AP Psychology Unit 4 Classical and Operant Conditioning ID Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:40 PM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Learning
a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience
2
New cards
John Locke
proposed the tabula rasa theory that at birth the (human) mind is a "blank slate" without rules for processing data, and that data is added and rules for processing are formed solely by one's sensory experiences

3
New cards
Environmental Determinism
A doctrine that claims that cultural traits are formed and controlled by environmental conditions.
4
New cards
John Watson
founder of behaviorism; emphasis on external behaviors of people and their reactions on a given situation; famous for Little Albert study in which baby was taught to fear a white rat

5
New cards
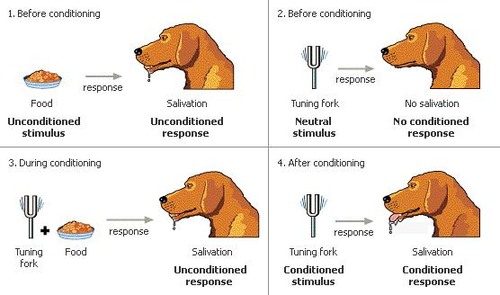
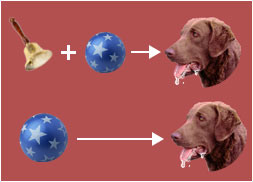
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell

6
New cards
classical conditioning
a learning process that occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired; a involuntary response that is at first elicited by the second stimulus is eventually elicited by the first stimulus alone
7
New cards
neutral stimulus
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that happens close in time with the unconditioned stimulus, but has nothing to do with it; does not naturally elicit a response

8
New cards
associative learning
learning that two events are linked together
9
New cards
stimulus response learning
learning to automatically make a particular response in the presence of a particular stimulus; includes classical and instrumental conditioning
10
New cards
acquisition
In classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
11
New cards
Unconditioned stimulus
in classical conditioning, an original stimulus that causes a response; something that elicits a natural, reflexive response

12
New cards
Unconditioned response
in classical conditioning, the unconscious response to the original stimulus

13
New cards
Conditioned stimulus
in classical conditioning, the once neutral stimulus that is associated with the unconditioned stimulus, thus learned to cause the same response; the same thing as the neutral stimulus

14
New cards
conditioned response
in classical conditioning, the unconscious response to the conditioned stimulus; the conditioning process is complete

15
New cards
contiguity
the shorter the time between the conditioned stimulus and neutral stimulus, the faster and stronger the acquisition
16
New cards
Taste aversion/Garcia effect
a type of classical conditioning in which a previously desirable or neutral food comes to be perceived as repugnant because it is associated with negative stimulation such as sickness

17
New cards
stimulus discrimination
in classical conditioning, a differentiation between two similar stimuli when only one of them is consistently associated with the unconditioned stimulus; you stop generalizing between stimuli

18
New cards
stimulus generalization
learning that occurs when stimuli that are similar but not identical to the conditioned stimulus produce the conditioned response

19
New cards
higher order conditioning
A procedure in which a neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus through association with an already established conditioned stimulus.
20
New cards
extinction
the diminishing of a conditioned response; occurs in classical conditioning when an unconditioned stimulus (US) does not follow a conditioned stimulus (CS); occurs in operant conditioning when a response is no longer reinforced.
21
New cards
spontaneous recovery
the tendency of a learned behavior to recover from extinction after a rest period
22
New cards
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorist that developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats

23
New cards
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher

24
New cards
Edward Thorndike
famous behaviorist; proposed the Law of Effect, a theory regarding the relationship between behavior and consequence

25
New cards
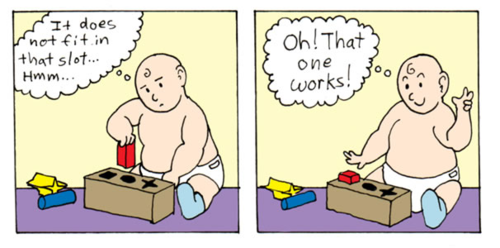
trial and error
a type of learning in which the organism successively tries various responses in a situation, seemingly at random, until one is successful in achieving the goal. across successive trials, the successful response is strengthened and appears earlier and earlier.
26
New cards
Law of Effect
Thorndike's principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
27
New cards
superstitious behaviors
behaviors that are repeated because they appear to produce reinforcement, even though they are not necessary

28
New cards
reinforcement
in operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows
29
New cards
punishment
in operant conditioning, any undesirable event that weakens the behavior it follows
30
New cards
primary reinforcement
an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need

31
New cards
secondary reinforcement
a reinforcing something that you have learned to value, like money.

32
New cards
positive reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food; any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.

33
New cards
negative reinforcement
increasing the strength of a given response by removing or preventing a painful stimulus when the response occurs

34
New cards
avoidance behavior
behavior that occurs before the aversive stimulus is presented and thereby prevents its delivery
35
New cards
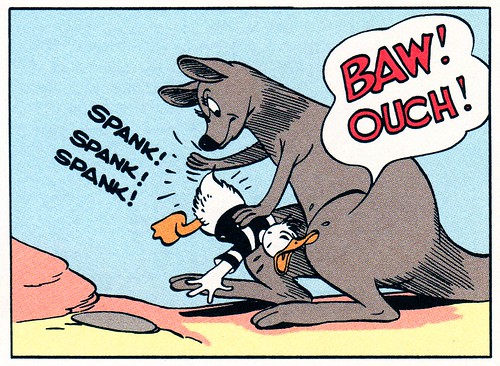
positive punishment
adding an undesirable stimulus, such as a spanking, to stop or decrease a behavior
36
New cards
negative punishment
taking away a pleasant stimulus to decrease or stop a behavior

37
New cards
escape conditioning
the process by which a subject acquires a response that results in the termination of an aversive stimulus. For example, if a monkey learns that pulling a string eliminates a loud noise; there is no warning signal before the aversive stimulus is presented
38
New cards
avoidance conditioning
training of an organism to respond so as to prevent the occurrence of an unpleasant stimulus; there is a warning signal before the aversive stimulus is presented
39
New cards
operant conditioning chamber
Skinner box; allows a researcher to study the behavior of small organisms in a controlled environment
40
New cards
schedules of reinforcement
different patterns of frequency and timing of reinforcement following desired behavior
41
New cards
continuous reinforcement
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs
42
New cards
partial reinforcement
reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement
43
New cards
ratio schedules
involve the number of behaviors that must be performed prior to reward
44
New cards
interval schedules
reinforcement after a certain amount of time has passed and the desired behavior has occurred
45
New cards
variable reinforcement
An unpredictable reinforcement schedule
46
New cards
fixed reinforcement
a predictable reinforcement schedule
47
New cards
fixed interval schedule
a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed
48
New cards
variable interval reinforcement
schedule of reinforcement in which the interval of time that must pass before reinforcement becomes possible is different for each trial or event
49
New cards
fixed ratio reinforcement schedule
set number of responses must occur before a behavior is rewarded
50
New cards
variable ratio reinforcement schedule
an intermittent schedule in which consequences are delivered following a different number of behaviors, sometimes more and sometimes less, that vary around a specified average number of behaviors
51
New cards
successive approximations
in the operant-conditioning procedure of shaping, behaviors that are ordered in terms of increasing similarity or closeness to the desired response.

52
New cards
chaining
each step of a sequence must be learned and must lead to the next until the final action is achieved