Ambulatory Exam 1
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
Ambulatory Care
Healthcare outside of the acute care setting (outpatient care)
Broader term for healthcare, encompassing unique communities and populations and the public health sector
Differences between pop health and ambulatory care
Pop health focuses on:
health promotion and disease prevention, not treating the ill
the aggregate, not the individual
tracking epidemiological data
policy development
Population in Population Health
a group of individuals within a defined geographic area or a group by other shared characteristics (like ethnicity, age, employment status, etc.)
Community in Community Health
refers to a group of people with shared geography and/or other characteristics, but tends to be more local, whereas population health has a broader scope
Screening
testing a group at a specific point in time
Surveillance
broader analysis, continuous data collection
Upstream prevention
Interventions that aim to treat the cause of a health problem
Primary and specialty services
care outside of the hospital, like PCP, outpatient surgery, specialist medical treatment, etc
Health disparities
differences in health outcomes among groups
Social determinants of health
The conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, shaped by the distribution of money, power, and resources at global, national, and local levels
What does an ambulatory care nurse focus on?
- Upstream Prevention
- Primary and specialty services
- Health disparities
- Social determinants of health
- Patient education
- Patient engagement & activation
- Effective provider-patient communications
- Transitions of care
- Long-term care planning
- Attention to nurse-sensitive indicators
Main goal of ambulatory care
Individual controls treatment plan, client self-determination
Difference in treatment plan for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Individual controls treatment plan
Acute: Healthcare team controls treatment plan
Difference in timing of care for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Time of care varies: singular, episodic or may be seen intermittently over a period of years
Acute: Individual seen in a specified time period – admission to discharge
Difference in focus of care for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Focus is on total healthcare picture
Acute: Focus is on a specific issue – cause for hospitalization
Difference in individual control for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Care is initiated by the individual
Acute: Care may be out of the individual’s control
Difference in nursing observation for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Nurse must rely on intermittent observations and the willingness and/or ability of the individual or caregivers to provide information
Acute: Nurse has direct and continuous observation of the individual
Difference in nursing skills for ambulatory vs acute care
Ambulatory: Broad range of nursing responsibilities
Acute: Specific responsibilities
Assessment-Based Approach for Ambulatory Care
•Identify client strengths and assets rather than just deficits
•Assess readiness to learn and motivation for change
•Evaluate current support systems and resources
•Determine barriers to independence (physical, financial, social, cultural)
Education and Skill Building for Ambulatory Care
•Health literacy development - teach clients to understand their conditions, medications, and treatment plans
•Self-care skills training - medication management, wound care, blood glucose monitoring, etc.
•Problem-solving skills - help clients learn to identify problems and generate solutions
•Decision-making support - guide clients through weighing options rather than making decisions for them
Resource Connection and Advocacy for Ambulatory Care
•Link clients to community resources - food banks, transportation services, support groups, financial assistance
•Navigate healthcare systems - teach clients how to schedule appointments, communicate with providers, understand insurance
•Advocate for accessible services - work to remove barriers in the healthcare system
•Connect with peer support - facilitate relationships with others who have similar experiences
Empowerment Strategies for Ambulatory Care
•Use collaborative goal-setting - involve clients in identifying their own priorities
•Encourage self-advocacy - teach clients to speak up for their needs
•Build on cultural strengths - incorporate traditional healing practices and family structures
•Promote gradual responsibility transfer - slowly shift tasks from nurse to client as competence grows
Environmental Modifications for Ambulatory Care
•Home safety assessments - identify and address fall risks, medication storage issues
•Assistive technology - help clients access and learn to use devices that promote independence
•Community accessibility - advocate for ramps, public transportation, accessible facilities
Home safety check can include...
- Assess need for client home modifications
- Apply knowledge of client pathophysiology to home safety interventions
- Educate client on safety issues
- Encourage client to use protective equipment when using devices that can cause injury
- Evaluate client environment for fire and environmental hazards
What does insurance or governmental support usually cover?
•As expected, depends on your level of coverage, but generally, all should cover some provider-prescribed, skilled, intermittent or episodic care outside of the hospital
•Medicaid tends to offer more benefits for nonmedical personal care
Medicare
federal health insurance for persons 65+ (note: also available for those <65yo with ALS or ESRD)
Medicaid
state-run (but joint federal- & state-funded) program to help cover medical costs for persons with lower income
Medicare Part A
helps cover inpatient care in hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities.
Also pays for some home health care and hospice care and inpatient care in a religious non-medical health care institution
Medicare Part B
helps cover medically necessary doctors' services, outpatient care, home health services, durable medical equipment, mental health services, limited outpatient prescription drugs, and other medical services.
Also covers many preventative services
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Founded in 1946 with first goal to prevent Malaria spread in US, expanded to all communicable disease; focus on disease surveillance overall
World Health Organization (WHO)
Founded in 1948, following WWII to create global cooperation on health issues; first focus was on TB and malaria, plus women & children's health, nutrition and sanitation
The Red Cross defines disaster as
“a sudden calamitous event that seriously disrupts the functioning of a community or society and causes human, material and economic or environmental losses that exceed the community’s or society’s ability to cope using its own resources"
Emergency Management
The managerial function charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to threats/hazards and cope with disasters
usually managed by state government or tribal government
Disaster Preparedness
usually managed by federal government
mass casualty incident
an event that overwhelms the local healthcare system, where the number of casualties vastly exceeds the local resources and capabilities in a short time
Natural Disaster
great destruction or loss of life caused by natural forces rather than by human actions
•hurricanes
•Wildfires
•Earthquakes
•Tornados
•Tsunami
•Heat/cold exremes
•Volcano
•Landslides/Avalanche
•Floods/monsoons
•Drought
Man-made Disasters
Disasters resulting from human actions or negligence.
Mass shooting
Nuclear
Gas leak/explosions
War, coups
Pollution
Chemical spills
Transportation
Terrorism
Cyber attack
Shootings
Fire/Arson
Infrastructure collapse
Beyond loss of life, illness, and injury, disaster lead to:
- disruption in services like hospital care
- environmental imbalances (mold, cholera, etc)
- Psychological, emotional, social wellbeing
- Food shortages (crops, displacement, work)
- Population movement
Mitigation
Risk reduction
Ex: improving infrastructure, coordinated public warning systems
Preparedness
planning & training for potential disasters
Ex: detailed and written emergency plan with training and recourses, practice simulation
Responce
activities that address the short-term, direct effects of an incident. This is the immediate action phase during and after a disaste
Ex: evacuations, immediate health needs, life-sustaining services like hydration, search/rescue, emergency services like backup power
#1 Goal of emergency management
Decrease loose of life
#2: decrease property loss
Why is it beneficial for President to declare disaster vs emergency
$$ and resources
Tribal and Territorial Governments
Puerto Rice
Guam
American Samoa
US Virgin Islands
Northern Mariana Island
Tribal Regions
Nursing Role in Mitigation
Community Education
Advocacy
Vulnerability Assessment
Community Education For Nursing Role in Mitigation
Nurses educate the public on topics such as creating family disaster plans, assembling emergency kits, and understanding local hazards.
* This one overlaps with preparedness*
Advocacy For Nursing Role in Mitigation
Nurses advocate for policy changes that promote community resilience, such as improved building codes and environmental protections.
Vulnerability Assessment For Nursing Role in Mitigation
Nurses help identify vulnerable populations within a community who may be at higher risk during a disaster, such as older adults, children, and those with chronic illnesses and limited mobility
Nursing Role in Preparedness
Developing Emergency Management Plans
Training and Drills
Resource Management
Developing emergency management plans (EMP) Nursing Role
•Nurses participate in the development of disaster plans for healthcare facilities and communities. (Sometimes called operational plans)
•For healthcare facilities, a robust EMP is not just a best practice. It is a critical component of client safety and a requirement by regulatory bodies like The Joint Commission and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
•An EMP is a detailed written plan that outlines specific roles, responsibilities, and procedures in the event of an emergency.
•There should be different plans for different emergencies or hazards.
Training and drills Nursing Role
Nurses actively participate in disaster drills and simulations to test EMPs and refine their skills.
Resource management Nursing Role
Nurses help ensure that adequate medical supplies, equipment, and personnel are available to respond to a disaster.
Nursing Role during Response
Leadership and Incident Command
Triage
Direct Client Care
Shelter Management
Leadership and incident command Nursing Role
Depending on the EMP, nursing leaders may be involved in incident command activities.
Triage Nursing Role
In mass casualty incidents, nurses are responsible for triaging clients, prioritizing care based on the severity of their injuries
Direct Client Care Nursing Role
Nurses provide essential medical care, including first aid, wound care, medication administration, and emotional support to victims.
Shelter Management Nursing Role
Nurses may work in temporary shelters, providing care to displaced individuals and families
Recovery
This final phase focuses on returning the community to a state of normalcy.
Nursing Role during Recovery
Long term care
mental health support
community rebuilding
Long Term Care nursing role
Nurses provide ongoing care for individuals with injuries or illnesses sustained during the disaster
Mental Health Support Nursing Role
Nurses play a crucial role in providing mental health support to both victims and fellow responders, helping them cope with the trauma of the event
Community Rebuilding Nursing Role
Nurses contribute to the rebuilding of healthcare infrastructure and the restoration of community health services.
RACE for Fires
rescue, alarm, confine, extinguish
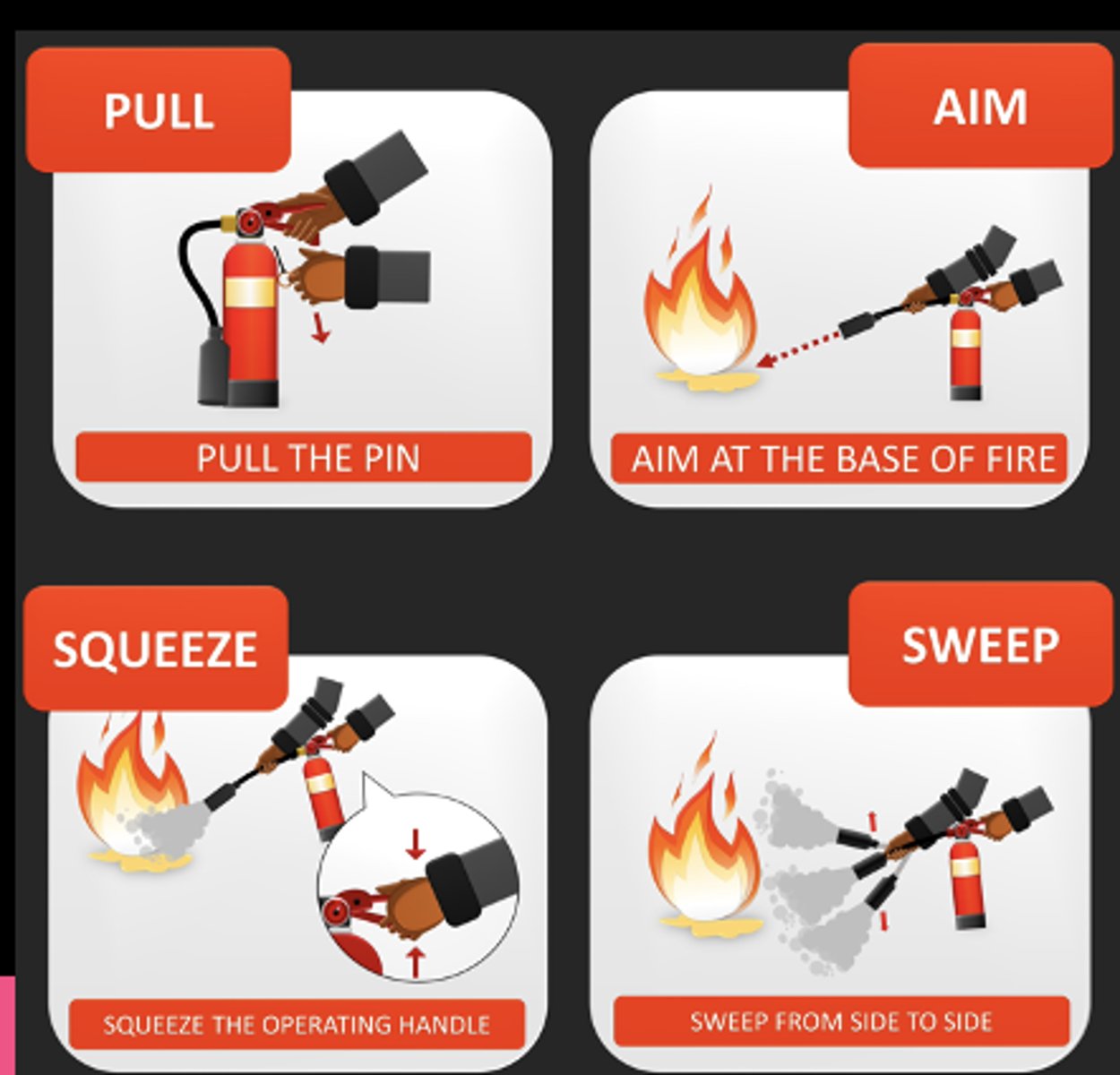
PASS for fire extinguishers
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
CUS
I am Concerned
I am Uncomfortable
This is a Safety issue
De-escalate
Whether you are arriving to scene as bystander or emergency response personnel, what is your first priority?
Safety
Cascading Events
Events that occur as a direct or indirect result of an initial event
Ex: earthquake leads to tsunami
_____ is the #1 cause of death from injury
bleeding
Manageable span of control: one supervisor to how many subordinates?
1 to 5
START and SALT
most common system used for mass casualties in the field
Triage
the medical screening of patients to determine their relative priority of need and the proper place of treatment
START Triage (Simple Triage and Rapid Treatment)
Primary use: Adult patients (typically ≥8 years)
Assessment criteria:
•Respiratory rate (breathing)
•Perfusion (circulation/pulse)
•Mental status (ability to follow commands)
Categories: Immediate (red), delayed (yellow), minor (green), deceased (black)
Time limit: Ideally 60 seconds or less per patient
SALT Triage
Primary use: All age groups, including pediatric patients
Process:
Sort: Global sorting of patients who can walk
Assess: Individual assessment using LSI and priority criteria (ABCs or ABCDs)
Lifesaving Interventions: Simple interventions like positioning airway, bleeding control
Treatment/Transport: Final prioritization for treatment and transport
Categories: Same color coding but more nuanced decision-making process
Prioitization
Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Dysfunction (neuro)
Red Triage Color
unstable, need immediate support to save their life
Yellow Triage Color
stable, but serious, likely need treatment but can be delayed ~ 30-60 minutes
Green Triage Color
stable, but wounded/ill, likely minor and can withstand waiting > 60 minutes for treatment; “walking wounded”
black triage color
deceased or expectant for death; injuries incompatible with life
SBAR
Situation
Background
Assessment
Recommendation
Mass Care and Emergency Assistance Includes
actions taken to protect evacuees and others from the effects of the event. Includes sheltering, food distribution, medical care, clothing, and other essential life support needs of those who have been displaced by a threat/hazard.
Health and Medical Services Provides
health and medical services in emergencies, including emergency medical, hospital, public health, environmental health, mental health, and mortuary services.
Hurricane Katrine Vulnerable Population
- elderly
- disabled
- low income
- children/families
Danger of Flood Waters
animals and insects
live wires
harmful bacteria
dangerous chemicals
sewage
sharp objects & debris
What is the epidemiology triad
Environment, agent, host
Susceptible host, what should we consider
immunity, age, genetics, co-morbidities, life style
Environmental factors, what should we consider
pollution, air, sanitation, water, geography (urban, rural, tropical, desert, etc), access to care, politics
Infectious agent. what should we consider
virus, bacteria, other, chemical, physical injury
Tests for TB
1. tuberculin skin test (TST or PPD)
2. IGRA Blood test
3. Sputum smear
4. Nucleic Acid Amplification
5. Chest X-ray or CT
Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)
Used to determine past or present tuberculosis infection present in the body. This is based on a positive skin reaction to the introduction of a purified protein derivative (PPD) of the tubercle bacilli, called tuberculin, into the skin.
IGRA Blood Test
for those vaccinated with BCG as a child it won't give false +
Sputum smear and culture
works if patient is actively coughing or in low income settings
Nursing Tips for Excellent Sputum Collection
1. Morning is best
2. Rinse mouth
3. have patient take deep breath, hold, out, try to initiate deep cough
4. Open container when about to spit
5. Spit about 5mL, or 1 tsp
6. Close container and date
TST Test Interpretation
≥5mm: HIV+, immunocompromised, recent exposire
≥10mm: high risk groups, immigrants from high-prevalence areas
≥15mm: low risk individuals
S/S of TB
unintentional weight loss
night sweats
loss of appetite
chest pain
couch lasting more then 3 weeks
fatigue
fever
coughing up blood
TB First-Line Meds
Rifampin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
TB first line med side effects
Isoniazide: hepatotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy (take vit B6)
Rifampin: orange discoloration of body fluids, hepatotoxicity
Ethambutol: optic neuritis
Phrazinamide: Hepatotoxicity, hyperuricemia
TB Infection controll protocols
airborne precautions until non-contagious
negative pressure room
N95 respirator
Latent TB
25% of the world has been exposed to TB
10% of those get active TB
Airborne Precautions
standard precautions + mask, negative pressure, clean hands
Droplet precautions
Standard + mask, googles, wash hands