Physics A U1-4 Language Development
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
centripetal acceleration
acceleration of an object toward the center of a curved or circular path
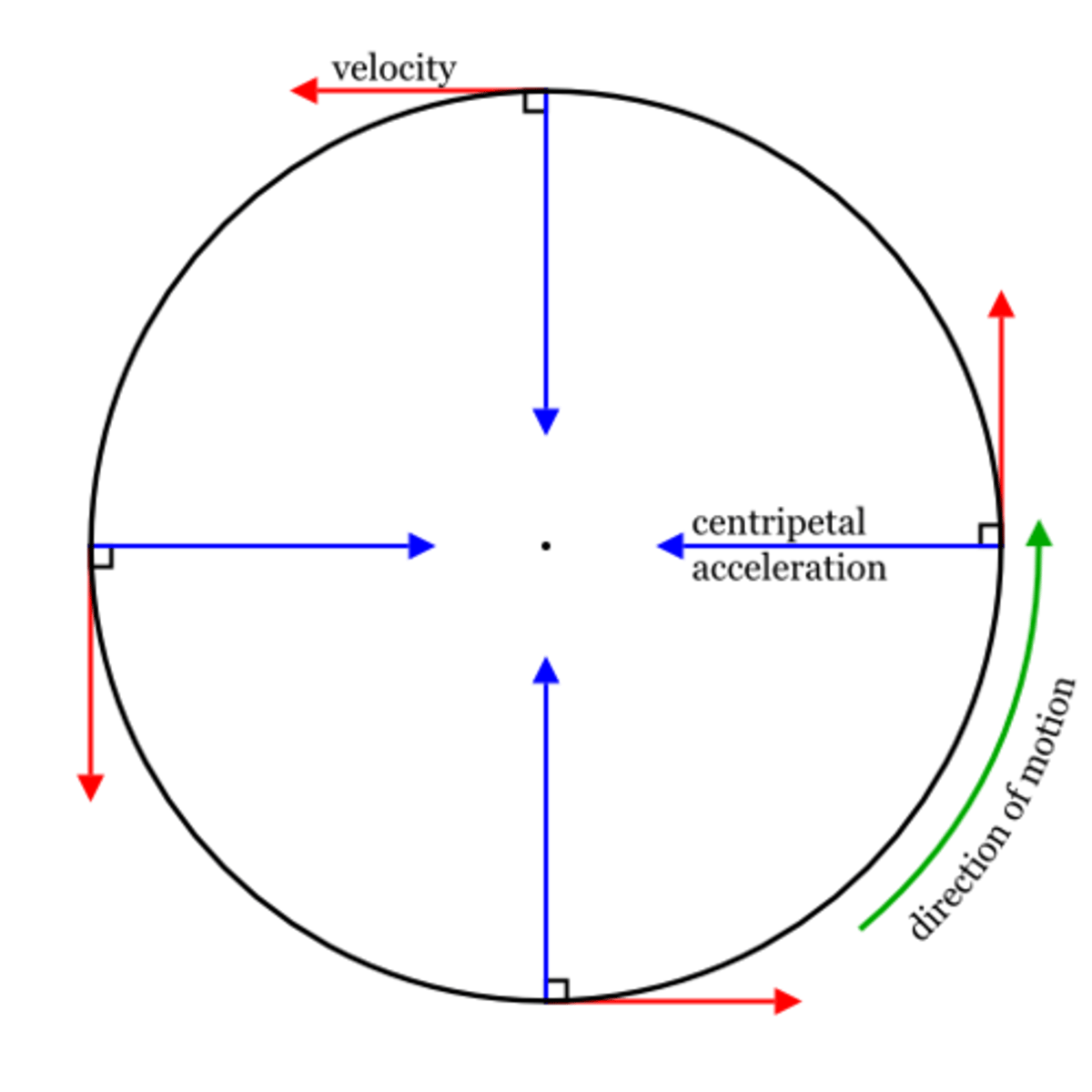
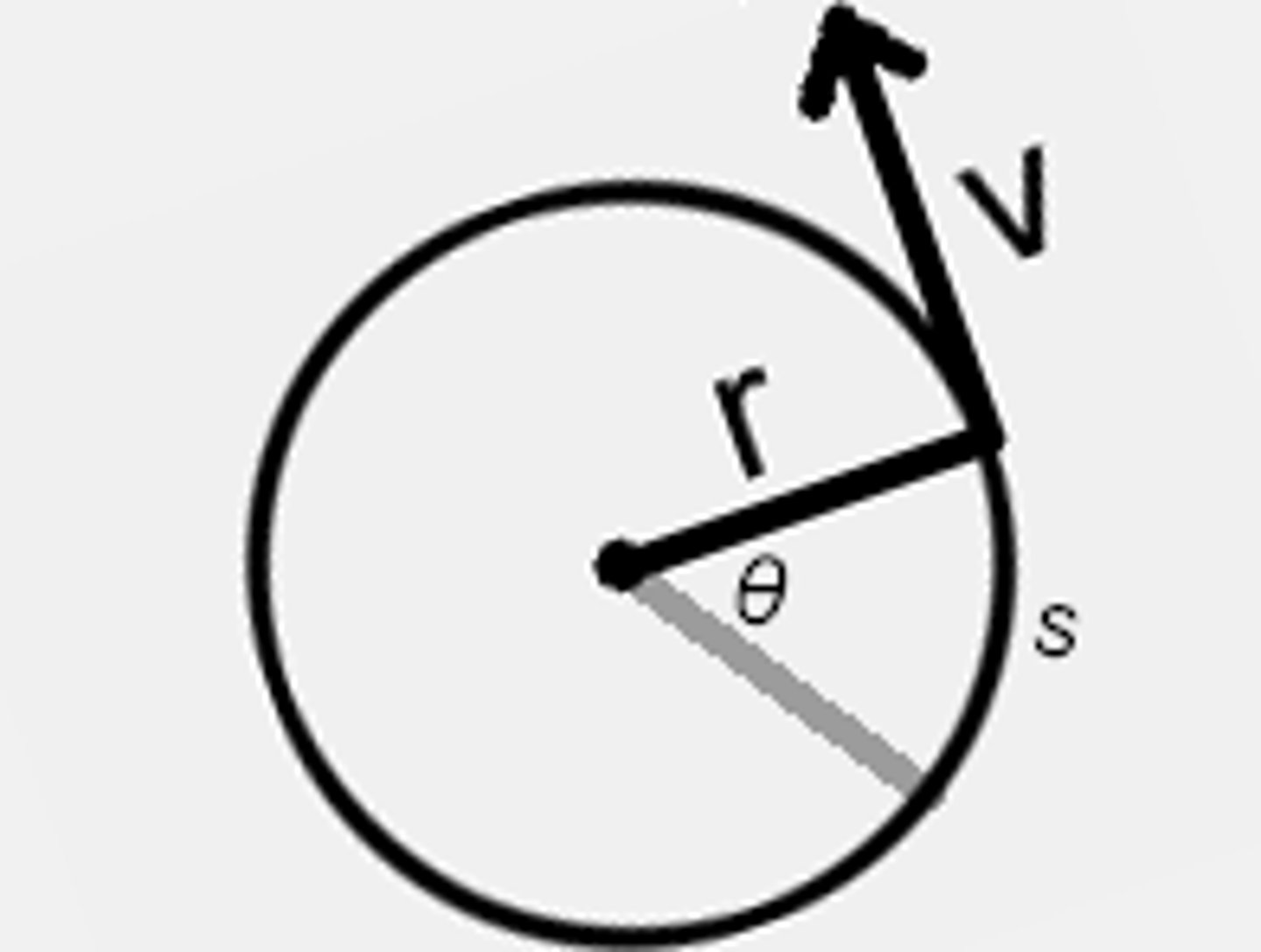
tangential speed
the linear speed of any object moving along a circular path and directs tangent to the circle
orrery
mechanical model of the solar system

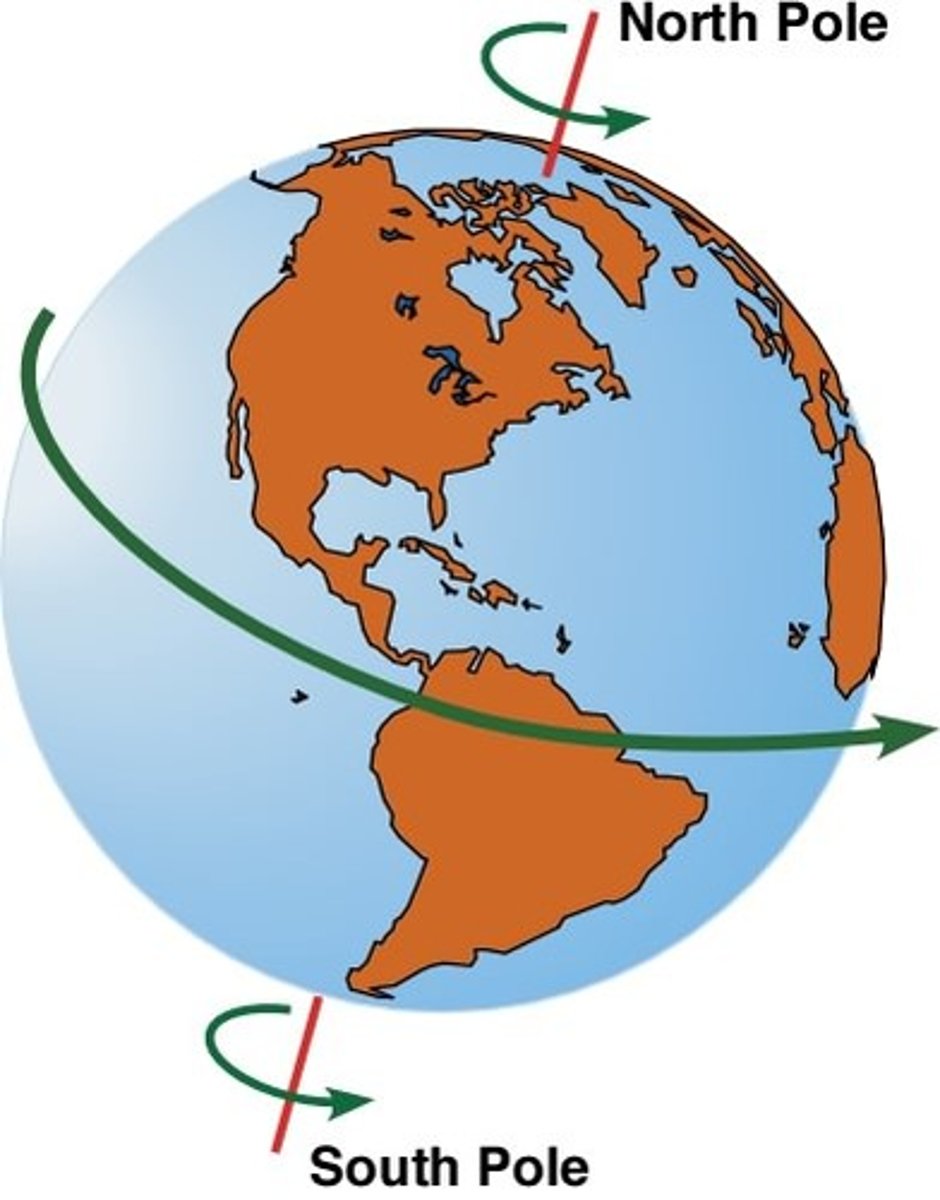
rotation
circular movement of an object around an axis of rotation; movement along circular path
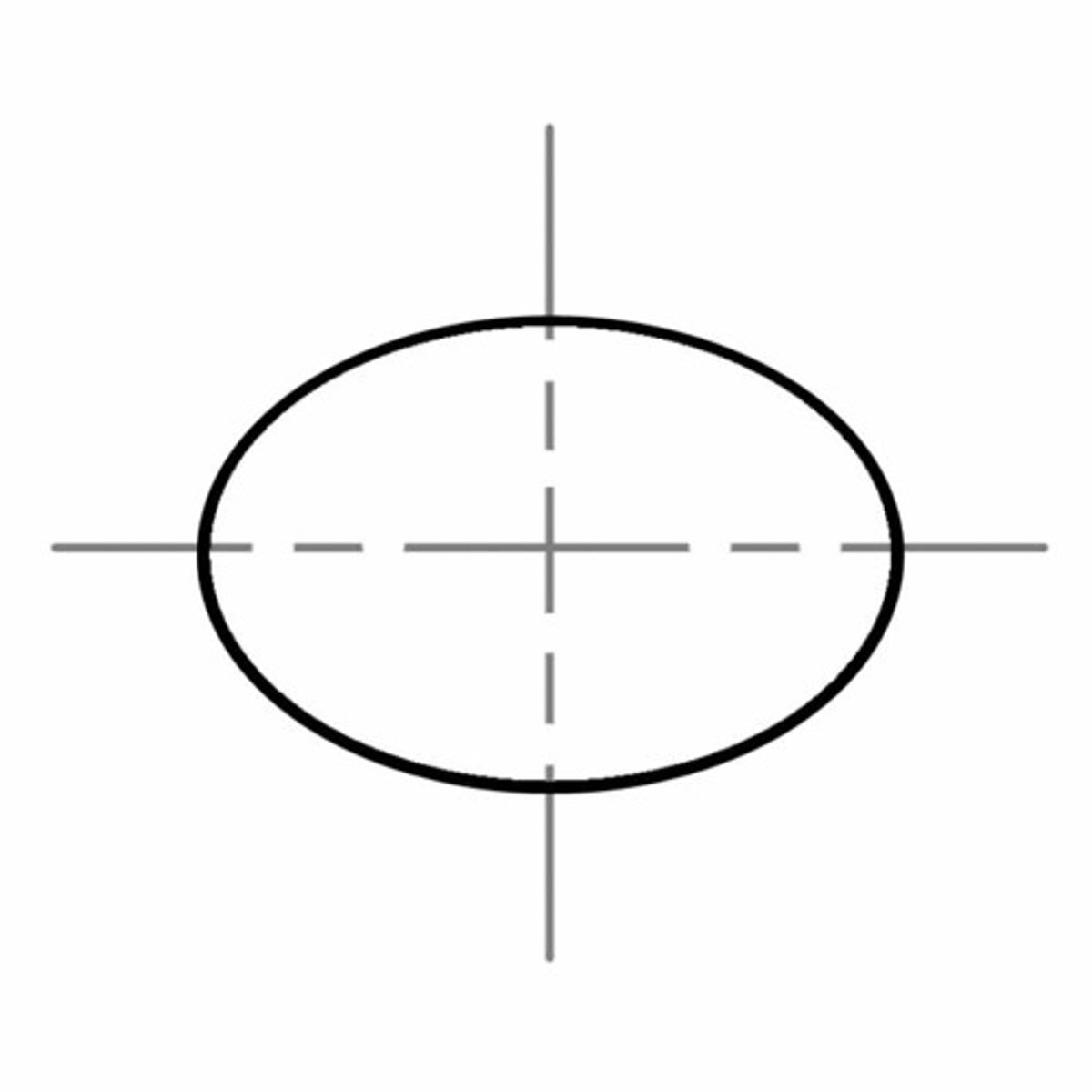
Ellipse
a flattened circle or oval that has two centers called the foci.
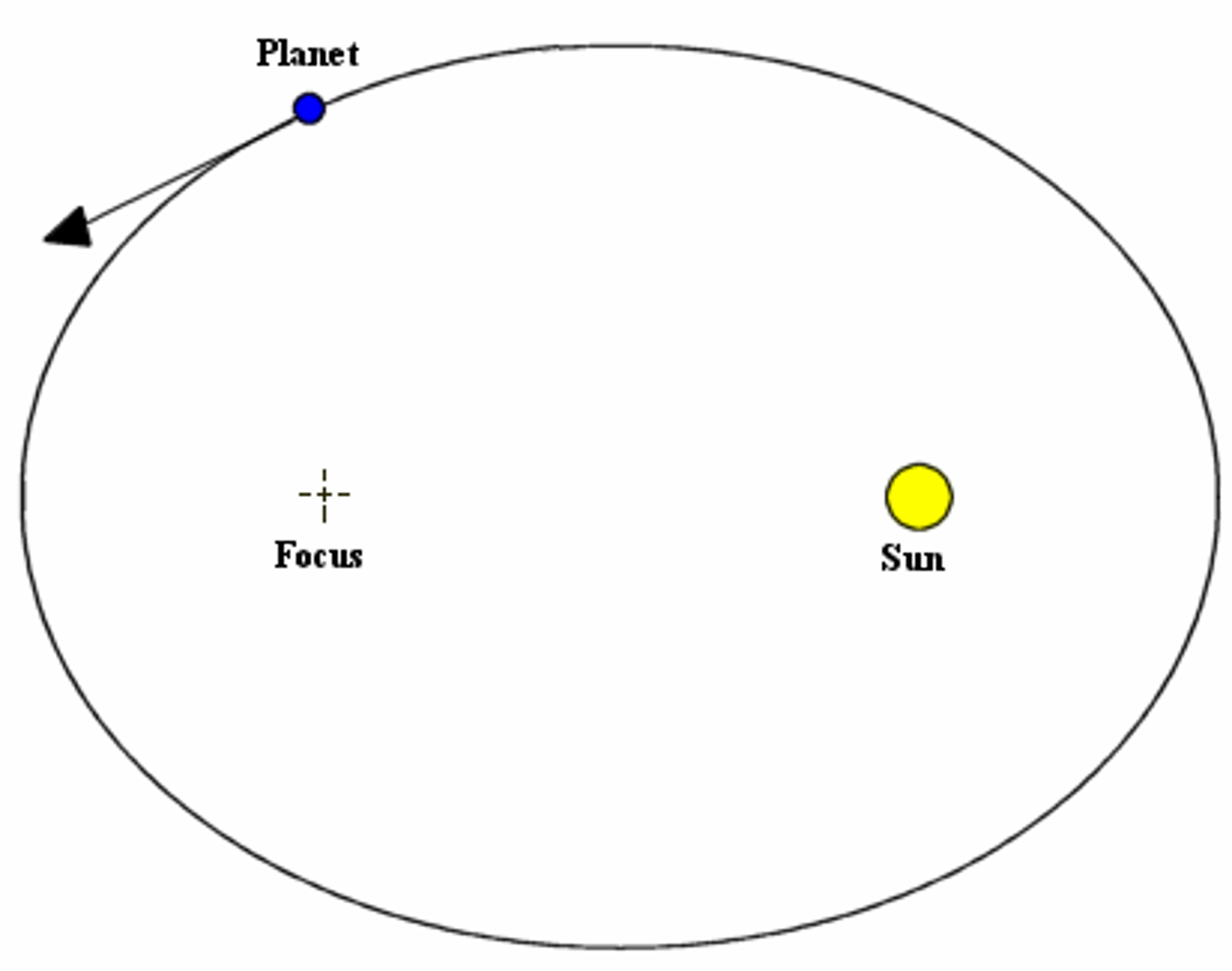
Kepler's first law of planetary motion
Planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the foci.
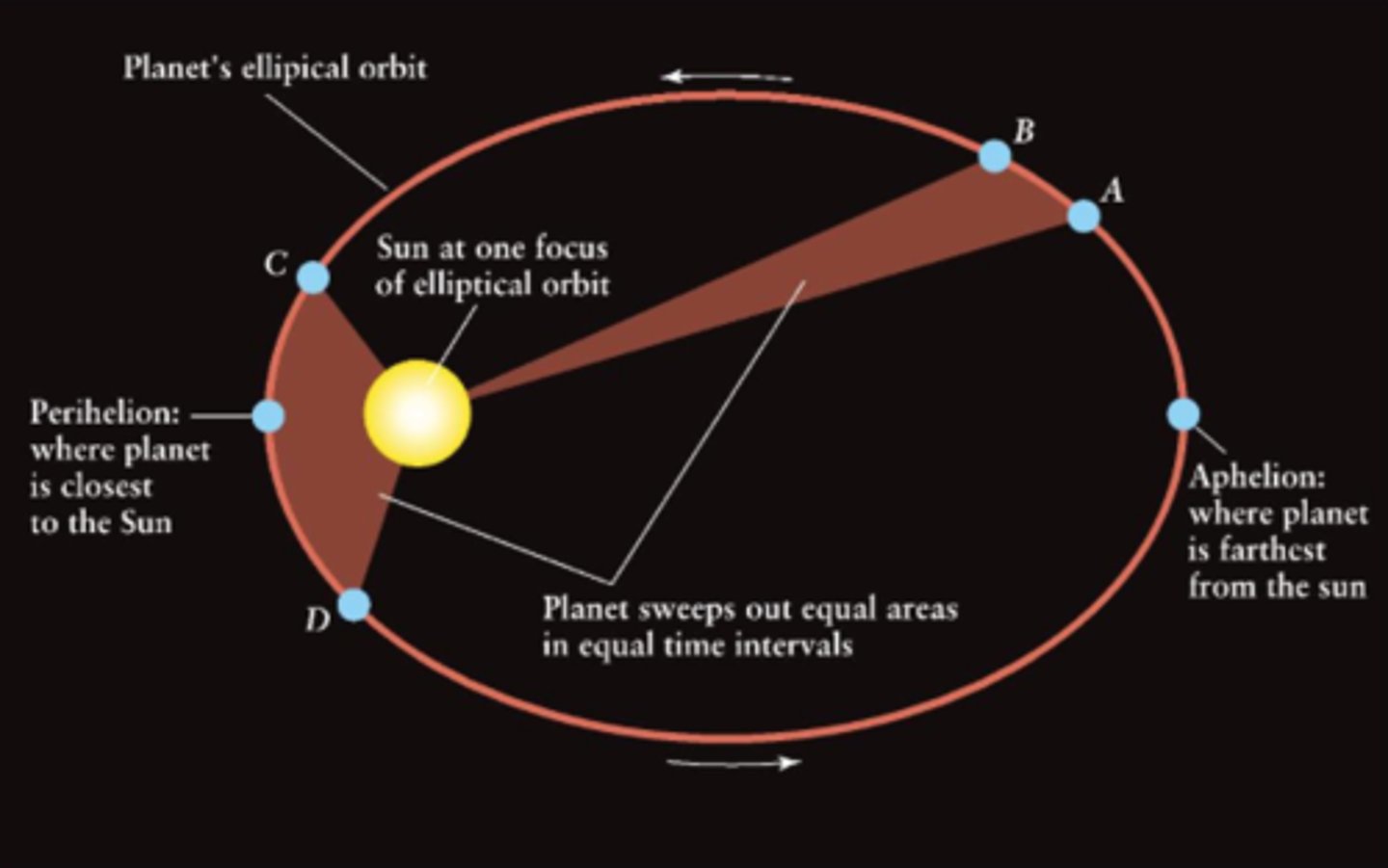
Kepler's second law of planetary motion
As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times
Kepler's Third Law of Planetary Motion
period (T) squared of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its average distance (r) from the sun
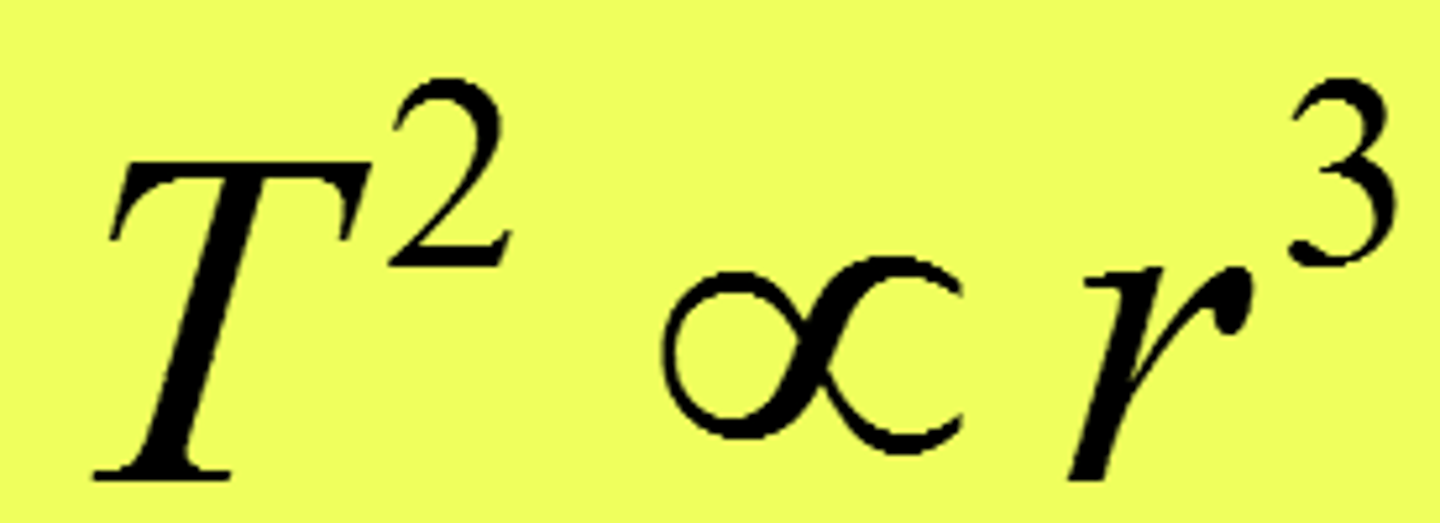
frequency
the number of complete rotations/revolution in a given time
period
the time to complete a full rotation/revolution
solar system
the collection of eight planets and their moons in orbit around the sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of asteroids, meteoroids, and comets.
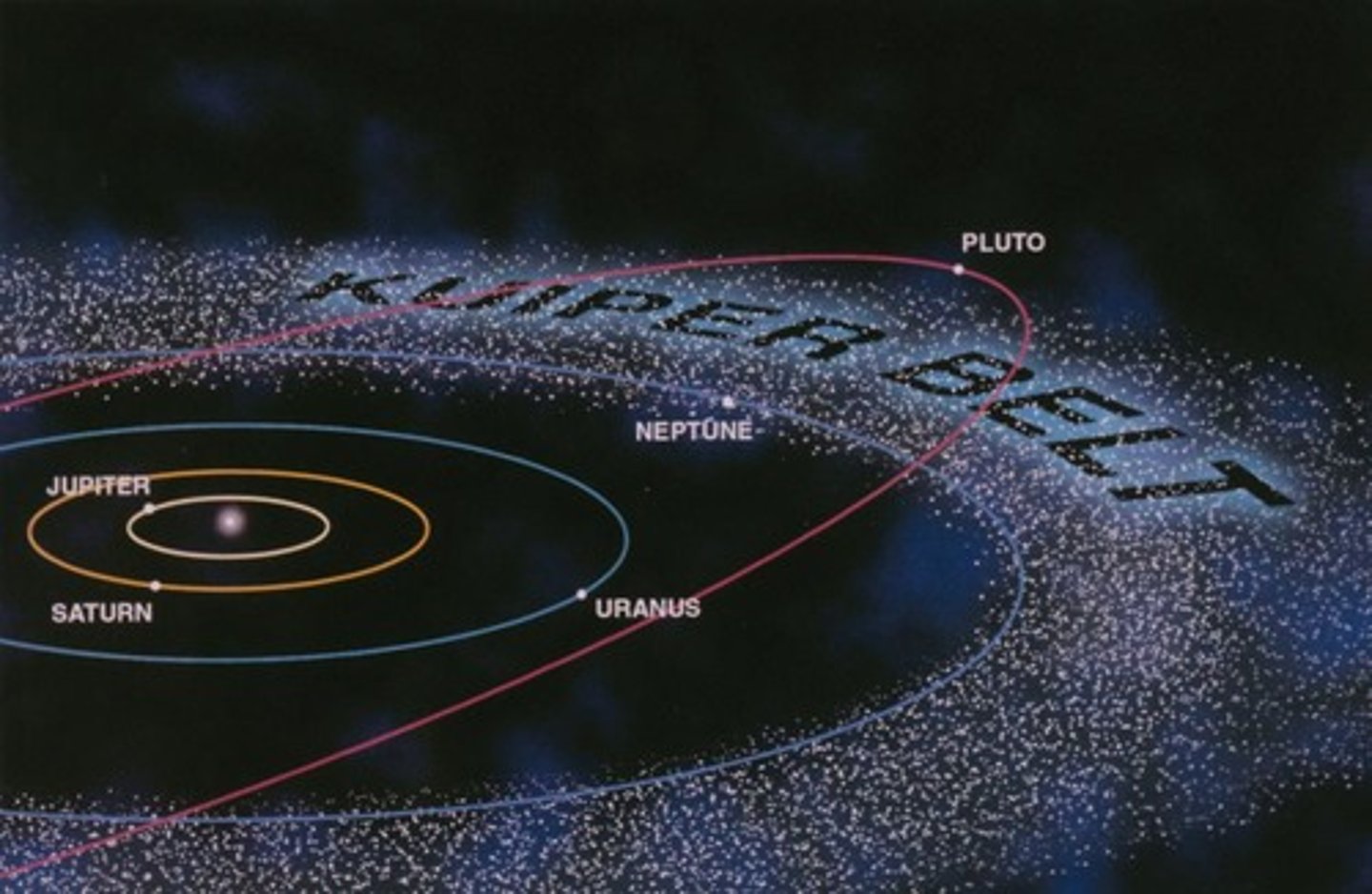
Kuiper belt
A region of the solar system that is just beyond the orbit of Neptune and that contains small bodies made mostly of ice
outer planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, & Neptune. Called Gas Giants.

inner planets
Small, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun including Mercury, Venus, Earth, & Mars

Revolution
The movement of an object around another object
work
one way to transfer energy; force causes displacement of an object (measured in J)

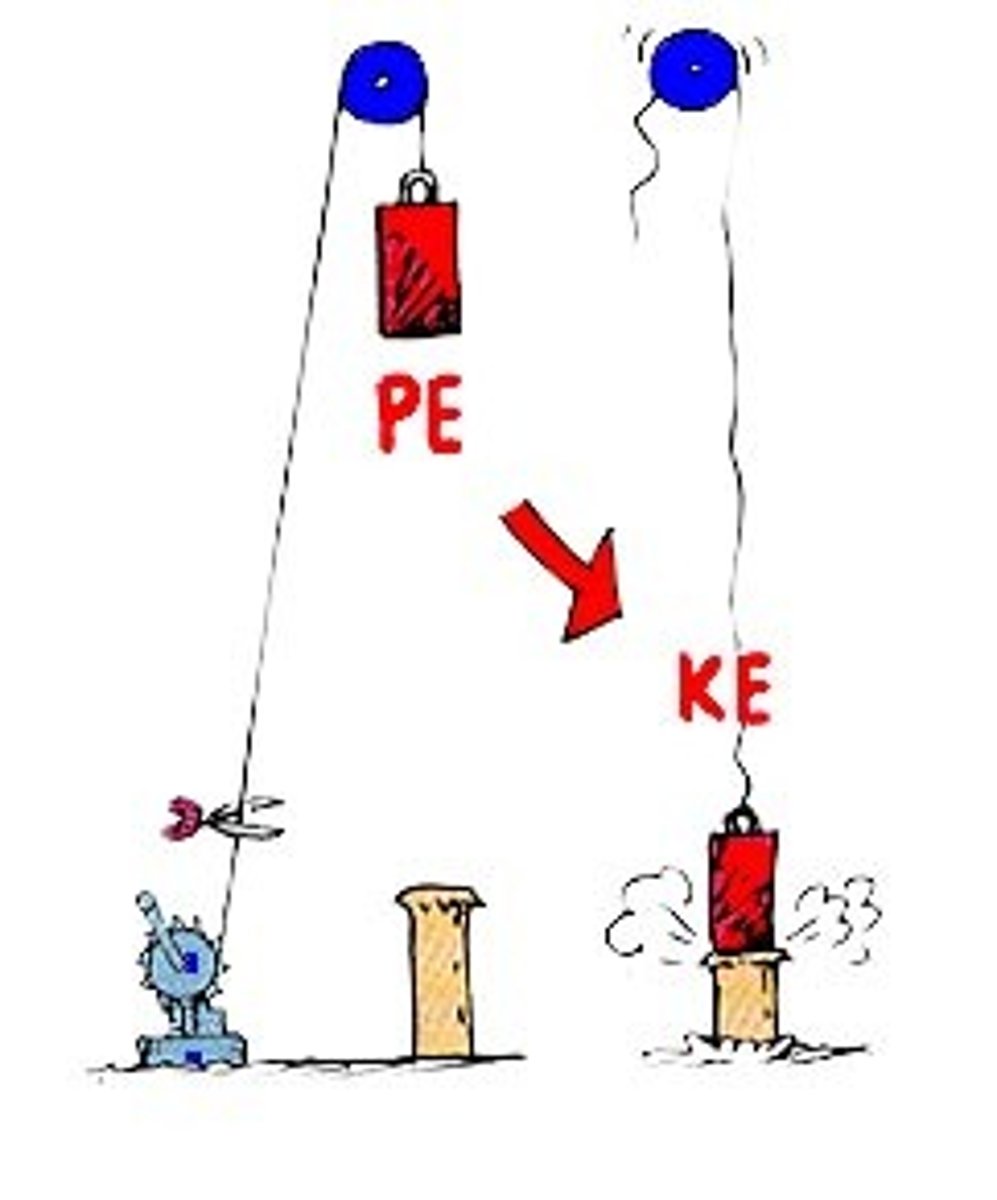
kinetic energy
object's energy because of its motion (measured in J) (1/2 x mass x speed^2)
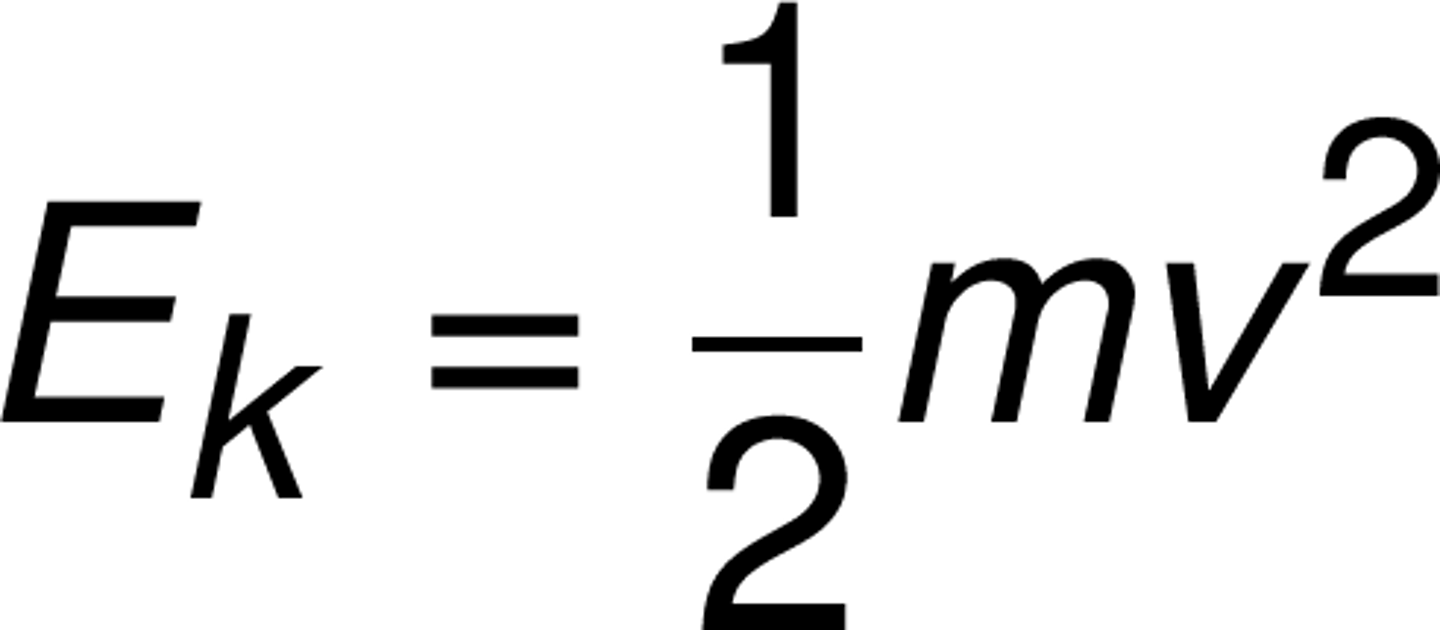
potential energy
energy associated to position, shape, or condition

gravitational potential energy
potential energy stored in gravitational fields (mgh, measured in J)

elastic potential energy
result of deformation of an elastic object like a spring
spring constant
k - measure of a spring's resistance to being compressed or stretched

mechanical energy
combination of kinetic and potential energy
power
rate of work done or energy transformed (work/time or force x speed, measured in W)
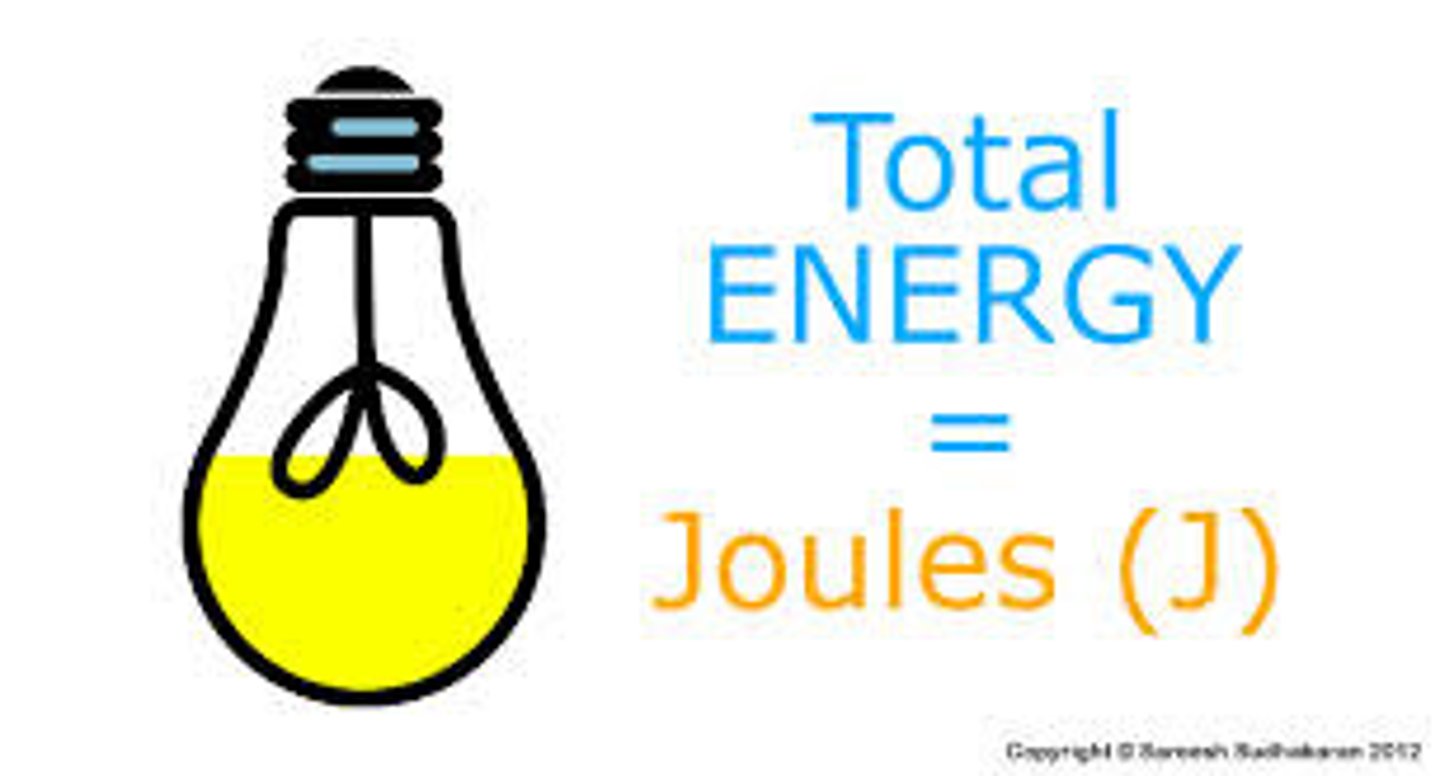
Joule
unit of energy
Watt
SI unit of power
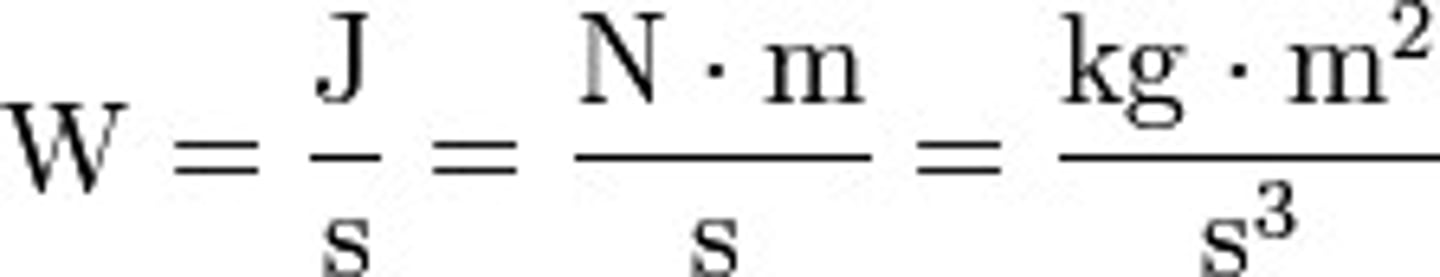
rate
a magnitude or frequency relative to a time unit OR any quantity divided by time
Work - Kinetic Energy theorem
net work done by all forces equal to object's KE change (network = kinetic final - kinetic initial)
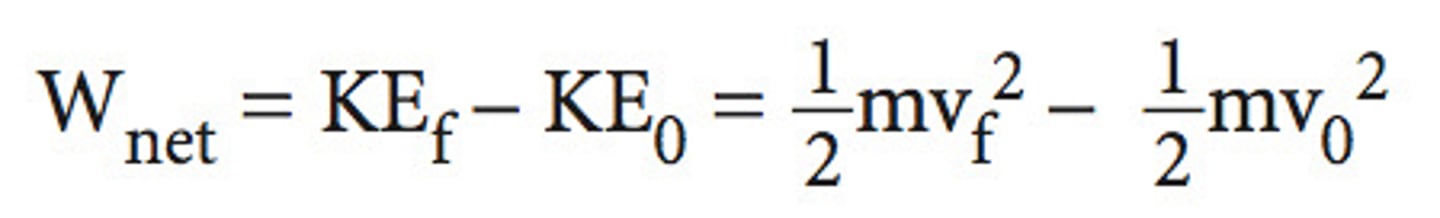
force
action exerted onto an object that may change its state of motion; a push or a pull; measured in Newtons

inertia
object's resistance to move
Newton's 3 Laws of Inertia
1) in the absence of net force, a body will preserve its state of motion
2) acceleration directional proportional to net force and is inversely proportional to mass
3) for every action, there is a equal and opposite reaction
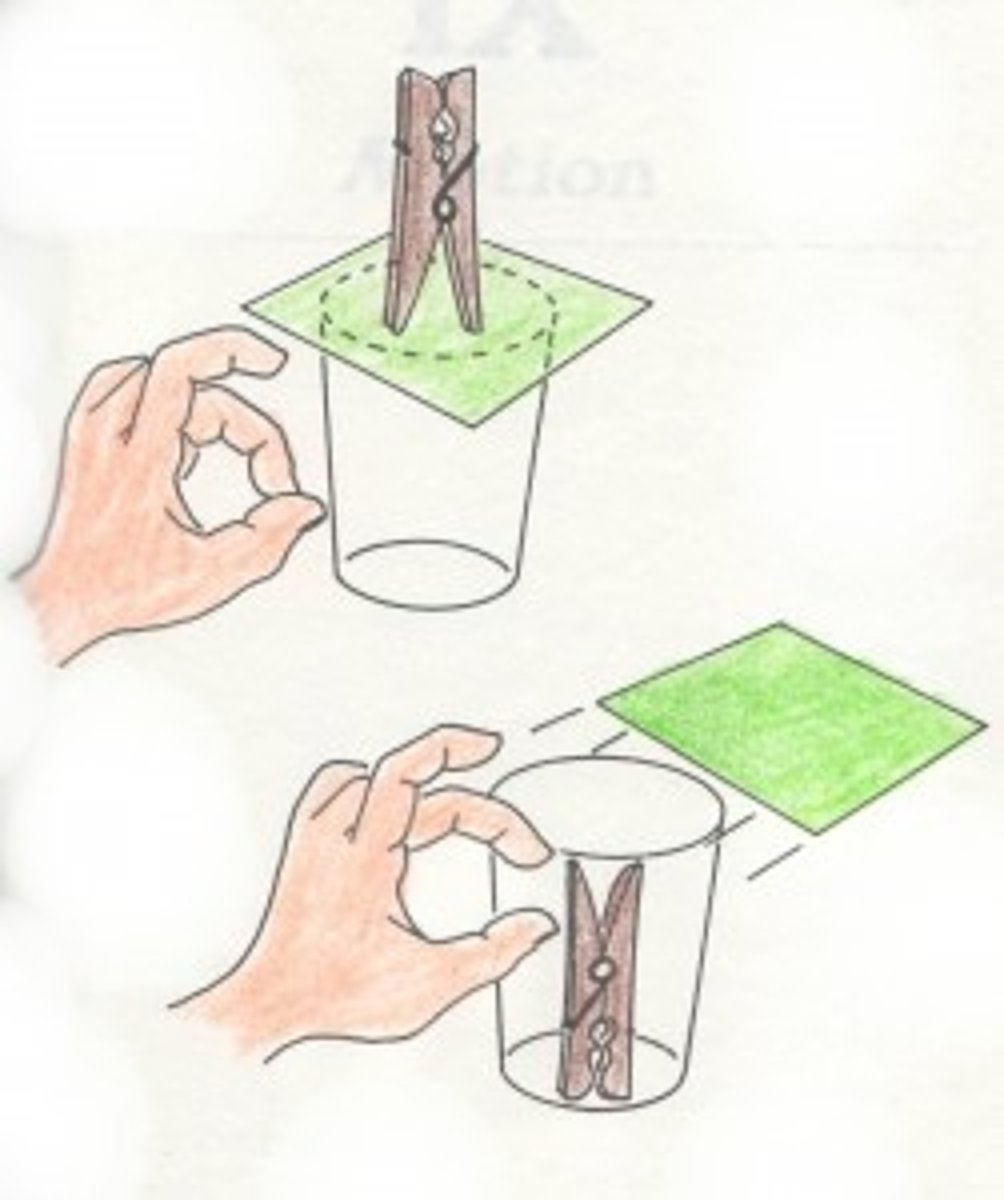
net force
vector sum of all the forces that act upon an object
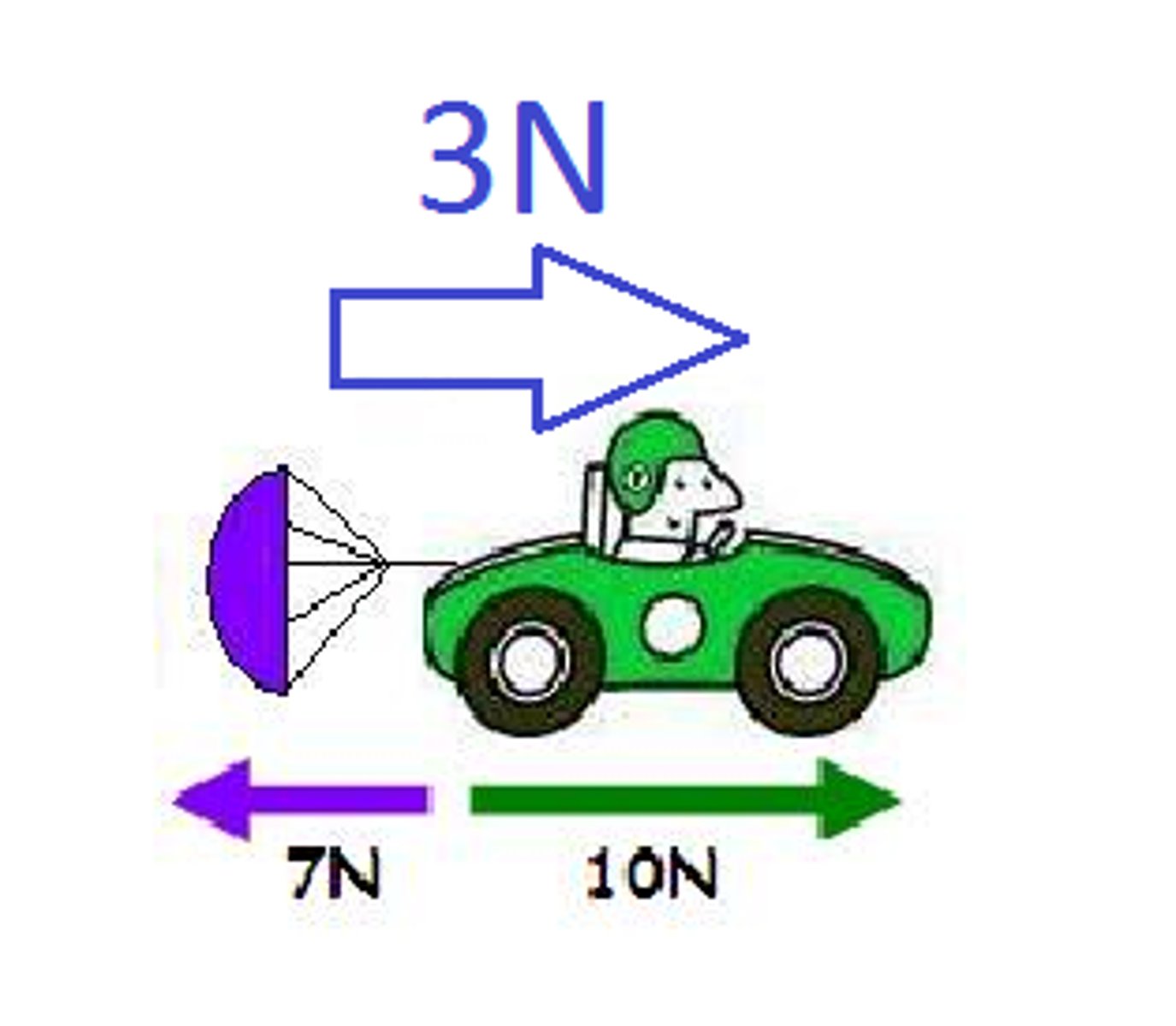
equilibrium
net force = 0; all forces balance out to zero
weight
mass x free fall acceleration;

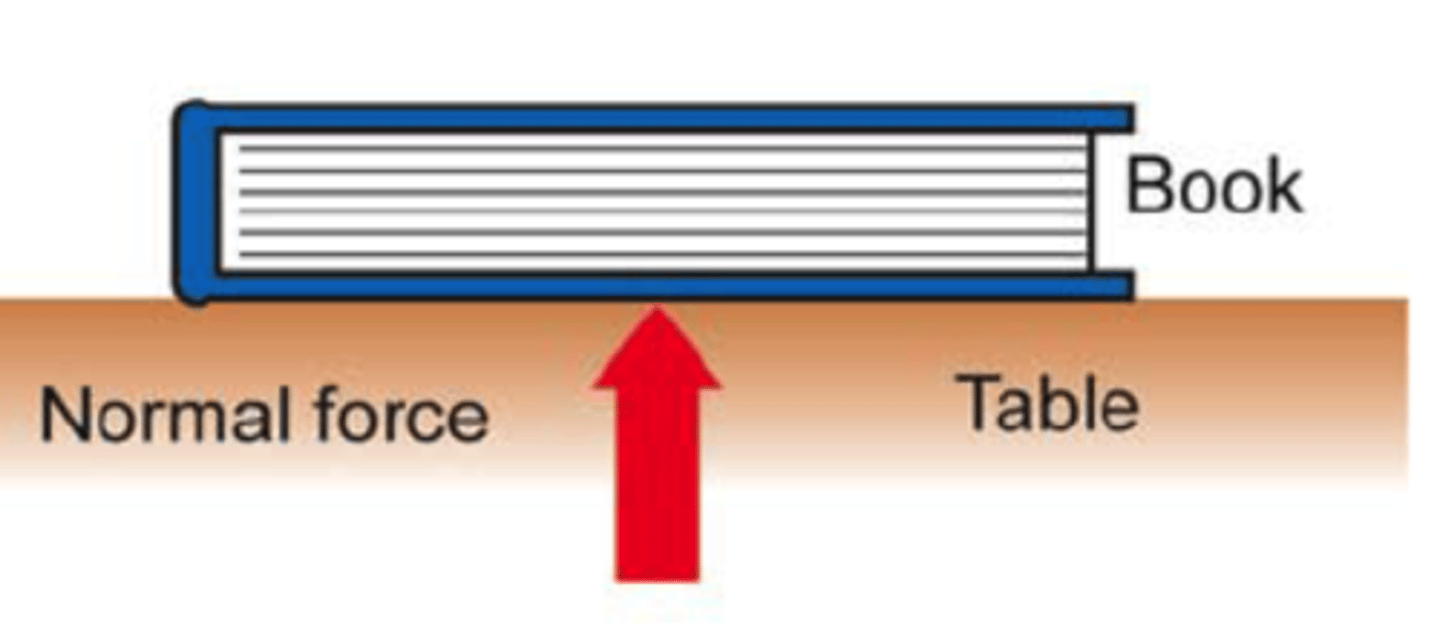
normal force
supporting force, perpendicular to the surface
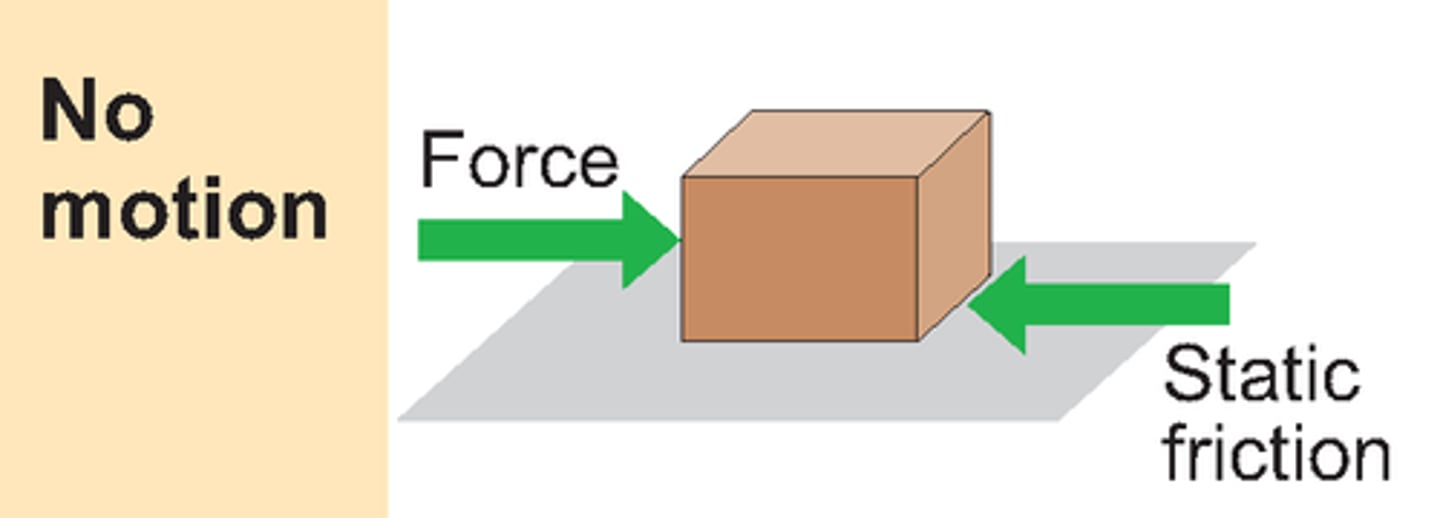
static friction
force that resists the initiation as a sliding motion
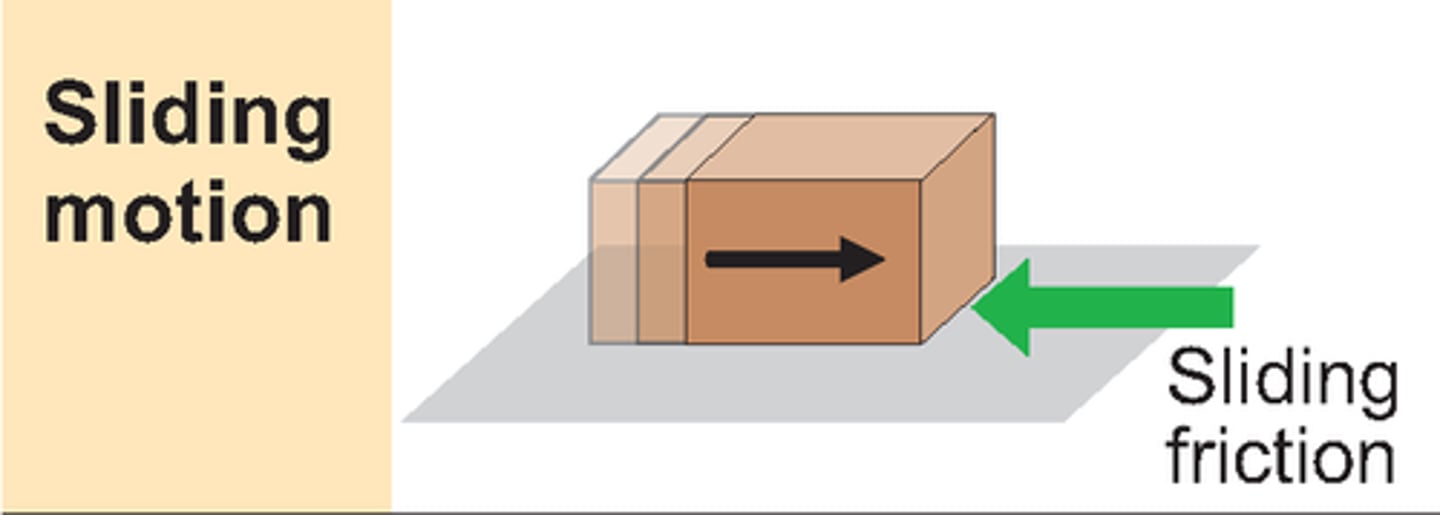
kinetic friction
force opposes the movement of two surfaces that are in contact
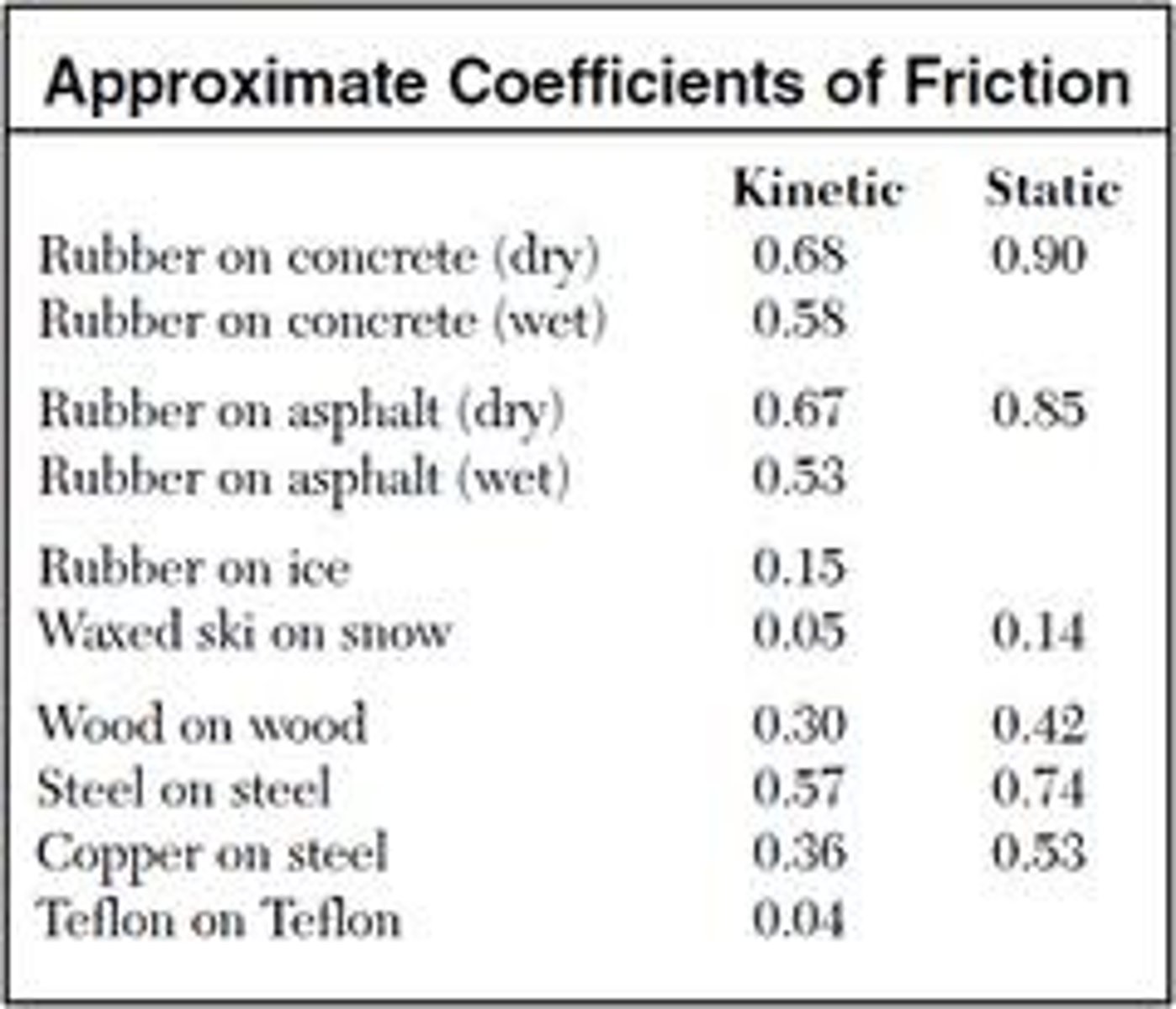
coefficient of friction
force of friction / normal force; a number that depends on the type of surfaces that are in contact
momentum
mass x velocity; inertia in motion

impulse
force x time; or change in momentum
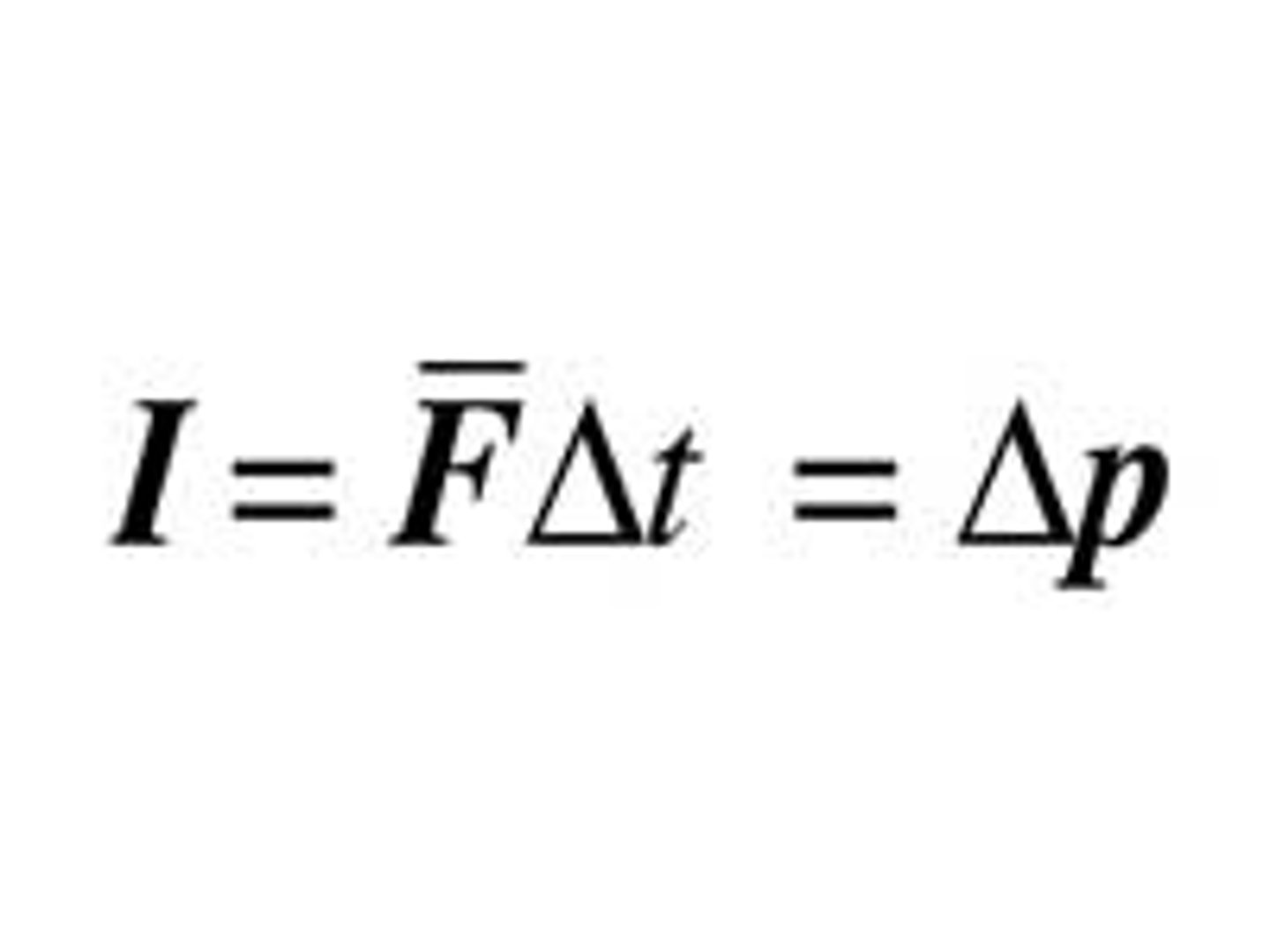
Impulse - change in momentum theorem
F*t = change in mv
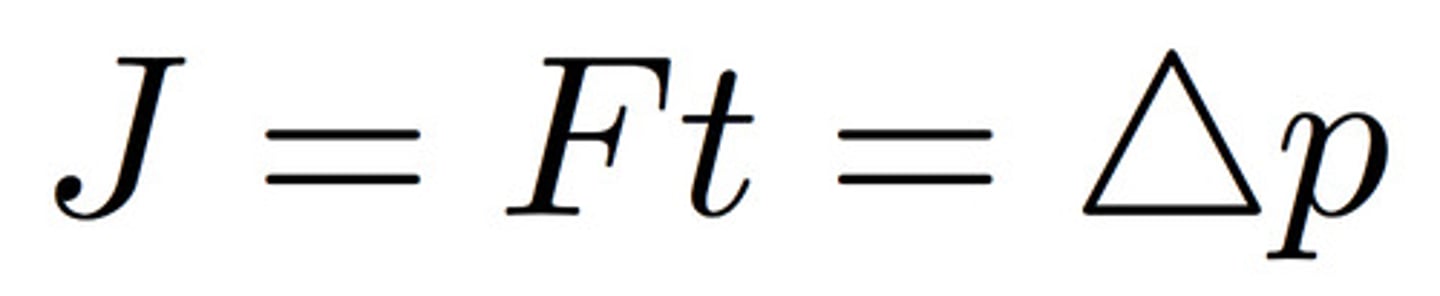
collision
two objects bump into each other
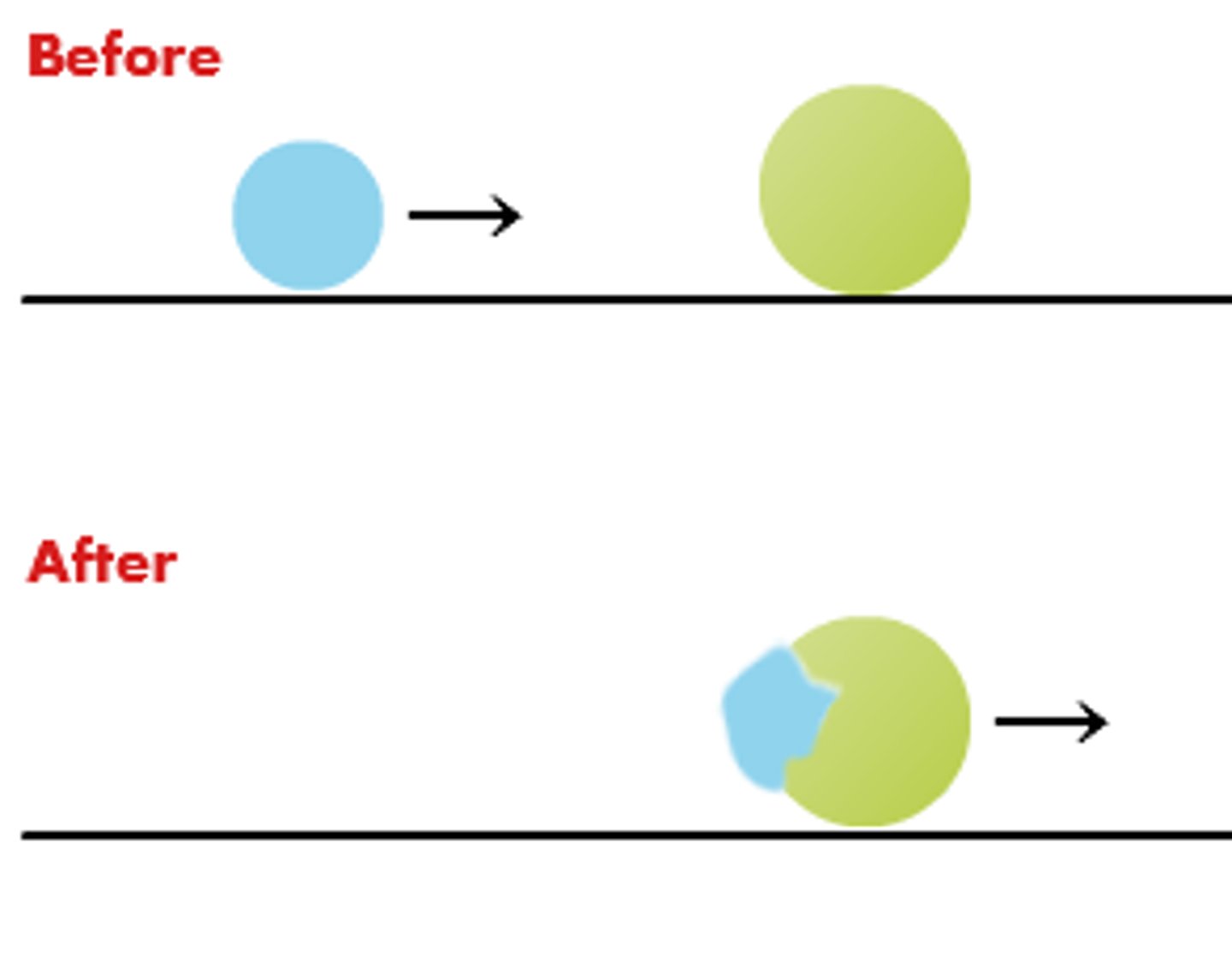
elastic collision
total momentum and KE are conserved

inelastic collision
a collision in which the total kinetic energy of the colliding bodies or particles is not the same after the collision as it was before (as opposed to elastic collision); momentum is conserved but KE is not conserved

perfectly inelastic collision
objects stick together after colliding; the maximum amount of kinetic energy has been lost
explosions
a special type of collision. It is a perfectly inelastic collision that seemingly happens in reverse. Before the 'collision', all objects are stuck together. After the 'collision', all objects are moving apart from one another.

Newton's First Law of Motion
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.

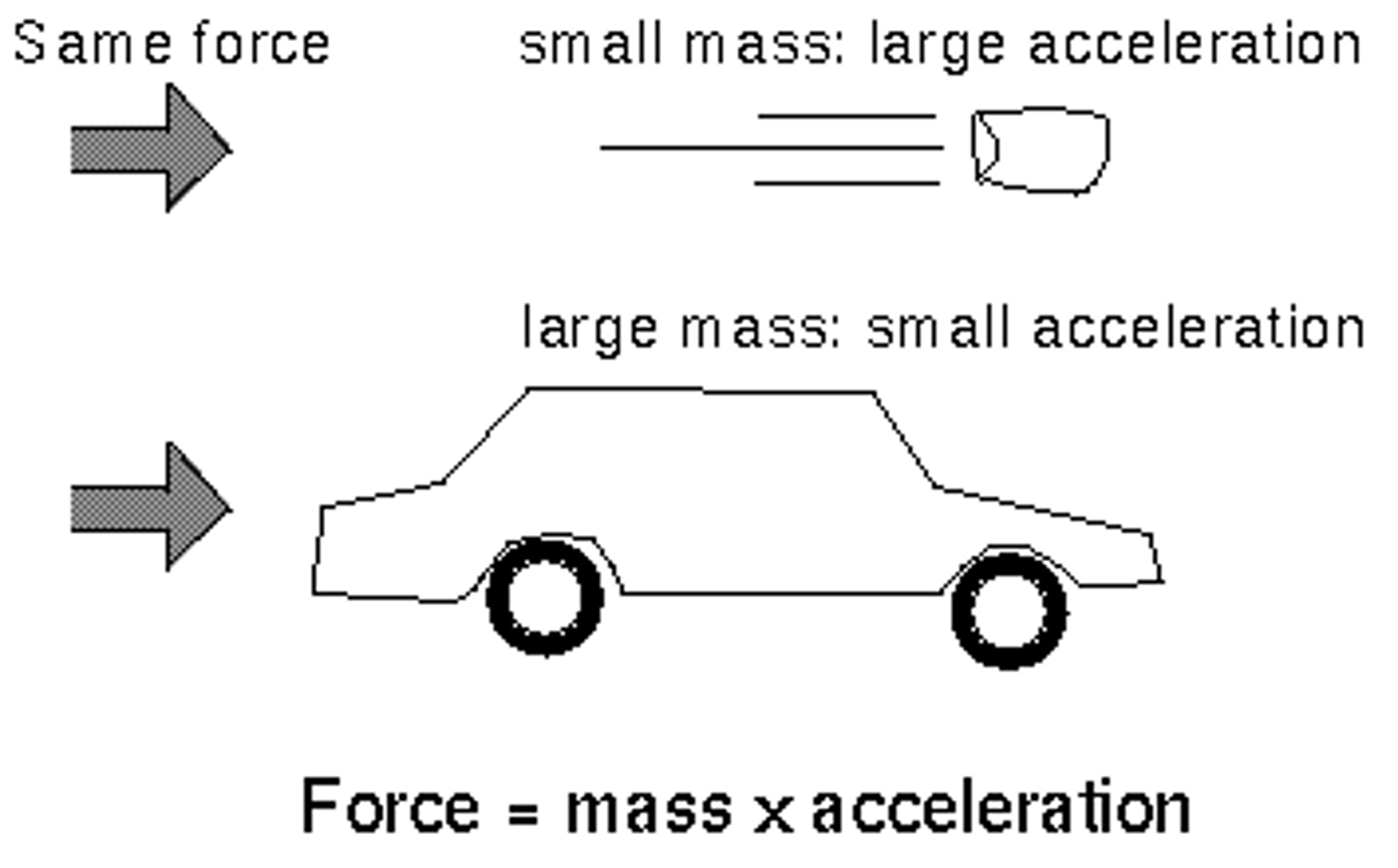
Newton's Second Law of Motion
F=ma; where a and F have the same direction
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.

range (of a projectile)
distance between the launch point and where the projectiles hits the ground
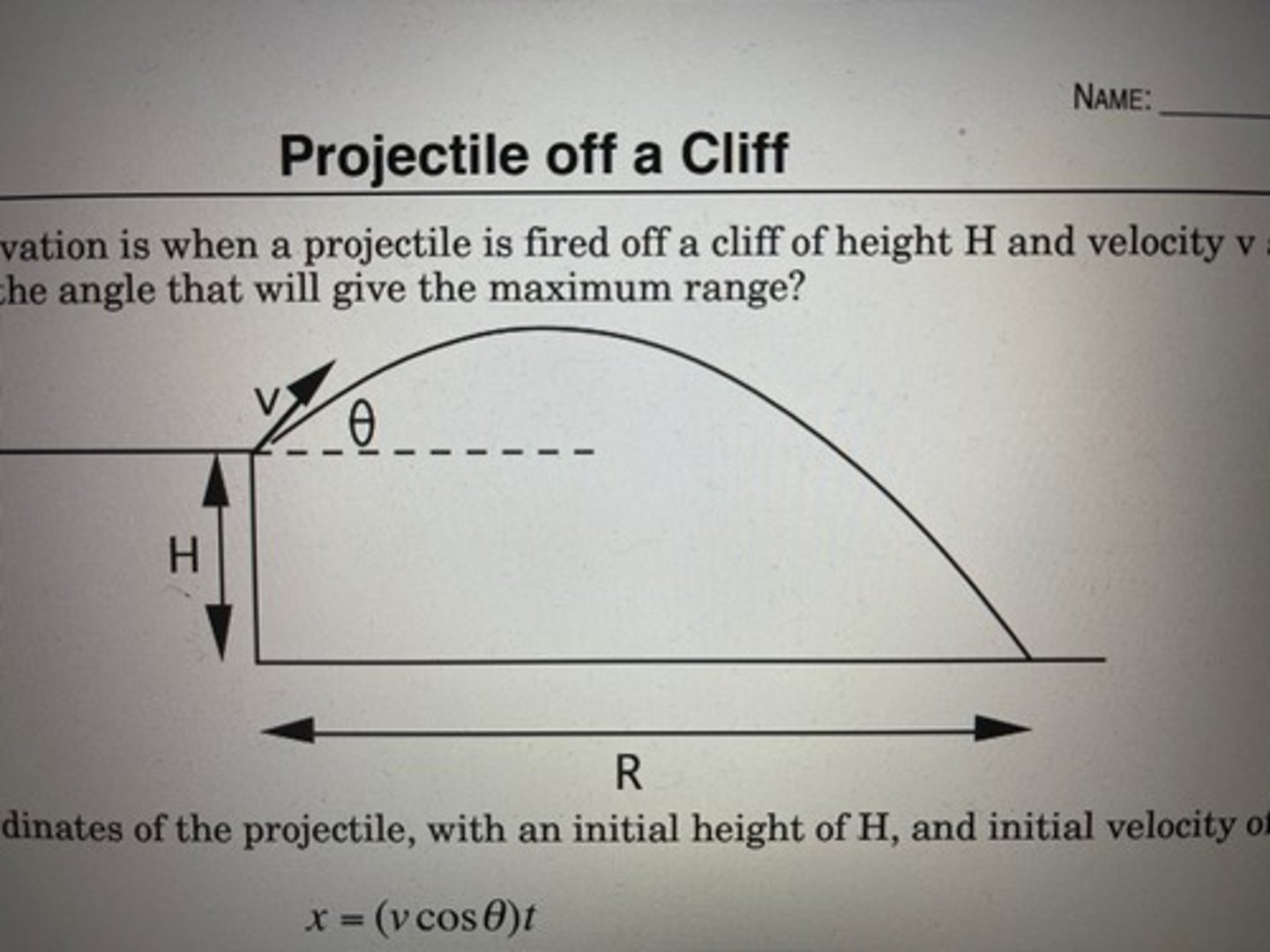
projectile (motion)
the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity
frame of reference: a set of criteria or stated values in relation to which measurements or judgments can be made.
a set of criteria or stated values in relation to which measurements or judgments can be made: positive - negative
right - left
up - down
north - south
east - west
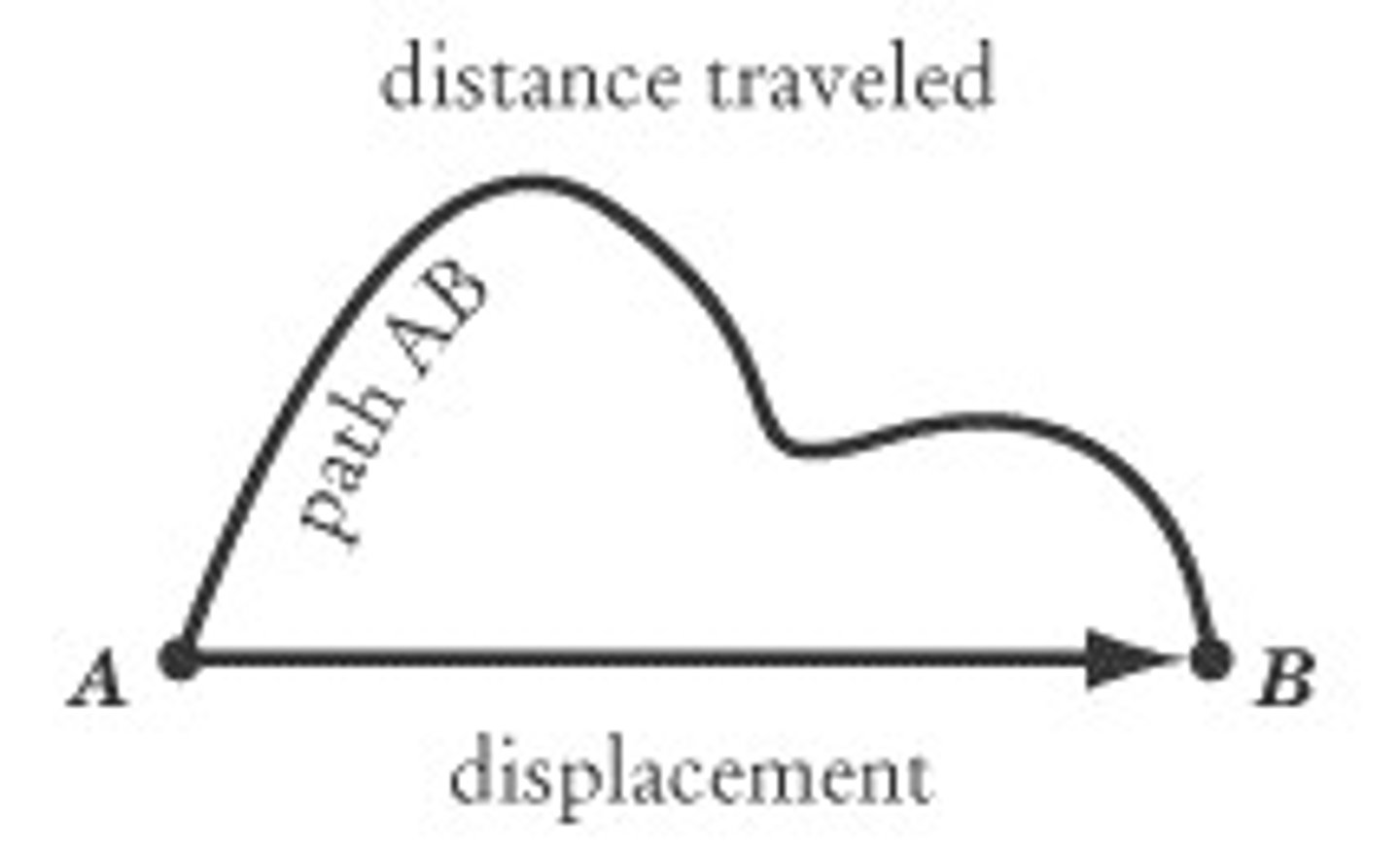
displacement
change in position (measured in m)
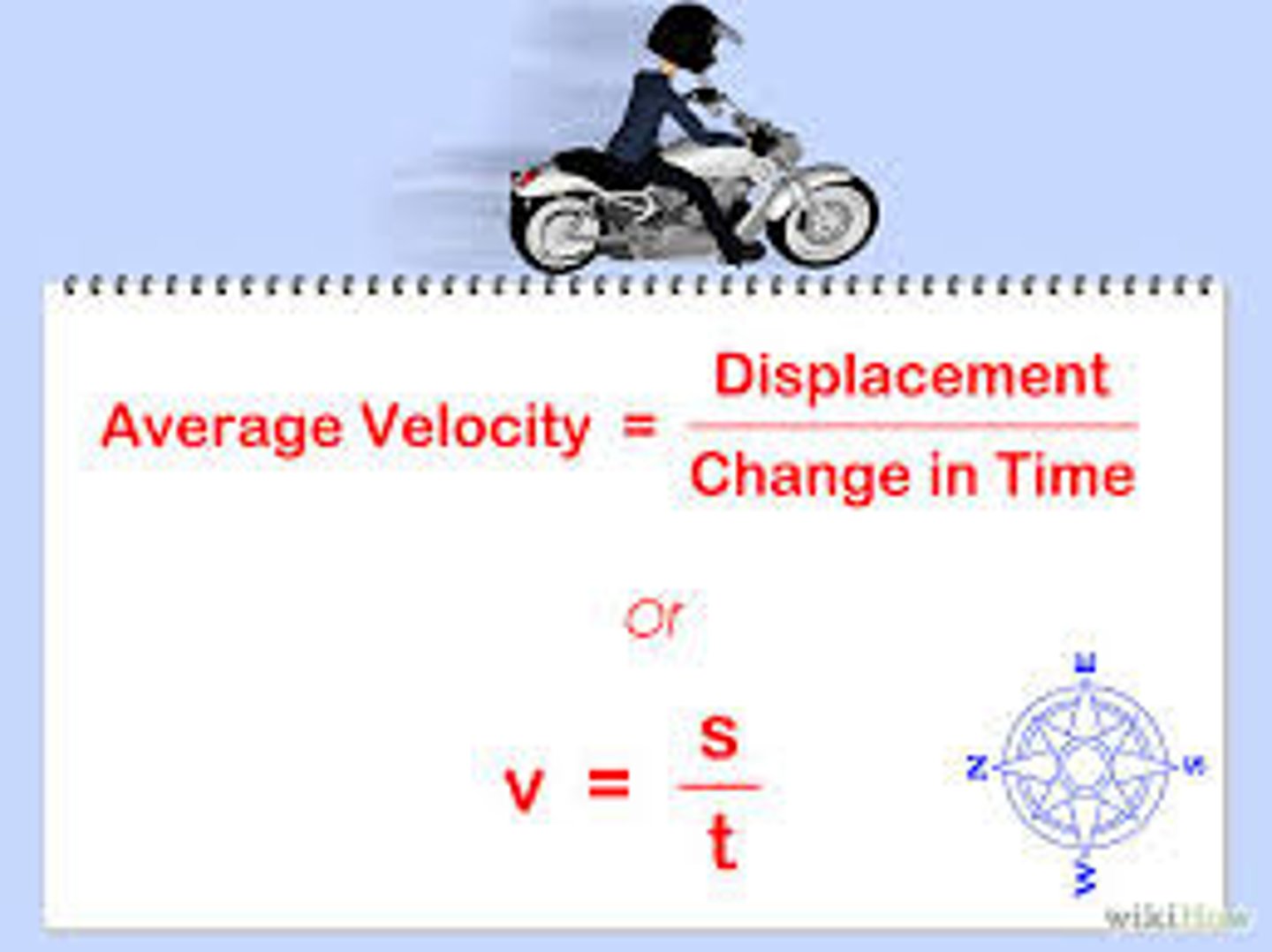
average velocity
total displacement divided by time during displacement occurrence (measured in m/s)
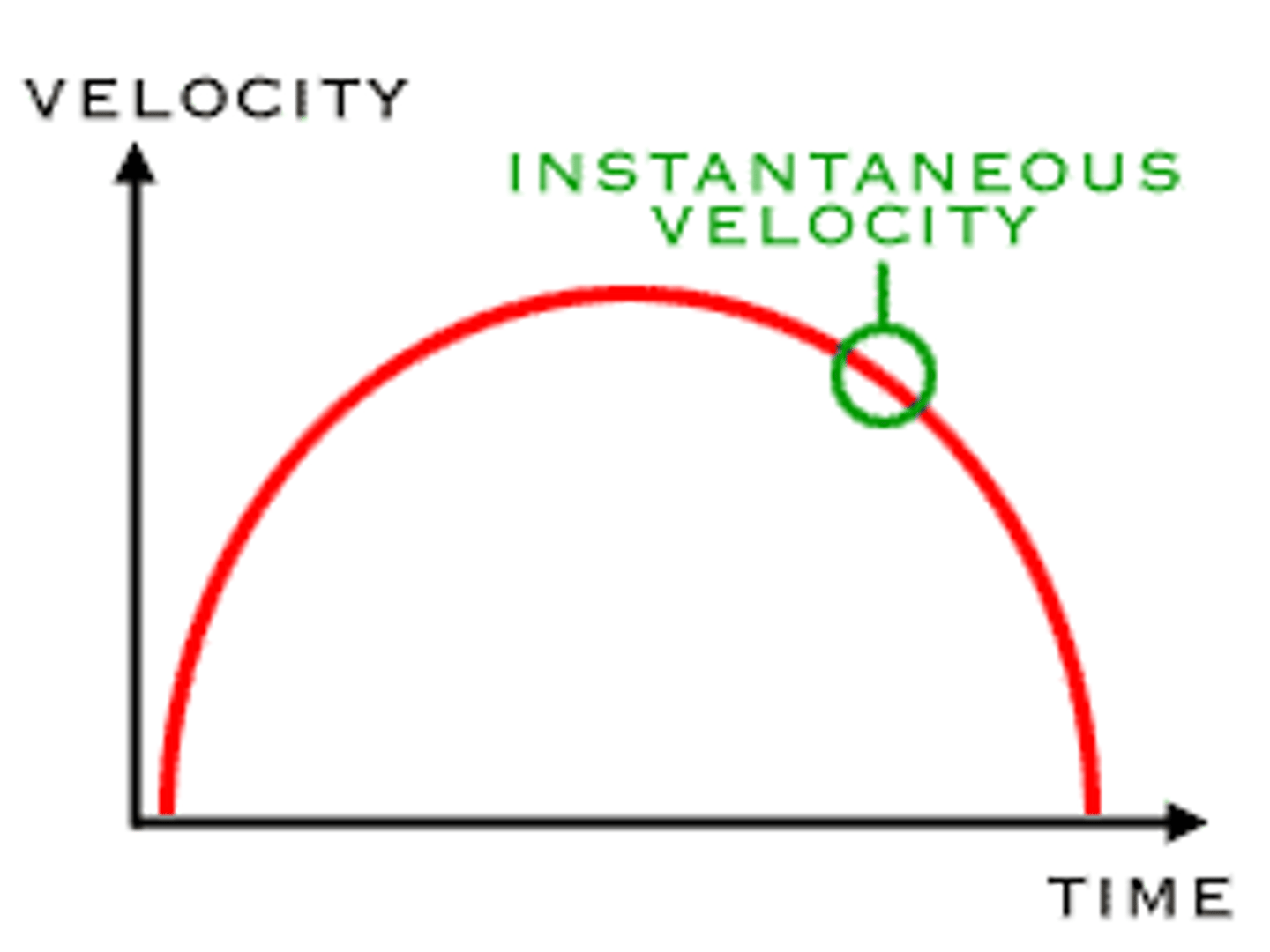
instantaneous velocity
velocity at a specific point in time
acceleration
change in velocity; velocity rate changes (change in velocity/time change; m/s^2)
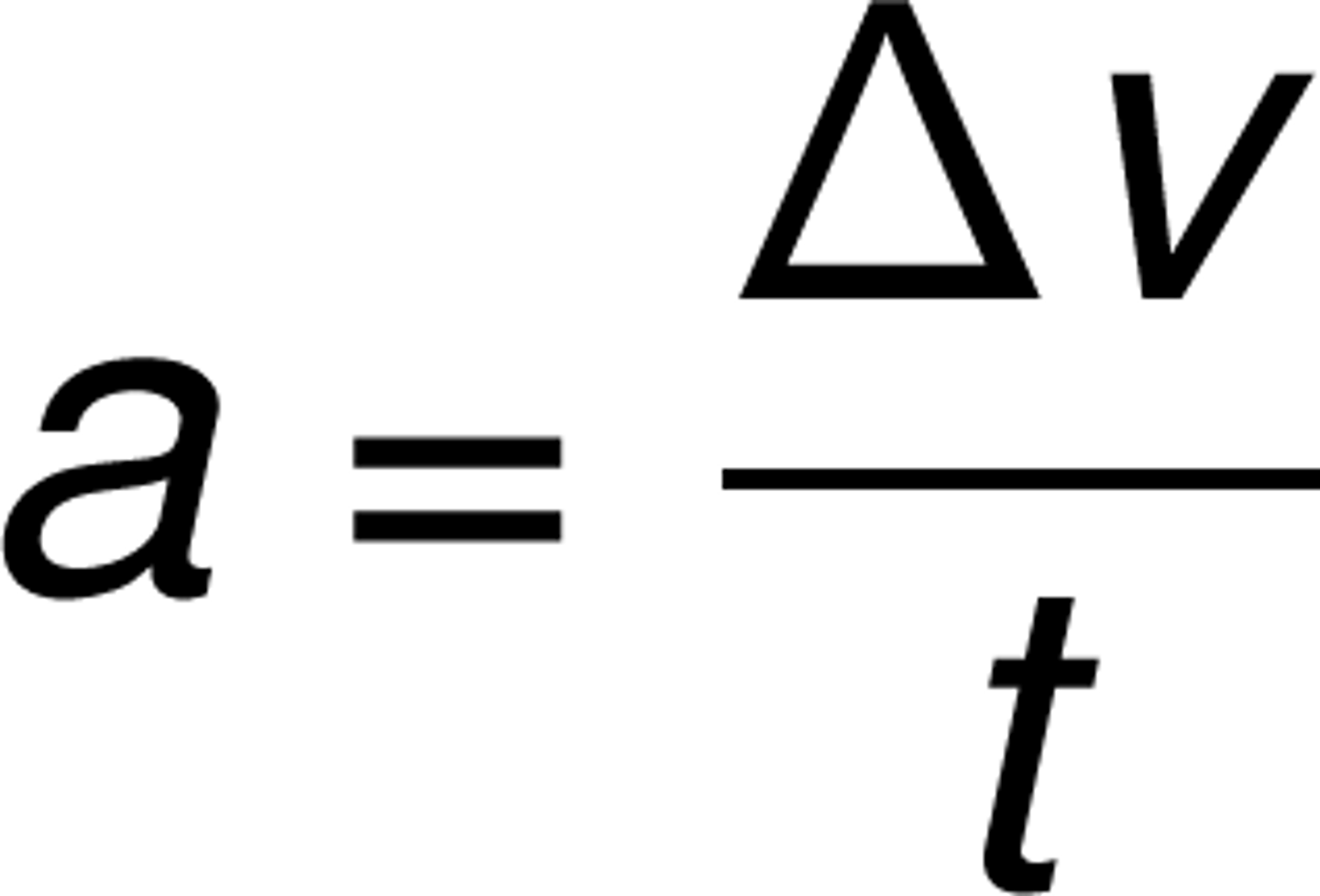
free fall
motion of an object when only the force due to gravity is acting on body

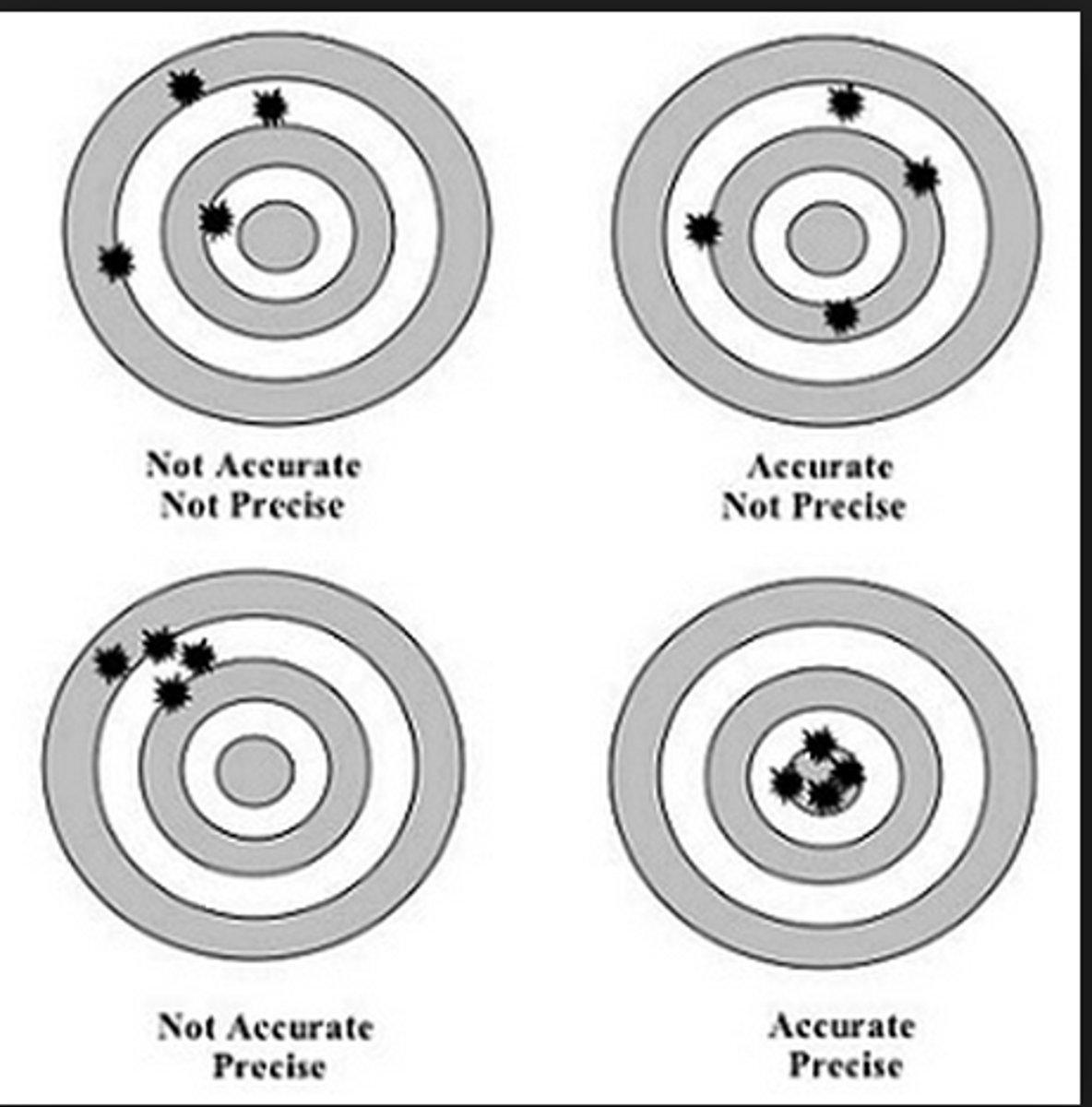
accuracy
how close a measurement is to the corrected or accepted value of quantity

precision
the degree of exactness of a measurement
hypothesis
can be tested or researched

model
plan or representation
controlled experiment
An experiment in which you change one thing (independent variable) and measure how this change affects something else (dependent variable).
