Hearing Science (Washnik)
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
8/25 & 9/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Oscillation
-A motion in which an object shows regular fluctuation in value, position, and/or state about a mean value
In Oscillation, there is no…
irregular movement
Oscillation is like a…
Pendelum (# of cycles per second)
Oscillations increase when what increases?
Speed
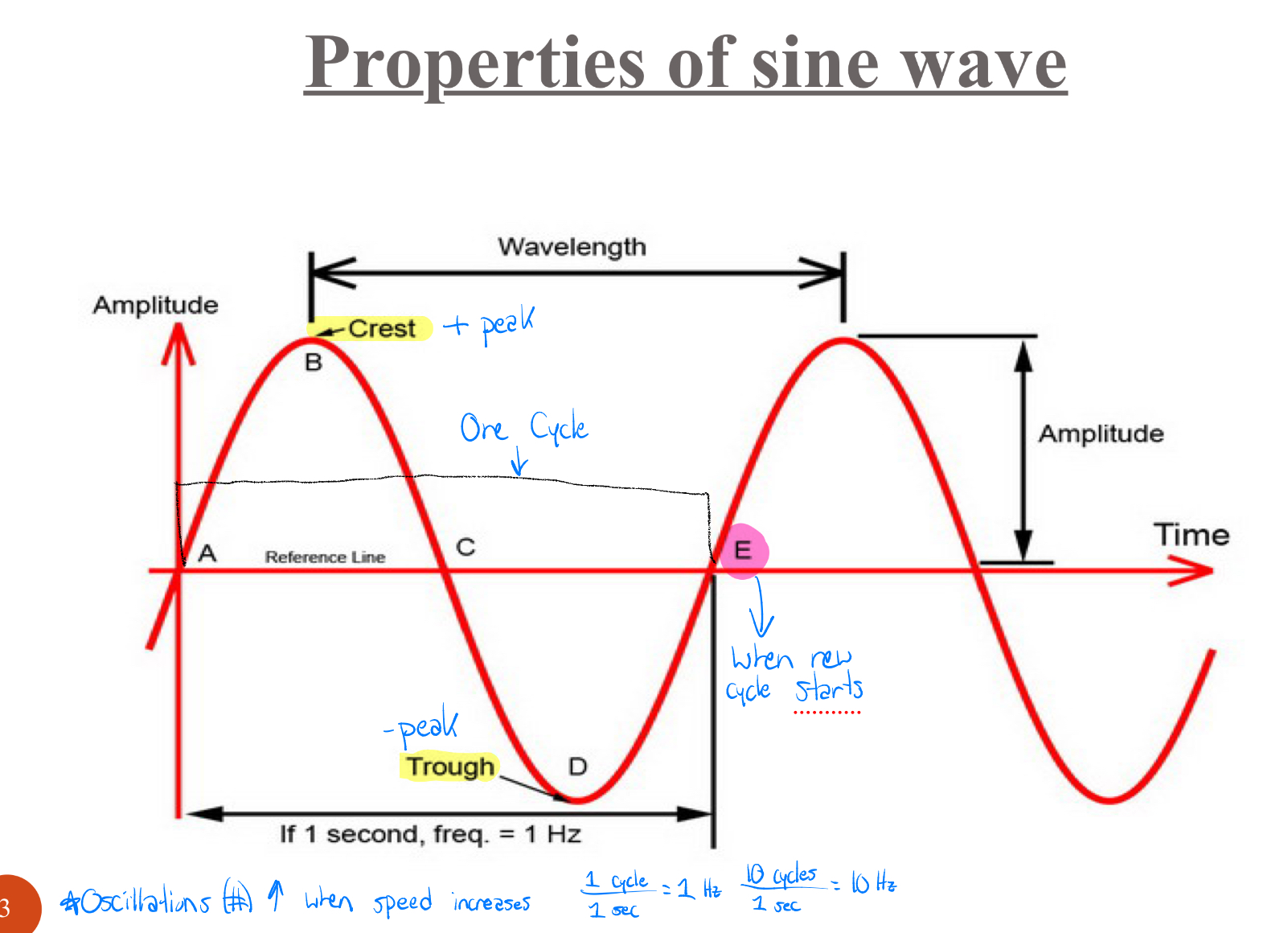
Draw the properties of a sine wave
*Answers in powerpoint because they won’t let me add a picture
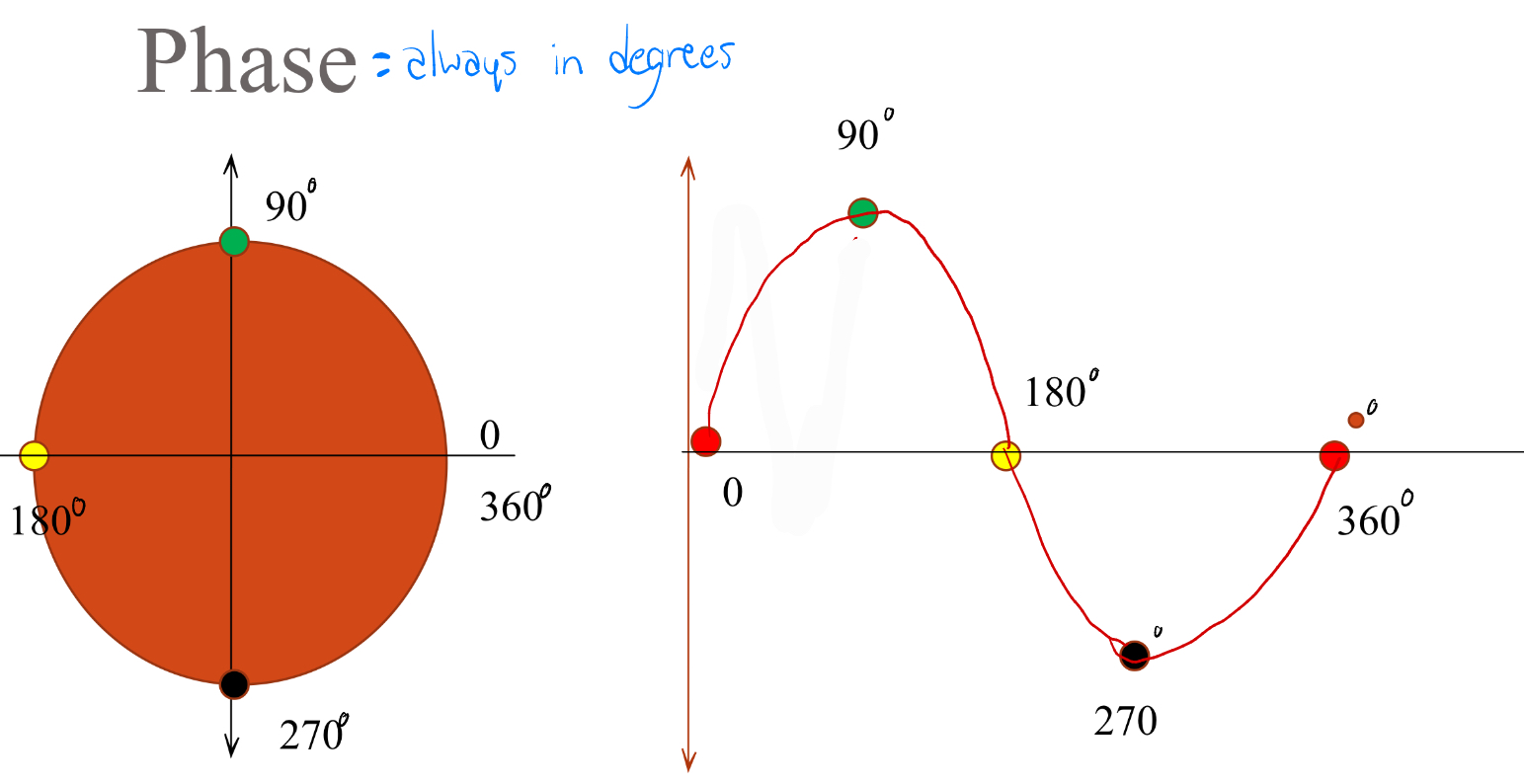
Phases are always in…
Degrees
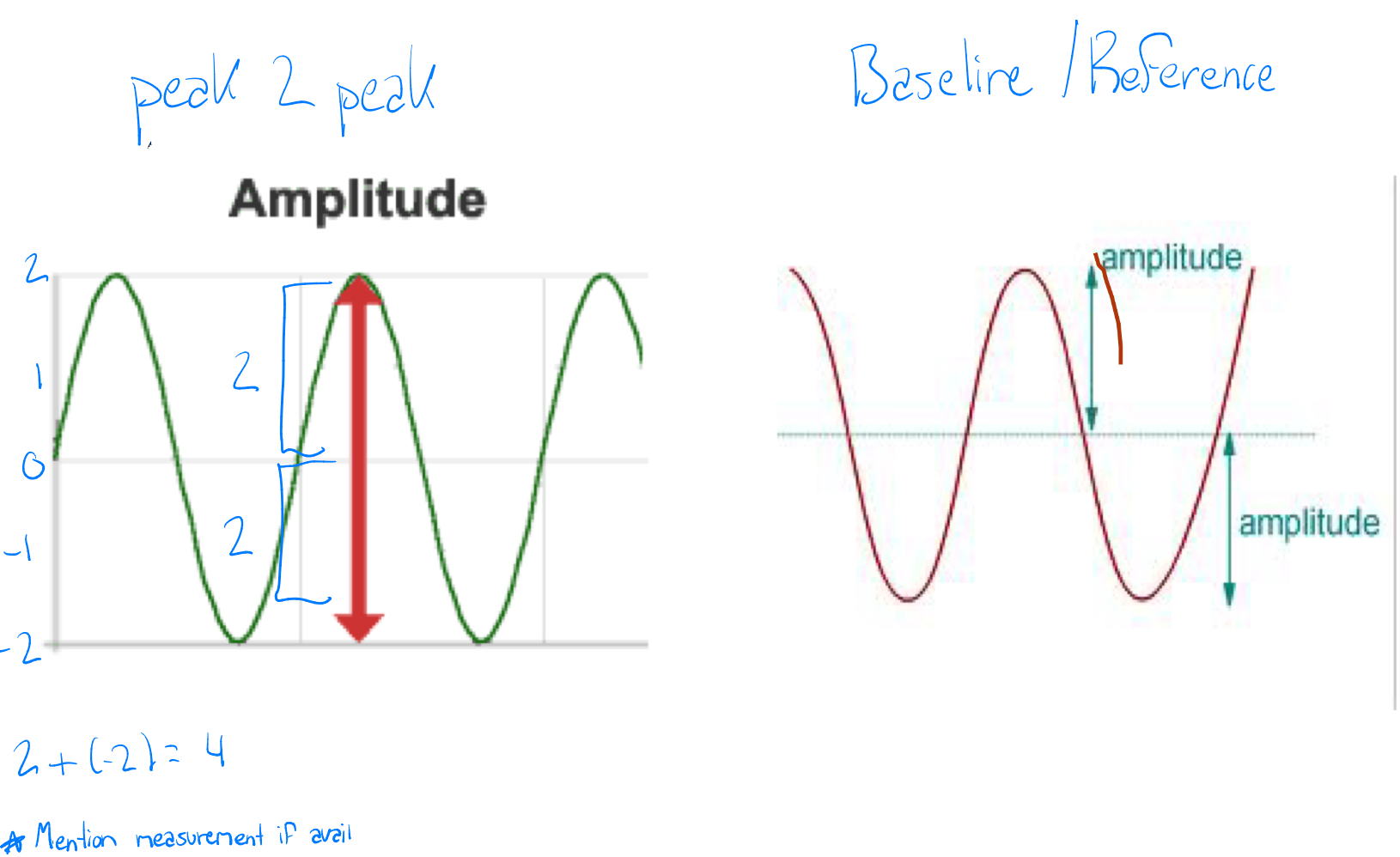
What are the 2 ways to measure amplitude
Peak to peak (+ peak to - peak)
Baseline/reference line to peak amplitude
Frequency (f)
Number of cycles per second
What unit is frequency in?
Hertz (Hz)
Period (T)
Amount of time required to complete one cycle
What unit is period in
Seconds (s)
Inverse Relationship
C=1/D
C increases → D decreases
C decreases → D increases
Direct Relationship
A=B
A increases → B increases
A decreases → B decreases
What is the relationship between f and T
Inverse
f=1/T
T=1/f
An object in simple harmonic motion completes 3000 oscillations in a second. Calculate its frequency.
3000Hz
Wavelength
-The distance from one peak/trough of the wave to the next adjacent peak/trough
-2 consecutive identical points
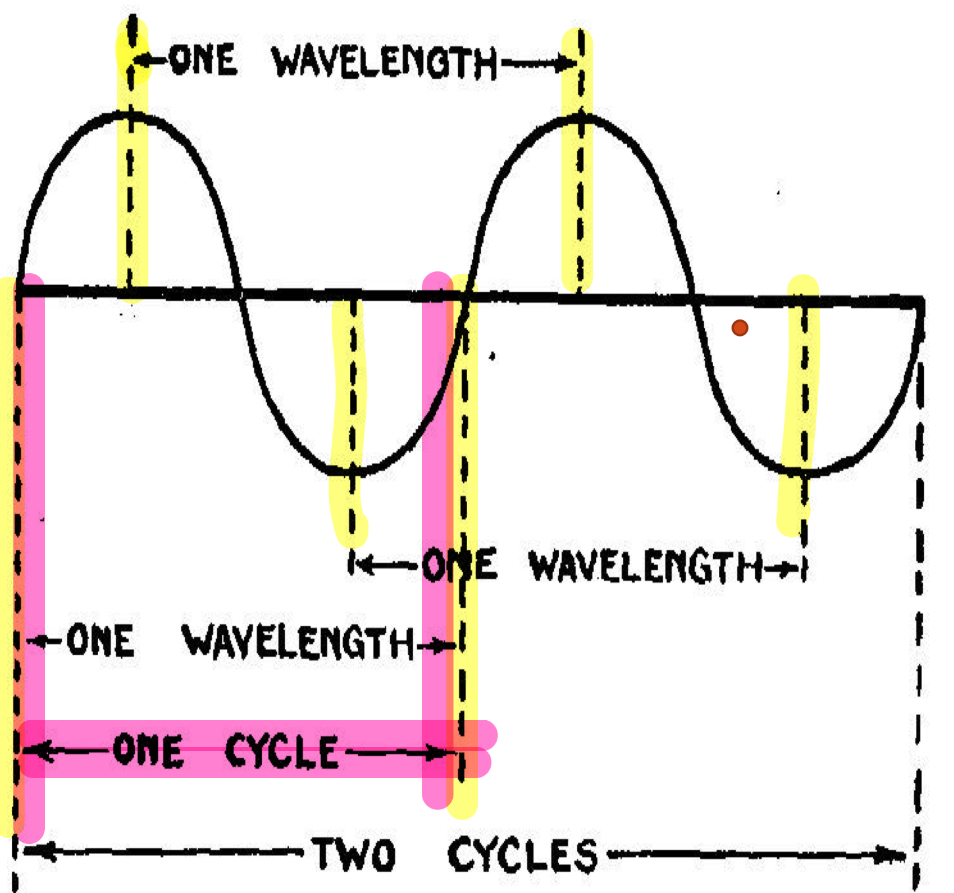
What unit is wavelength in?
Meter
High frequency has…
Peaks closer together making shorter wavelengths
Low frequency has…
Peaks farther apart making longer wavelengths
Physical Perception of Frequency
100 Hz, 1000Hz, 8000Hz
Psychological Perception of Pitch
No sound, low, medium, high
Is there a relationship between frequency and pitch of a sound wave?
Yes! Frequency is related with pitch of a sound
Mechanical Waves requires…
A medium to propagate
Mechanical waves are disturbances traveling in a what?
Elastic medium (like air, glass, metal, etc)
Transverse Waves
Particles of the medium move in perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels (string waves)
Longitudinal Waves
Particles of the medium move parallel to the direction in which the wave travels
100 Hz sine wave has _____ wave length than 1000 Hz sine wave
Longer
Shorter
Equal
Longer
What kind of relationship do wavelength and time have?
Direct
F↑ → T↓ → λ↓
What kind of relationship do wavelength and frequency have?
Indirect
F↓ → T↑ →λ↑
What is the frequency of a sine wave with 10 sec. period?
0.1 Hz
1 Hz
10 Hz
100 Hz
0.1 Hz
What are the 3 prerequisites for production of sound
A medium of transmission
A source of energy
A vibrating object that generates audible pressure
What are the 3 important properties of any medium
Mass, Density, and Elasticity
What is the best and fastest medium and why?
Solid because the molecules are closer together and can hit each other faster
What is mass
Amount of matter that is present
Is there a difference between mass and weight?
Yes! Weight takes gravity into account, mass does not
Density is…
The amount of mass per unit volume
Elasticity
Application of force on solid, liquid, or gas → distortion of either shape or volume or both
Is a thicker or thinner wire more elastic and why?
Thicker wire is more elastic because it has a higher elastic limit and needs more force to be squished
Hooke’s Law
The magnitude of restoring force of elasticity is directly proportional to the magnitude of spring displacement
What is the formula for Hooke’s Law
Fr=-kx
Fr= restoring force of elasticity
x= magnitude of displacement of the spring
K=spring constant
Stiffness explains why springs require…
Greater force than others to be compressed or extended
Stiffer spring →
More force needed to squish
Compliance and stiffness have a ____ relationship
Inverse
Newton’s 1st Law
All bodies remain at rest or in a state of uniform motion unless another force acts in opposition
Newton’s 3rd Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
MKS System
Meter, kilogram, and second system (most used)
CGS System
Centimeter, gram, second system
Displacement
Changes in position
Distance
Changes in position with direction AND distance
Scalar Quantities
Mass, time, and energy, only described by reference to magnitude
Velocity is a _____ quantity
Vector (has magnitude and direction)
Acceleration(a)
△c/time (△c=change in velocity)
If a train travels at a velocity of 20 m/sec and then is accelerated to a velocity of 50m/sec, and if this change is accomplished in 6 seconds then acceleration is what?
5 m/sec2
Newton’s 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the next force applied to the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object (F=ma)
Pressure
Amount of force per unit area (p=F/A)
Momentum=
Mass x velocity
Kinetic Energy
-A form of energy that results from an object in motion
-Types of motion → translation, rotation, vibration
-K.E. (1/2)mv2
Potential Energy
-Form of energy that results from object position or arrangement of parts. STORED ENERGY
-P.E.= mgh
-m=mass, g=gravity, h=height
Work
-When force succeeds in moving a body that the force acts upon, and the quantity of work is given by the product of magnitude
-W=Fd (F=force, d=displacement
Speed of Sound in air is given by…
s=√E/p
E=elasticity, p=density
What does speed of sound not affect?
Frequency & intensity
Complex Sound
More than 1 frequency component
Periodic Sound
Repeating sound
Fundamental Frequency
-The lowest frequency (f0)
Harmonics
-Higher frequency components
-Integer multiples of f0
Time Domain for Periodic Sounds
-Repeating pattern of pressure change
-Within the cycle, things looks complex
Frequency Domain for Periodic Sounds
-Spectral peaks at evenly spaced frequency intervals
-”picket fence” appearance
Complex Wave
-Any sound wave that is not sinusoidal
-Consists of a series of simple sinusoids that can differ in amplitude, frequency, and phase
-AKA Fourier Series
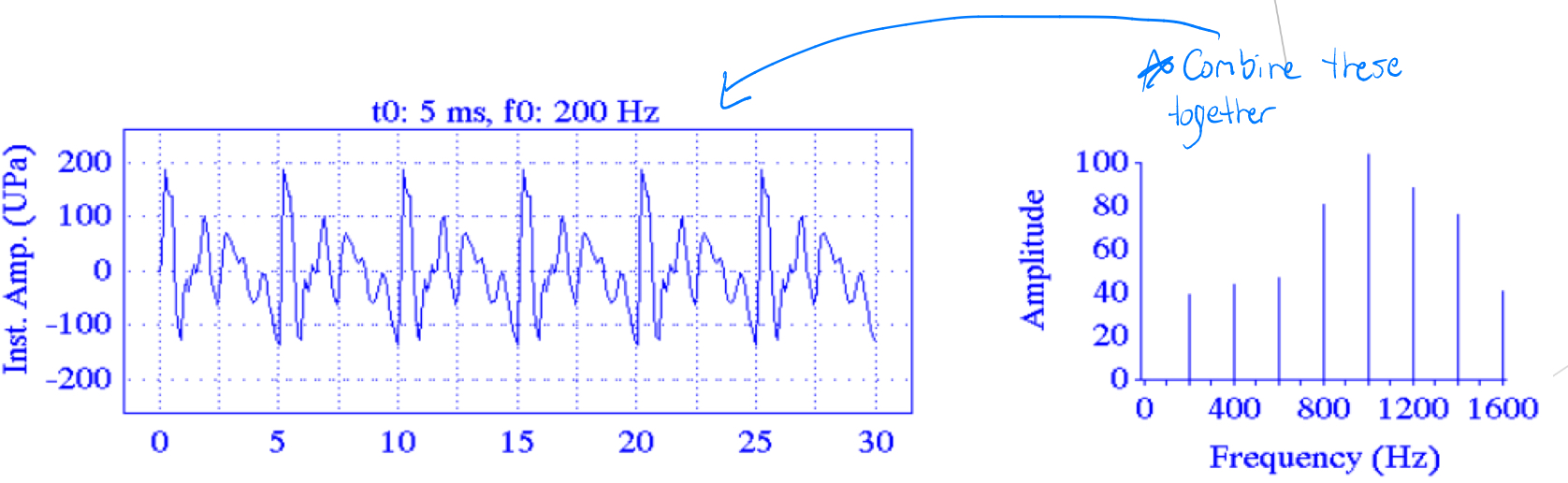
Fourier Analysis
Any complex wave can be decomposed to determine the amplitudes, frequencies, and phases, of the sinusodal components
Sawtooth Wave
-Complex periodic wave with energy at all harmonics (odd & even)
-Amplitude decreases as the inverse of harmonic number
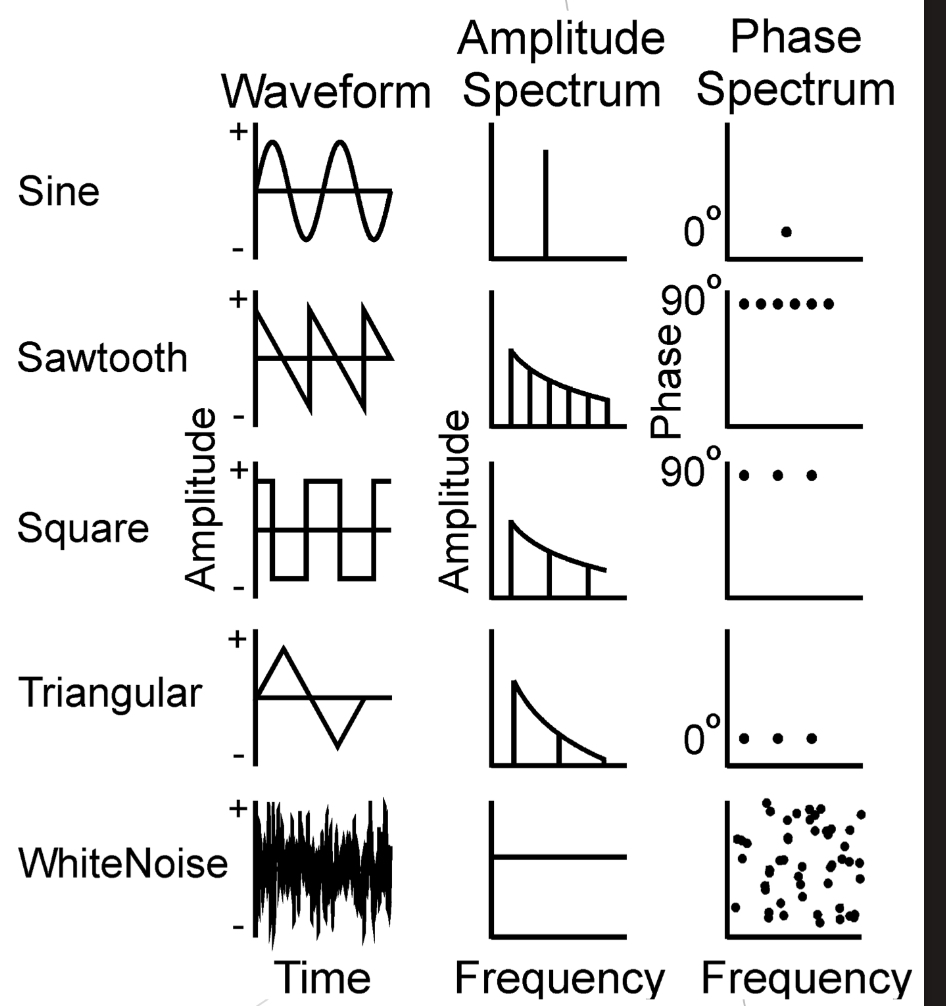
Square wave
-Complex periodic wave where energy is only at odd multiples of f0
-Spectral Envelope slope of -6dB/octave
-Amplitudes decrease as the inverse of the harmonic number
Octave
Doubling frequency (can go up or down)Tri
Triangular Wave
-A complex periodic wave with energy only at odd harmonics
-Slope of envelope is steeper for triangular wave
-Spectral Envelope Slope of -12dB/octave
Pulse Wave
-Complex periodic wave derived from the square wave
-The second part of the cycle is replaced by absolute silence
-Each pulse in the wave has some width or duration Pd
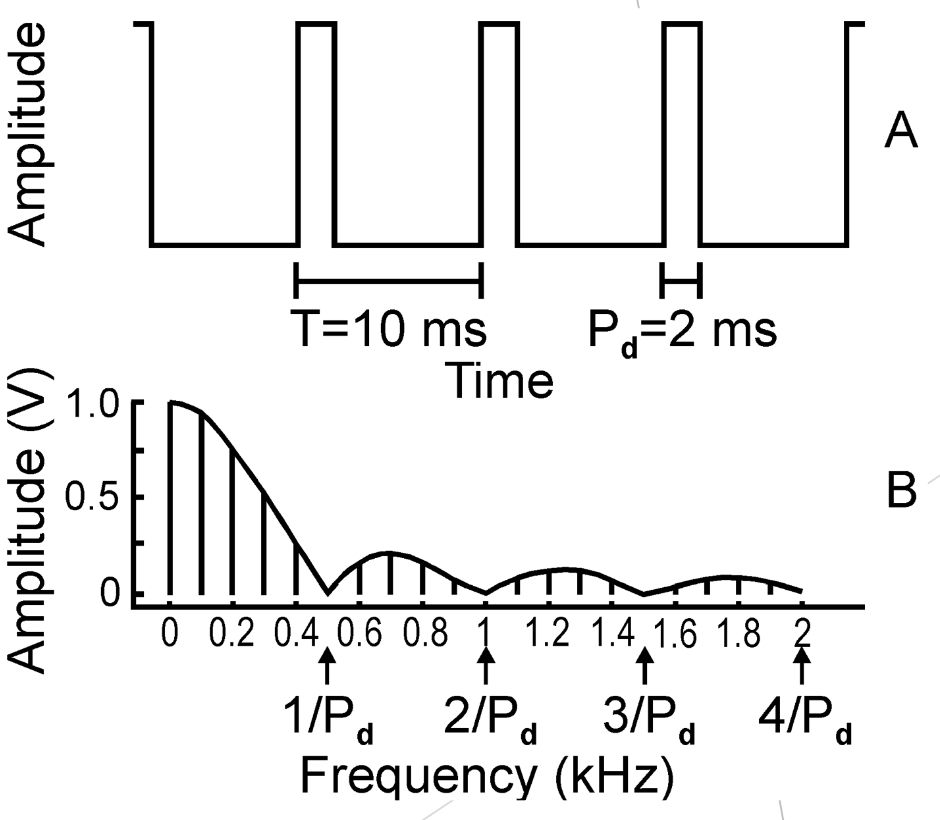
Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF)
1/T
A pulse wave has harmonics at…
Odd and even integer multiples of the pulse repetition frequency
What does the amplitude spectrum show for pulse waves?
Lobes and valleys (nulls)
-Nulls occur at integer multiples of reciprocal of Pd
Aperiodic Sounds
Do not repeat themselves
What do aperiodic sounds not have?
Fundamental frequency (can have lower though)
Time Domain for Aperiodic Sounds
No repeating patter of pressure change
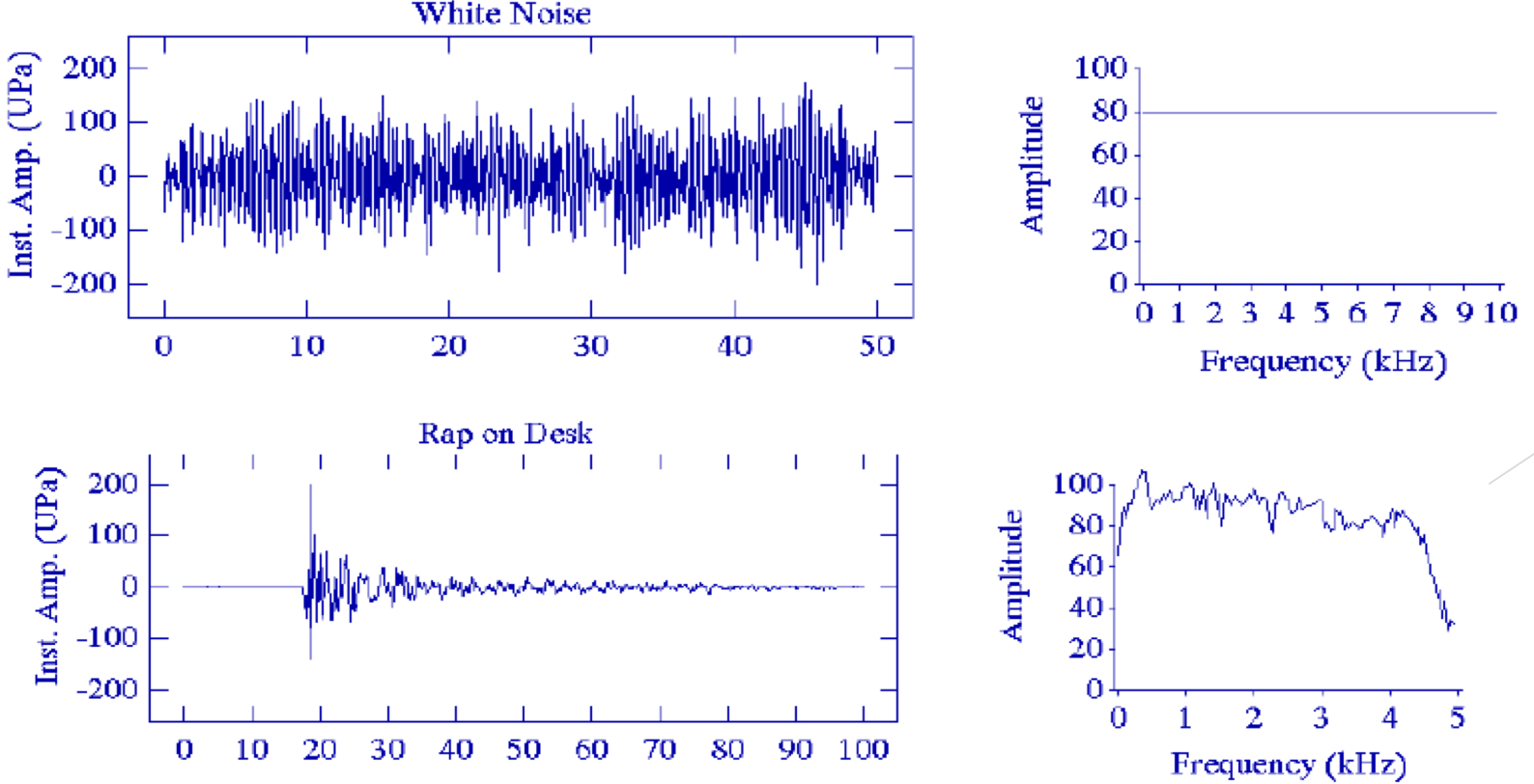
Frequency Domain for Aperiodic Sounds
-The spectrum is dense
-No “picket fence”
-Auditory impression sounds noisy
Reflection
When a sound wave encounters obstacles in the mechanical medium, it changes its traveling path

Refraction
Bending of sound waves when they enter in a different medium with any angle except 90 degrees
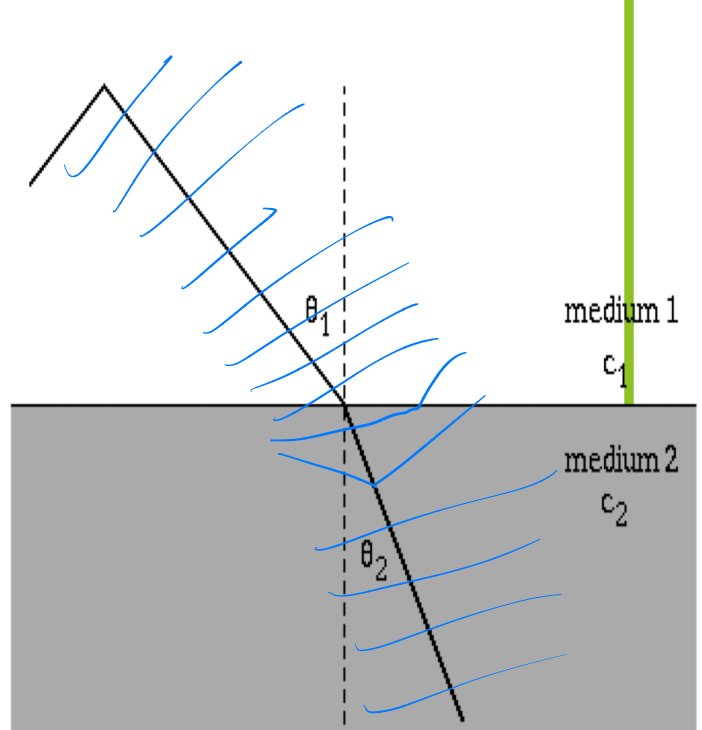
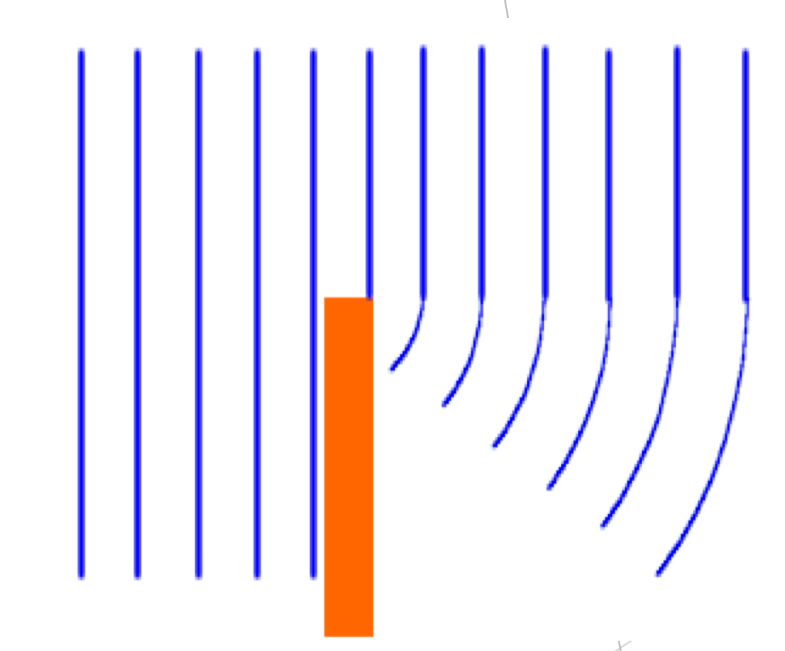
Diffraction
Involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through as opening or around a barrier in their path
What is Interference?
-A condition in which two or more waves carrying energy meets up and overlap
-The energy carried by them get mixed up during interference
Constructive Interference
Amplitude of the final wave will be larger compare to the original waves
-Add together
-Must have same amplitude, phase, and frequency
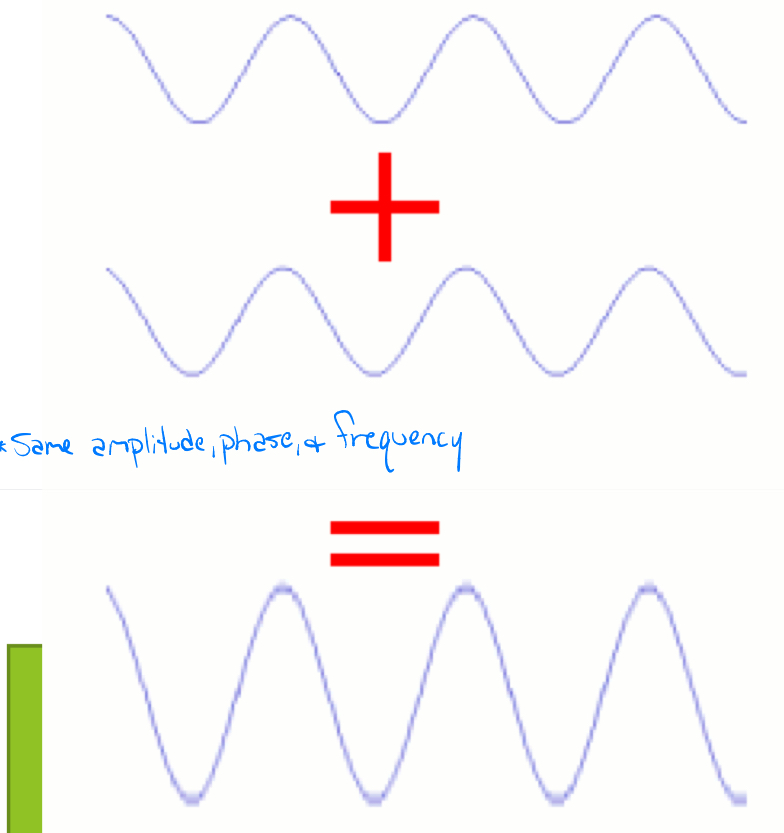
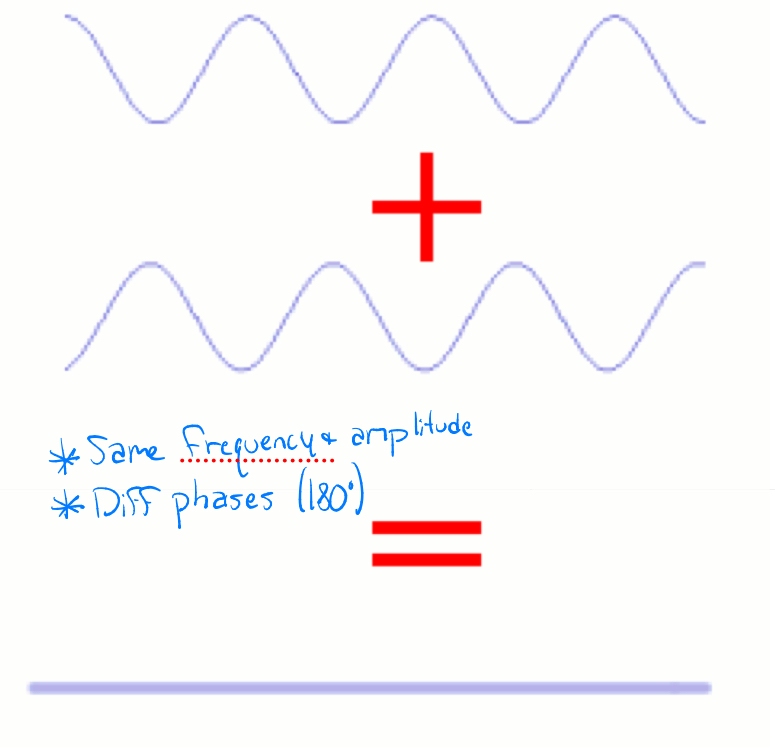
Destructive Amplitude
Amplitude of the final wave will be smaller than the original waves
-Same frequencies and amplitudes
-Different phases
String Waves
Can be produced by stretching a string
Standing/Stationary Waves
Results of interference between two waves traveling in opposite directions
Harmonics/Partial
A component frequency of the output signal that is an integer multiple of the f0
The 1st harmonic is known as what?
The fundamental frequency (f0)
The 2nd harmonic is known as what?
The 1st overtone
Beat
An interference between two sounds of slightly different frequencies
What are beats perceived as?
Periodic variations in volume whose rate is the difference between the two frequencies
Combining a 250 Hz tone with a 253 Hz tone results in how many beats per second?
3
What is the 5th harmonic of 1000Hz?
500
50
50,000
5000
5000
Two sine waves propagating in opposite directions will result in a ______
Standing wave
Reflection will be best if there is a ___
Hard barrier
Loose barrier
Soft barrier
No barrier
Hard barrier