Transcription of DNA to RNA -9
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Recognize and recall the key steps in the expression of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene.
Transcription
-processing
-Transportation out of the nucleus
-translation
-Protein folding and modification.
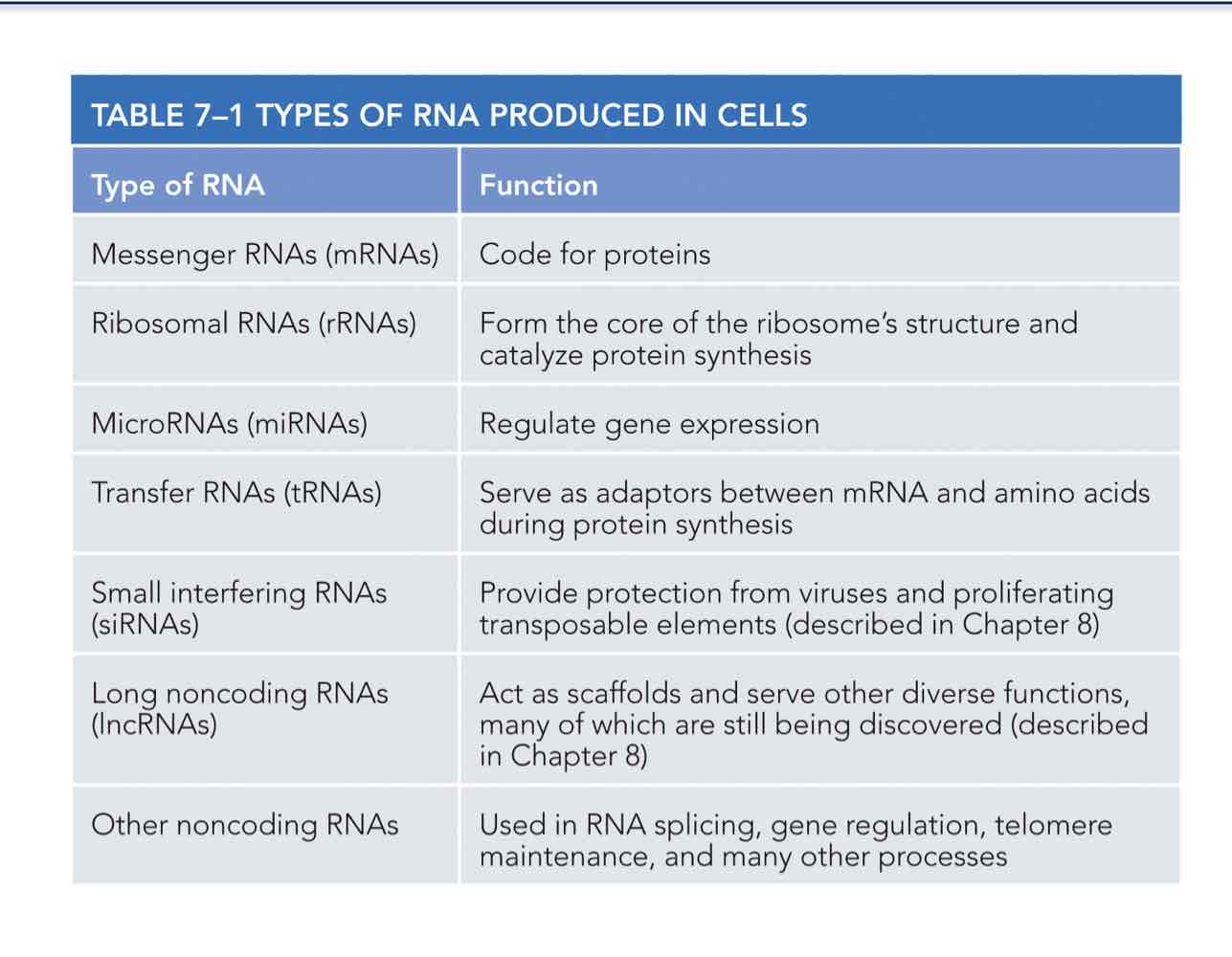
List the most common types of RNA produced by transcription and identify those that
represent the final product of gene expression.
Look at image
Describe transcription in the expression of how genes that codes for proteins are expressed
Transcription:RNA polymerase II transcribes a complementary RNA sequence from the DNA template, resulting in a single- stranded pre-mRNA molecule.
Describe processing in the expression of how genes that codes for proteins are expressed
Processing: The pre-mRNA transcript undergoes processing to make a finalized messenger RNA strand.
-processed in a cap and a poly A tail or it is being spliced out by cutting out introns
Job of eukaryotic RNA poly II for mrna synthes
Unwinds the DNA strands
ii. ReadstheDNAtemplatestrandina3’to 5’ direction
iii. Catalyzes the polymerization of ribonucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction (adds the next base 5’ phosphate to the 3’ hydroxyl of the previous base)
iv. Uses ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP as substrate
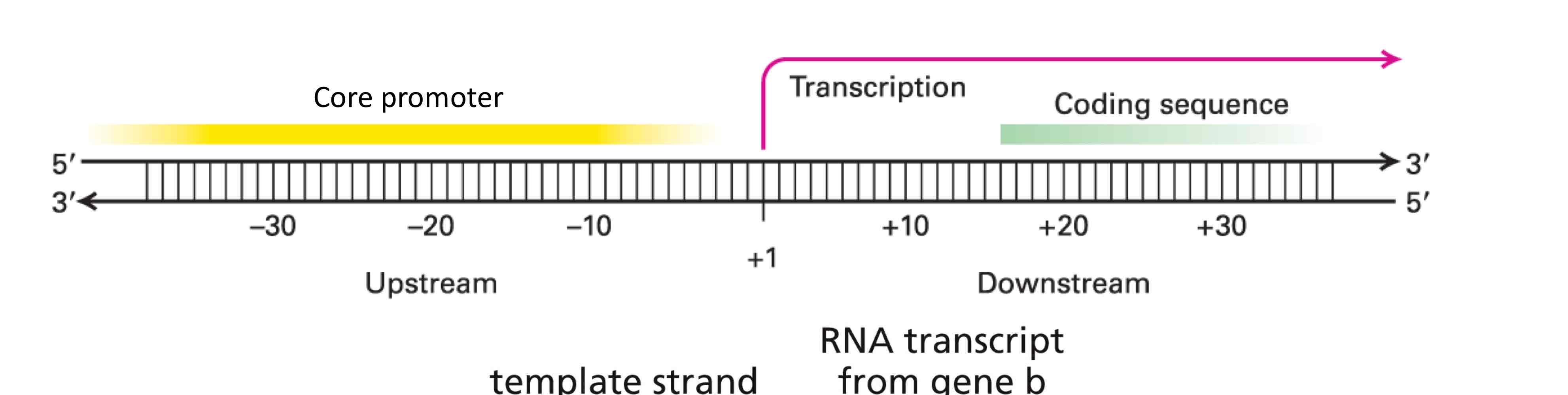
What is the core promoter
The core promoter is just ‘upstream’ of the transcriptional start site and is where RNA pol II binds prior to initiating transcription.
RNA pol II requires the help of What to recognize the part of the promoter and form a what complex
RNA pol II requires the help of general transcription factors (GTFs) to recognize the part of the promoter and form a pre- initiation complex (PIC)
Explain the initiation of RNA pol II transcription
TATA binding protein binds to the promoter and causes a chwnge to the Dna. When TFIID + TATA binds together it sets the stage for the assembly of the complete Pre initiation complex
-The three GTFs bound to the promoter allows the binding of RNA polymerase II with its TFIIF.
• The spacing of the TATA box and the other GTS means that RNA pol II is positioned right at the transcriptional start site
As long as TFIID remains bound to the promoter, additional RNA polymerases may be able to attach for additional rounds of transcription. true or false
True So multiple mRNAs can be made from a gene at once... amplification. From each of these mRNAs, multiple proteins can be transcribed
The C-terminal domain of the RNA poly II serves as a scaffold for other factors involved in RNA processing what does this mean
RNA processing – Capping, polyadenylation and splicing Goes through the C- terminal of rna poly II during transcription
Before RNA processing is done what are the RNA known as
Before these steps are completed, the RNA transcript is known as a precursor- mRNA or pre-mRNA
Modifications capping and polyadenylation increase the stability of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule True or false
True during processing
Many molecules of RNA polymerase can simultaneously transcribe the same gene true or false
True at different stages
State the Structure of the 5’ cap
Cap structure:
• “inverted” guanine nucleotide added (5’ to 5’ bond)
• Methyl group is added to G.
State the functions of the 5’ cap
Functions of the cap:
• Stabilizes the 5’ end, protecting it from exonucleases
• Aids in transport out of the nucleus
• Helps to start the translation process
What is the sequence required for intron removal
Adenosine
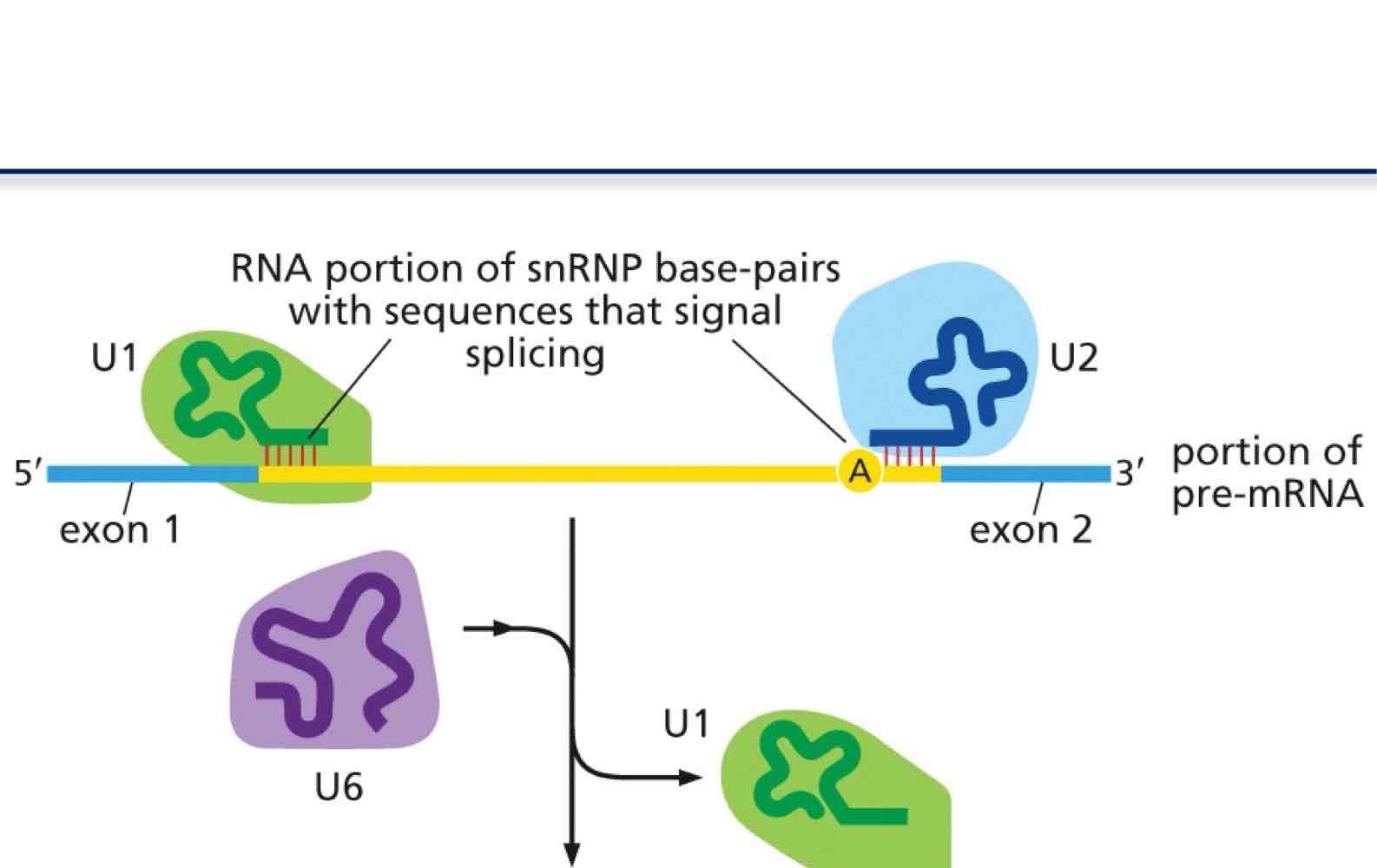
What is the Mechanism of splicing
Splicing is done by a number of protein/RNA molecules
• small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) bind to proteins (the U proteins)
to form snRNPs
-the RNAs recognize the splice sites by base-pairing
spliceosome
the complex of snRNA and proteins is called a spliceosome
• Spliceosome is formed in nucleus, as transcription takes place
Polyadenylation
Is Processing at the 3′ end and it consists of two events:
Cleavage and addition of the poly-A-tail
Explain cleavage as a part of polyadenylation
Cleavage: an enzyme that cuts the growing mRNA chain at a particular sequence of nucleotides, which separates the mRNA from the transcribing RNA polymerase II
Explain addition of poly-A-tail as a part of polyadenylation
A special type of RNA polymerase adds 50–250 adenosine (A) residues to the end of the cleaved mRNA.
Functions of the 3’ Poly A tail
• Increases the stability of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule
• Facilitate its export from the nucleus to the cytosol
After polyadenylation, the polymerase dissociates from the DNA template, and transcription is terminated.
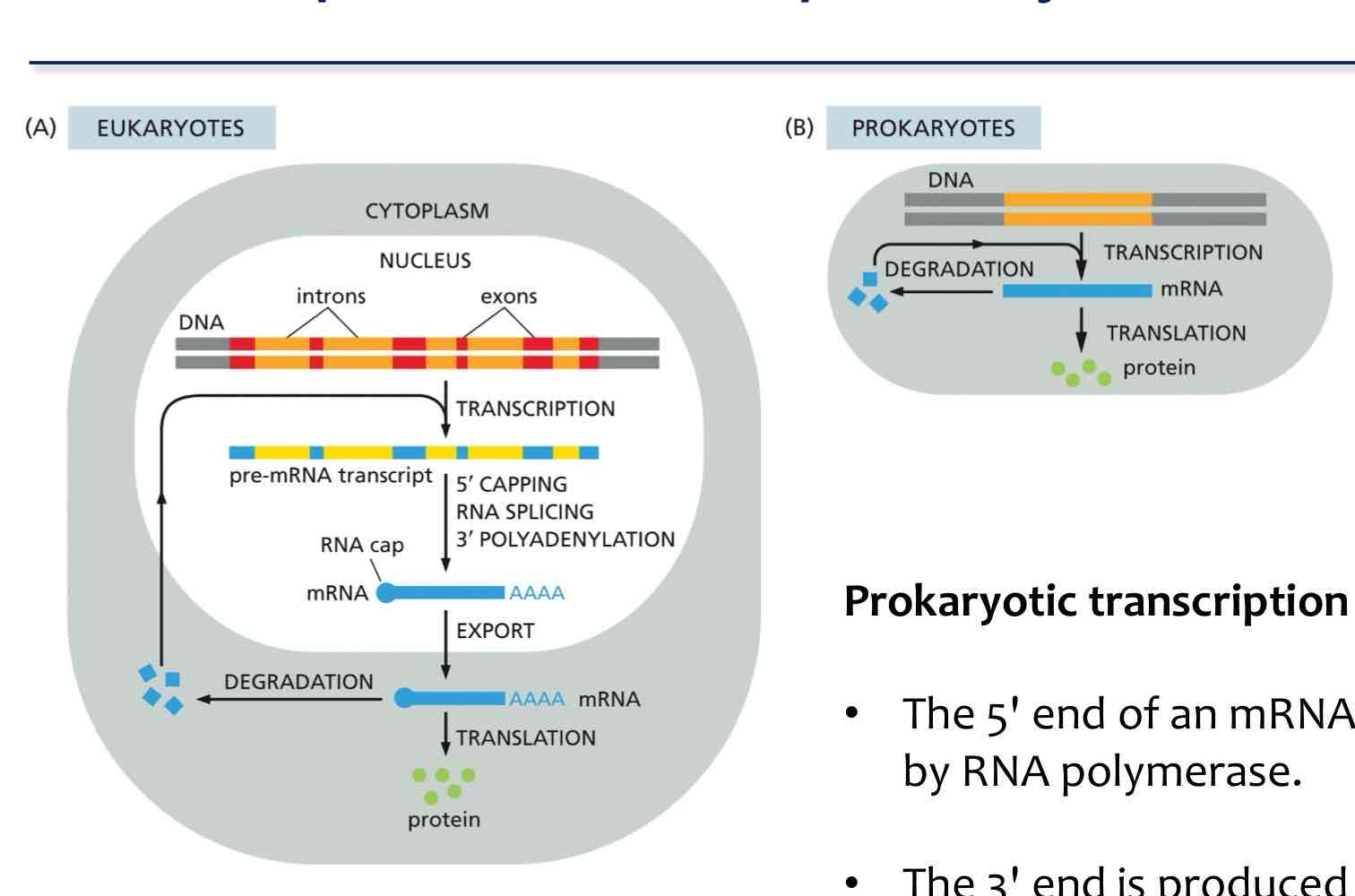
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNA production
Prokaryotic transcription
• The 5' end of an mRNA molecule is produced by the initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase.
• The 3' end is produced by the termination of transcription.
• Translation and transcription occur in the same compartment.
• Translation of a prokaryotic mRNA begins before its synthesis has been
16
completed.