Dairy
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Dairy Production
Most is milk
much os this goes to industry
second is cheese
then cream and yogurt
then ice cream
lowest is butter
Dairy industry quotas
prevents the over production of milk
ensures the everyone is not creating wasted milk
Milk Biosynthesis
synthesized and secreted by mammary gland cells
thousands of Kg milk in pactation periods
smallest unit of synthesis is alveolus
contained in these alveoli are secretory epithelial cells
Mammary gland structure
secretory tissue with cistern at the end
in the large duct there is
blood vessels
capillaries
connective tissues
alveolus
contains myoepithelial cells
lumen,
capillaries
Secretory cell in alveoli
nulceus,
lipid droplets
free ribosomes
mitochondria etc
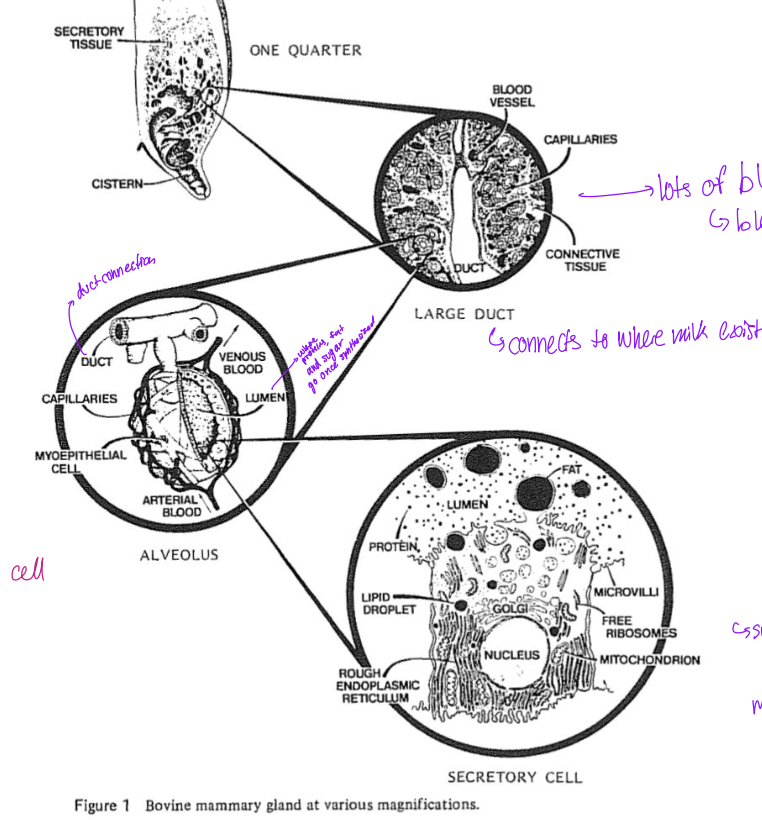
large duct of mammary gland
has lots of blood flow
this is why milk has pH similar to blood through the interaction of the two
lactose is synthesized at goli
into vesicles emptying into luminal side
connects to where the milk exits
Alveolus
duct connection
lumen is where the protein, sugar and fat go once synthesized
lactosre synthesis in individual cells
Secretory cells
golgi adds sugars and modifies products
move into lumen
then it can fuse with membrane and empty into the lumin
allows fat, sugars etc to enter the milk flow
vesicles fuse with the apical cell end and pinch into the lumen
Holstein cows
bread to produce large volumes of milk during lactation
calf stays with the mother in order to have good growth and to stimulate milk production
fed non-pesticide foods to allow for better products
Swiss dairy cows and jersey cows
well kept
jersey cows are aggressive cows
have a higher fat content and are used for clotted cream
Milking technology
modern farm technology attaches cups to milk the cows
cleaned and sanitized to ensure good quality products being made
cooling milk
milk must be reducte din temperature from 37 degrees to 4 degrees quickly
taken out of the danger zone
uses a plate heat exchanger
cold water on one side and the milk will flow over the plates to cool quickly
this is an energy efficient mechanism of cooling milk
Milk testing
must be tested for foodborne pathogens
especially Escherichia coli
is also tested for levels of fat, sugars etc
Milk composition
large proportion water 86-88%
fat 3.4-5.1%
amount depends on the cows
eg jersey cows have higher levels of fats
protein 3.6%
lactose 5.0%
has lower lactose than human milks
ash - minerals 0.7%
salts
calcium, Mg, PO4--, NaCl, citrates (citric acid salts)
Milk freezing
freezes at -0.57 degrees celcius
allows for a way to check how much water is in the product
Dairy scams
the producers make more money if they have a higher amount of product
they are also priced based on fat content
if farmers have a higher fat content milk, they could water it down to make a lower fat product that also has a hgiher volume
they can get caught cause the product will freeze at a higher temperatuer
Milk proteins
Caseins - 80%
Whey - 20%
Casein proteins
these are not very heat sensitive
will not denature below 100 degrees celsius
alpha - s caseins - 40% proteins
beta caseins - 25% of proteins
K-casein - 9%
K is glycosolated with one or more glucose on its strutcture
beta and k are both phosphorylated at the rough ER
Whey proteins
easily denatured at >70 degrtees
water soluble → heated → now insoluble
will remain on top of the milk anf form the film that is seen with heated milk products
types of whey proteins
beta-lactoglobulins
this is what is responsible for allergic reatctions to milk (not lactose intolerence)
alpha-lactablumin
Blood proteins in whey
important part of immune system antibodies
this is why it is important for calf to spend time with the mother
allows for passive immunity
collustrum in milk - yellow milk
high in antibodies to allow for apsstive immunity to beformed
Serum albumin and immunoglobulins
Milk fat and processing
remove/skim off the fat from the top
butter, cream whipped cream
want more fat in these products
residual fat can undergo honogenization
this involes forcing the fat through small holes to break them into smaller dropplets
this makes it harder for the fat to seperate and float to the top of the water preventing milk separation in higher fat milks
fat floats cause it si less dense
Minerals and salts of milk
Ca++
soluble Ca - Whey
Semi-soluble Ca with casein proteins
after digestion the formation of phosphopeptides allows it to remain soluble in the intestine
Mg++
Citrates (citric acid salts)
CaPO4
NaCl
Heating of milk
cooked flavour occurs because of the release of H2S
sulphur amino acids contain SH and SS bonds exchange and form the H2S
often in methionine and cysteine amino acids
Sulfur amino acids
methionine and cysteine
Acid and milk proteins
involved in the formation of gel/ coagulation of milk proteins
Yogurt - lactic acid
H20 gets trapped int eh gel
Milk pH of 6.6
casiens with a charge
have isoelectric point of 4.6
Casein isoelectric point (PI)
4.6
this means they are least soluble at 4.6 pH
this is related to lactic. acid production
usually htey ahve a - charge cause of the phosphate group
lactic acid production results in bonds with the - charge
hydrogen bonds neutrilize the charge
Better explination of acid and coaggulation
casiens ahve an isoelectric point of 4.6 where they are the least soluble
when making yogurt, the acid produces (lactic acid)
and the use of lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophillus results in the formation of acid
acid brings the pH down to the isoelectric point for casein proteins
this means that they will not be soluble and therefore wil coagulate and form the semisolid gel
the caseins also typically ahve a negative charge
with the acid present, the H+ ions will bind to the negative charges and result in the molecules no longer repelling one another
now they will bond
Enzymes (rennin) - rennet in lab
chymosin - liquid is the naturally occuring product
this is replaced by rennet which is biologically created
Casein proteins are found in spheres and k-casein exists within these with a phydrophobic and hyrdophillic end
the balls are called the casien micelle
rennet will cleave the hydrophili end off resulting in the individual casein molecules clustering together
this creates coaggulation and trapping of moisture within the brpduct
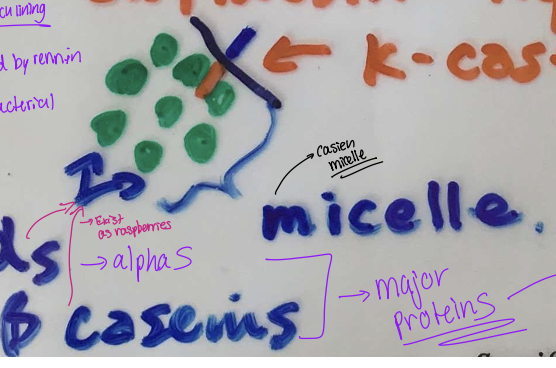
Rennet better explination
rennet is the lab grown version of chymosin
this is in a cows stomach lining
Rennet acts to cleave the hydrophillic end from the kappa-casein protein molecule that sticks out of the balls of alpha and beta caseins
this results in the micelles now binding to one another and forming a gel structure
depending on what cheese the moisture that is trapped and released may need to be removed from the product
Milk protein fouling
occurs when proteins precipitate onto the surface of the product
in a pot of sauce there is a sticking of whey proteins
denatured whey proteins
70 degrees or more
protein + Ca + lactose
all 3 precipitate in overheating of the product
Milk pasteurization
occurs 63-72 degrees and must eb careful to not denature the whey proteins
the higher temperature now used allows for a shorter duration of heating which means that the product only needs to be heated for a few seconds and therefore will minimize damage to the proteins
Skin formation on milk surface
denaturation and dehydration of the product
prevented with stirring
foaming milk will also help to prevent
Milk curdling
similar to custards
slow denaturation of whey and casein proteins → forming a gel
heating of the product to 100 degrees
temperature of casein denaturation
especually when held at this heat for long periods of time
creates a semisolid gel