Accounting Reports & Analysis - Week 11
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Business Sector Decisions
These are all decisions that people have to make when running a business.
But in order to make good decisions, you need good information.
Cash flow management example:
If you want to out and buy a brand new machine tomorrow, do you have the finances for it? Do you actually have cash in the bank right now to go buy that new thing?
If you don't, what decisions do you have to make?
Go to the bank and get a loan, what if something that is crucial to your business pops up and you cannot buy it because you've now utilized all your cash on something else.


Decisions in Action
Dynamic pricing: price changes depending on demand
E.g. Uber
Seasonal prices:
Ice cream
In summer consumers are more willing to pay a premium price for ice cream
These are all decisions made by management

Types of costs: CVP
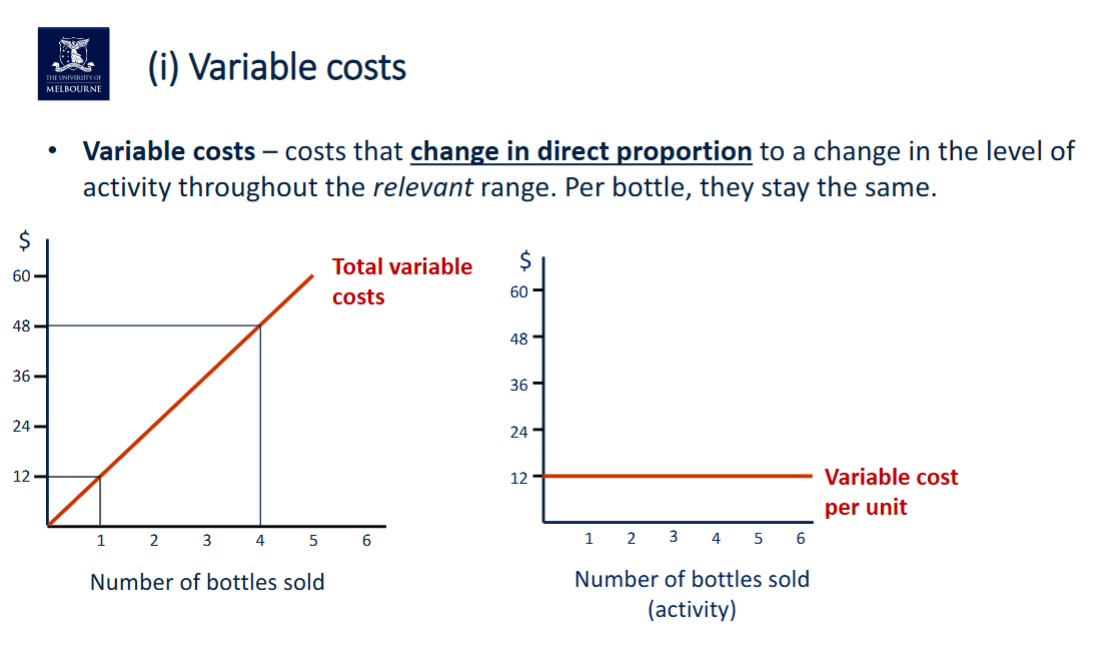
Variable costs: Costs that vary in total based on the number of bottles sold.
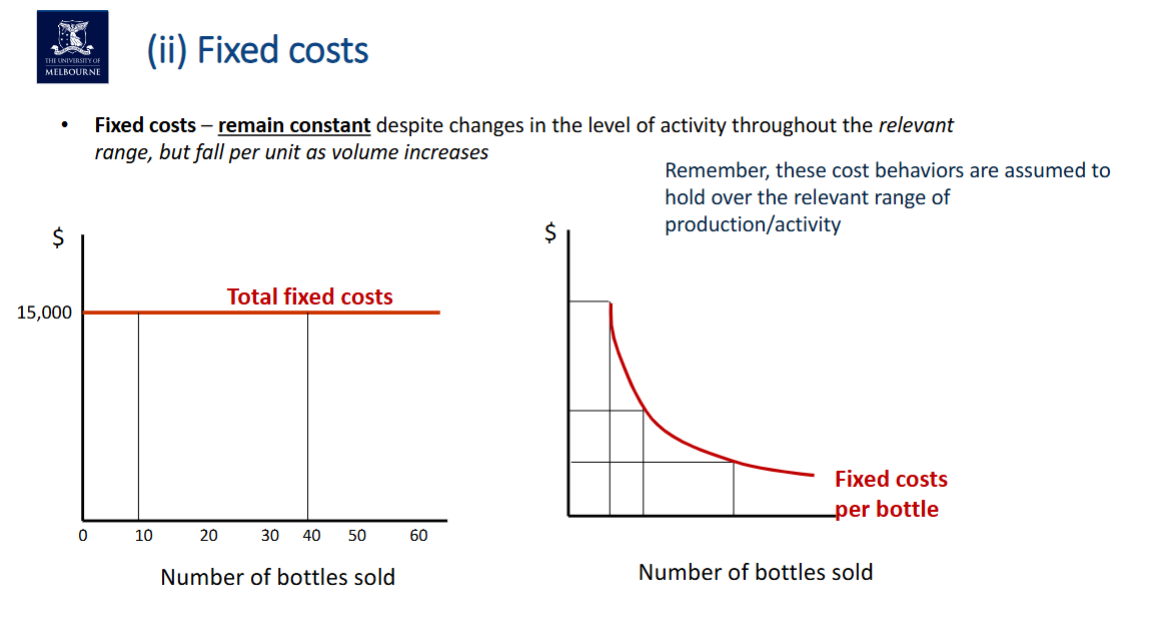
Fixed costs: Costs that DO NOT vary in total vary in direct proportion to a change in the number of bottles sold.
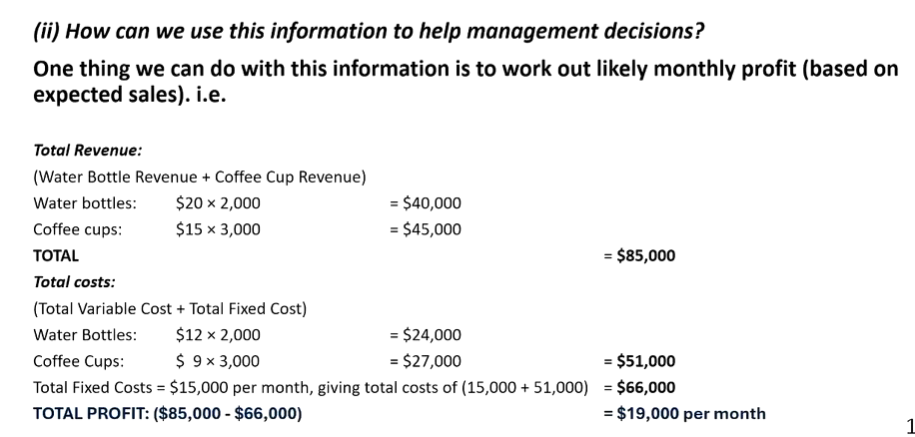
Is $19,000 per month a good profit?
Based on this is appears that the business is profitable for now… but note:
This is based on expected sales volume and prices
Are those expectations reasonable? Will they hold? What about competition?
Will cost behaviours really hold for the relevant range?
What are alternative outcomes for this investment?
What if our assumptions are wrong? How will we know when our assumptions are wrong?
What is the opportunity cost of producing water bottles?
Since all our figures are expectations, is it possible that we will sell 2000 coffee cups per month?
What if we only sell to UniMelb students and in a couple of months every student has their own cup?
Contribution Margin
Contribution margin: how much revenue do we have after deducting variable costs from sales revenue?
In other words, of the revenue that we've generated, once those necessary costs have been deducted, how much is left for us to pay the fix costs before we generate a profit.
Can be expressed per unit or overall
This can be used in various calculations
A negative contribution margin, means we are losing money every single time we sell a water bottle.
If you're selling a greater variety of products, are you opening up your customer base?
It depends on your constraints
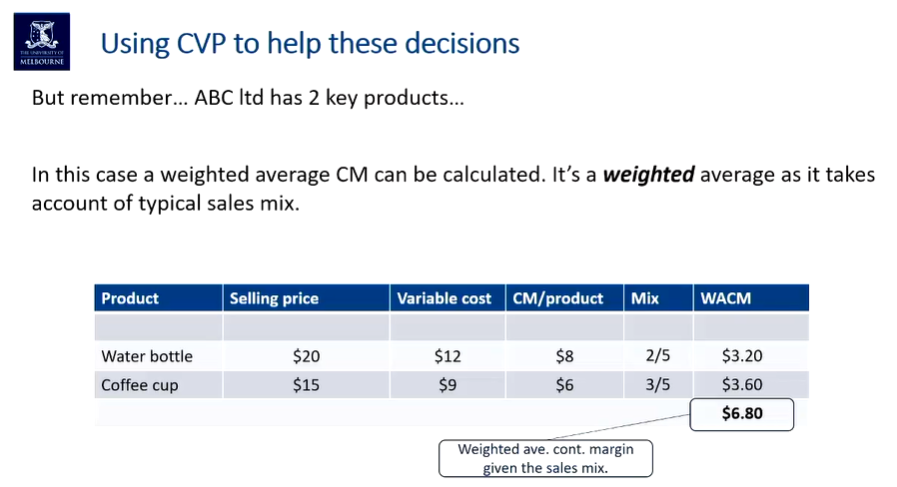
Weighted Average Contribution Margin
Why do we need this weighted average contribution margin?
What is the WACM if we reduce the wattle bottles and coffee cups to introduce new products for new customers to buy? What is going to be that WACM?
What is the WACM for a new product?
Is this going to result in opportunity loss or gain
Break-even point
In order for us to sell our products, we need to spend $34,000 every single month

Break Even Formula
Time Break Even = Annual Fixed Costs / Total monthly CM
Unit Break Even = Annual Fixed Costs / WACM per unit
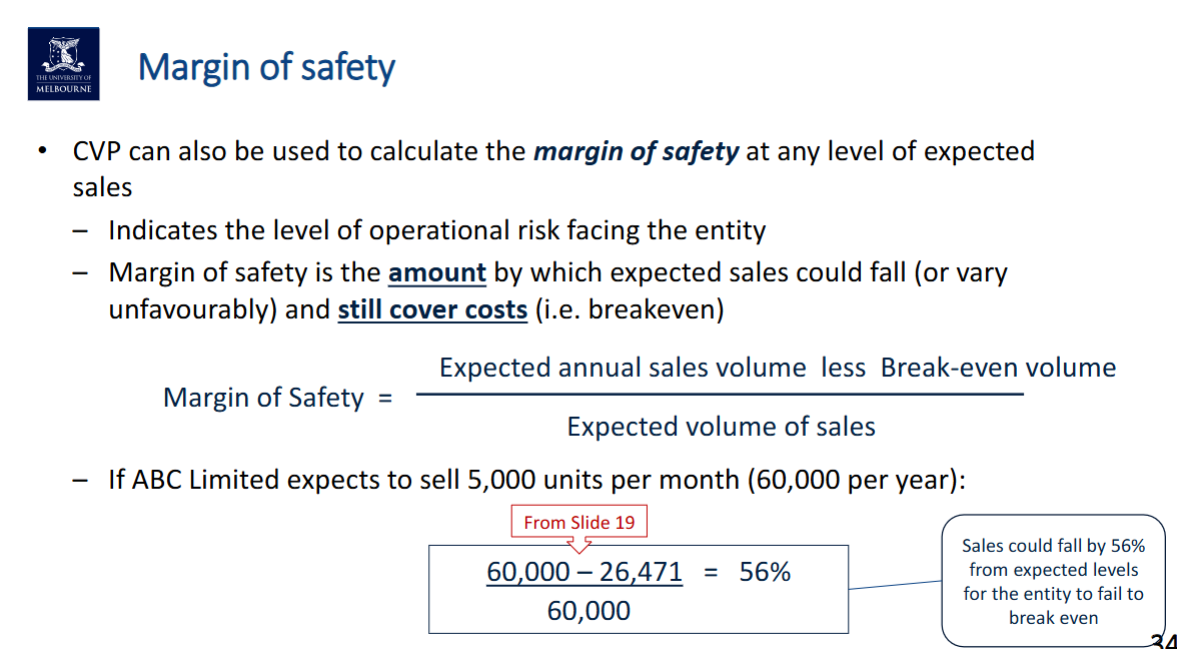
To understand whether the break even is realistic a margin of safety can be calculated.
What break even point means?
At your current selling price and at your current selling volume you will break even in our business after 5.3 months.
After selling 26,471 units, we have broken even.
We need to sell 10.589 bottles and 15,883 cups each month to break even
Desired Profit
Sales volume (units) = (Fixed costs + Desired profit before tax) / WACM margin per unit
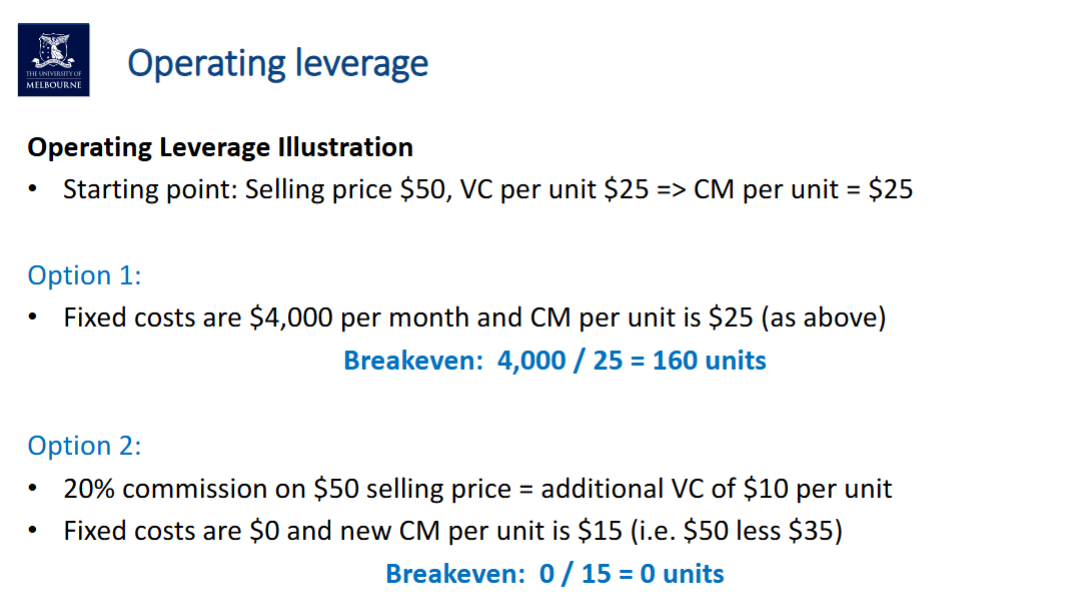
Operating Leverage
Refers to the relative mix between fixed and variable costs in the entity's cost structure
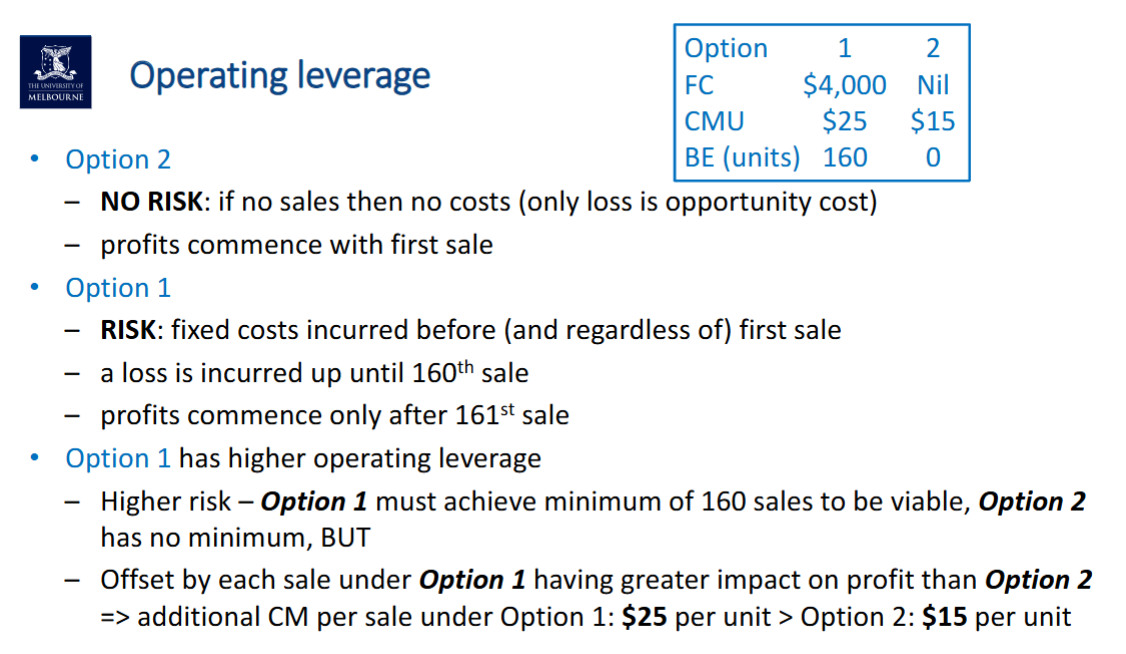
Entities with higher levels of fixed costs relative to variable costs are said to have higher operating leverage
Higher FC means higher sales are required to break-even
BUT, once break-even is achieved, the impact of additional sales is more significant => leverage (LOWER VC => HIGHER CMU)
The reverse also applies - a decline in sales will have a greater adverse impact
Higher operating leverage => less agility and higher operating risk
Industries with high operating leverage:
Airlines
Hardly any flights during COVID
Lots of fixed costs
Tollways
Entertainment venues
Universities
Extremely high fixed costs
Did not disappear during COVID like staff salaries.
Pivoted to online and fixed costs like tutorial staff were reduced

Outsourcing (make or buy) decisions
Whether to make a product (or service) or outsource to an external party
Compare the cost of outsourcing to the benefit of any cost savings
Special order decisions
Whether to accept a one-off order that differs from normal orders
If idle capacity, then can increase output with no change in fixed costs - generate additional profit
If no idle capacity, then need to consider the opportunity cost of taking the order
CVP assumptions
All costs can be classified as fixed or variable and mixed costs can be separated into their variable and fixed components
Cost and revenue behaviors will hold constant over the period and over the relevant range of activity
All unit selling prices, unit variable costs, fixed costs, and sales mix are as expected and remain constant
Production / purchases during the period = Cost of sales
Variable Costs Appendix
Fixed costs Appendix
Operating Leverage #1

Operating Leverage #2
Operating Leverage #3
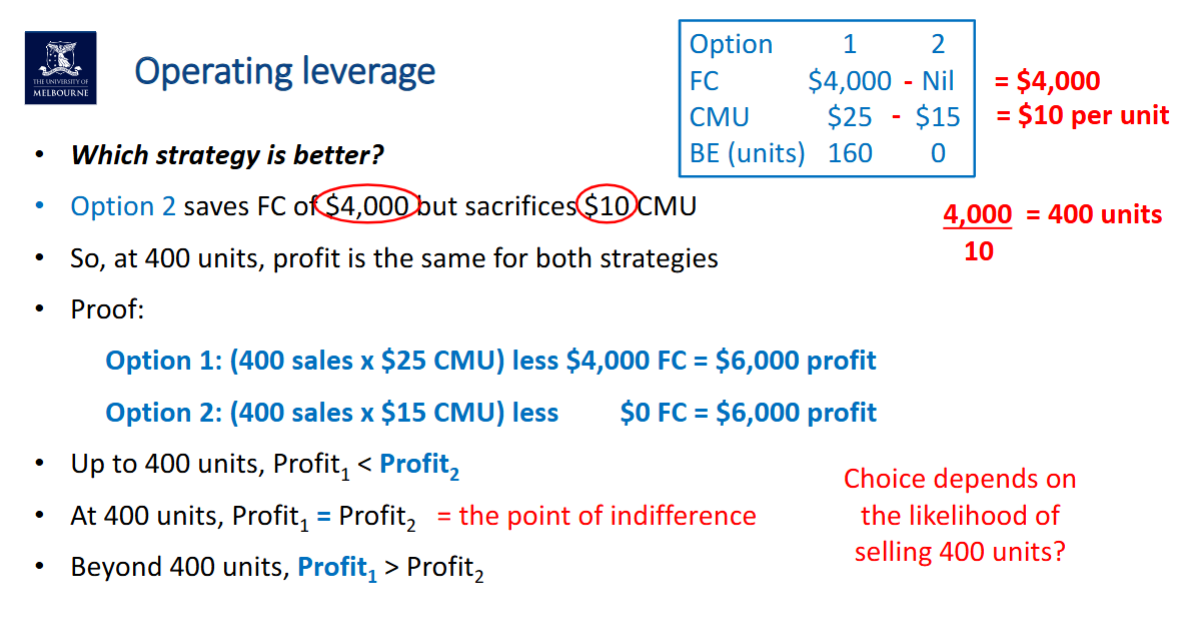
Operating Leverage #4
Margin of Safety