Basic Economic Concepts
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Economics
The study of choices made by people who are faced with scarcity
Scarcity
A situation in which resources are limited but can be used in different ways
Three Fundamental Economic Questions
1. Who consumes the products?
2. What products do we produce?
3. How do we produce these products?
Trade-off
An alternative that we sacrifice when we make a decision
Opportunity Cost
The most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision
Capital Goods
Goods that are used to manufacture other goods

Consumer Goods
Goods bought by users for their own personal needs or wants

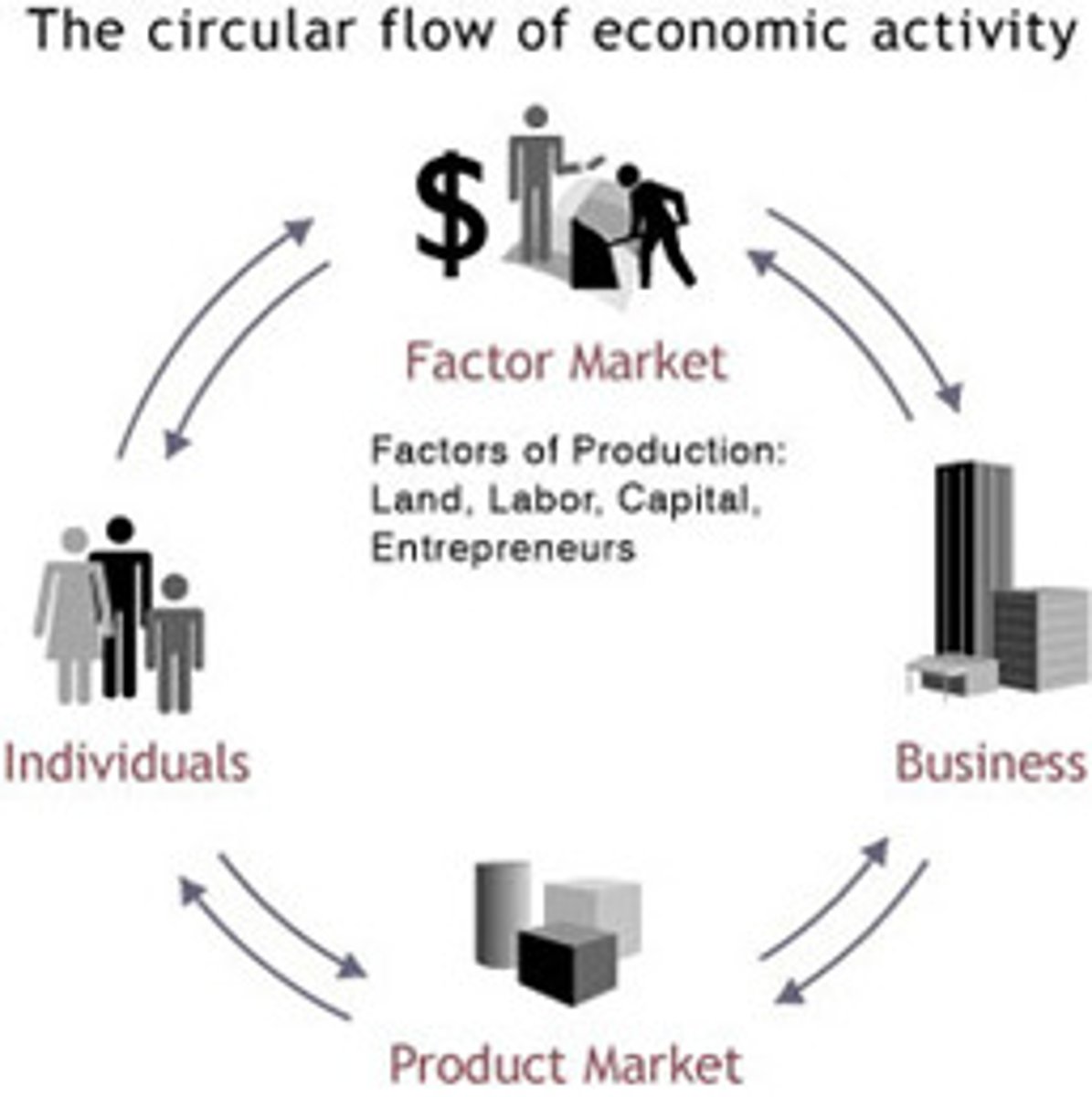
Factors of Production
The resources that are used to produce goods and services
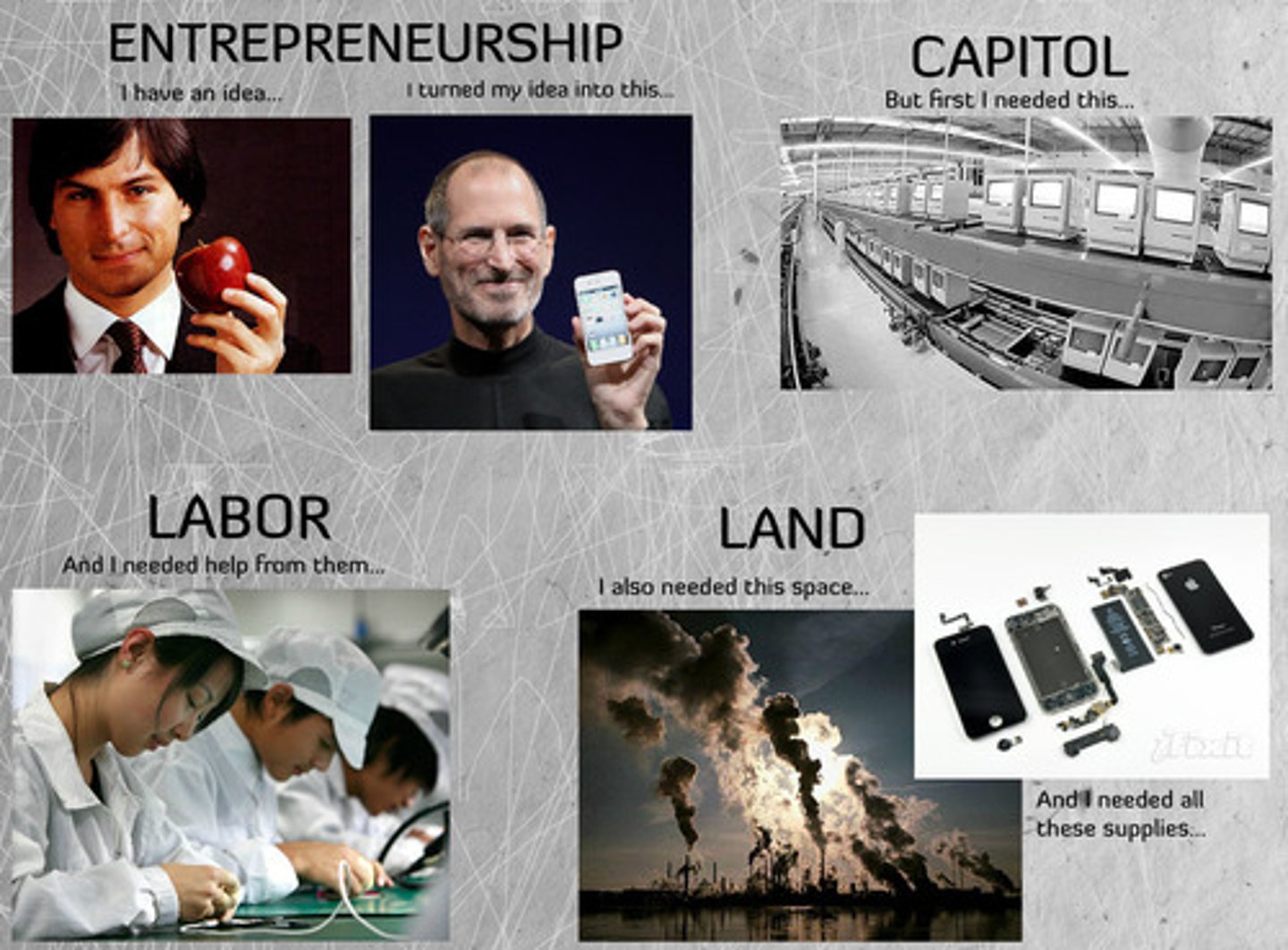
Land
Things created by acts of nature, such as land, water, mineral, oil and gas deposits, renewable and non-renewable resources

Labour
The human effort, physical and mental, used by workers in the production of goods and services

Physical Capital
All the machines, buildings, equipment, roads, and other objects made by humans to produce goods and services

Human Capital
The knowledge and skills acquired by a worker through education and experience

Entrepreneurship and Technology
The effort to coordinate the production of sale of goods and services. Entrepreneurs take risk and commit time and money to a business without any guarantee of profit

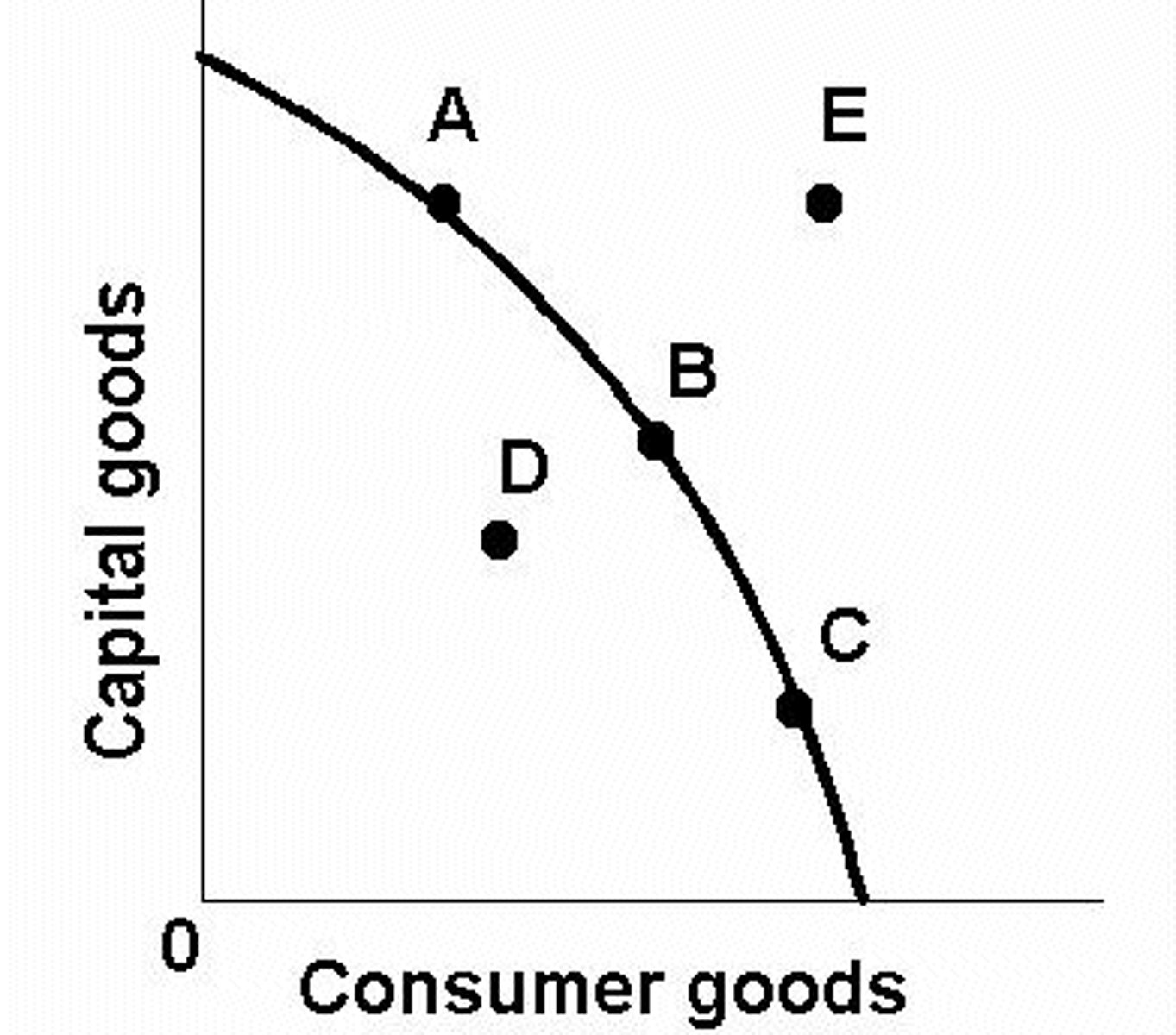
The PPF Curve
This curve shows the possible combinations of goods and services available to an economy, given that all factors of production/resources are fully efficiently employed
Market
An arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things

Basic Capitalist Principles
1. Goods and services are produced for profitable exchange through self interest
2. Labour is the source of value
3. The "invisible hand" of the market, market is self regulating
4. The law of supply and demand
5. The law of competition
6. A social division of labour
7. Laissez faire (Leave things alone)

Pure monopoly
A market in which there is only one seller of the product (Ex. Utilities, such as cable, electrical, sewer, gas lines, phone companies.) They have a great deal of control over the price, the product is indistinguishable

Oligopoly
A market which has few sellers that provide most of the goods and services. They have standard products, they rely heavily on advertising to distinguish themselves (Ex. Auto industry, airline industries)

Monopolistic Competition
Many sellers and many products
The ability to differentiate goods and services is very important.

Pure Competition
Many sellers and identical products
All products are standard and identical. (Ex. Agriculture Products)