IB Economics 3.3 Macroeconomics objectives
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Define economic growth
Refers to increases in real GDP over time
What is actual output
It refers to the level of real GDP in an economy
Define actual growth
Occurs when real output (real GDP) increases through time and is a result of greater or better use of existing resources. In the PPC model it can be illustrated by a movement from a point inside a PPC to another point in the northeast direction
How is short term actual growth illustrated on the PPC curice?
Illustrated by a movement from one point within the PPC curve to another point closer to the PPC curve
How is short term actual growth illustrated in the AD/AS model?
Illustrated by a shift outwards of the AD curve
Define potential output
Output produced by an economy when it is at full employment equilibrium, or long-run equilibrium according to the monetarist/new classical model
What is potential growth?
It is when there is an improvement in the quantity and/or quality of a country's factors of production, illustrated by an outward shift of the PPC
How is long term growth illustrated in the PPC curve?
An increase in potential output or long term is illustrated by a outward shift in the PPC
How is an increase in potential growth or long term growth illustrated in the AD/AS model
An increase would shift the LRAS curve outwards towards the right
What are the factors effecting economiv growth?
- Factor endowments
- Size and skills of the labour force
- Investment expenditure
- Discovery of raw materials
- Labour productivity
- Labour mobility
What are factor endowment?
Refers to the quantity and quality of a country's factors of production. The more resources a country owns the more likely they are to acheive economic growth
Why is size and skills of the labour force important
A larger and highely skilled labour force like in Switzerland has significantly contributed to the economic growth
How does investment expenditure effect economic growth?
Investment in physical and human capital improves the productive capacity of an economy which is essential for long term growth
How does discovery of raw materials improve economic growth?
Discovery of tradable commodities or natural resources will boost an economy's productive capacity and will shift the PPC curve outwards
What does labour productivity refer to?
Refers to the output produced in each time period, and is affected by factors such as experience, health, skills, and abilities of the workforce.
What are the two types of labour mobility?
Occupational mobility - It's the ease at which workers can move in between jobs in different fields
Geographical mobility - It's the ease at which workers can move between different physical locations. The more mobile workers there are, the higher the level of economic mobility tends to be
What are the positive consequences of economic growth?
- A reduction absolute poverty
- A reduction unemployment
- An increase in tax revenue
- Higher profit from firms due to increased consumption
- Improved social welfare due to an increase in the quantity of merit goods
- However there is an increased risk of inflation due to excessive AD in the country
What are the negative consequences of economic growth on income distribution
The increase in economic growth may creater greater disparities in income distribution, where the richer get richer. However, the increased tax revenue may get spent on supporting lower income households
What are the negative consequences of economic growth on the environment?
The economic growth may lead to negative externalities such as environmental pollution, climate change, resource depletion, and
road congestion
What does employment refer to?
Refers to the use of factors of production in the production process, usually applied in the labour forces
Define unemployment
When a person (who is above a specified age and is available to work) is actively looking for work, but is without a job
What is formal sector employment?
Refers to officially recorded employment, with workers paying income taxes and contributing to the country's official GDP labour marker diagram
What is the labour force?
Refers to people of working age who are in employment (inc self-employed) plus those who are seeking work, that is , those who are available for work
Why does the government aim to acheive low unemployment?
Because a lower unemployment rate means greater national income, output and expenditure which increases the economic
well-being and standards of living. There would be greater tax revenue from indirect taxes and a lower financial burden on the government
How is the unemployment rate measured
Nr of unemployed people/unemployed people + nr of employed people (labour force) x 100
What is the first way of determining unemployment?
Following criteria from the International Labour Organisation (ILO):
- Willing and able to work but unable to find employment
- Been actively looking for work for the past 4 weeks
- Able to start working in the next 2 weeks
- Waiting to start a new job in the next 2 weeks
What is the second way of determining unemployment?
Countries can measure unemployment using the claimant account, which includes people who are actively seeking employment but are without work and claiming unemployment benefits
Why is the claimant account not totally accurate?
It underestimates the employment rate, because some people may be deterred to claim unemployment benefits as they cannot prove they are actively seeking employment. In addition some peope make fraudulent claims to qualify for unemployment benefits
What are the difficulties in measuring unemployment
- Hidden/Disguised unemployment
- Voluntary unemployment
- Underemployment
- Disparities, unemployment rate ignores regional, ethnic, age, and gender disparities
Define cyclical unemployment
Unemployment that is a result of a decrease in aggregate demand and thus of economic activity; it occurs in a recession
What does cyclical unemployment look like in a diagram?
Is represented by a deflationary gap in the AD/AS model and Keynesian model. Labour reosurces are not fully employed
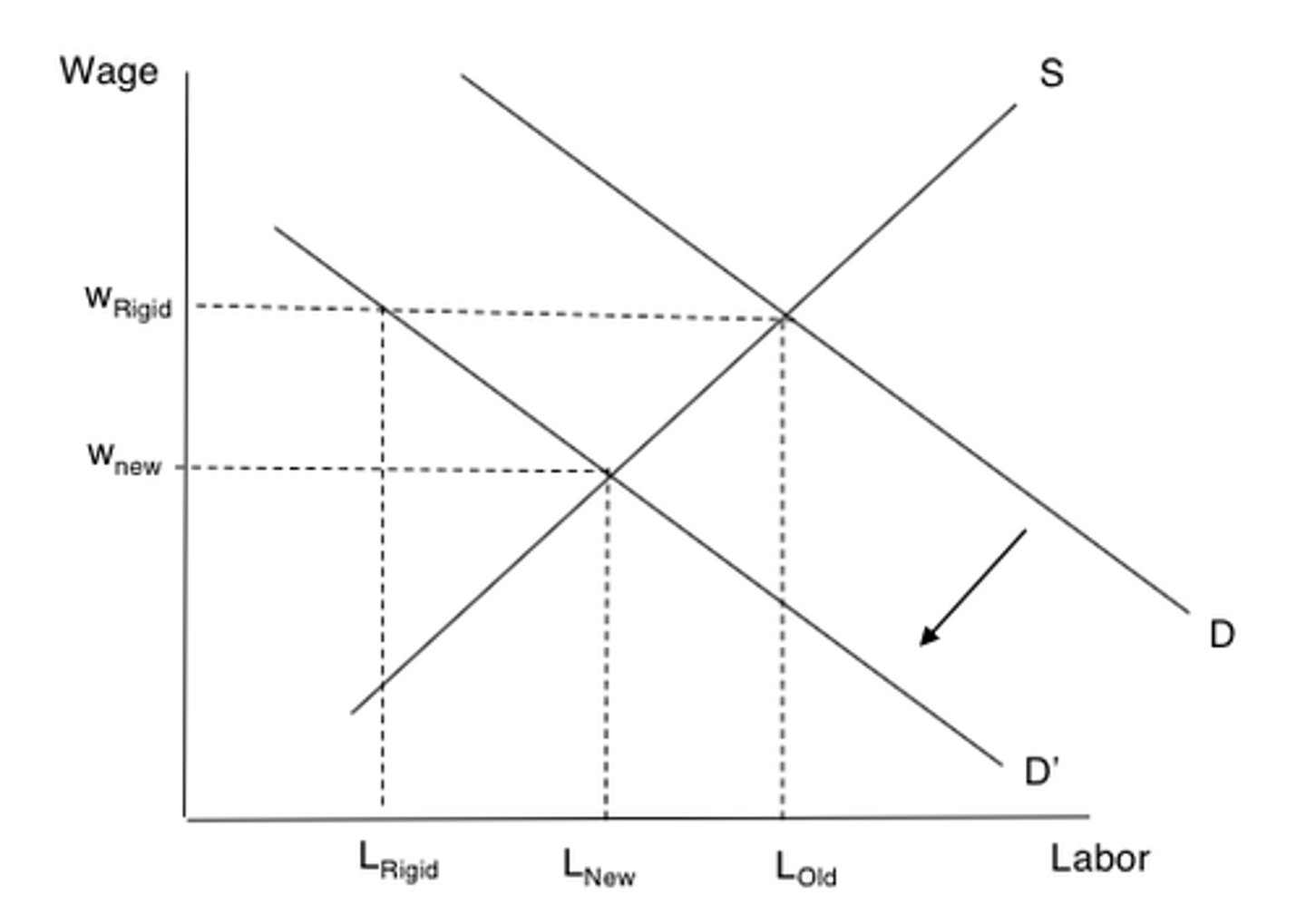
What might the government do to reduce cyclical unemplyment?
Governments may use demand-side policies to boost the AD to close the deflationary gap
Define structural unemployment
A kind of long-term unemployment that arises from a number of factors including: technological change; changes in the patterns of demand for different labour skills; changes in the geographical location of industries; labour market rigidities
Why is low unemployment a key macroeconomic objective?
- Complements economic growth
- Increases tax revenues
- Reduces the burden on the government
- Prevents "brain drain", where skilled workers pursue better employment opportunities oversea
Define inflation
A sustained increase in the average level of prices
What is price stability
It is acheived when the price level remains broadly constant
How is inflation rate measured?
Typically measured using the consumer price index (CPI)
Define Consumer price index (CPI)
The average of the prices of the goods and services that the typical consumer buys expressed as an index number. The CPI is used as a measure of the cost of living in a country and to calculate inflation
How is CPI used to calculate inflation?
Calculating percentage change in CPI from the base year. Adding all values of goods in a basket, dividing the result by the base year price x 100, and then calculating the price change which is the inflation rate
What are the limitations to using CPI as a measure of inflation rate
- Different income earners, CPI does not account for different income levels
- Change in product quality
- Changes in consumption patterns over time
- Atypical households, only accounts for consumption by average household
- Regional and international disparities
- Time lags
- Value of quantities purchased
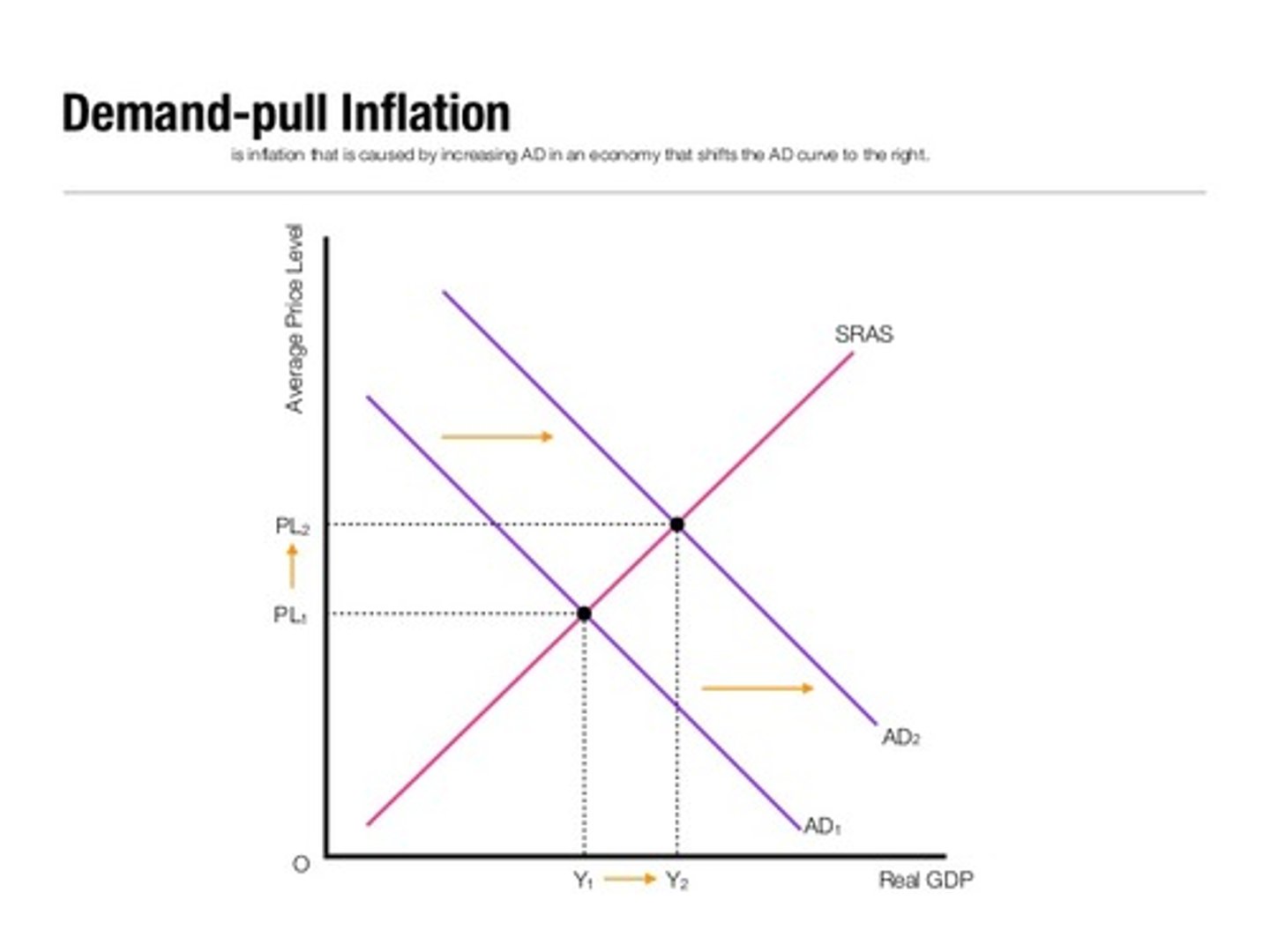
What is demand-pull inflation?
Inflation caused by an increase in aggregate demand in the economy
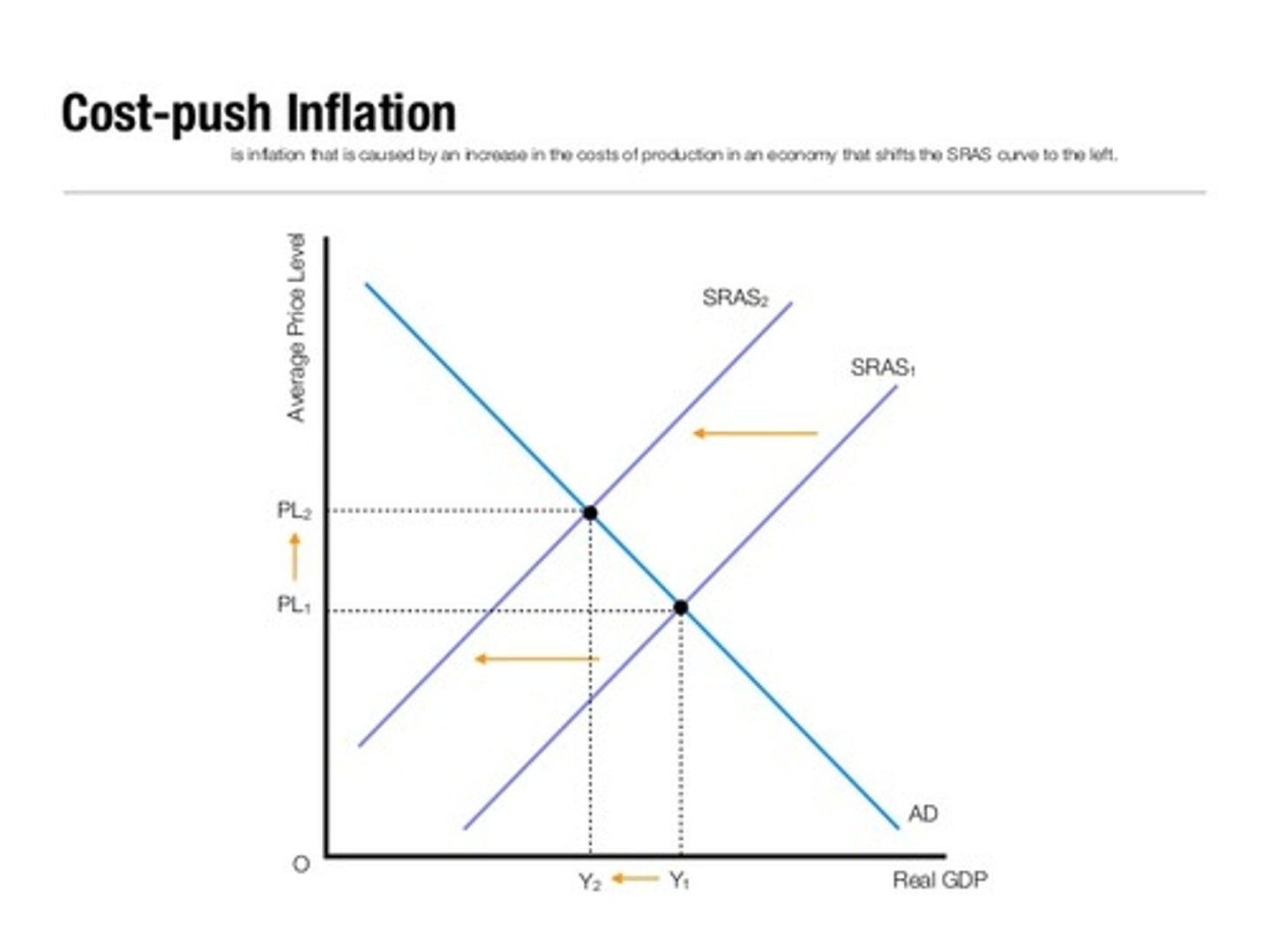
What is cost-push inflation?
Inflation caused by higher costs of production. Might be due to increased price of raw materials or labour costs
What are the costs of high inflation?
- Lowers the purchasing power of stakeholders
- Uncertainty about economy, causes lower levels of consumption and business confidence
- Redistributive effects, effects of inflation are not distributed evenly
- Effects of saving, savers lose as real rate of return decreases and borrowers gain as the value of their debt decreases
Define budget deficit
When government expenditures exceed government (tax) revenues usually over a period of a year
Define government debt (national debt)
The sum of all past budget deficits minus any budget surpluses; the total amount the government owes to domestic and foreign creditors
Why can budget deficits be good in the short run (government spending>government revenue)?
In the short-run there will be more money injected into the circular flow of income, boosting economic growth and creating jobs. Useful in a deep recession. Long-term it is unsustainable due to debt interest.
What are the costs of government debt?
- Debt servicing costs, refers to the costs of financing debt
- Credit ratings, a measure of a debtor's ability ro repay
- Impact on future taxation and government spending
What is austerity?
Refers to the policies used to reduce government debt, such as increasing tax and/or reducing spending
What is a trade-off
When one macroeconomic objective is trade off for another, as they cannot be acheived simultaneously
What is the trade-off between low unemployment and low inflation?
During an economic boom, AD increases and unemployment falls, which there's and increase in disposable income which will result in demand-pull inflation. Low unemployment can also lead to cost-push inflation in the short run
Define Phillips curve
A curve showing the relationship between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation
Define short-run phillips curve
A curve showing the inverse relationship between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation, which suggests a trade-off between inflation and unemployment
What does a increase in AD look like in the SRPC?
Outward shift in AD, is illustrated by a upward movement in the SRPC
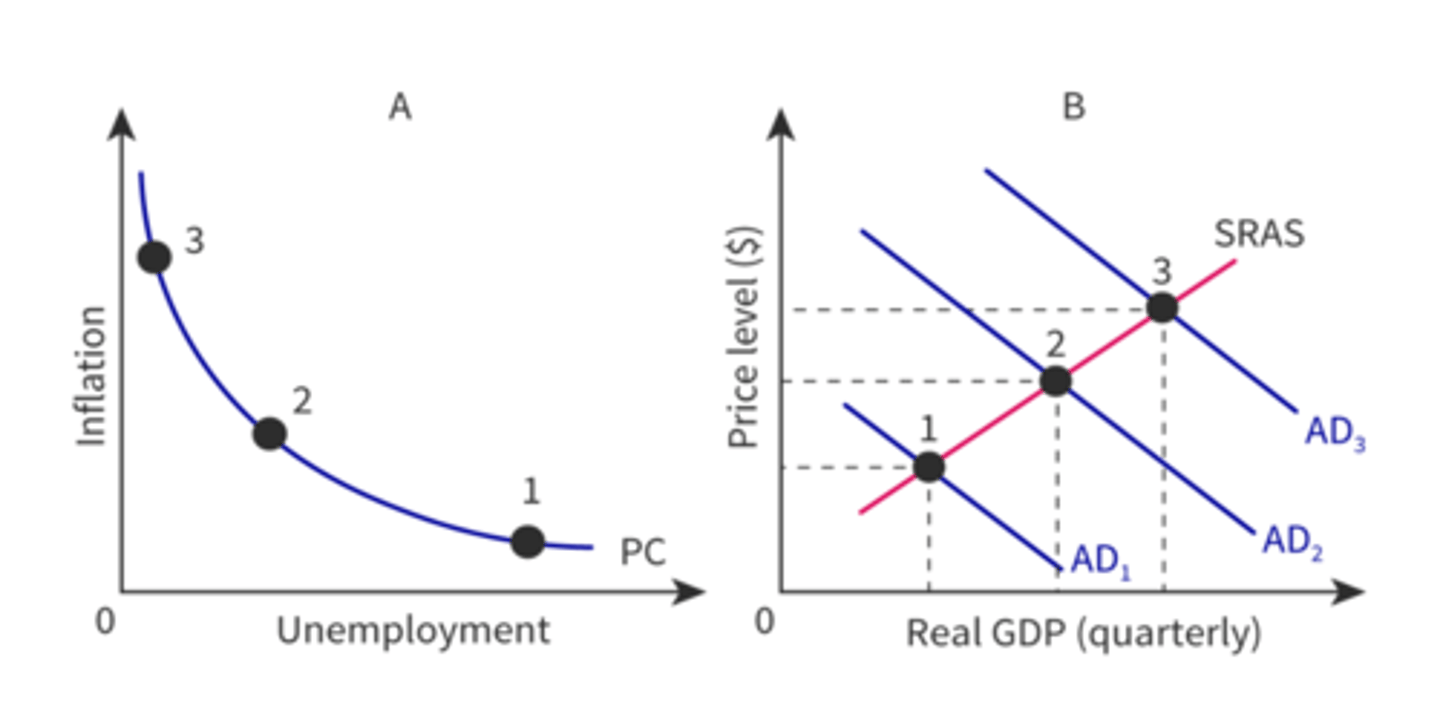
What does a decrease in AD look like in the SRPC
Inward shift in AD is illustrated by a downward movement along the SRPC
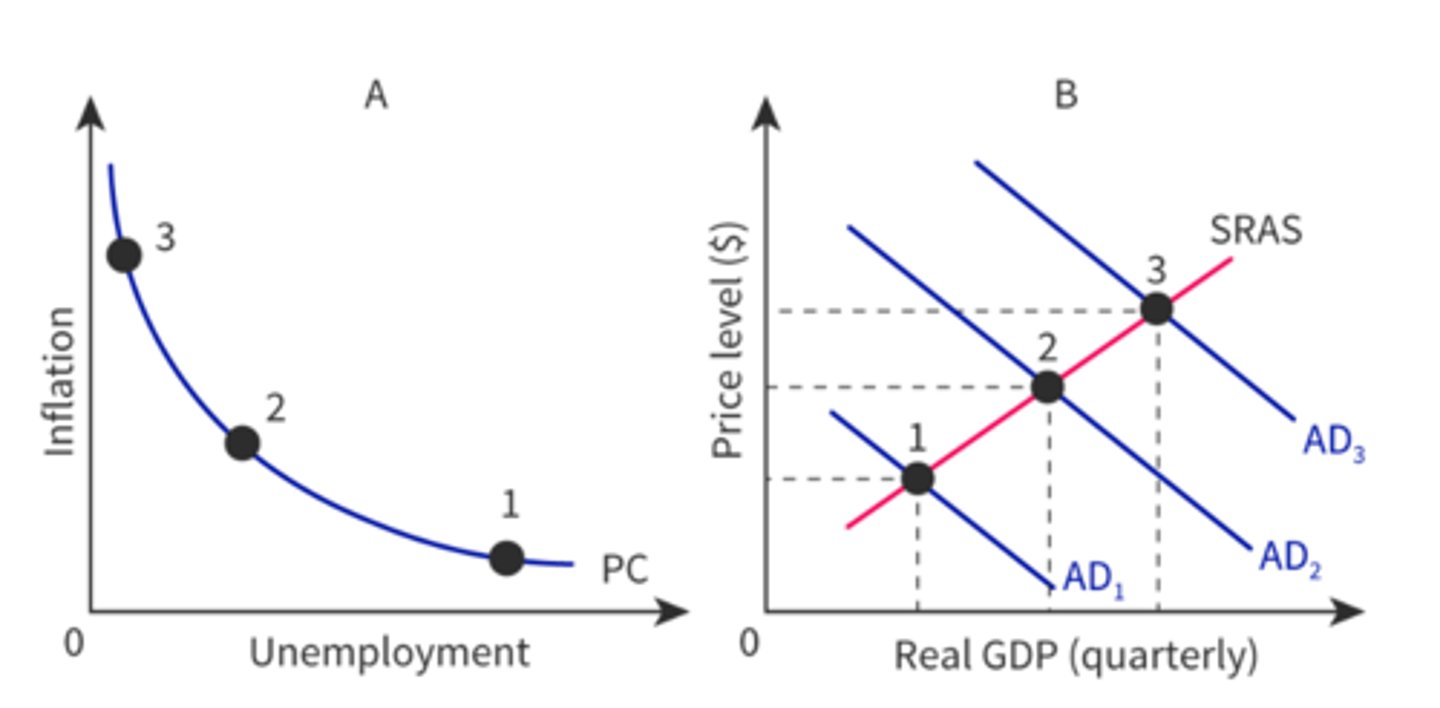
Define long-run phillips curve
A curve showing the monetarist view that there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run and that there exists a natural rate of unemployment at the level of potential output.
What does a long run phillips curve look like?
On the monetarist model the unemployment will naturally fix itself in the long-run due to flexible resource costs. For example a higher AD will result in in reduced employment and higher inflation will cause the SRAS to shift to the left