BURNS
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
what is the definition of burns?
o Cellular destruction of the skin layers and underlying tissues
2
New cards
what are the overall nursing considerations for burns
o Airway injury
o Fluid imbalance
o Sepsis
o Mobility
o Psychosocial
o Nutrition
o Wound care
o Fluid imbalance
o Sepsis
o Mobility
o Psychosocial
o Nutrition
o Wound care
3
New cards
Before securing ABC’s, what must you do FIRST?
remove pt from the site of fire
4
New cards
once pt has been removed from the source of the fire, what will you do next?
§ Focus on ABC’s
· Secure airway
· Apply O2
· Check for pulse
· Raise burn above heart level
· Secure airway
· Apply O2
· Check for pulse
· Raise burn above heart level
5
New cards
why must a burn be raised above the level of the heart?
o Blood flow can be restricted due to massive edema that occurs in burns
6
New cards
Once the pt’s ABC’s has been established what will you focus on next?
\-Decrease rate of the burn by removing any clothes or jewelry
\-IV fluids and pain management
\-IV fluids and pain management
7
New cards
what are the initial interventions for contact burns?
o Cover in clean damp towel to stop the burning process – max 10 mins
Cannot be ice!!
Cannot be ice!!
8
New cards
what are the initial interventions for chemical burns?
o Flush with water to remove chemical
9
New cards
in order for a pt to be transferred to a burn center, what criteria must be met?
o Full-thickness burns greater than 10% TBSA
o Partial-thickness burns greater than 25% TBSA
o Age older than 60
o Presence of chronic cardiac, pulmonary, or endocrine condition
o Presence of electrical burn injury
o Presence of inhalation injury or other complicated injury
o Burns to the eyes, ears, face, hands, feet, or perineum
o Burns over 20% of the body
o Partial-thickness burns greater than 25% TBSA
o Age older than 60
o Presence of chronic cardiac, pulmonary, or endocrine condition
o Presence of electrical burn injury
o Presence of inhalation injury or other complicated injury
o Burns to the eyes, ears, face, hands, feet, or perineum
o Burns over 20% of the body
10
New cards
what is an electrical burn?
a burn caused by a power line
11
New cards
what are the complications of an electrical burn?
cardiac arrest
muscle injury leading to kidney injury
falls leading to a spine injury
muscle injury leading to kidney injury
falls leading to a spine injury
12
New cards
how can an electrical burn cause cardiac arrest?
the electricity from the power line can cause cardiac dysrhythmias
13
New cards
how can an electrical burn cause Muscle injury leading to kidney injury?
the burn leads to __myoglobin’s__ being released leading to kidney damage
14
New cards
what organs will be most affected from an electrical burn
o Electricity likes water (H2O is a conductor of electricity) – so the heart, brain, kidneys will be at a greater risk than bone and fat as electricity conducts through the system
\
– expect an entrance and exit wound
\
– expect an entrance and exit wound
15
New cards
how can an electrical burn cause a fall possibly leading to a spinal injury?
o Fractures can occur d/t a fall from electrical shock and d/t intense muscle contractions fracturing the bone
16
New cards
what are the unique interventions for an electrical burn?
· C-Spine precautions
· EKG
· Assess limb movement
· EKG
· Assess limb movement
17
New cards
what are the common causes for a chemical burn?
· Household cleaners
· Acids
· Acids
18
New cards
what are the complications for a chemical burn?
· Chemical eye splashes
· Respiratory distress if it is inhaled
· Respiratory distress if it is inhaled
19
New cards
what are the unique interventions for a chemical burn?
* identify the type of chemical FIRST (priority) before irrigating with water
* Rinse eye for 20 minutes
* Rinse eye for 20 minutes
20
New cards
what is the cause for a thermal burn?
· Contact with a hot item
21
New cards
what is the Complication of a thermal burn?
· Vascular damage can stop blood flow to extremity
22
New cards
what are the unique interventions for a thermal burn?
* Elevate the burn above heart to promote circulation because Blisters can occur d/t blood flow constriction from edema preventing circulation
23
New cards
what is the cause for carbon monoxide poisoning d/t smoke inhalation?
· Inhalation of carbon monoxide smoke or fumes from being in an enclosed space with fire (Carbon monoxide will bind to the hemoglobin)
· Carboxyhemoglobin > 10% = Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
· Carboxyhemoglobin > 20% = FATAL!
· Carboxyhemoglobin > 10% = Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
· Carboxyhemoglobin > 20% = FATAL!
24
New cards
what will you assess for in a pt with *Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?*
cherry red skin (PRIORITY)
headache
confusion
headache
confusion
25
New cards
what are the unique interventions for *Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?*
· Treat CO poisoning with 100% humidified O2 with nonrebreather mask
26
New cards
what is the common cause for mechanical injury d/t smoke inhalation?
heat exposure directly to the face causing smoke inhalation
27
New cards
what is a major complication of mechanical injury?
Swelling and eschar compress the airway
o AIRWAY ISSUE – d/t trachea swelling
o AIRWAY ISSUE – d/t trachea swelling
28
New cards
what will you assess for in a pt who sustained a mechanical injury?
Singed nose hairs, smoky breath, neck facial burns, sooty sputum,
29
New cards
what is the priority assessment for a pt who sustained a mechanical injury?
· Stridor, difficulty swallowing, pulmonary edema 12-48hrs later
30
New cards
what are the unique interventions for *mechanical injury?*
* Prepare for intubation
* Assess for decrease in respiratory status (Diminished lung sounds and Crackles)
* Assess for decrease in respiratory status (Diminished lung sounds and Crackles)
31
New cards
How can an airway issue be prevented for a pt with a mechanical injury?
* If you pick up the singed hair (burned hair) early, let the provider know and prepare for intubation b/c It is easier to intubate the pt before the edema in the trachea begins
32
New cards
what is a full thickness burn?
3rd degree burn
33
New cards
what are the S/S of a pt with 3rd degree burn?
· Dry, leathery, hard skin
· No pain or minimal sensation
· No pain or minimal sensation
34
New cards
why does a pt with 3rd degree burn have no pain?
**o d/t nerve damage – no blood supply**
35
New cards
how is a 3rd degree treated?
with a skin graft sx d/t no blood supply and not being able to regenerate on its own
36
New cards
what are the locations of 3rd degree burns?
· Face
· Neck
· Chest
· Back
· Neck
· Chest
· Back
37
New cards
what causes an airway obstruction in burns?
**Edema or eschar**
38
New cards
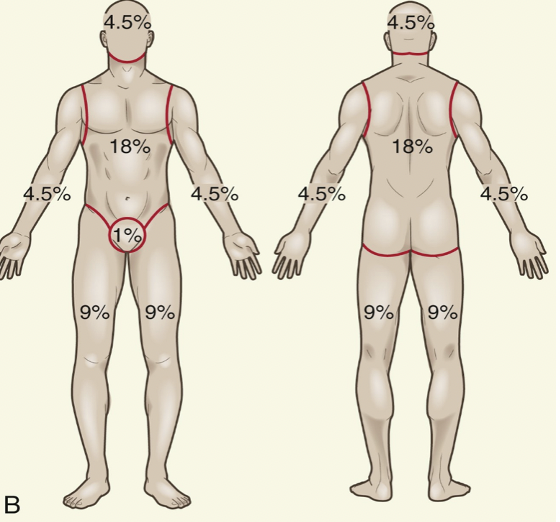
how will you measure the extent of a burn?
with rule of 9
39
New cards
what is rule of 9?
o TOTAL head (front and back): 9%
o TOTAL arm (each, front and back): 9%
o Total leg (each, front and back): 18%
o Total trunk (front and back): 36%
o TOTAL arm (each, front and back): 9%
o Total leg (each, front and back): 18%
o Total trunk (front and back): 36%
40
New cards
what are the S/S of a partial thickness 1st degree burn?
* Red, blanchable blisters
* Painful blisters
* Can regenerate
* Painful blisters
* Can regenerate
41
New cards
what are the S/S of a partial thickness 2nd degree burn?
· Moderate edema
· Wet
· Shiny
· Severe pain
· +/- eschar
· Can regenerate
· Wet
· Shiny
· Severe pain
· +/- eschar
· Can regenerate
42
New cards
what are the locations of a 1st or 2nd degree burn?
the Extremities causing permanent self-care limitations
43
New cards
what is the definition of emergent phase?
Initial tissue injury, fluid shifts into the tissue, vasculature is left dry
Occurs in the first 24-48 hours
Occurs in the first 24-48 hours
44
New cards
what will you assess for in emergent phase of a burn?
Airway
edema
hypotension
hyperkalemia
High hemoglobin and hematocrit
edema
hypotension
hyperkalemia
High hemoglobin and hematocrit
45
New cards
why do you see edema and hypotension in the emergent phase of a burn?
* Fluid leaks out into the 3rd space causing the BP to drop
* pt will be on fluid volume deficit
* pt will be on fluid volume deficit
46
New cards
why do you see hyperkalemia in the emergent phase of a burn?
o Tissue damage d/t potassium being released
o Potassium lives inside the cell and the burn causes potassium to break out of the cell and into the body
o Potassium lives inside the cell and the burn causes potassium to break out of the cell and into the body
47
New cards
what must a pt with hyperkalemia be on during the emergent phase of a burn?
on a cardiac monitor
48
New cards
why do you see high hemoglobin and a high hematocrit in the emergent phase of a burn?
d/t blood being concentrated from leaking fluid
49
New cards
what will you administer to a pt who has a high hemoglobin and a high hematocrit in the emergent phase of a burn?
o Isotonic Fluids - LR or 0.9% NS
50
New cards
what is the definition of acute care phase?
· Signals fluid shift out of tissue and into vasculature - Edema goes down, fluid moves back into blood vessels
· Occurs from 36 hrs – several weeks
· Occurs from 36 hrs – several weeks
51
New cards
what will you assess for in acute phase of a burn?
diuresis
hypokalemia
diluted hyponatremia
hyperglycemia
Constipation or diarrhea
hypokalemia
diluted hyponatremia
hyperglycemia
Constipation or diarrhea
52
New cards
why do you see diuresis, hypokalemia, and diluted hyponatremia in the acute phase of a burn?
d/t fluid administration during the emergent phase
53
New cards
why do you see hyperglycemia in the acute phase of a burn?
o r/t stress
o when the body is stressed, the body will release cortisol making the glucose rise
o when the body is stressed, the body will release cortisol making the glucose rise
54
New cards
what are the interventions for the acute phase of a burn?
· Administer PPI’s to prevent stress ulcers - AKA Curling’s ulcer
· Begin PT/OT
· Passive/Active ROM
· Begin PT/OT
· Passive/Active ROM
55
New cards
what are the complications that can occur during the emergent phase?
hypovolemic shock
edema
hypothermia
hyperthermia
edema
hypothermia
hyperthermia
56
New cards
why can hypovolemic shock (complication) occur during the emergent phase?
d/t No volume in blood vessels
57
New cards
what are the priority assessments of hypovolemic shock (complication) during the emergent phase?
· Hypotension - d/t no volume
· Tachycardia - d/t body trying to compensate
· Tachycardia - d/t body trying to compensate
58
New cards
what are the interventions of hypovolemic shock (complication) during the emergent phase?
* Administer IV fluids - Isotonic – LR or 0.9% NS
* Monitor for fluid overload in clients with CHF
* Insert foley if burns are >15%
\
NOTE: calculate with parkland (baxter) formula
* Monitor for fluid overload in clients with CHF
* Insert foley if burns are >15%
\
NOTE: calculate with parkland (baxter) formula
59
New cards
what is the parkland (baxter) formula?
o 4 ml x ____ kg X ___ (% TBSA) burned = ______total ml in 24 hours
\
o ½ in first 8 hr, 1⁄4 of total in second 8 hr, 1⁄4 of total in third 8 hr
\
o ½ in first 8 hr, 1⁄4 of total in second 8 hr, 1⁄4 of total in third 8 hr
60
New cards
what is the goal when administering Iv fluids for hypovolemic shock (complication) of the emergent phase?
A 0.5-1.0 mL/kg/hr of urine output
61
New cards
why can edema (complication) occur during the emergent phase?
§ Inflammatory cytokines released due to injury (immune response) > Increased capillary permeability means that water, sodium, plasma proteins (albumin!!), moves into interstitial space (third spacing)
§ Loss of albumin causes more fluid shifting > massive hypovolemia and edema
§ Loss of albumin causes more fluid shifting > massive hypovolemia and edema
62
New cards
what is hypothermia?
temp < 96.8
63
New cards
why can hypothermia (complication) occur during the emergent phase?
d/t fluid evaporation from wet/open wounds
64
New cards
what are the interventions for hypothermia (complication) during the emergent phase?
· Warm humidified O2
· “tropical” room – 85 degrees
· Warming blankets
· Bear hugger
· Keep wounds covered
· Wear PPE!
· “tropical” room – 85 degrees
· Warming blankets
· Bear hugger
· Keep wounds covered
· Wear PPE!
65
New cards
why can hyperthermia (complication) occur during the emergent phase?
§ may occur due to increased metabolism or infection
§ Expected for several weeks
§ Expected for several weeks
66
New cards
why must a pt in the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn be on an “aggressive” nutrition diet?
to decrease mortality
\-started on day 1 or 2
\-started on day 1 or 2
67
New cards
what type of diet will a pt be on if the TBSA is < 20?
§ Oral nutrition
· High protein diet
· High carbs
· High calories
· High protein diet
· High carbs
· High calories
68
New cards
what type of diet will a pt be on if the TBSA is > 20 or is intubated?
§ Enteral nutrition (preferred)
69
New cards
what do open burns increase?
metabolic demands
70
New cards
who calculates the caloric needs for a burn pt?
dietician
71
New cards
what will you assess for in a pt in the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn when it comes to the GI?
for diarrhea and ileus
72
New cards
what is a pt at risk for in the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn when it comes to the GI?
§ gastroparesis or paralytic ileus d/t reduced blood flow to the GI tract so check for complications of feeding (abdominal distension, vomiting, etc.)
73
New cards
What are the mobility interventions during the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn pt?
o Splinting to decrease skin contractures
o Keep limbs straight
o Relieve pressure - Turn every 2 hours
o Keep limbs straight
o Relieve pressure - Turn every 2 hours
74
New cards
What are the wound care interventions during the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn pt?
o Full PPE for open burns (Gloves, gown, mask)
o Remove old dressing with clean gloves
o DON sterile gloves
o Cleanse with saline - Gently debride necrotic tissue to promote wound re-epithelization
o Cover with silver product
o assess for infection during each dressing change
o Remove old dressing with clean gloves
o DON sterile gloves
o Cleanse with saline - Gently debride necrotic tissue to promote wound re-epithelization
o Cover with silver product
o assess for infection during each dressing change
75
New cards
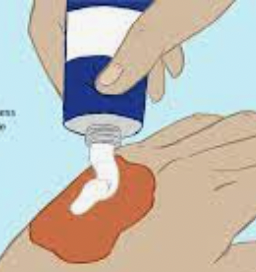
what is “silver product” used for in a pt with a burn?
to prevent bacteria from growing d/t the antimicrobial properties
THIS IS NOT AN ANTIBIOTIC!!!! it is an ointment
THIS IS NOT AN ANTIBIOTIC!!!! it is an ointment
76
New cards
why arent pts on prophylactic ABX during the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn?
b/c it is only used for an active infection
77
New cards
What are the client teaching for pruritus during the emergent and/or acute phase of a burn pt?
educate to pat instead of scratch
78
New cards
what medications will a pt be on during a burn?
* narcotics for pain (PCA Pump)
* Topical ointments - Silver impregnated dressed, silvadene ointment
* ABX Topical - remember ABX is only for an active infection
* IV fluids - 0.9% NS or LR (Isotonic)
* Tetanus immunization
* VTE - enoxaparin/heparin
* Mechanical VTE
* Topical ointments - Silver impregnated dressed, silvadene ointment
* ABX Topical - remember ABX is only for an active infection
* IV fluids - 0.9% NS or LR (Isotonic)
* Tetanus immunization
* VTE - enoxaparin/heparin
* Mechanical VTE
79
New cards
why does a pt need a tetanus vaccine for a burn?
to prevent a bacterial infection
80
New cards
why does a pt need to be on VTE meds?
§ Enoxaparin/heparin
§ To prevent thrombus and clots
§ To prevent thrombus and clots
81
New cards
why does a pt need to be on mechanical VTE ?
§ AKA Compression devices
§ To prevent thrombus and clots
§ To prevent thrombus and clots
82
New cards
what are the surgical procedures for a burn?
surgical skin graft
escharotomy
escharotomy
83
New cards
what is a surgical skin graft for in a pt with a burn?
§ Replaces skin that will not regenerate on its own
§ For 3rd degree burns – full thickness
§ For 3rd degree burns – full thickness
84
New cards
what is a surgical escharotomy for in a pt with a burn?
to prevents necrosis
85
New cards
what is the indication of a Surgical Thoracic Escharotomy?
o ventilatory failure
o Used to relieve pressure from edema to allow circulation or chest expansion for respiration
o Used to relieve pressure from edema to allow circulation or chest expansion for respiration
86
New cards
what is the focus of rehab care for a pt with a burn?
o Psychosocial
o Physical Therapy
o Physical Therapy
87
New cards
what is the focus of psychosocial rehab care for a pt with a burn?
§ Body image
§ Fear
§ Hopelessness
§ Sexual dysfunction
§ Encourage pt to discuss
§ Encourage counseling
§ Encourage independence
§ Never ask why - therapeutic communication only
§ Fear
§ Hopelessness
§ Sexual dysfunction
§ Encourage pt to discuss
§ Encourage counseling
§ Encourage independence
§ Never ask why - therapeutic communication only
88
New cards
what is the focus of physical therapy for a pt with a burn?
§ Pressure wraps aid circulation and prevent scarring
§ Scarring causes skin contractures - Treated with splinting and pt must Avoid bending joints
§ Scarring causes skin contractures - Treated with splinting and pt must Avoid bending joints