Pathophysiology final- TTU- Dr. Gollahon
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
266 Terms
1. Vascular resistance
2. blood viscosity
3. turbulence
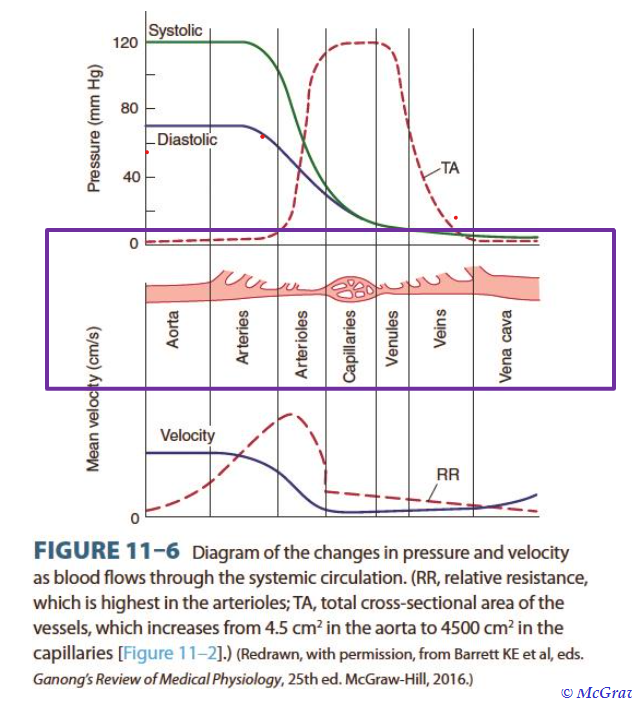
note the changes in velocity and pressure
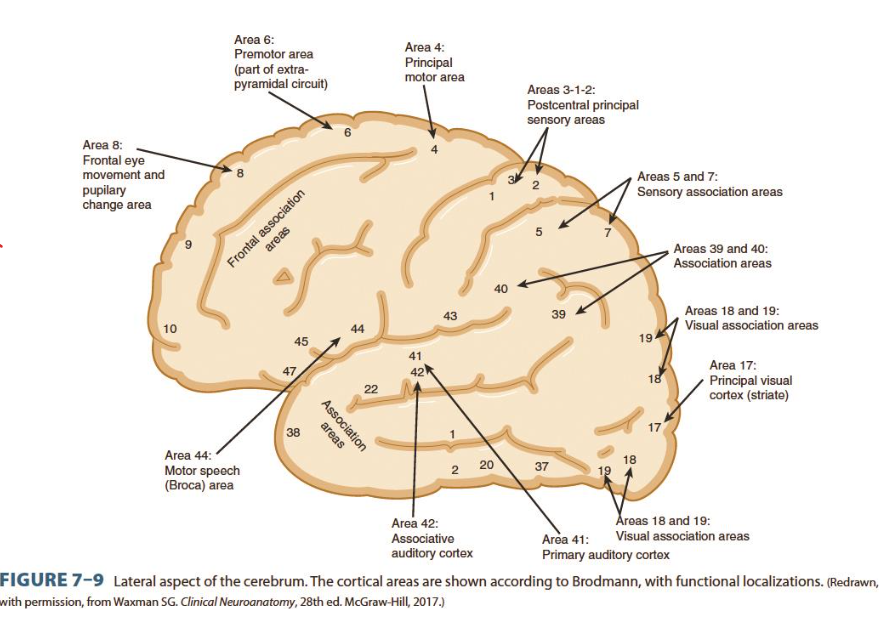
brain areas and corresponding function
friction created by eddies and swirls that cause high flow rates, irregular surfaces, and sudden changes in diameter that disrupt uniform flow
A. Intracellular fluid
B. extracellular fluid
1-interstitial fluid
2-intravascular fluid
3-lymph, synovial, intestinal, pleural, peritoneal, pericardial, intraocular fluids
4-CSF, sweat, urine
1) Heart (volume rate/velocity)
2) Kidneys (renin/vasoconstriction)
3) blood vessels (vasoconstriction)
remove CO2 and WASTE
- primary ECF CATION (+)
- regulates OSMOTIC FORCES (water)
- roles in acid-base balance, chemical reactions, membrane transport
- primary ECF ANION (-)
- provides electroneutrality (neutral substance charge)
Renin- Aldosterone- Angiotensin System
aldosterone- sodium (and H2O) reabsorption angiotensin- promotes aldosterone secretion Renin- vasoconstriction
Atrial Natriuretic peptides- secreted by atria
response system to changes in the chemicals in blood or CSF
1) CO2
2) Oxygen
3) pH levels
response system to cardiovascular regulation, and cardiac output and peripheral resistance (how much blood is being pumped and at what pressure)
- carotid sinus
- aortic sinus
- wall of right atrium
Primarily High BP which can lead to:
1) Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
2) Obesity
3) Arteriosclerosis
4) Stress
- Skeletal Muscle
- Heart
- Skin
- Total output
- Kidney
- Abdomen
- Misc.
consistently high BP
- systolic >140 or
- diastolic >90
Diagnosing Hypertension
70 million people UNdiagnosed
must have high BP readings months apart (different doctor visits)
- Idiopathic
- may be genetic or environmental
- 92-95% all hypertension patients have primary
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
- RAAS
- Natriuretic Peptides
- RAAS-blocking
Drugs:
ACE, Renin, ARB, and Aldosterone inhibitors
Malignant Hypertension
Rapidly progressive Hypertension
Diastolic > 140 causes organ damage due to high pressure tearing organs
-Chronic hypertensive damage to blood vessels and tissues - leads to target organ damage (heart, kidney, brain, and eyes)
-Myocardial hypertrophy
Genetic and Environmental vulnerabilities - cause neurohormonal dysfunction in SNS, RAAS, and Natriuretic peptides
- promotes inflammation
- creates insulin RESISTANCE
Secondary hypertension
-caused by systemic disease (infects entire body)
-raises peripheral or
-resistance or cardiac output
could be renal vascular or parenchymal disease, tumors, or drugs
100%, all-or-none response
faster at transmitting signals
slower at transmitting signals
- cardiac muscle
- skeletal muscle
- smooth muscle
- glands
- Na OUTSIDE cell
- more positive outside cell
- K INSIDE cell
- less positive inside cell
membrane potential = -70mV
- action potential stimulus causes channels to open, Na IN, K OUT, inside cell becomes MORE POSITIVE, reaches point to send action potential to next cell
- made by schwann cell
- wrap around axon to keep electrical charges concentrated around axon
- makes for faster action potential
- Na initiates depolarization
- Ca stimulates neurotransmitter release
- imbalance in these chemicals messes up neural function
- drugs can either intervene on the Pre-synaptic or Post-synaptic terminals to work
Neural Activity is Multi-modal (multiple means of working): CHEMICAL
neurotransmitters (ligands) bind to receptors
ex. dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine
Neural Activity is Multi-modal (multiple means of working): ELECTRICAL
ion charges can encourage or inhibit activity down an axon
ex. Na/K activity in axon encourage
Cl inhibits activity
Neural Activity is Multi-modal (multiple means of working): MECHANICAL
pressure on membranes or membrane distortion causes depolarization
1)chemical
2)electrical
3)mechanical
multiple places were neurons can go wrong and be modified
excitatory, when the ligand binds to receptor, it causes ions to enter and depolarize cell
ex. norepinephrine
ligand binds to receptor and keep membrane potential below -70mV, repressing impulse
ex. GABA
- Purely neural- problem in brain/cerebrum
- Somatosensory and somatomotor- faulty connection in nerves throughout body and signals
cerebrum is affected
1) Trauma- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
affects memory and emotions
2) Aneurysms- Stroke
affects Broca (speech) Area 4 (motor) Wernicke (understanding speech)
3) Consciousness, Cognition, Awareness- trauma, medication, drugs
can be structural or non-structural
Physical damage to brain
ex. concussion, blunt force trauma to brain
ex. drugs inhibit action potential reaching the the next postsynaptic terminal
Incoming Signals
Outgoing signals
or the ability to correctly interpret said signals
swelling on brain that is placing pressure on a certain section of brain, causing inflammation, cell damage, and/or loss of function in said area
how the brain is being compressed determines what brain functions are influenced/inhibited
some examples:
- drugs
- cerebral ischemia
- hyperglycemia
- hypoglycemia
- hypoxia
- seizure
- hypothyroidism
Purely Neural v. Somatosensory/motor
Degenerative changes:
only somatosensory/motor, mostly changes (irreversible damage) in myelin
metabolic imbalances
BOTH
structure changes
BOTH
cancers
BOTH
Inflammation
BOTH
Pathophysiology of Selected Neural Disorders Continued
can be hyperactive(seizure) or under active (post stroke)
functional disorders- what body/brain function affected is dependent upon which NEURAL NETWORK is affected
ALS- upper and lower motor
Parkinson-dopaminergic (dopamine release), motor system
Ischemic stroke- large areas of brain
Gaits- very different from each other, very informative
both arms or both legs are affected, often spazzing
foot movement is weakened causing foot drop, looks like foot is pointing
described as waddling, weakness in pelvic muscles that would keep pelvis horizontal during walk, pelvis droops on one side
severe muscle rigidity, patient remains in hunched over posture, takes small steps, struggles to initiate steps
Parkinson posture- stooped head, small steps, tuck hands at sides, hunched over
irregular, jerky movements in all extremities
feet sensory fails to detect when foot has made contact with ground, patient slams foot into ground to sense it.
wide gait, clumsy movements, patients body swings from side-to-side as they walk
-ataxic gait
-truncal gait (needs arms for support)
-Dysmetria (no smooth coordination, cant do finger to nose touch)
-limb ataxia (uncoordinated limb tremor, slows movement down to compensate)
-vertigo (spinning dizziness)
-static and kinetic tremors (shaking when still or moving)
- cerebellar dysarthria (slurred speech)
-Nystagmus and ocular dysmetria (shaking eyes, eyes unable to focus)
dependent on:
1) human host
2) which infectious agent
3) exogenous or endogenous environmental factors
KEY FACTOR-
how susceptible the patient is to disease
leading causes of death GLOBALLY
- significant morbidity and mortality
- elderly
- very young
- immunocompromised
- disenfranchised
someone or something that carries the disease and can pass on to others
includes animals, people, objects, and food
animals carrying infectious agents and even amplifying it
ex. rats and the black plague, mosquitos and malaria
microorganism in the body, don't cause harm, and can even prevent infection
an infection that is not obvious in a patient, may be hard to diagnose
steps of causative agent (pathogen that causes illness)
1) encounter host
2) enter host
3) multiply and spread at entry site
4) cause tissue injury in host
- directly (cytotoxin) indirectly (inflammation response from body)
1) acute (rapid, onset)
2) subacute (in the middle)
3) Chronic (long, drawn out)
1) Resolve (recovery)
2) Chronic Infection
- active (parasitic)
- prolonged asymptomatic excretion of agent (agent is being produced in body for period without patient knowing)
- latency of agent within host (sleeps for a time then awakes)
3) Death of Host