ISM - Lesson 2 - Global Markets-Karteikarten | Quizlet
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Macro Environment - Definition
The general environment, that can affect the working of all business enterprises
=> Uncontrollable factors
Macro Environment - Elements
PESTLE:
1. Political
2. Economic
3. Sociocultural
4. Technological
5. Legal
6. Environmental
Macro Environment - Nature of Elements
General
Macro Environment - Influence
Indirectly and Distantly
Micro Environment - Definition
Nearby environment under which the firm operates
Micro Environment - Elements
COSMIC:
1. Competitors
2. Organization itself
3. Suppliers
4. Market
5. Intermediaries
6. Customers
Internationalization Strategy
Combination of macro and micro environment factors:
1. Competitive Strength
2. Country Attractiveness
Competitive Strength
Result of the analysis of all the assets the company owns that form its ability to compete in foreign market
Country Attractiveness
Level of appeal a certain country has after the assessment of the different macro environmental criteria
Why assessing a country?
International marketers must learn and adopt tools to help hem understand the scenario and to make educated choices based on data
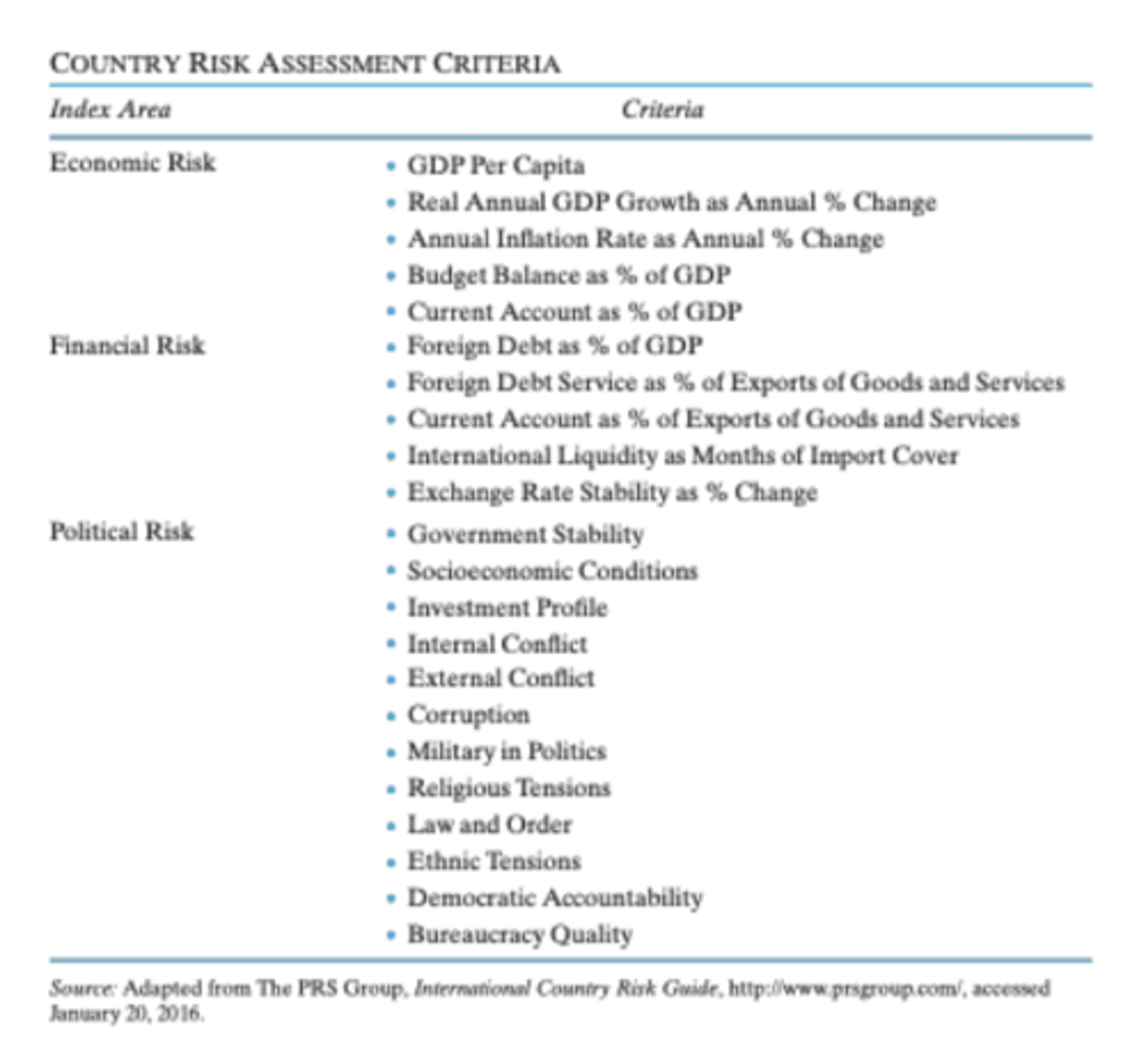
How should a country assessment be done?
1. Taking into account the most important macro areas: economic, financial, political, etc.
2. Defining which key criteria should be analyzed per area
3. Identify a final "score" to lead further decisions
Factors to consider for country assessment
1. Demographic
2. Economic
3. Competitive
4. Cultural
5. Political & legal
=> Simplified framework based on PESTLE & COSMIS
Important demographic factors
1. Market size, growth rate
2. Unemployment trends
3. Levels of education
4. Age
5. Life expectancy
6. Income
7. Work (Availability, technical expertise, skills level)
Country Competitiveness - Definition
Refers to the productiveness of a country, which is represented by its firms' domestic and international productive capacity
Country Competitiveness - Components
1. Human, natural and capital resources of a country primarily shape the nature of corporate productive capacity in the world and thus the nature of international business
2. A country's relative endowment in those resources shapes its competitiveness
Global Competitiveness Index 4.0 (GCI 4.0)
1. By WEF
2. National competitiveness
3. Set of institutions, policies and factors that determine the level of productivity
4. Organized into 12 pillars of productivity that cover broad socio-economic elements (0-100)
GCI 4.0 - Pillar Categories
1. Enabling Environment
2. Human Capital
3. Markets
4. Innovation Ecosystem
GCI 4.0 - Pillars - Enabling Environment
1. Institutions
2. Infrastructure
3. ICT adoption
4. Macroeconomic stability
GCI 4.0 - Pillars - Human Capital
5. Health
6. Skills
GCI 4.0 - Pillars - Markets
7. Product Market
8. Labour Market
9. Financial System
10. Market Size
GCI 4.0 - Pillars - Innovation Ecosystem
11. Business dynamism
12. Innovation capability
Prices across the world - "Indexes"
1. Big Mac Index
2. Starbucks Tall Latte
3. Iphone Index
Concept of export and import
1. Individuals in US & Japan (established developed economies) tend to find domestic sources for their needs due to diversified and extremely large economies
2. Individuals in smaller and rich economies tend to rely more heavily on international trade (e.g. Netherlands)
Intertwined world economy - Implications
1. The higher the per capita trade, the more closely intertwined is that country's economy with the rest of the world
2. Intertwining of economies by the process of specialisation due to international trade leads to job creation in both the exporting & importing country
Convergence
Convergence of consumer needs at the macro level once reached the subsistence level towards brands of high appeal at a global level from the diverse industries
Divergence
Globalization does not suffocate local culture but can liberate them from ideological conformity of nationalism
Porter's Five Forces
1. Rivalry among competitors
2. Threat of new entrants
3. Bargaining power of buyers
4. Threat of substitute products or services
5. Bargaining power of suppliers
Technology as significant force to lower barriers to entry & create substitutes
1. Sector with the highest number of companies and the highest market capitalization among top 100 companies
2. Role of E-Commerce is slowly getting more important at a global level
Global E-Commerce - Implication
Internet has fundamentally changed customers' expectations about convenience, speed, comparability, price & service
Role of Culture
1. Cultural norms and values can often have a major impact on the success of a company's marketing strategy in the host country
2. Consumers' cultures are a key driver on their buying motivations, attitudes toward the brand or marketing campaign and their ultimate buying behaviour
3. => At the same time, cultural mistakes are easily made
Culture and buying behaviours
4 stages of consumption processes:
1. Access
2. Buying behaviour
3. Consumption characteristics
4. Disposal
Culture and buying behaviours - Access
Does the consumer have physical and/or economic access to the product/service?
Culture and buying behaviours - Buying behaviour
How do consumers make the decision to buy in the foreign market?
Culture and buying behaviours - Consumption characteristics
What factors drive the consumption patterns?
Culture and buying behaviours - Disposal
How do consumers dispose of the product (in terms of resale, recycling, etc.)?
Important cultural forces
1. Attitude towards foreigners
2. Attitudes towards work
3. Knowledge of English
4. Quality of life
5. Attitude and interest in foreign products
Hofstede Cultural Dimensions
1. Power Distance Index (PDI)
2. Individualism vs. Collectivism (IDV)
3. Masculinity vs. Femininity (MAS)
4. Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI)
5. Long term orientation vs. Short term normative orientations (LTO)
6. Indulgence vs. Restraint (IND)
Soft Power - 3 principal resources
1. its culture (in places where it is attractive to other
2. its political values (when it lives up to them at home and aborad)
3. its foreign policies (when others see them as legitimate and having moral authority)
Soft Power - Result
Resources can make a nation more attractive to others and co-opt, rather than coerce, them into aligning with interests
Political & Legal Environment - Takeaway
International marketing executives should be concerned about host government's policies and their possible changes in the future, as well as their home government's political climate
2 legal environments to understand for operations
1. Legal environment in each country in which they do business. They determine the legal procedures for doing business in a foreign country
2. The more general international legal environment including the bodies that evaluate the international law
Legal Issues facing a company
1. Pricing
2. Packaging
3. Product
4. Competitive
5. Selling
6. Production
7. Channel
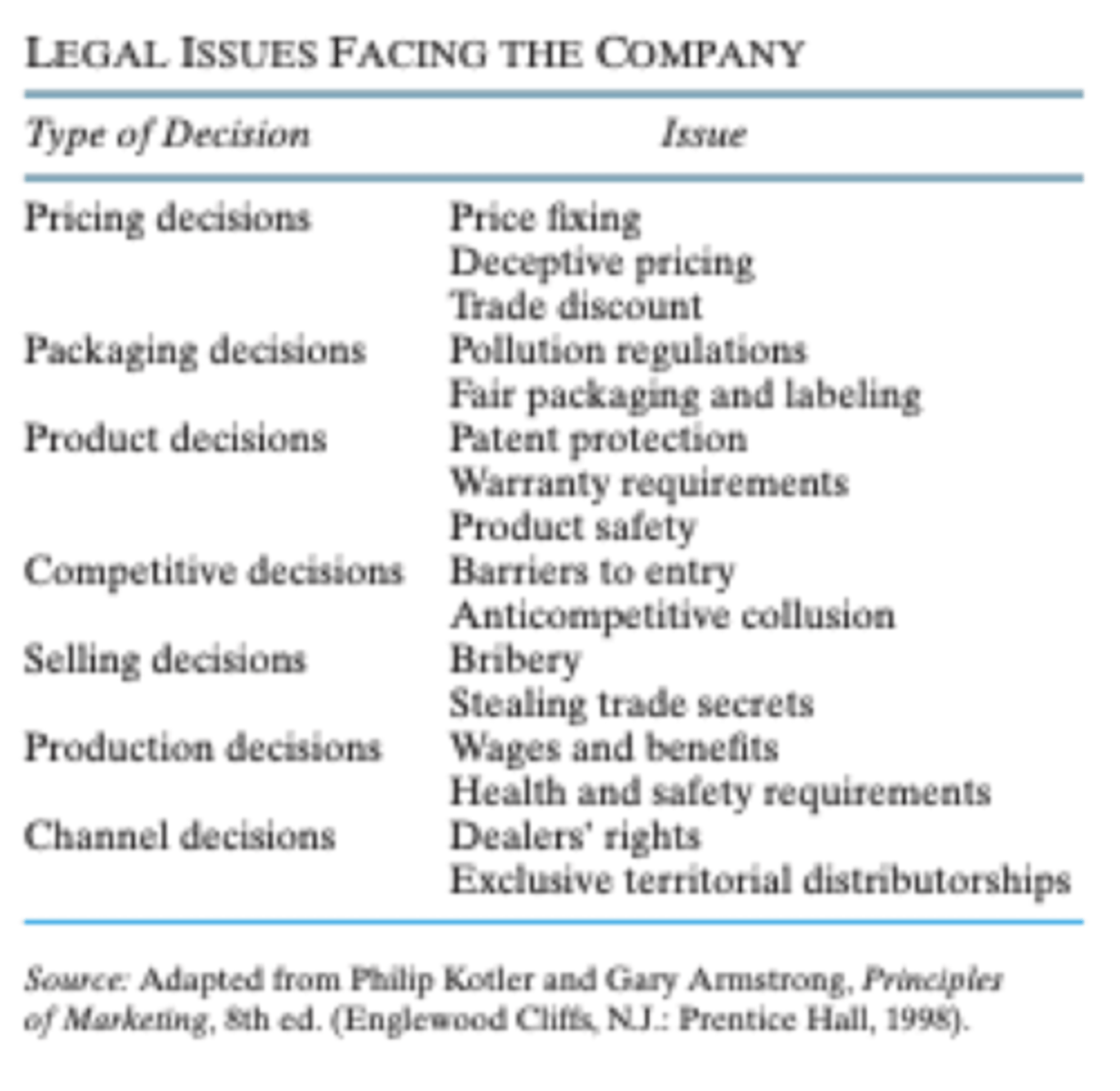
Main legal aspects to take into account from international business perspective
1. Jurisdiction
2. Arbitration
3. IP
4. Antitrust
5. International Standards adherence (ISO)
6. Others (corruption, bribery, etc.)
Jurisdiction
No body of international law exists: the key to evaluating an international contract is by determining which country's laws will apply and where any conflicts will be resolved
Arbitration
1. Due to difficulties and length of litigating over a conflict, many international contracts rely on a prearranged system of arbitration for settling any conflict
2. Both parties agree to accept any rulings from a neutral party, but it is not binding
=> no "international police" exists to force a foreign company to pay damages
Political Country Risk Index
Evaluation of a country by accessing the level of threat posed to the government by different criteria:
1. Political
2. Economical
3. Operational
=> Measures of Economic Distress & Vulnerability to Unrest are taken into account
Relevant International Organizations
1. General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
2. World Trade Organization (WTO)
GATT
1. Objective of ensuring free trade among nations through negotiated lowering of trade barriers after WW2
2. Provided a forum for multilateral discussion among countries to reduce trade barriers
3. Nations met periodically to review the status of world trade to negotiate mutually agreeable reductions in trade barries
WTO - Overview
1. Born after 8th round of GATT (1986-1994)
2. Permanent institution with its own secretariat and includes GATT under GATS acronym
WTO - Components
1. Main function is to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably and freely as possible according to multilateral trade accords
2. Has statutory powers to adjudicate trade disputes among nations it features
3. 164 members (since July 2016)
WTO - Major issues & Agendas
1. Dispute Settlement Mechanism
2. Trade-Related Aspects of IP Rights (TRIPS)
3. Global E-Commerce
WTO - Major issues & Agendas - Dispute Settlement Mechanism
Mechanism is faster, more automatics and therefore much less susceptible to blockages than the old GATT system
WTO - Major issues & Agendas - TRIPS
Increasing volume and values of exports of IP royalties and license fees
WTO - Major issues & Agendas - Global E-Commerce
Global effort to regulate international e-commerce has become increasingly necessary
Free Trade Area
FTA has a higher level of integration than a loosely formed regional cooperation and is a formal agreement among two or more countries to reduce or eliminate customs duties and non-tariff trade barriers among partner countries
Relevant FTAs
1. NAFTA: North American Free Trade Agreement among Canada, US & Mexico
2. EU: Not just free trade area => Single market, but countries have to allow the free movement of goods, service, capital and people
3. EFTA: Includes Iceland, Norway, Switzerland & Lichtenstein
Trade Barriers
1. Tariffs
2. Non-Tariffs
Tariffs
A tax imposed by a government on goods entering its borders
Non-Tariffs
1. Quota
2. Voluntary Export Restraints
3. Boycott
4. Exchange control
5. Standards
Quota
Unit limit applied to a specific type of good
Voluntary Export Restraints
Agreement between importing & exporting country for a restriction on the volume of export
Boycott
Absolute restriction by the government against the purchase & importation of certain goods
Exchange control
When exchange rate is fixed by authorities
Standards
Barriers related to health, safety & quality