Computer Programming
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Computer Programming
It means giving instruction or directions to accomplish specific task
Programmers
people who write computer programs
Programming Language
programmers use a specific language called _______ to communicate with the computer
9000+
there are approximately ______ programming languages used by software and web developers and other professionals
Compiler
converts programming language program to machine language
Interpreter
converts programming languages to machine language line by line
C. source code—compiler—assembler—machine code
How it works: code translator from source code to executable output
A. source code—assembler—-compiler——machine code
B. source code—machine code—compiler—-assembler
C. source code—compiler—assembler—machine code
Machine Language
Instructions written in 0s and 1s are called _______. ___________ language (each type of machine has its own language) represent the only way to communicate directly with the computer.
low level languages and can directly understand by computer but difficult to ready by humans
Assembly language
it simplify the programmer’s job by allowing the programmer to use mnemonics in place of the 0s and 1s in the program.
a representation of machine language. these are instructions translates to machine language instruction called assembler
High level language
It represent the next major development in programming languages. These languages are a vast improvement over machine and assembly language because they allow the programmer to use instructions that more closely resemble the English language.
these are mostly used by programmers today. these are easy to read and portable. it can be classified into functional, procedure oriented, object oriented, programming and logic programming languages
Step 1: Analyze the problem- problem outline and list of requirements
Step 2: Plan the algorithm- design algorithm using pseudo-code, IPO and flowcharts
Step 3: Check the algorithm- trace algorithm.
Step 4: Code the algorithm into a program- implement algorithms into code.
Step 5: maintenance: evaluate and modify the program if necessary. IPO chart is also applicable
steps in problem solving process
Algorithm
step by step solution to solve a problem or to accomplish specific task
Flowchart
graphical representation of algorithm. there are symbols and illustration to use
Pseudo code
tool to plan the algorithm and use short English statements.
The short English statements that represent an algorithm are called _________
programs
instruction given to a computer
IPO chart
use to organized the result of program analysis
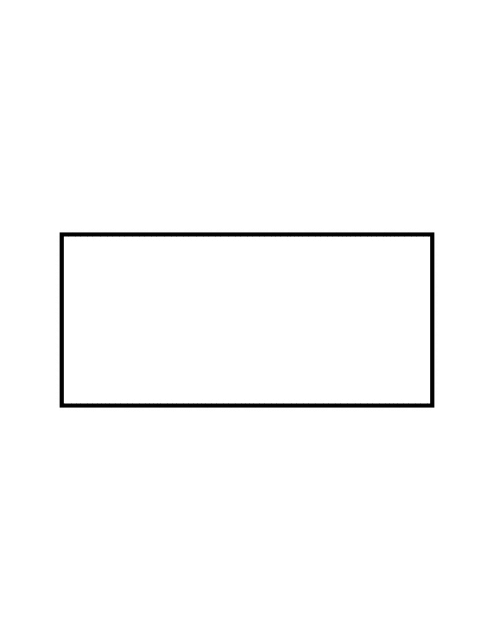
Process
indicates any type of internal operation inside the Processor or memory

input/output
used for any _____/______ operation. indicates that the computer is to obtain data or output results
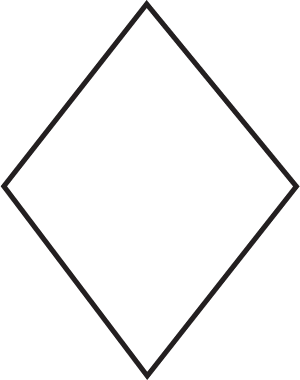
Decision
used to ask a question that can be answered in a binary format (yes/no, true/false)
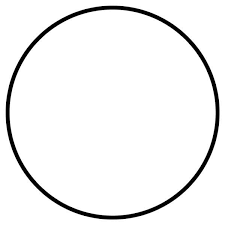
Connector
Allows the flowchart to be drawn without intersecting lines or without a reverse flow.

Pre-defined Process
Used to invoke a subroutine or an interrupt program.
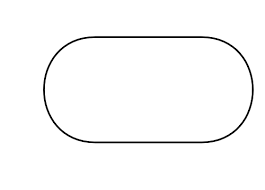
Terminal
Indicates the starting or ending of the program, process, or interrupt program.
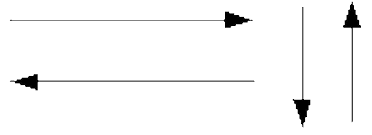
Flow lines
shows direction of flow
Integer 4 bytes
int
float 4 bytes
float
double 8 bytes
double
boolean 1 byte
bool
character 1 byte
char
string 1 byte per character
string
identifiers
All C++ variables must be identified with descriptive unique names.
These unique names are called
•Names can contain letters, digits, and underscores
•Names must begin with a letter or an underscore (_)
•Names are case sensitive (myVar and myvar are different variables)
•Names cannot contain whitespaces or special characters like !, #, %, etc.
•Reserved words (like C++ keywords, such as int) cannot be used as names
The general rules for naming variables are:
==
equal to
! =
not equal to
<
less than
<=
less than or equal to
>
greater than
>=
greater than or equal to
true + true = true
true + false = false
false + true = false
false + false = false
&&
true + true = true
true + false = true
false + true = true
false + false = false
||
Sequence Structures
In a computer program, the _________ structure directs the computer to process program instructions, one after another, in the order listed in the programs.
a series of actions that is completed in a specific order. Action 1 is performed, then Action 2, then Action 3, etc,. until all of the actions in the sequence have been carried out.
Selection
indicates that a decision (based on some condition) needs to be made followed by an appropriate action derived from that decision.
Repetition
last of the three control structures. It directs the computer to repeat one or more instruction until some condition is met, at which time the computer should stop repeating the instructions. This structure also is referred to as a loop or an iteration.
or loops, are used when a program needs to repeatedly process one or more instructions until some condition is met, at which time the loop ends. Many programming tasks are repetitive, having little variation from one item to the next.
Control Structures
All computer programs, no matter how simple or how complex, are written using one or more of three basic structures: Sequence, Selection, and Repetition. These structures are called __________ or logic structures because they control the flow of a program’s logic.
while loop
The loop construct in C++ is used when the number of iterations is known beforehand is called _________
braces
In a C++ program, the body of a function is enclosed in ______
false
true && false
true
true || false