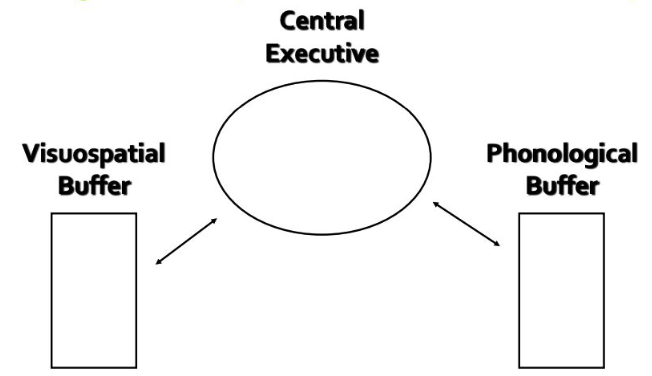
central executive
_____ ________ uses information stored in the buffers, supervising attention, planning, and monitoring.
frontal lobe syndrome
distractibility, difficulty concentration
problems with organizing/planning
perservation - failure to stop inappropriate behavior
phonological loop
__________ _____ holds and manipulates auditory information over short time intervals
only holds information for about two seconds
non-auditory inputs (like visually presented words) can be converted into phonological format and stored here
acoustic
evidence for phonological loop
________ similarity: confusion occurs for words that sound alike
not for meaning but for words that look similar (cough, through)
and for words that sound alike (cat, map, cap, mad)
suppression
evidence for phonological loop
articulatory ________: the method used to inhibit subvocal rehearsal (inner speech)
asking someone to count out loud impairs working memory
acoustic confusion goes away
irrelevant
evidence for phonological loop
_________ speech effort: working memory can be disrupted by simultaneously speaking irrelevant material
duration
evidence for phonological loop
articulatory ________ effect: memory span for short words is better than longer words
you will remember “sum, wit, hat” better than “individual, opportunity, university.”
effect disappears with articulatory suppressionchunk
visuospatial sketchpad
_________ ________: a part of the working memory that’s associated with temporarily storing and manipulating visual/spatial information
chunking
_________ refers to the process of organizing information into meaningful units to improve memory.
bad: FB ICI AFD RJF K
good: FDR CIA FBI JFK
word length
time effects
______ _____: subjects can generally remember about as many words as they can say in 2 seconds
longer words = longer to pronounce, occupies more of the limited capacity of phonological loop
coding
phonological ________ is how the phonological loop is responsible for processing/storying sounds and speech-based information
speed of speech
______ ___ _______: memory span is better for…
words that are pronounced quickly (bishop vs. harpoon)
for people who speak quickly
languages where words are pronounced quickly (Chinese better than English)
visuospatial buffer, visual, long-term
_________ _____ is the component of working memory devoted to visual imagery and spatial processing
information can enter either from _______ perception or ____-_____ memory
information can then be treated like a percept: scanned, rotated, enlarged, etc.
left, Broca’s
phonological loop neuroimaging evidence:
studies showed that the ____ hemisphere and _____ area involved in phonological loop
implicit
_______ memory is unconscious change including procedural knowledge (skills) and priming. ex) remembering how to ride a bike or how to read
explicit
_______ memory is conscious recollection and includes declarative knowledge. consciously trying to recall certain info
priming
previous exposure to stimuli facilitates processing upon (partial) exposure
amnesia
______ is the loss of previous memories or ability to form new memories
psychogenic
_______ amnesia: amnesia due to psychological trauma (not physical). very rare
organic
_______ amnesia: loss of memory due to physiological factors (brain trauma, disease, Korsakoff syndrome)
anterograde
________: inability to learn new explicit information
retrograde
______: inability to retrieve explicit information prior to trauma
temporally graded
_________ _______: memory for information worse closer to the time of injury
ex) getting a concussion and not remembering events leading up to concussion
hippocampus, anterograde
Patient H.M
surgically removed ________ to relieve seizures
led to severe ________ and temporally-graded retrograde amnesia
severely impaired explicit memory
preserved implicit memory
mirror reading
_______ ________ study: tasked with reading mirrored words, some repeated, some new.
non-repeated words: implicit
repeated words: implicit + explicit
amnesics worse for repeated words but same for new words
Tower of Hanoi, priming
other evidence for implicit vs. explicit
______ ___ _______: amnesics show similar improvement in learning “cognitive” implicit skills to controls
_______: amnesics show normal priming (implicit), but poor recognition (explicit)
semantic
__________ memory is stored general knowledge about the world.
ex) a close friend’s name
type of explicit memory
episodic
_________ memory is stored personally-experienced events or episodes.
ex) remembering meeting a friend for the first time
type of explicit memory
explicit
semantic and episodic memory are both types of ______ memory
hippocampal
explicit memory (semantic and episodic) is involved in the _______ region of the brain
striatum, cortex, amygdala and cerebellum
parts of the brain involved in implicit memory:
skills and habits = ______
priming = _____
classical conditioning = ________ and _________
categorization
___________ is the process by which objects, events, and people are grouped based on shared characteristics and features that distinguish them from other groups
categorization by pigeons (wasserman, 1987)
pigeons put on tables with four food wells, each one associated with a category (cat, flower, car, chair)
let pigeons peck category depending on the stimulus. ex) shown photo of specific flower and had to peck that flower to give food
after 30 days, pigeons ended up being 80% accurate BUT could’ve been due to classical conditioning or associations
classical
__________ view: when items within a category must have defining properties of that category. it is clearly defined and mutually exclusive
hard boundaries
classical view
_____ __________ is when either an item is contained in a category or isn’t
necessary, sufficient
problems with classical view
_______: features an item must have to be in that category
______: features that make an item belong to a certain category if they have them
ex) bachelor: unmarried, adult male. but is a monk a bachelor? no
modern
_______ view: properties/features are characteristic, not definite or defining. something belongs to a category if it is similar to members of that category. boundaries are fuzzy.
rating, sentence verification, hedges
evidence for fuzzy categories (typicality)
______: exemplars with more characteristic properties are rated as being more typical of a category
order from most → least typical: apple > banana > pineapple > fig > olive
________ ___________: people are more faster to verify more typical exemplars than less typical exemplars
“a robin is a bird” (faster) vs. “a chicken is a bird” (slower)
_______: linguistic expressions that can indicate uncertainty or imprecision: “kind of” and “sort of”
a whale is a mammal vs. a cow is a mammal
exemplar
________ theory: example of a category. multiple exemplars are stored in memory. categorize new things based on similarity to stored exemplars.
prototype
_________ theory: a best, ideal, or average example is stored in memory
geometric
_________ approach: concepts may lie in geometric space
similarity is then measured by how close in a space a concept or item is to the category (or another item) in this space
inconsistent
minimality
metric axioms
_________: dissimilarity of an item/concept with itself must be the smallest possible
violation: a highly familiar concept is rated more similar to itself than a less familiar one
apple - apple is more similar than pomegranate - pomegranate
symmetry
metric axioms
_______: similarity between two items/concepts should be the same regardless of order
violation: an unfamiliar category is judged more similar to a familiar category and vice versa
pomegranate → apple (d4) vs. apple → pomegranate (d8)
triangle inequality
metric axioms
_______ ________: if A is similar to B and B is similar to C, then A and C should be similar.
similarity judgments do not always follow this. (A and C are not similar)
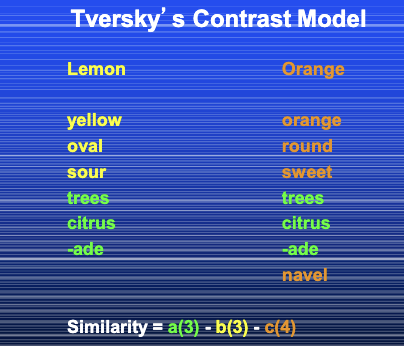
Tversky’s Featural
________ _______ Approach: feature-based similarity approaches do not require these metric axioms.
Similarity (A,B) = a*f(A and B) - b*f(A but not B) - c*f(B but not A)
hierarchical
TLC MODEL (Collins and Quillian)
_________ structure: more general categories are higher and specific ones are lower. features of a category are stored at each node.
mcclelland: semantic demetia: general info is kept but specific knowledge is lost as disease progresses
in language, kids learn more general levels before specific
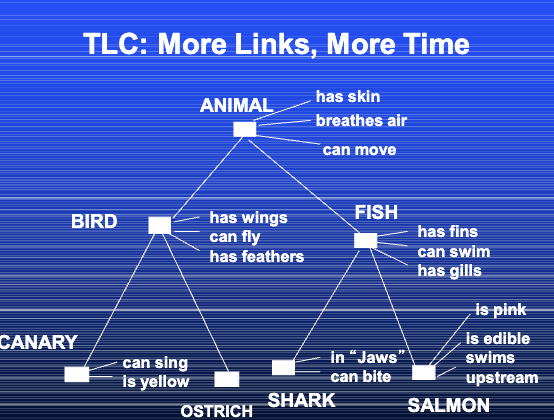
TLC Model
distance
_______ effects: longer reaction times for statements that involve information that is further apart in the model
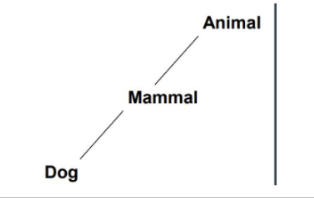
reverse distance
______ ______ effects: faster at responding to “a dog is an animal” than “a dog is a mammal.” TLC predicts the opposite should be true
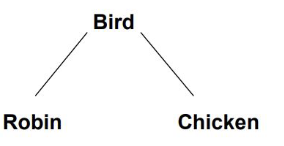
typicality
_______ effects: faster at responding to items that are more representative of a category
ex) “a robin is a bird” is responded to faster than “a chicken is a bird”
TLC can’t explain this if items are at the same level of hierarchy
cognitive economy
TLC MODEL
______ _______: only store the features at the highest level so it takes up less space in your mind
feature inheritance
TLC MODEL
_______ _________: lower category nodes inherit the features of nodes above them
basic-level
_____-_____ effects: tend to be basic descriptions rather than more specific or general categories
ex) “a dog was chasing me” vs. “an animal was chasing me”
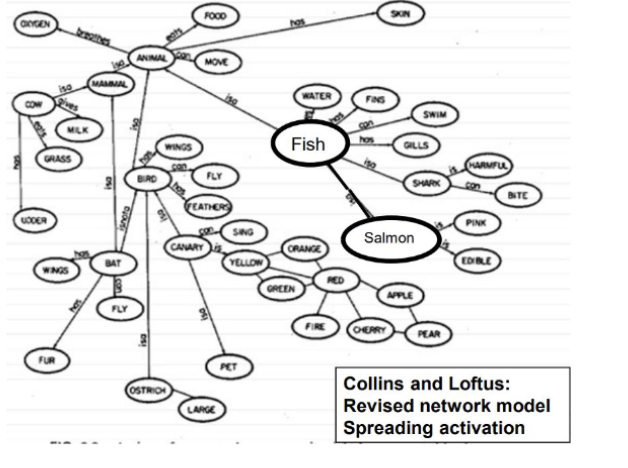
revised
_______ TLC: non-hierarchial, connectionist model
a node is activated when a person reads, hears, sees, or thinks about a concept
activation spreads to adjacent nodes
links between nodes vary in strength
can explain reverse distance and typicality effects, unlike original TLC

lexical decision task
________ _______ ______: given two words, respond yes if both are words, no if one is not a word
semantic priming
________ _______: faster when the second word is semantically related to the first
Revised TLC explains this → second-word benefits from spreading activation due to the first word
verbatim
_________ information: remembering something as it was (word for word). we do not remember everything we hear.
gist
____ information: remembering the main or general idea of something. we remember this better than verbatim information
recall
galileo experiment (gist vs. verbatim memory)
read the long story and then participants are tested on _____ for various sentences.
syntactic
___________ information: same idea but different grammatical structure. syntax information doesn’t matter because it means the same thing
“Prof. Lee thanked the mole”
“The mole thanked Prof. Lee”
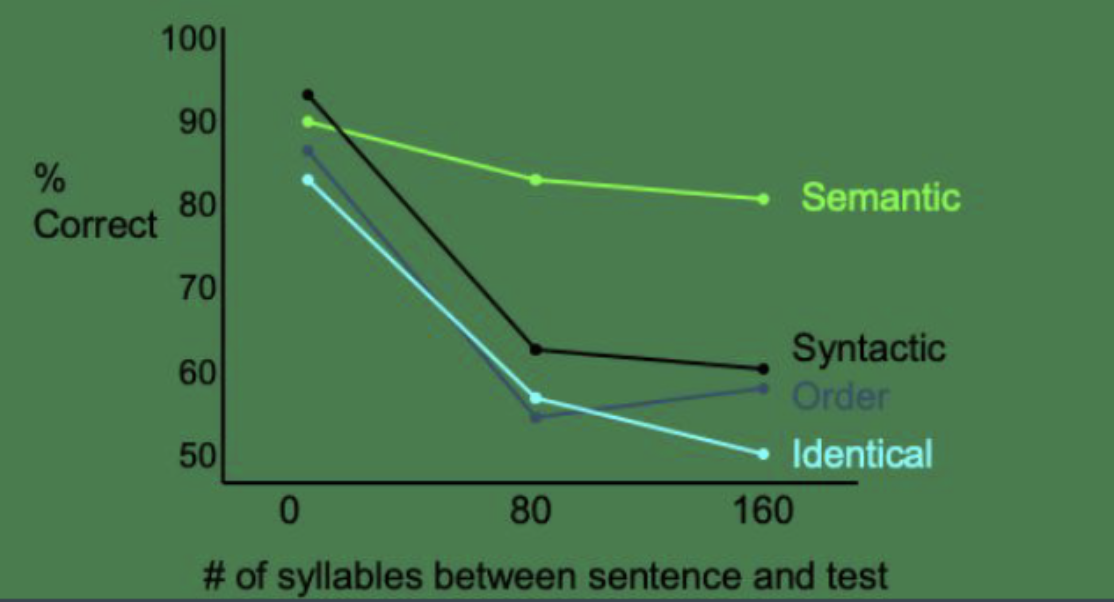
semantic, syntactic
galileo experiment
identical: he sent a letter to Galileo, the great Italian scientists
________ difference: Galileo, the great Italian scientist, sent him a letter
same words, different meaning
________ difference: a letter was sent to Galileo, the great Italian scientist (passive voice)
same meaning, different sentence structure
word order difference: he sent Galileo, the great Italian scientist, a letter
titles
laundry example
______ help with recall if they are given prior to ambiguous story
illustrations
balloon story
__________ help with recall as long as they are appropriate with the story

distorted
war of ghosts
tested on recall after reading the story
found that memory tended to be ________ to fit own knowledge
schema
_______: collection of basic knowledge that serves as a guide
helps us know what to expect
meaningfully organizes information
enables inference
sometimes disruptive: previous knowledge/experience can lead to systematic distortions of new memory
scene schema
_______ _______: tend to remember things consistent with the scene (desk, chair)
memory is not as good if there are no expectations (bulletin board)
false memories for things not present in the scene but typically in the schema (books)
event schema
_______ ______: people tend to agree on what is in the script
recall things that are in a script in order
faster reading
false recall for script items not in a story
transience
_________: decreasing accessibility of information over time
long term: could be problem with storage or retrieval
can also be observed in working memory
absent mindedness
_______ __________: shallow processing and insufficient attention to events or items weakens memory formation
change blindness, depth of processing effect
blocking
_________: temporary inaccessibility of episodic and/or semantic memory
“tip of the tongue” state
increase with age but unclear if TOT due to interference
misattribution
_________: attributing memories or ideas to the wrong source
suggestibility
_________: the effects of misinformation from external sources that leads to the creation of false memories (Loftus)
bias
_____: distortions of past events by current beliefs, feelings, and knowledge
consistency: have a bias to think our beliefs are more consistent than they are
source confusion
_______ ________: correctly remembering item or fact from past experience, but misattributing the source
cryptomnesia
____________: misattributing a thought or idea to own imagination
ex) a musician unintentionally copies a melody from another song without realizing it
increased
Roediger and McDerott Experiments
showed false alarms greatly _________ for test words that were thematically related to a list of studied words
frontal lobe
______ ______ is important for monitoring and damage to this leads to errors and false recognition
persistence
_________: memories we cannot forget even if we prefer to
directed forgetting and PTSD

logical inferences
________ __________: when we hear new information, we often make additional inferences, and we remember them as if they are a part of what we experience
spatial relations
tend to make inferences consistent with spatial organization
do not tend to make inconsistent inferences
pragmatic inferences
________ __________: inferences that are not guaranteed to be true but are plausible
hammer experiment, assertions in advertisements

hammer
_________ experiment
misinformation (or new information) doesn’t overwrite hammer (original memory). instead, the new and original information are competing during recall
assertion, implication
advertising experiment, Harris (1977)
________: type of advertisement
“taking tabcin pills as direction will get you through a whole winter w/o colds”
________: another type of advertisement
“aren’t you tired of sniffles all winter? get through a whole winter w/o colds. take tabcin”
hedges, comparisons
advertising experiment, Harris (1977)
_____: people ignore these
“taking tabcin pills may help relieve colds”
__________: unclear
“tabcin makes you healthier” (healthier than what?”)
inferences at all memory processing stages
encoding
context affects what is encoded and later recalled
washing clothes and story example
storage
war of ghosts example
extend the delay period between testing
more distorted memory with more delay
memory tends to fit schema better and forgetting happens
retrieval
helen keller
eyewitness testimony can be distorted due to interim misinformation and questioning techniques

misinformation
see event → _________ → memory test
“hit” vs. “smashed” → very different answer based on what word was used
proactive
______ interference: old information interferes with the learning of new information
ex) remember a friend’s new phone number after previously learned the old number
retroactive
__________ interference: new information interferes with the retrieval of old information
ex) having trouble recalling how to play guitar after learning how to play the piano