Placentation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
monotremes
egg laying mammals
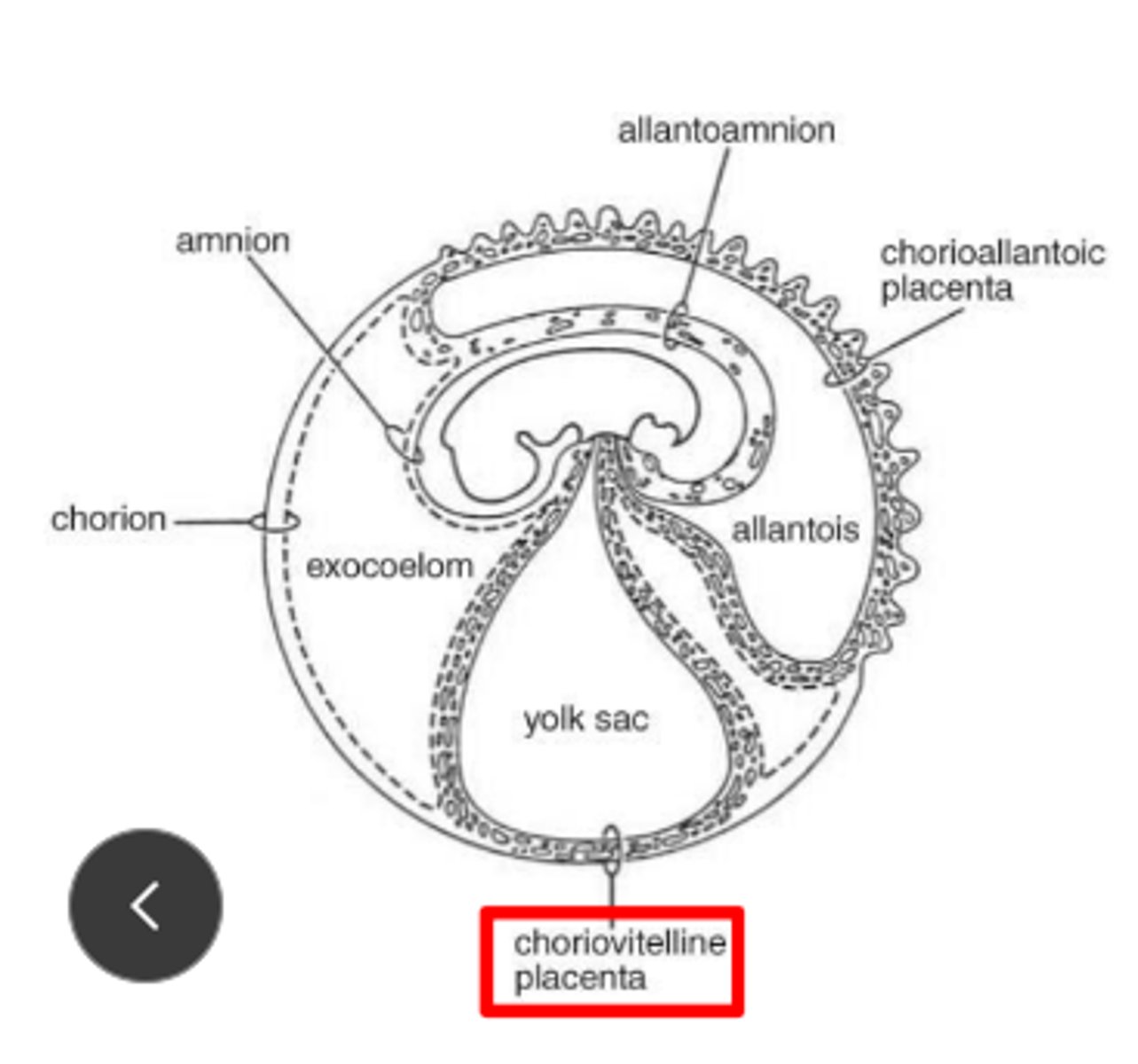
marsupial placenta
Choriovitelline
Simple contact with maternal cells
Most nourishment from yolk
eutherian mammals
mammals with placenta
why is the placenta considered a transient organ?
has both metabolic and endocrine functions
T/F: There are two parts of the placenta: fetal and maternal.
true
what extra-embryonic structures create the umbilicus?
yolk sac and allantois
which extra-embryonic structure eventually becomes the mature placenta?
allatnochorion
maternal fetal interface
Region where maternal and fetal tissues interact via interdigitating microvilli
what is the functional unit of the placents?
chorionic villus to maximize exchange between conceptus and dam
How are placentas classified?
based on distribution of chorionic villi
which placenta is characteristics of all carnivores?
zonary
what animals have a diffuse placenta?
horse, pig
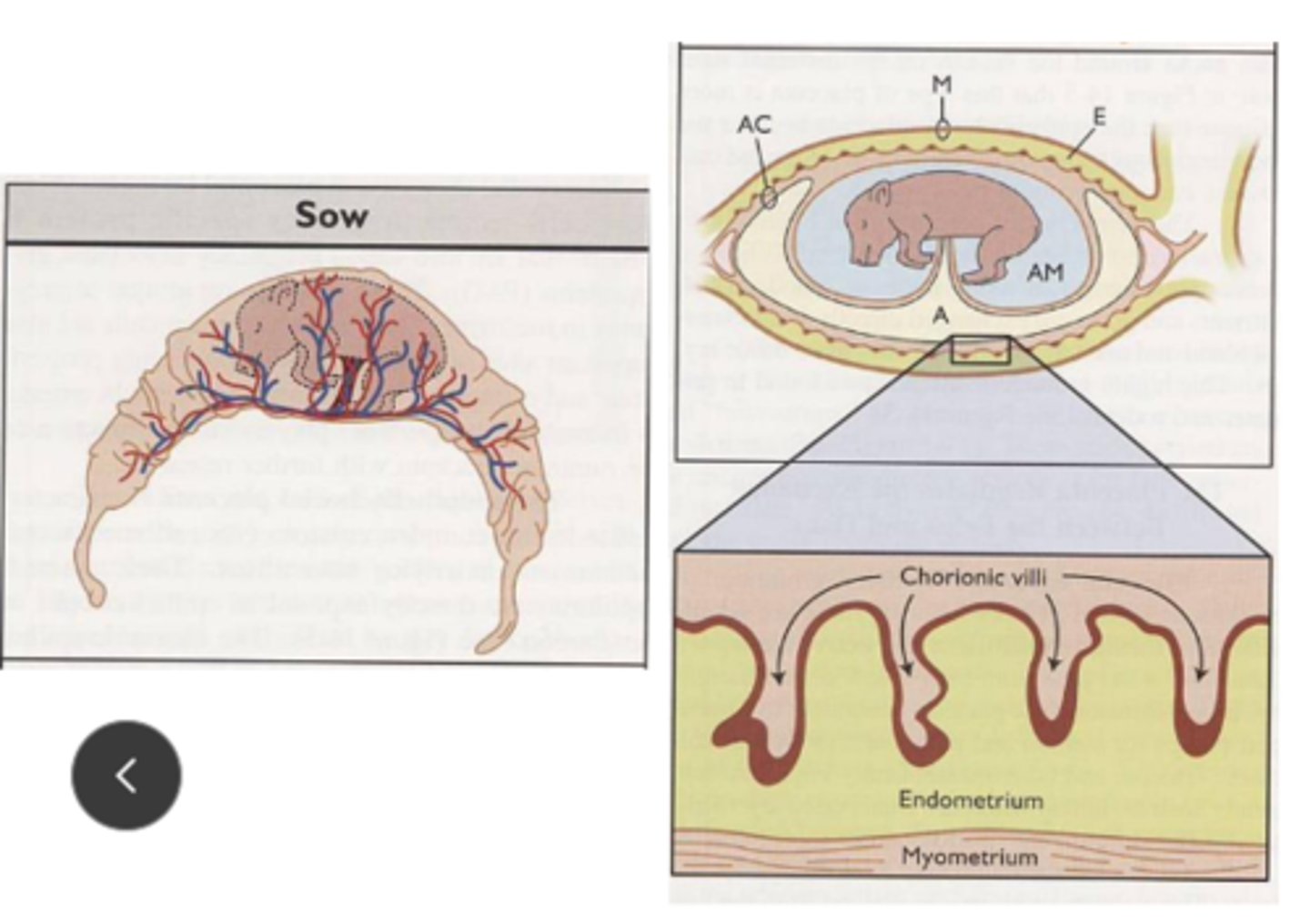
Explain diffuse placenta in sows
chorionic villi are closely spaced and uniformly distributed
penetrate into endometrium to form maternal-fetal interface
Explain diffuse placenta in mares
made up of microzones called microcotyledons
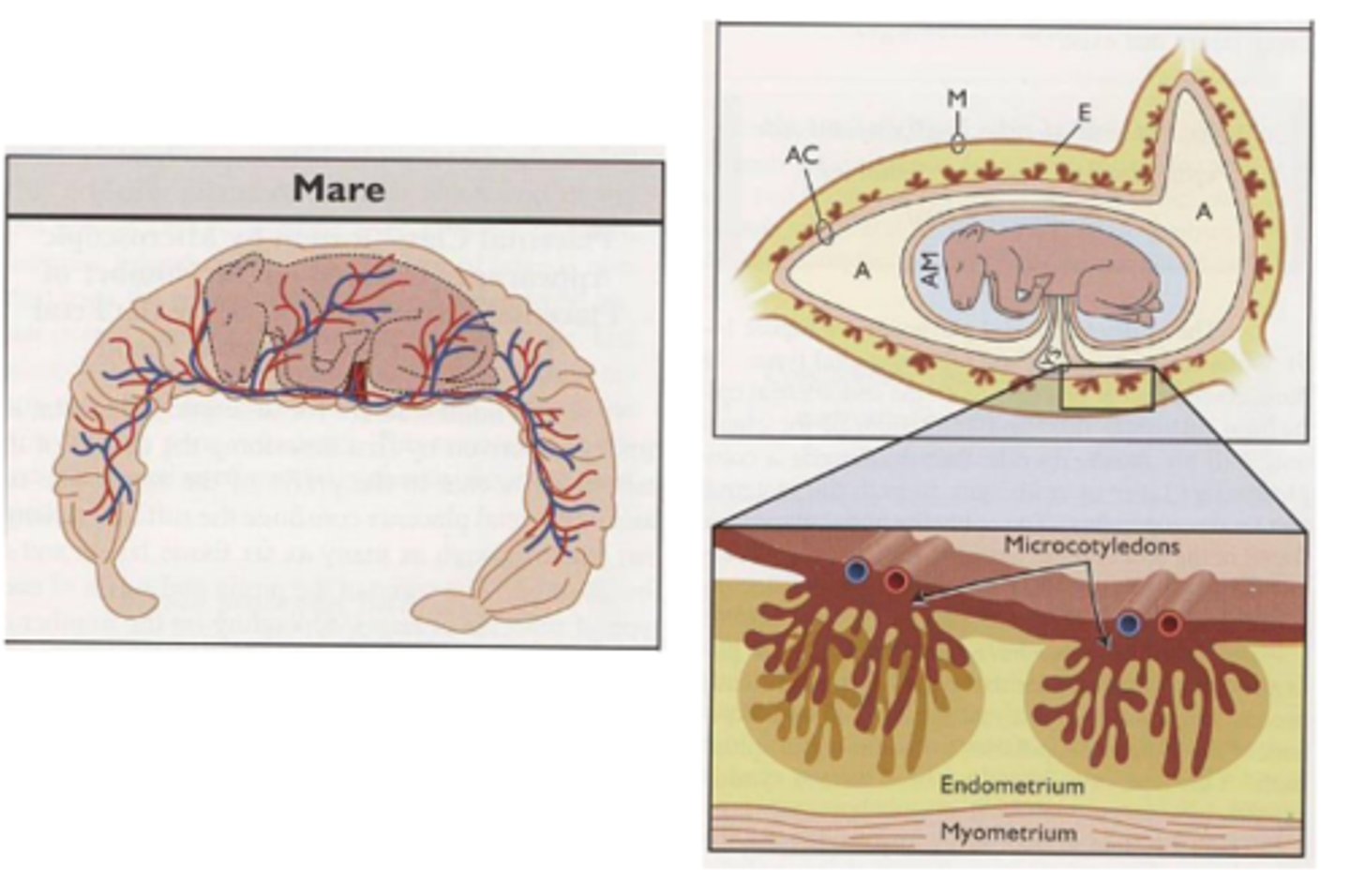
what is a unique structure of the mare placenta that helps maintain pregnancy?
endometrial cups via chorionic girdle
what is the purpose of endometrial cups?
To produce ECG/PMSG, which stimulates ovulation and thus forms a secondary CL in the ovary, which maintain the pregnancy by continuing to produce progesterone until about D100 when the placenta takes over as the main P4 producer
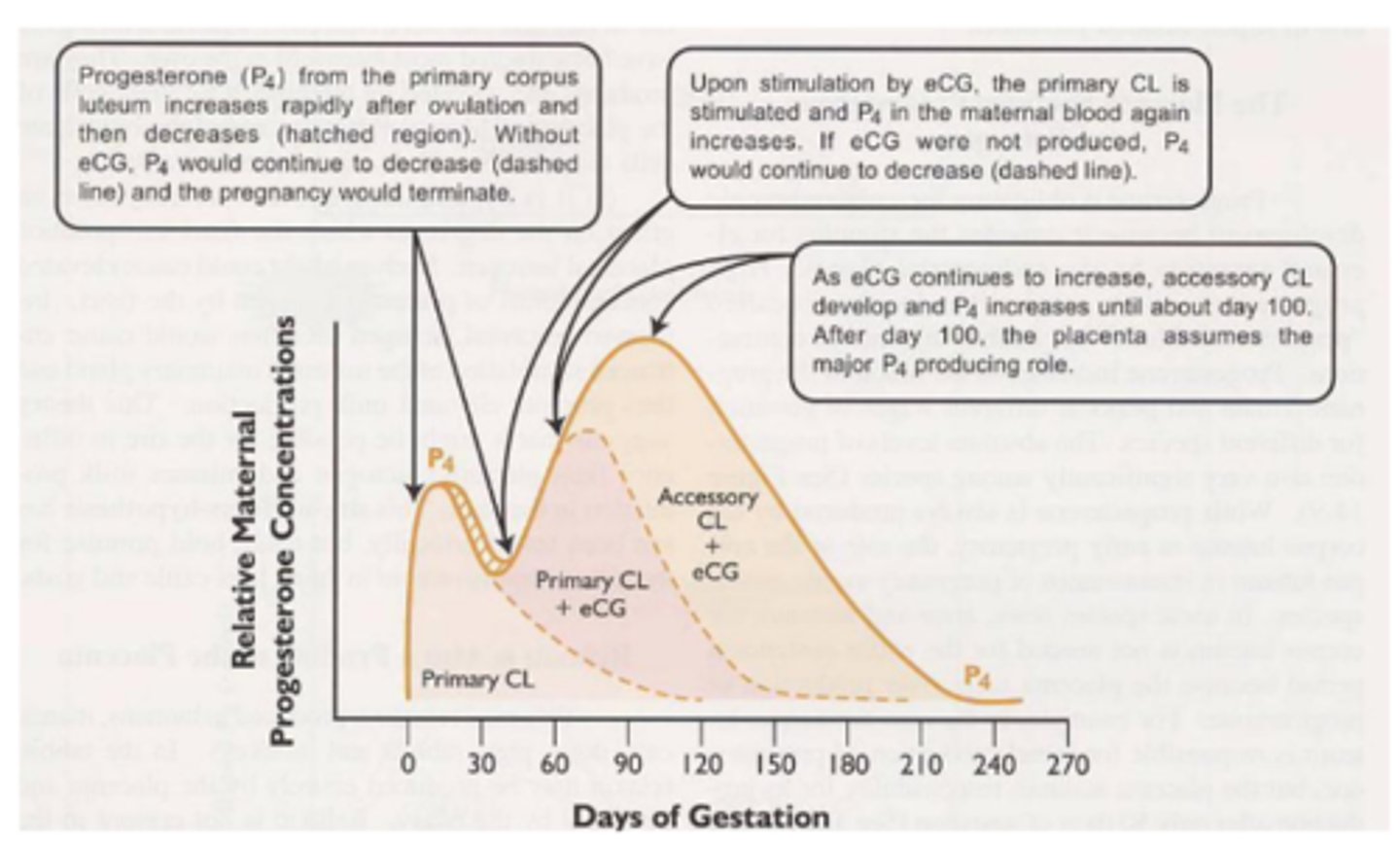
T/F: eCG in mares can be tracked to determine progression of pregnancy
FALSE, endometrial cups continue to produce eCG for entire life span of cup - regardless of pregnant or non-pregnant
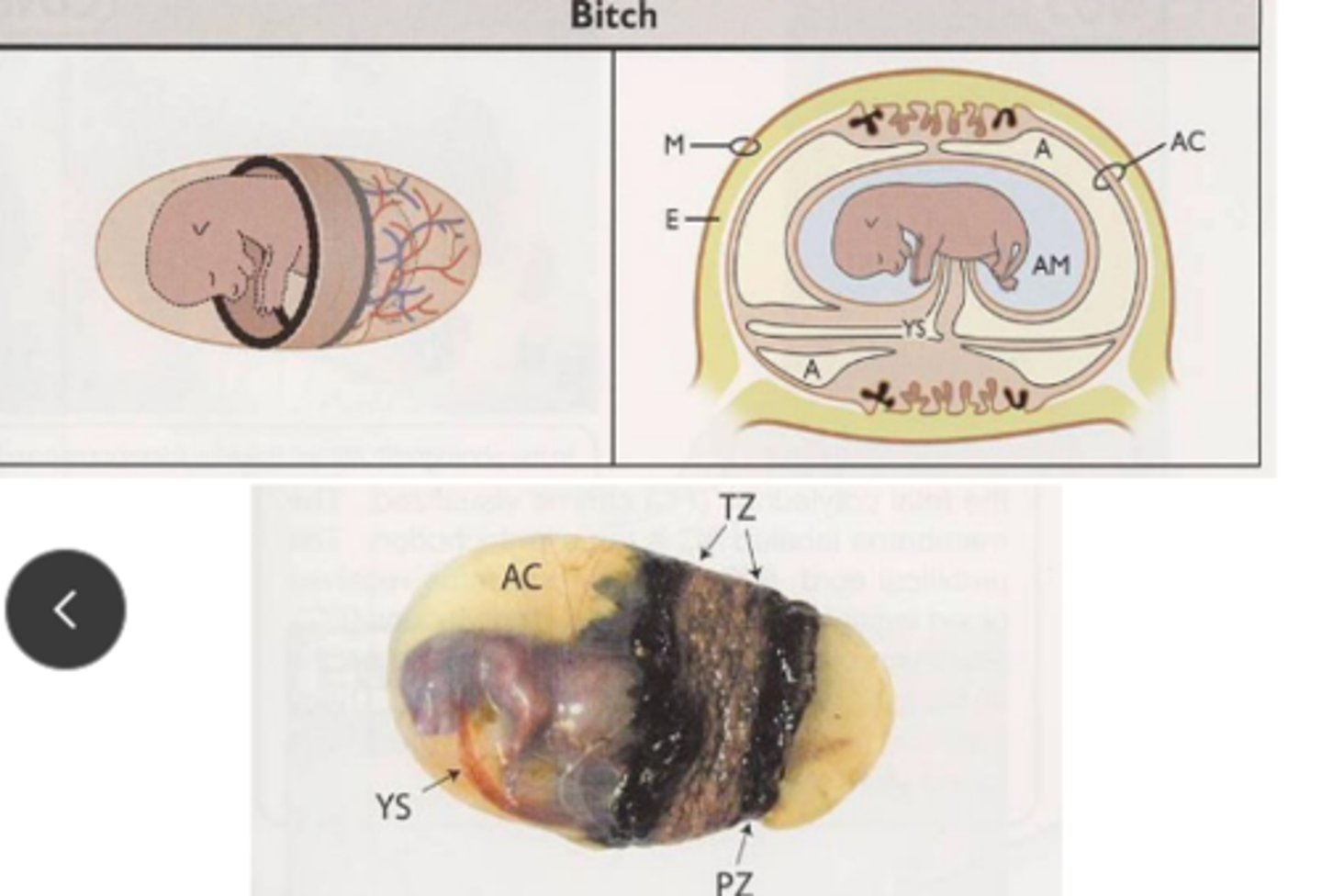
Which animals have a zonary placenta?
dogs and cats
explain zonary placenta (HINT describe regions)
1. bandlike zone of chorionic villi aka transfer zone
2. second region on either end on original band called paraplacenta (iron transport)
3. clear regions for direct absorption of materials from uterus
what animals have a discoid placenta?
humans, rodents, primates
explain discoid placenta
round disc containing all chorionic villi in one place forming maternal fetla interface
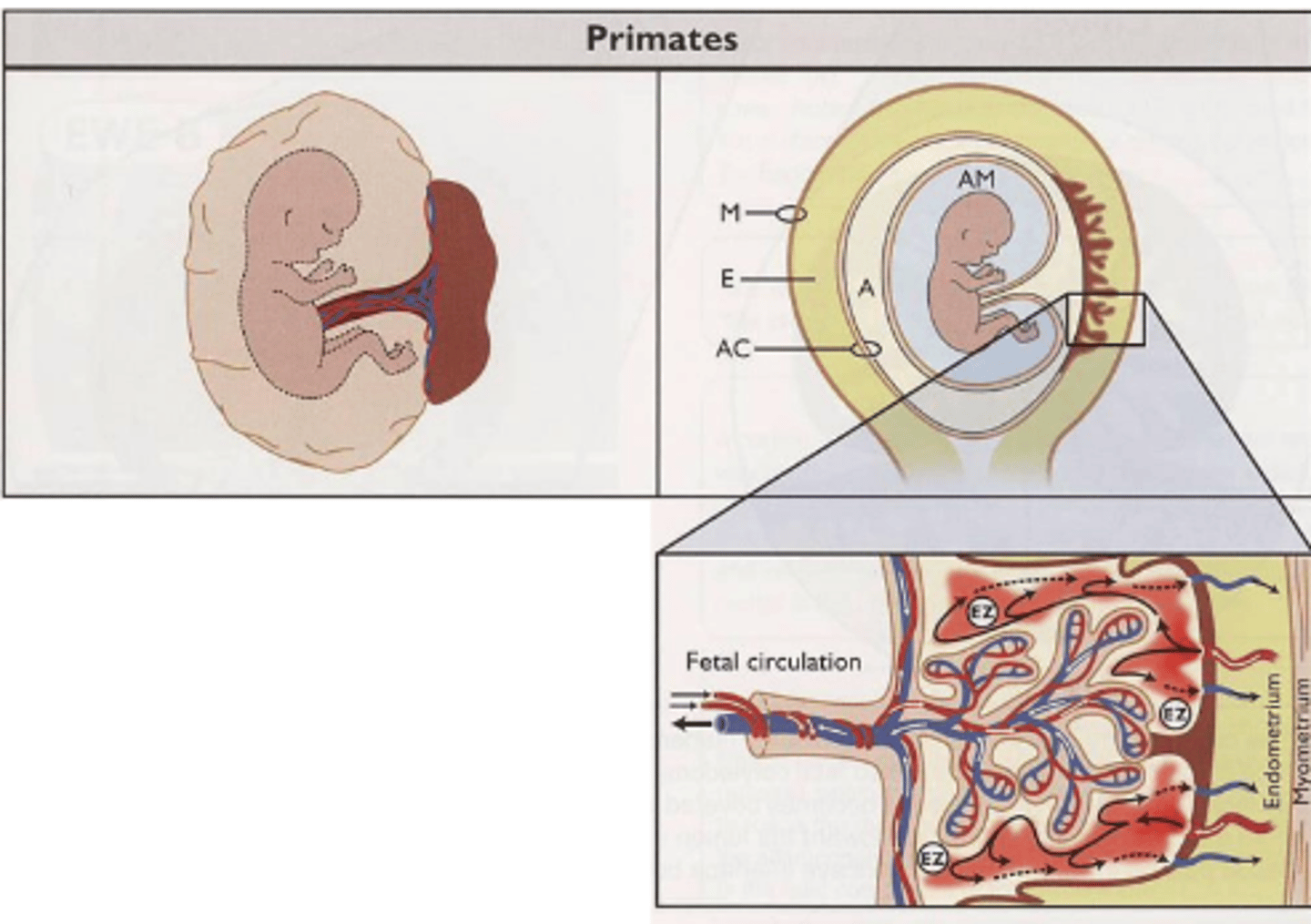
which placenta type interacts directly with maternal blood?
discoid
what animals have a cotyledonary placenta?
ruminants
A cotyledonary placenta has different parts:
a. _______________ = fetal portion
b. _____________ = maternal contact site
cotyledon
caruncle
_________ is the cotyledon-caruncle complex
placentome
Explain how the cotyledons of cows and ewes are different.
cows are convex and sheep are concave
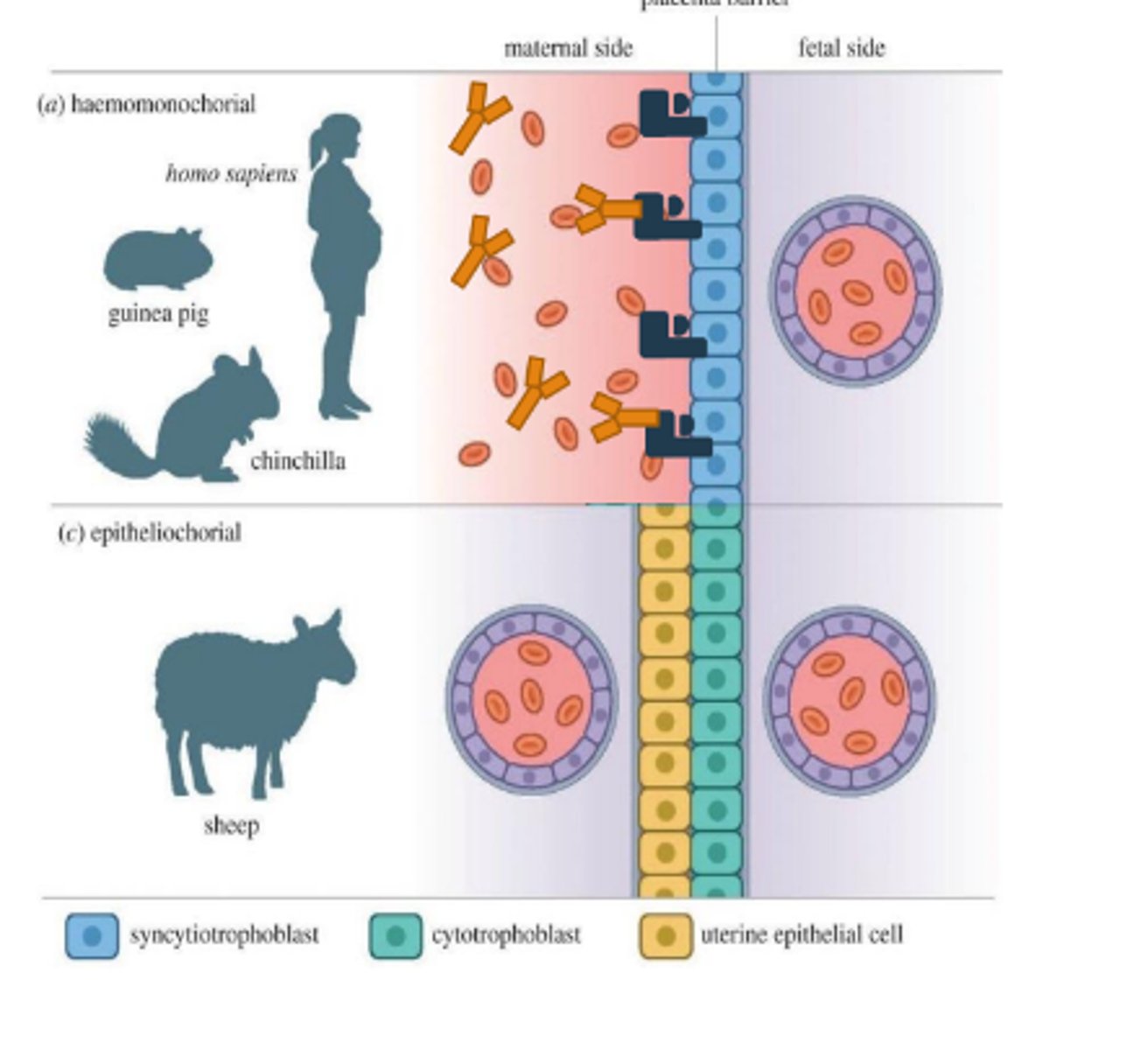
Placentas can also be classified based on the type of intimacy between maternal and fetus. explain
number of placental layers that separate fetal blood from maternal blood
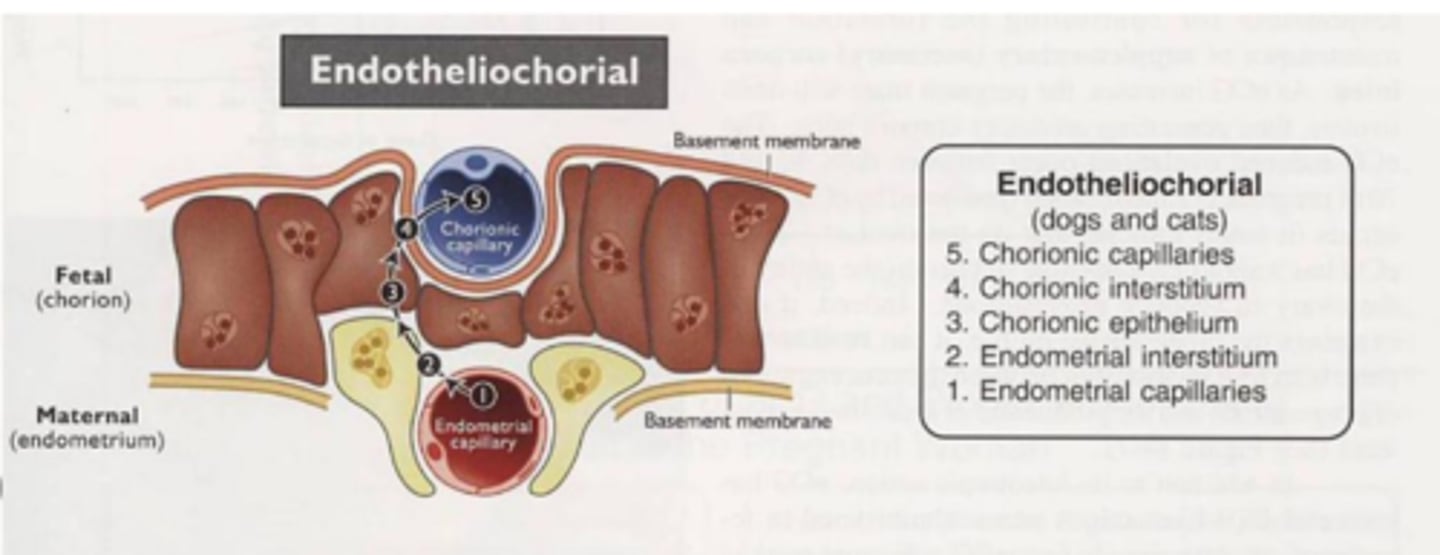
epitheliochorial is found in what animals?
cow, pig, horse
epitheliochorial placenta
6 layers
intact layer of fetal and maternal epithelium
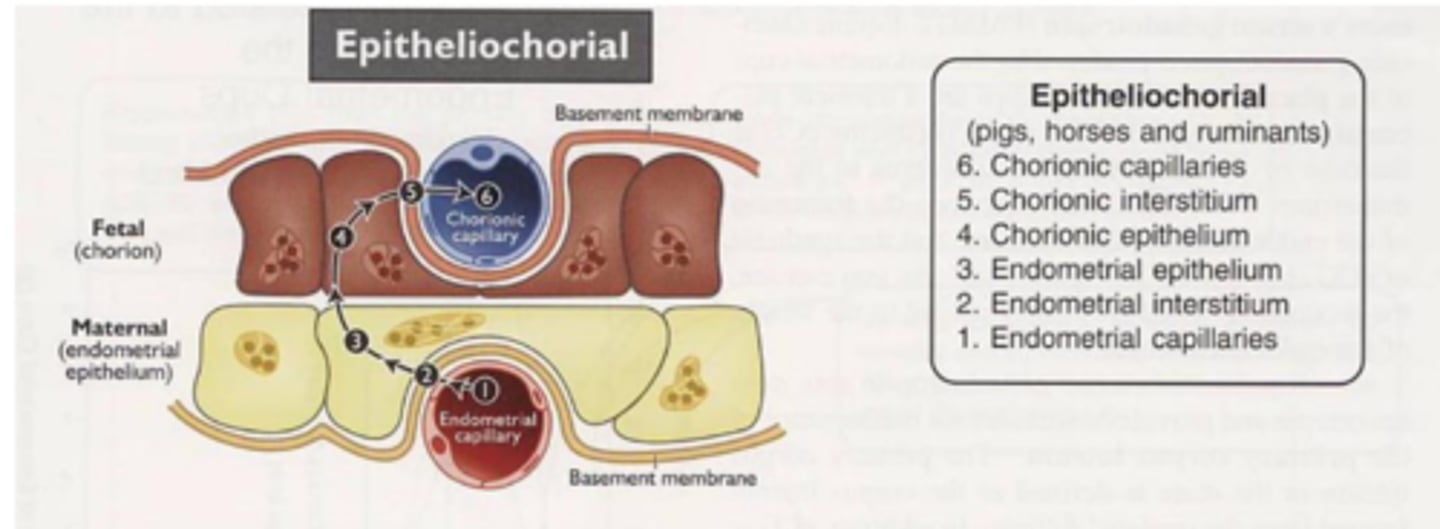
endotheliochorial placenta is found in what animals?
dogs and cats
endotheliochorial placenta
5 layers
semi-invasive
complete erosion of endometrial epithelium and underlying interstitium - maternal capillaries are directly exposed
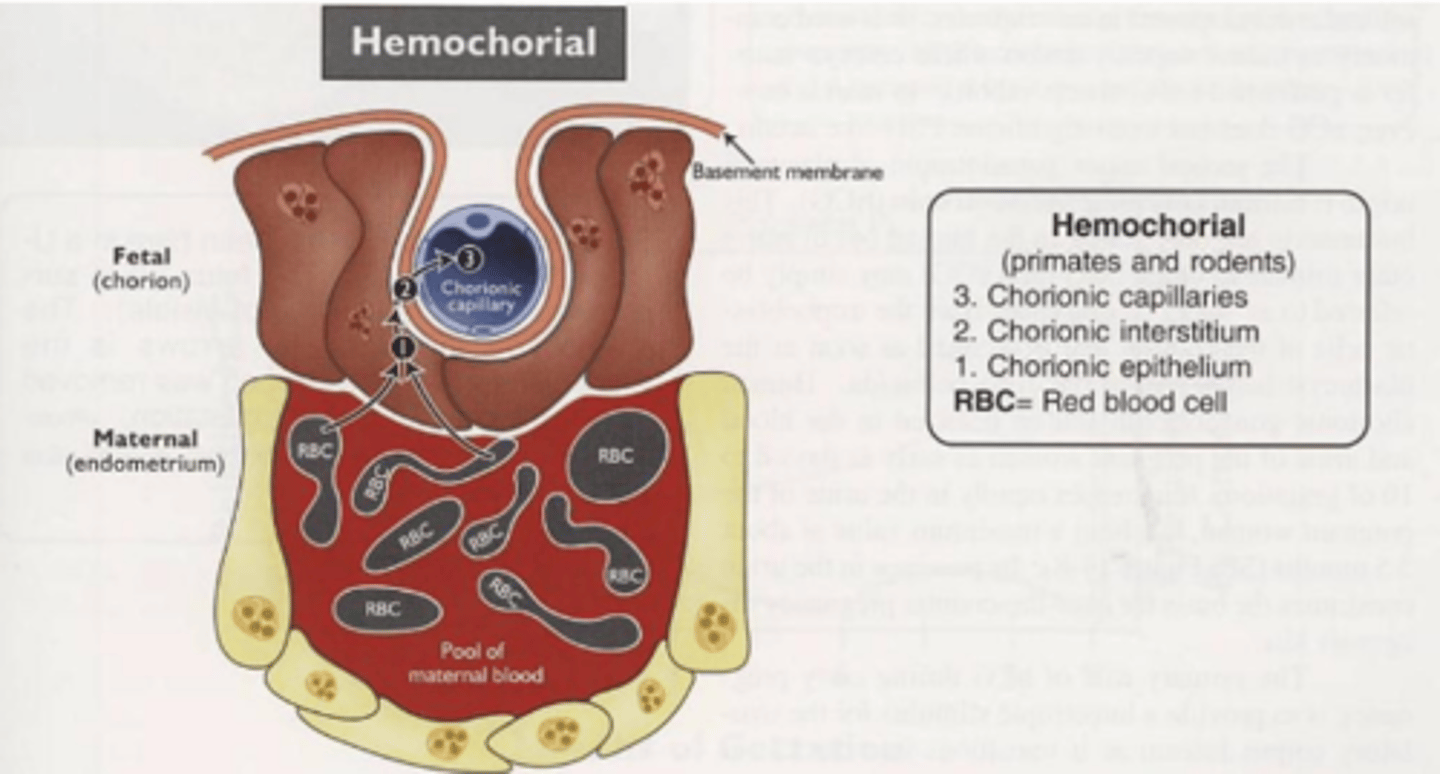
what animals have a hemochorial placenta?
primates and rodents
hemochorial placneta
3 layers
most invasive
chorionic epithelium in direct apposition to maternal pools of blood
Pig
a. chorionic villus patterning
b. maternal fetal barrier
c. loss of maternal tissue at birth
diffuse
epitheliochorial
none
Mare
a. chorionic villus patterning
b. maternal fetal barrier
c. loss of maternal tissue at birth
diffuse
epitheliochorial
none
Sheep, goat, cow
a. chorionic villus patterning
b. maternal fetal barrier
c. loss of maternal tissue at birth
cotyledonary
epitheliochorial
none
dog, cat
a. chorionic villus patterning
b. maternal fetal barrier
c. loss of maternal tissue at birth
zonary
endotheliochorial
moderate
primate, rodent
a. chorionic villus patterning
b. maternal fetal barrier
c. loss of maternal tissue at birth
discoid
hemochorial
extensive
Method of transfer in the placenta for:
a. gases and water
b. sodium and potassium
c. glucose and amino acids
simple diffusion
active transport
facilitated diffusion
Antibody transfer only occurs in which type of placenta?
hemochorial placenta because antibodies can cross placenta border and enter fetal circulation
T/F: The placenta serves as an endocrine organ. in most species the placenta takes over P4 production
true, however bitch, sow, and queen gestation is so short the CL maintains P4 entire pregnancy
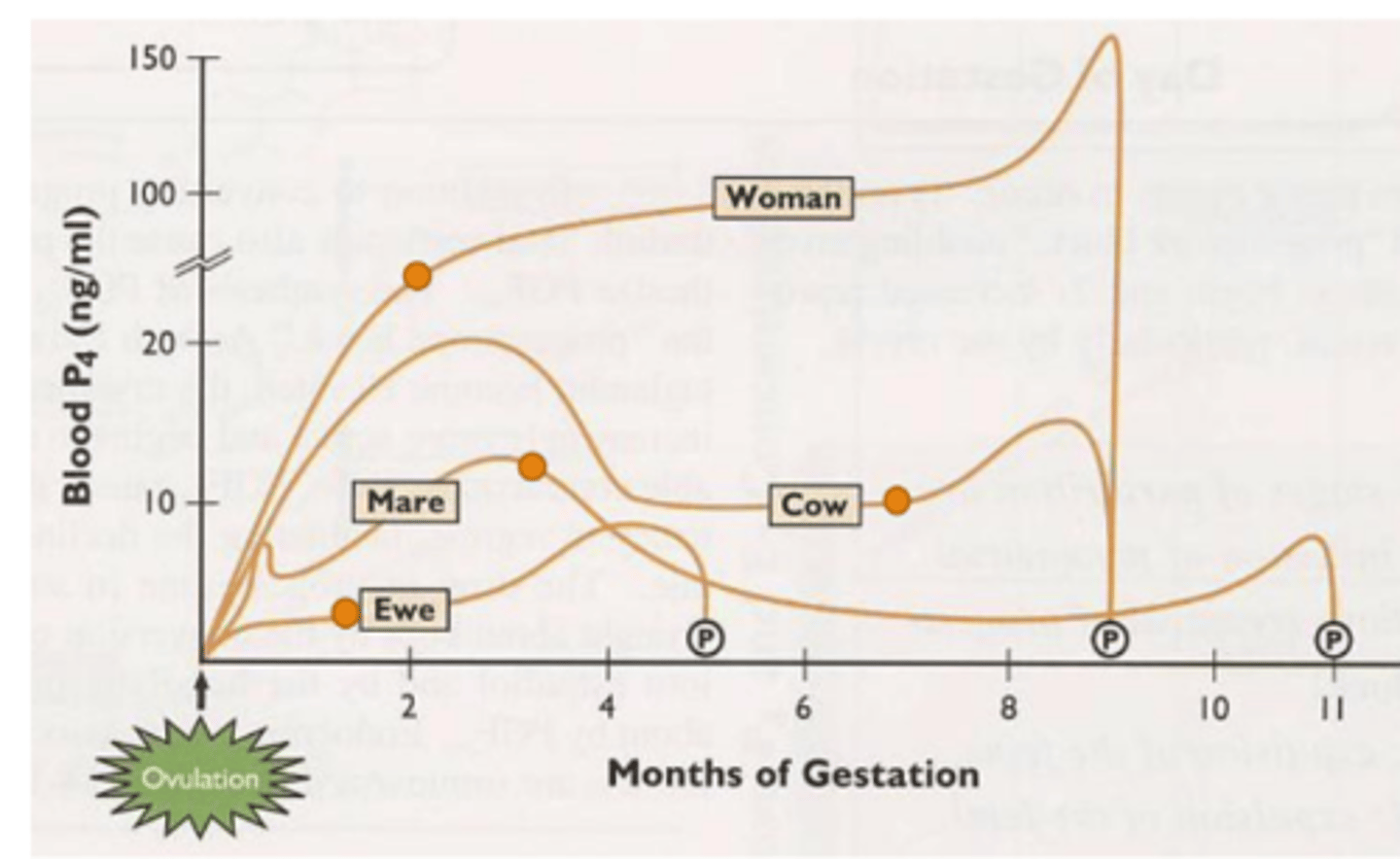
What hormone rises at the beginning of the parturition period?
estradiol