Human Anatomy - Joints and Knees
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
synarthrosis joint
immovable joint
suture
a fibrous synarthrotic joint found only between the bones of the skull
gomphosis
a fibrous synarthrotic attachment of a tooth to its sockets
amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joint
synovial joints (diarthrosis)
Movement and permits a wide range of motion
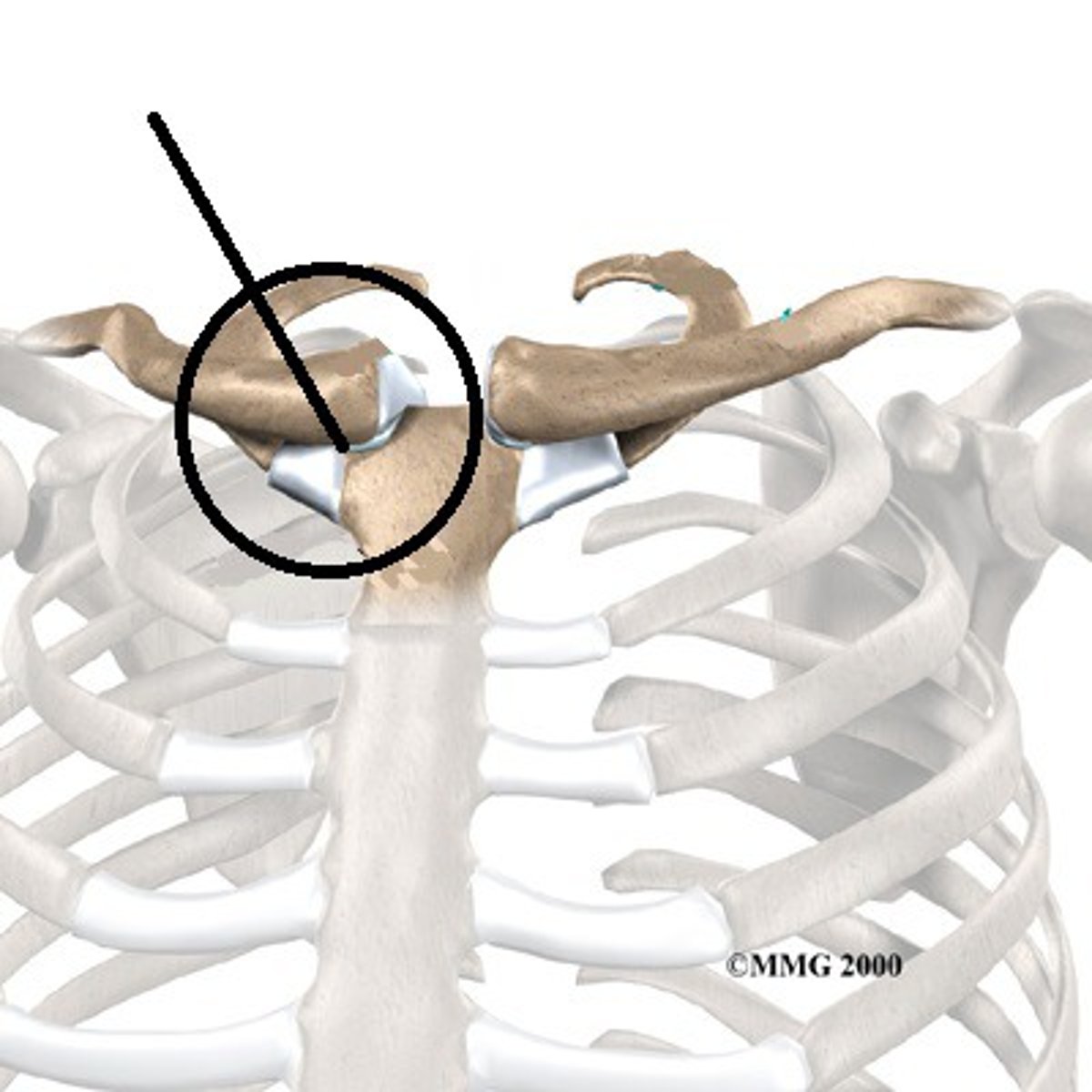
gliding (sternoclavicular)
uniaxial
synoval joint between the medial end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum.
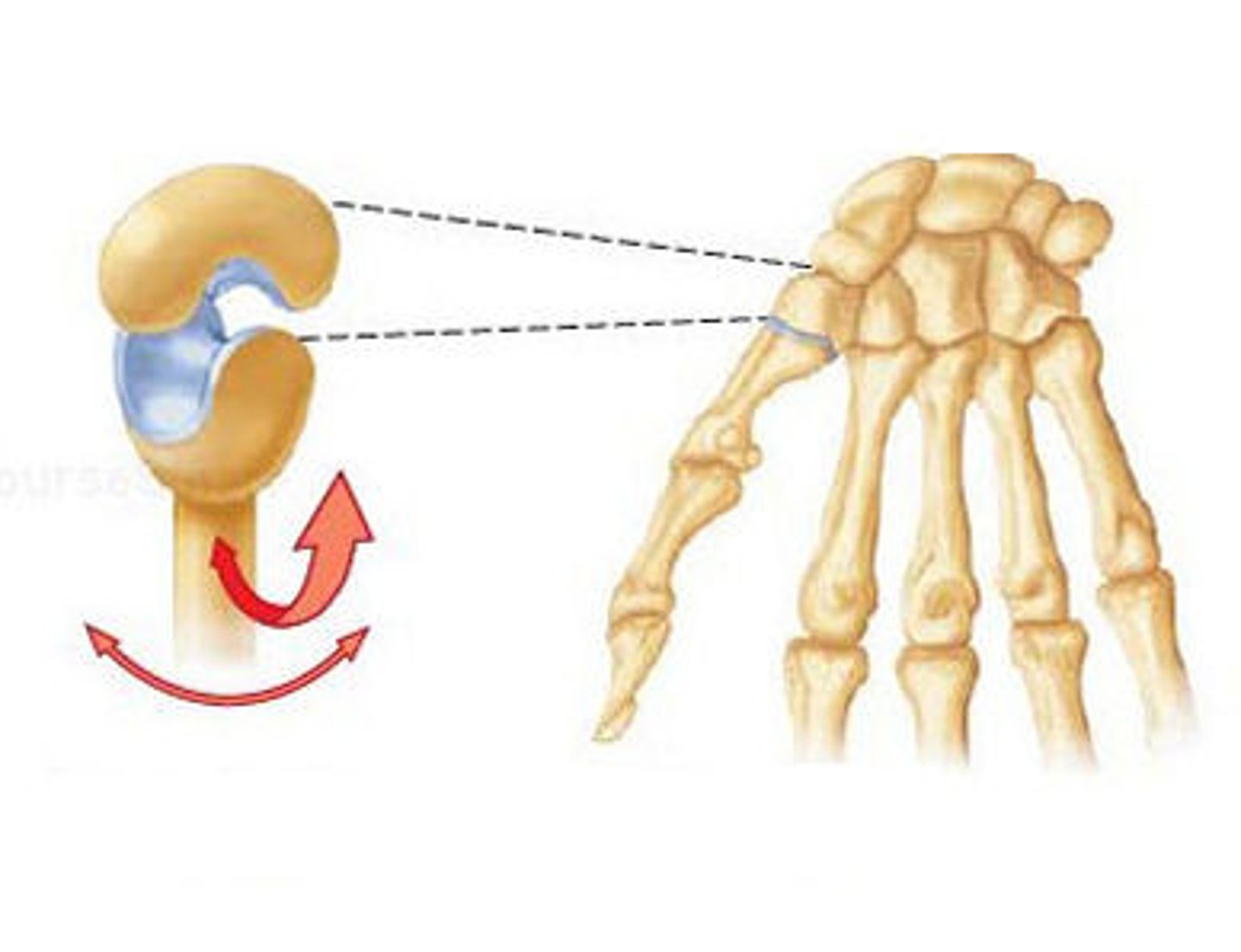
saddle (carpometacarpal of thumb)
biaxial
shaped heads that permit movement in two different planes.
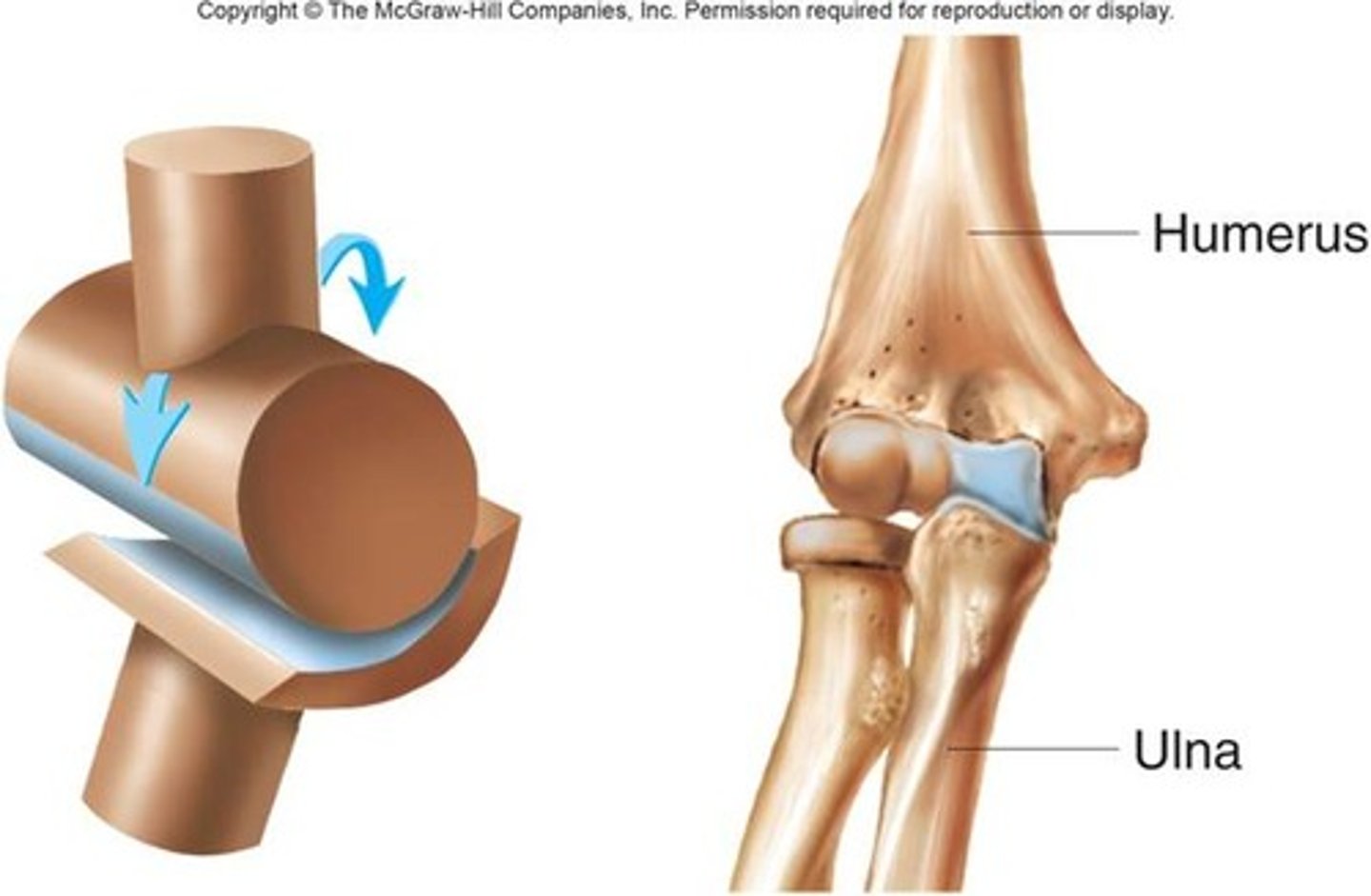
hinge joint (elbow)
uniaxial
permits flexion and extension in a single plane, like the opening and closing of a door.
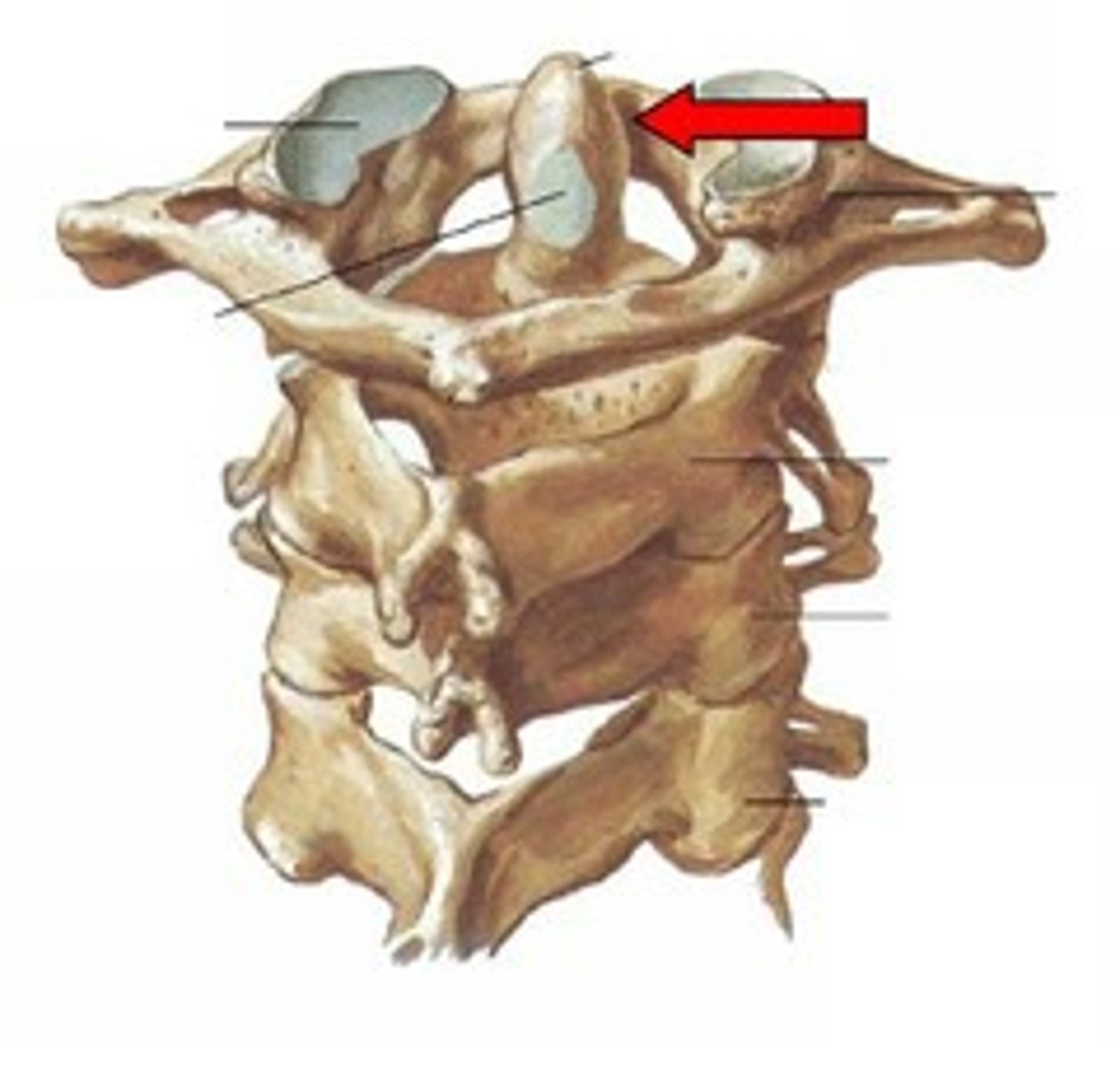
pivot (atlantoaxial)
uniaxial
a rounded process of bone fits into a bony ligamentous socket, permitting rotation.
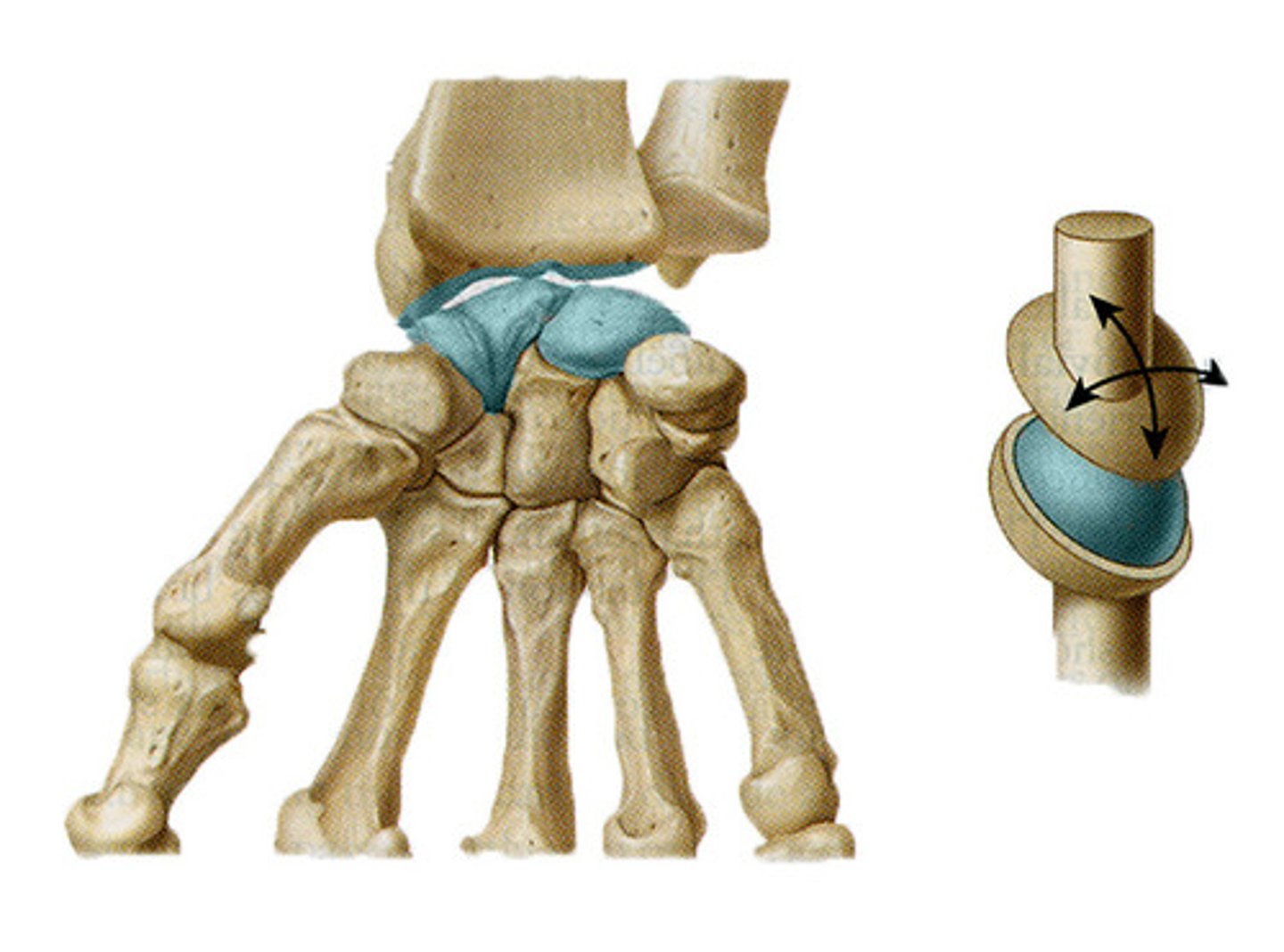
condyloid (radiocarpal)
biaxial
permits flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and circumduction.
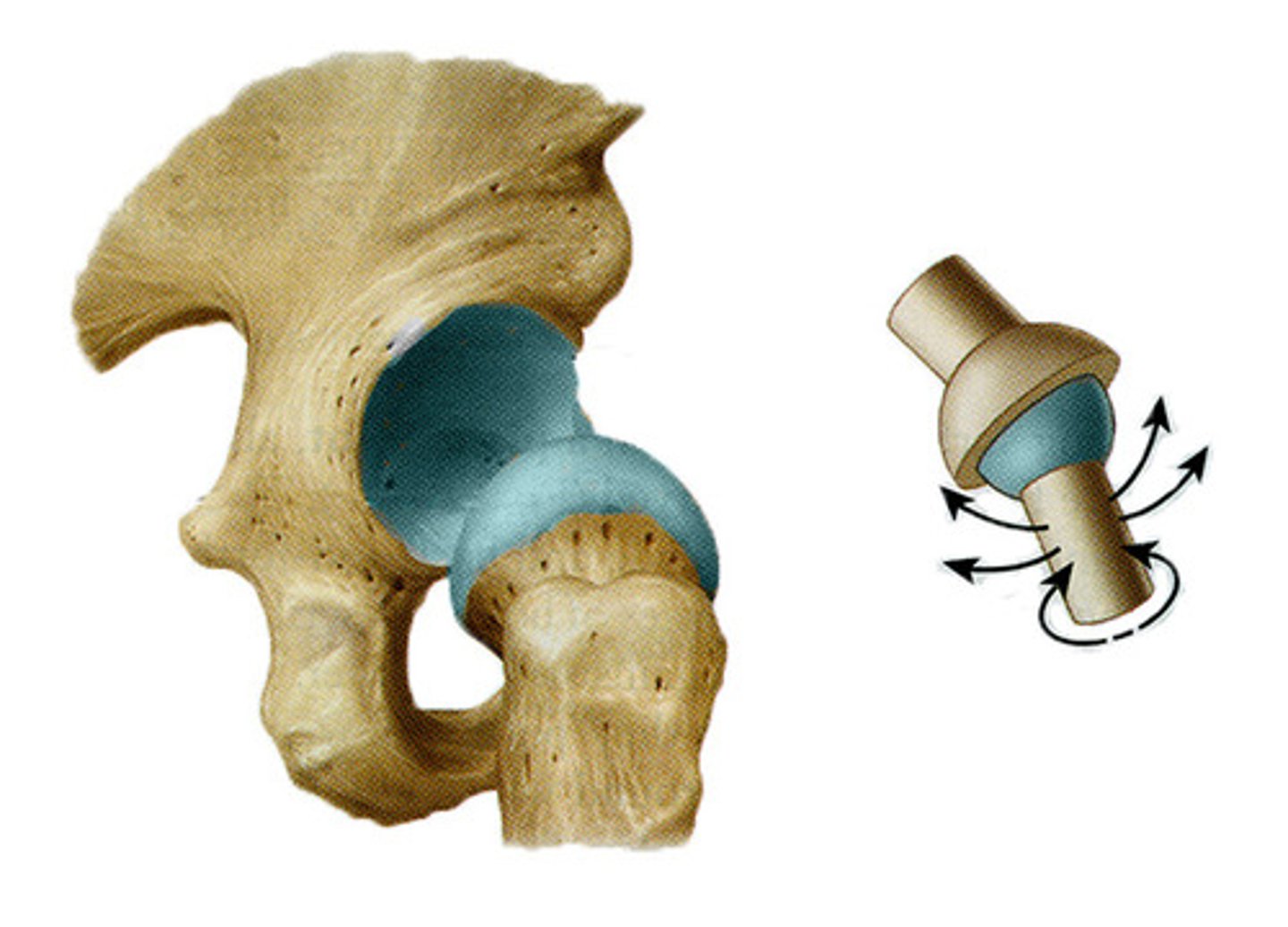
ball and socket (hip)
multiaxial
a rounded head fits into a concavity. permitting movement on several axes.
gliding joint movement (intercarpal)
a joint between the distal end of the radius and the proximal row of carpal bones. bones glide past each other along the plane of the joint
special movements
Certain terms that apply to specific joints or unusual types of movements
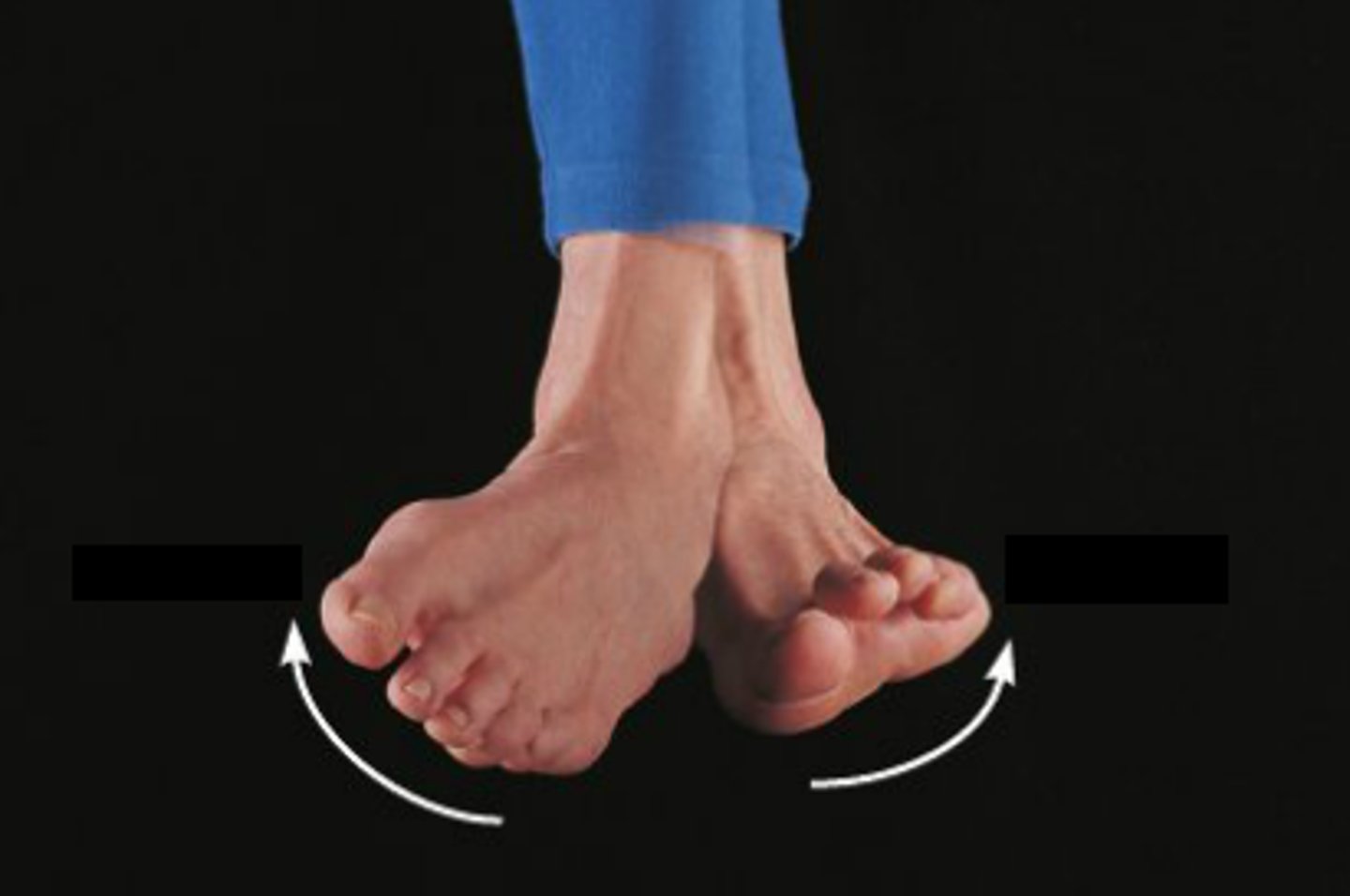
inversion/eversion (special movements)
movements of the sole of the foot medially or laterally
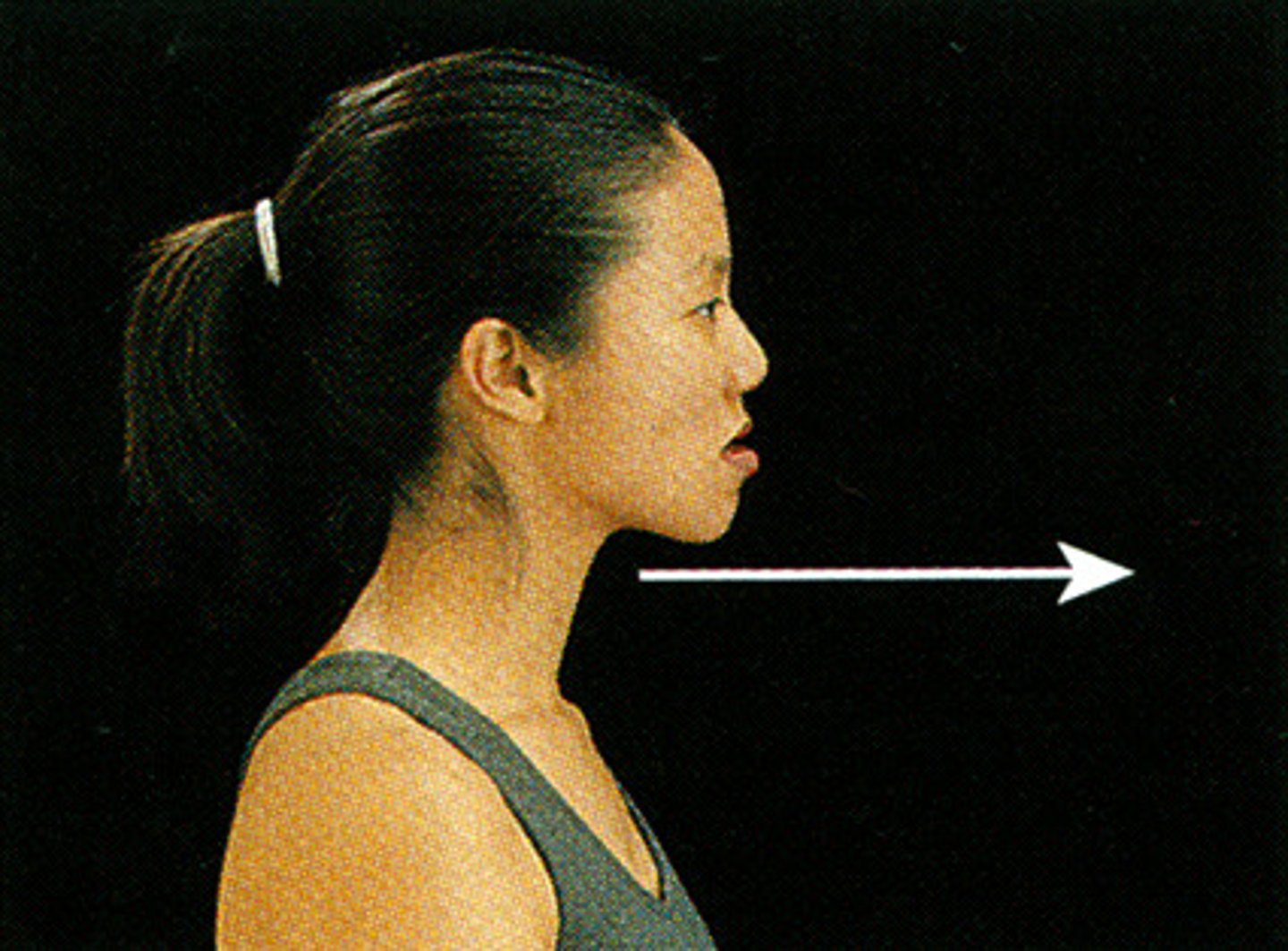
Protraction (special movements)
moving a body part forward
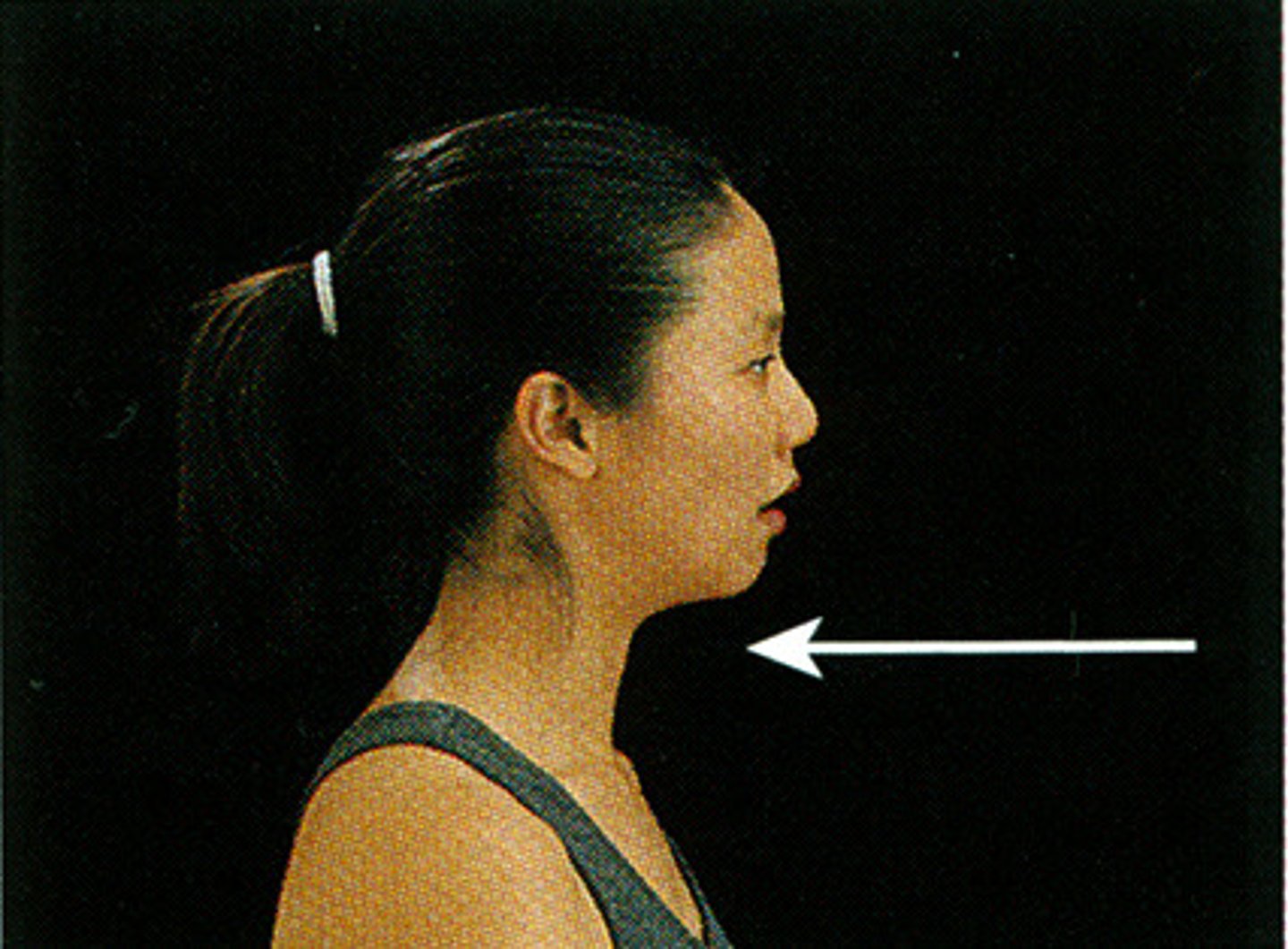
Retraction (special movements)
moving a part backward
hyperextension
the extreme or overextension of a limb or body part beyond its normal limit, can result in joint damage (angular)
dorsiflexion
elevates the distal portion of the foot and the toes (special movement)
abduction/adduction
movement away from and toward the body (angular)
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground (special movement)
elevation
movement in a superior direction (special movement)
supination
movement that turns the palm up (rotation)
depression
inferior movement of a body part (special movement)
pronation
movement that turns the palm down (rotation)
circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
rotation
circular movement around an axis
flexion and extension
bending and extension of a limb (angular)
angular joint movement
increase or decrease in angle between bones, around an axis
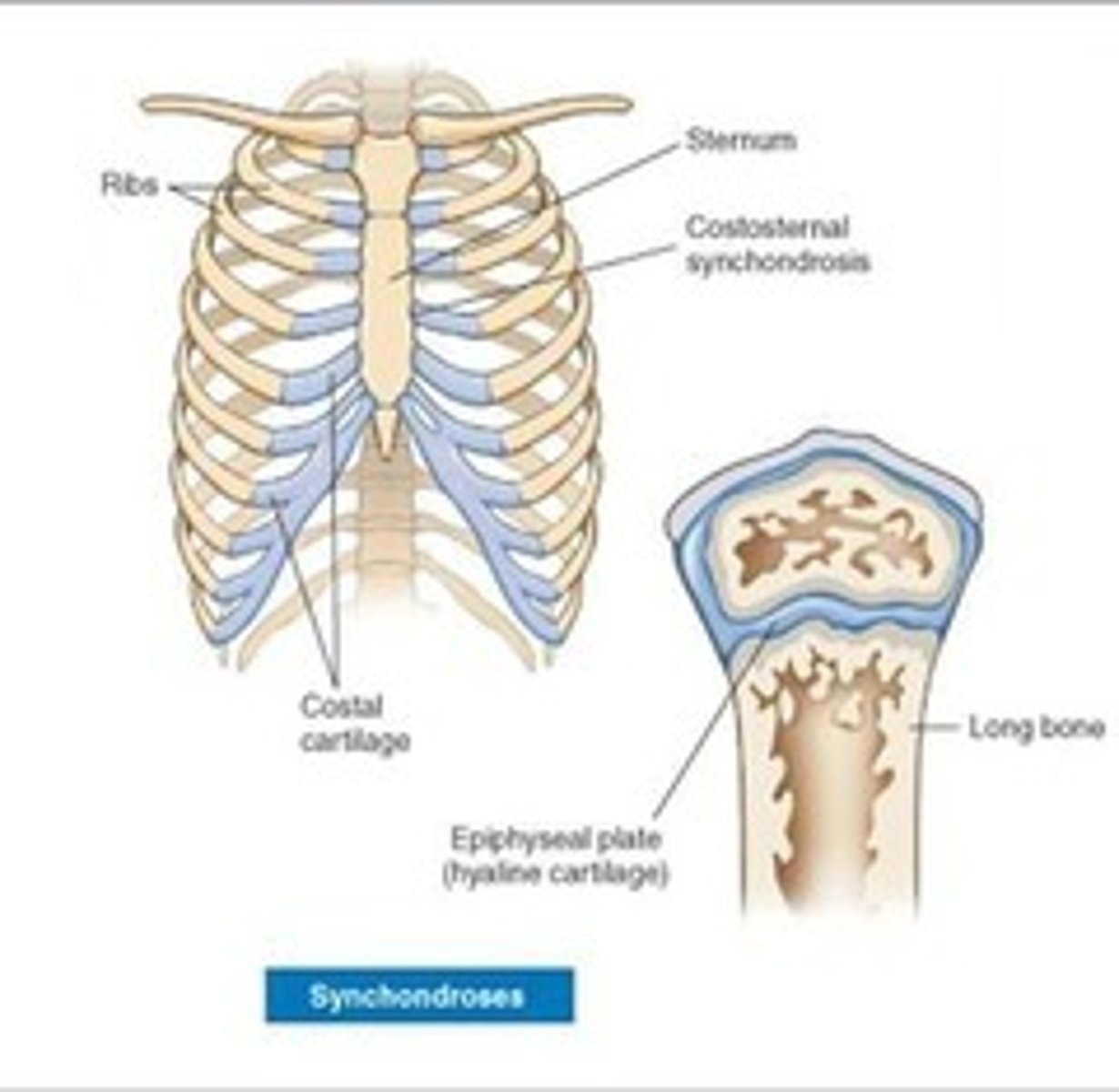
Synchondrosis (Epiphyseal Plate)
Composed of hyaline cartilage that connects diaphyses and epiphyses of developing long bones
(Ex: First sternocostal and costochondral joints are synchondroses that persist into adulthood)
cartilaginous
adjoining bones united by cartilage; no joint cavity
syndesmosis
a ligament connects the bones and limits movement at the joint (FIBROUS amphiarthrosis)
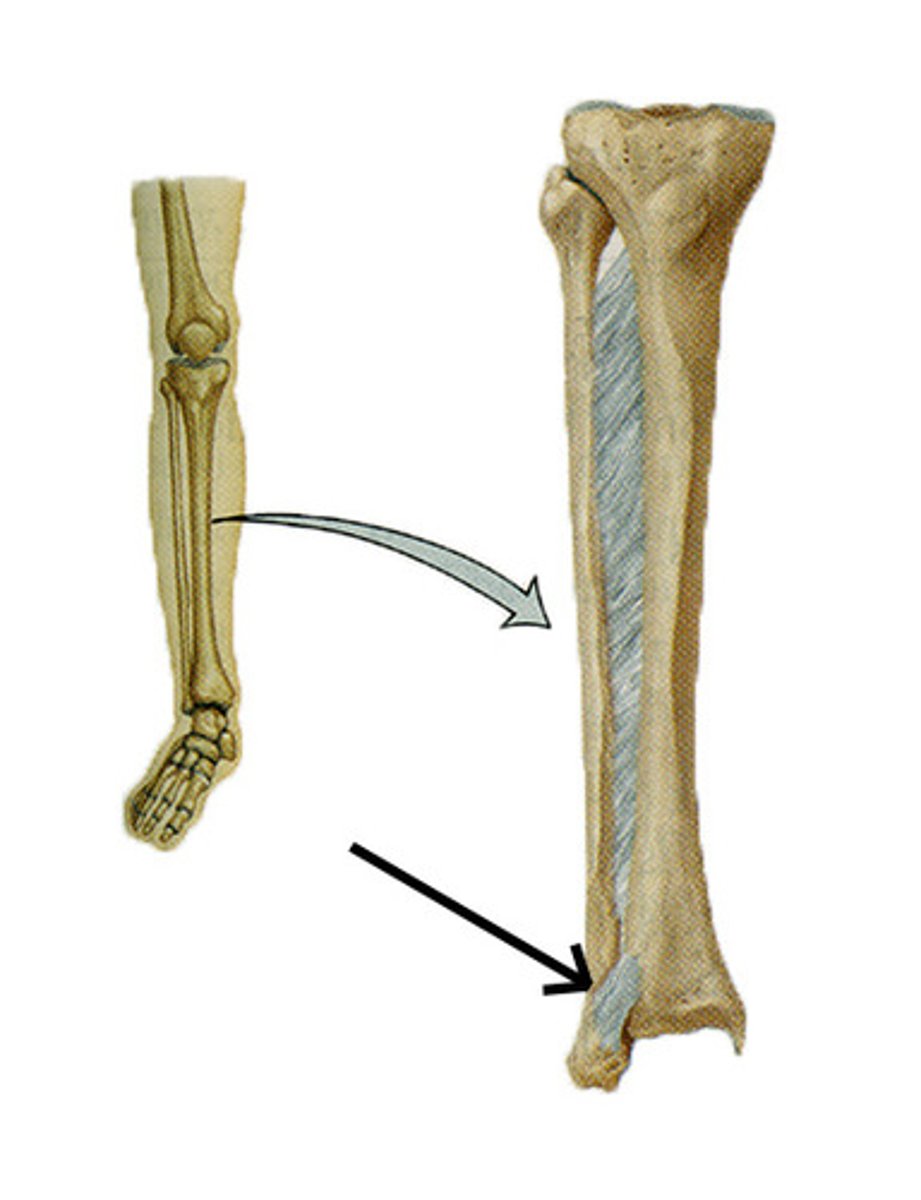
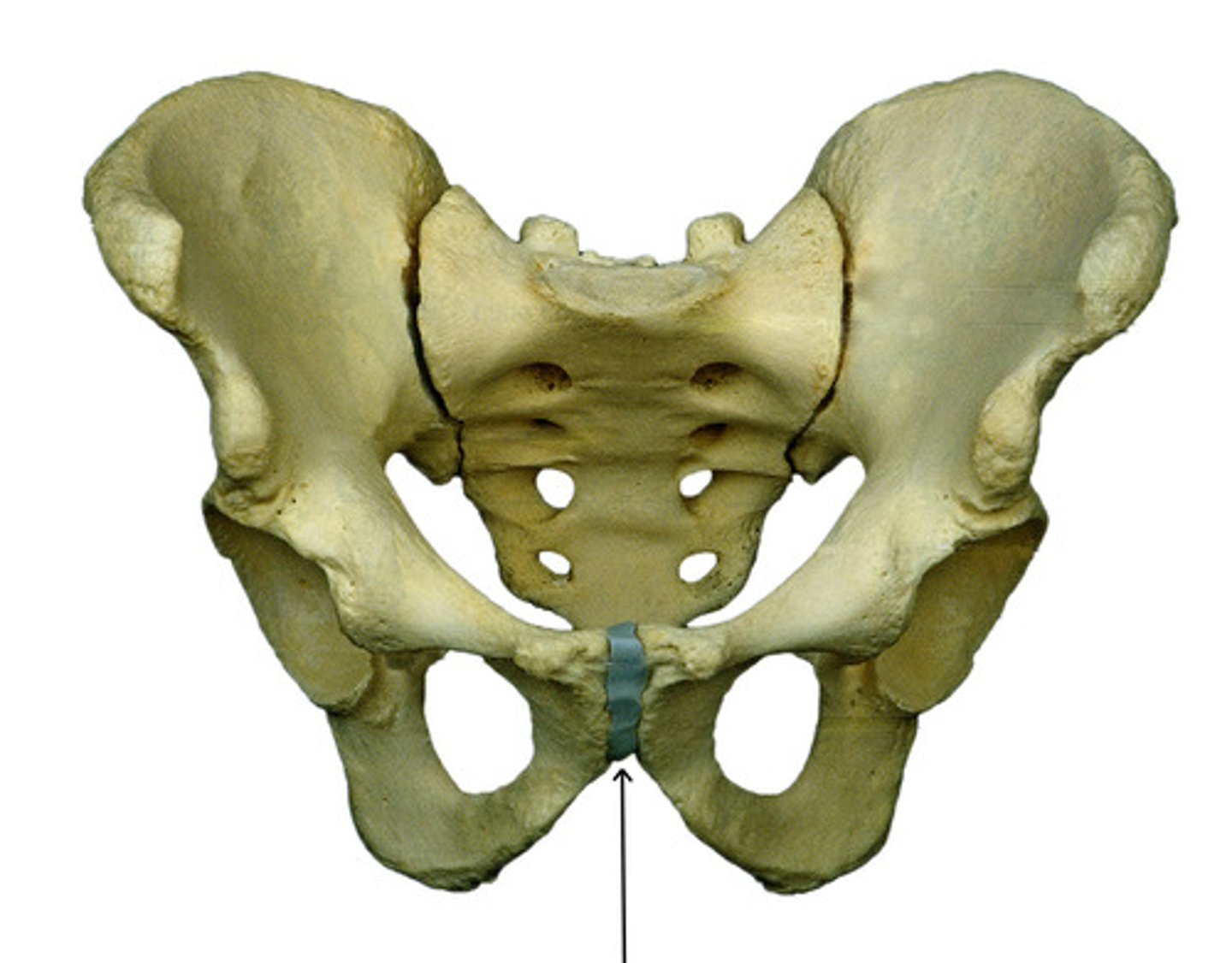
symphysis
a wedge or pad of fibrous cartilage separates the articulating bones. (amphiarthrotic)
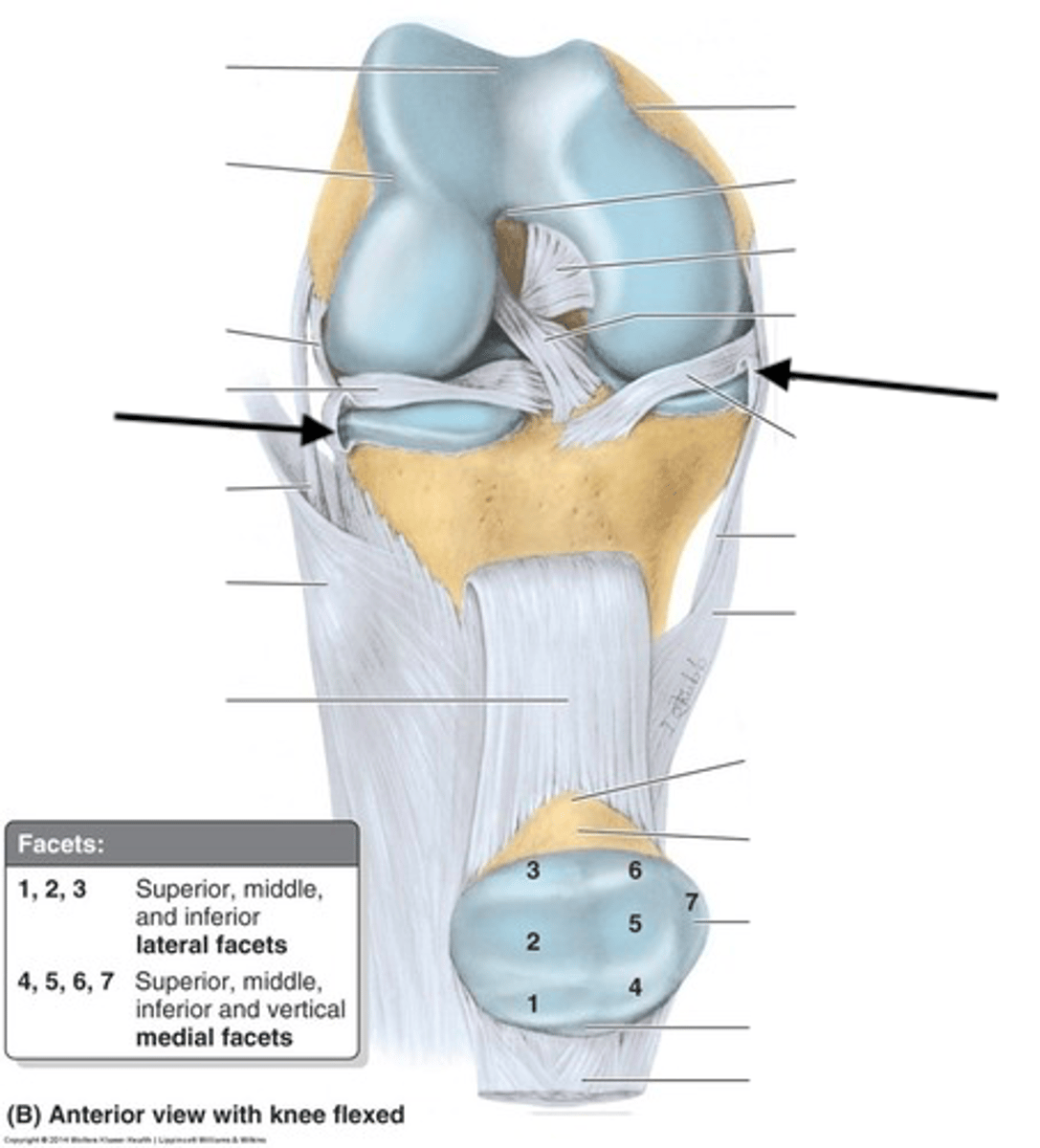
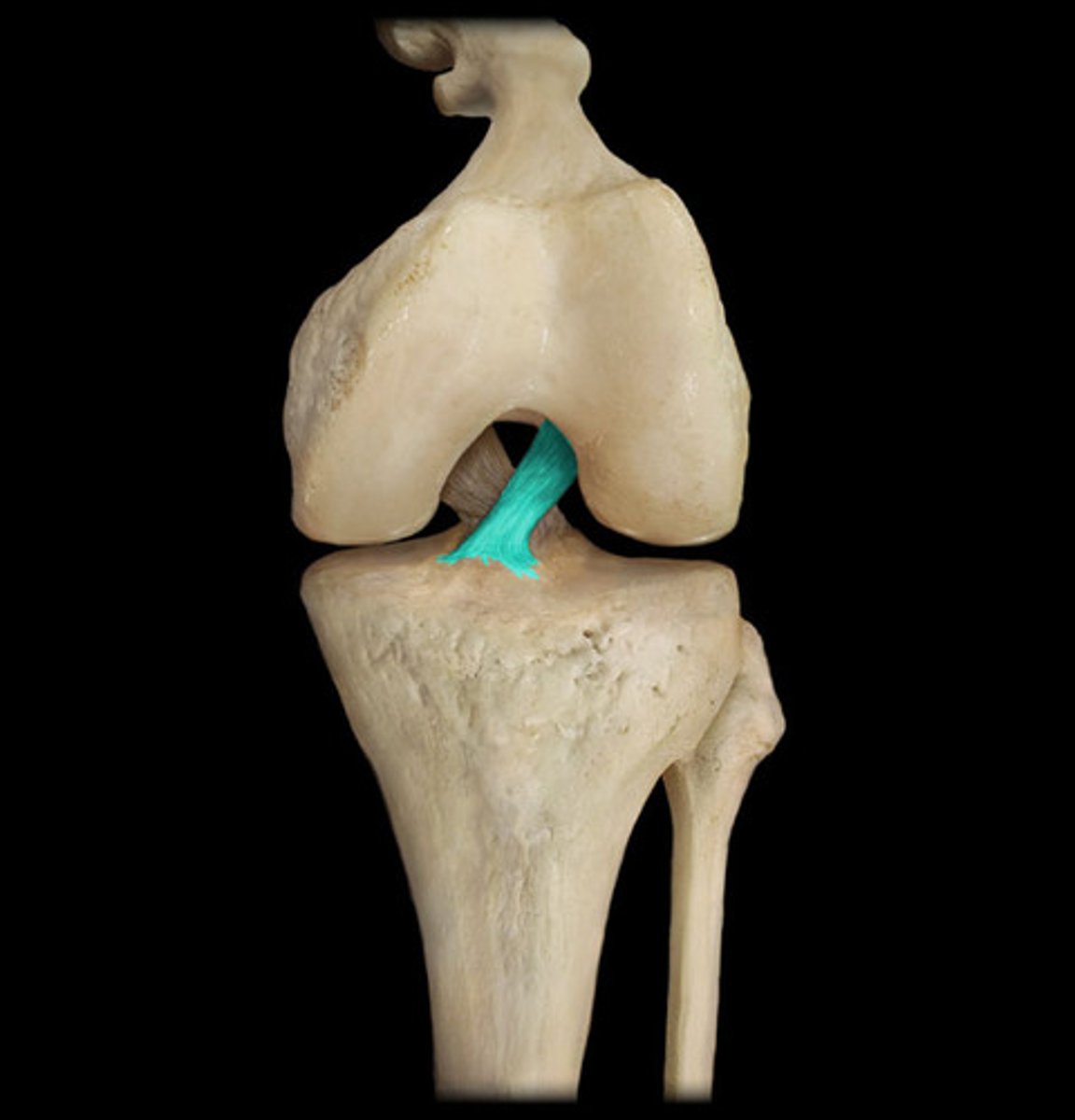
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
A ligament in the knee that attaches to the anterior aspect of the tibial plateau. restricting anterior movement of the tibia on the femur
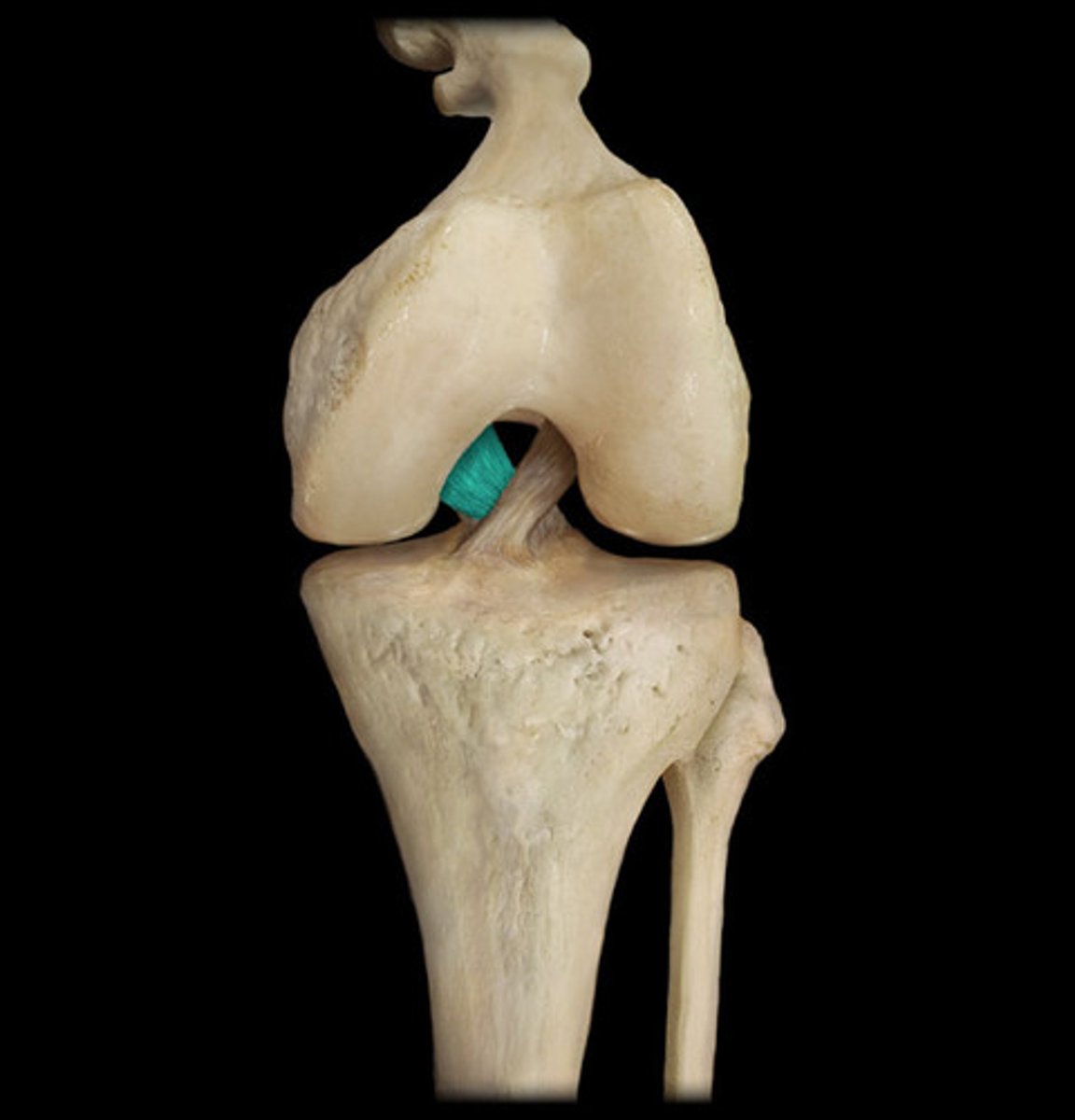
posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
A ligament in the knee that attaches to the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau, restricting posterior movement of the tibia on the femur
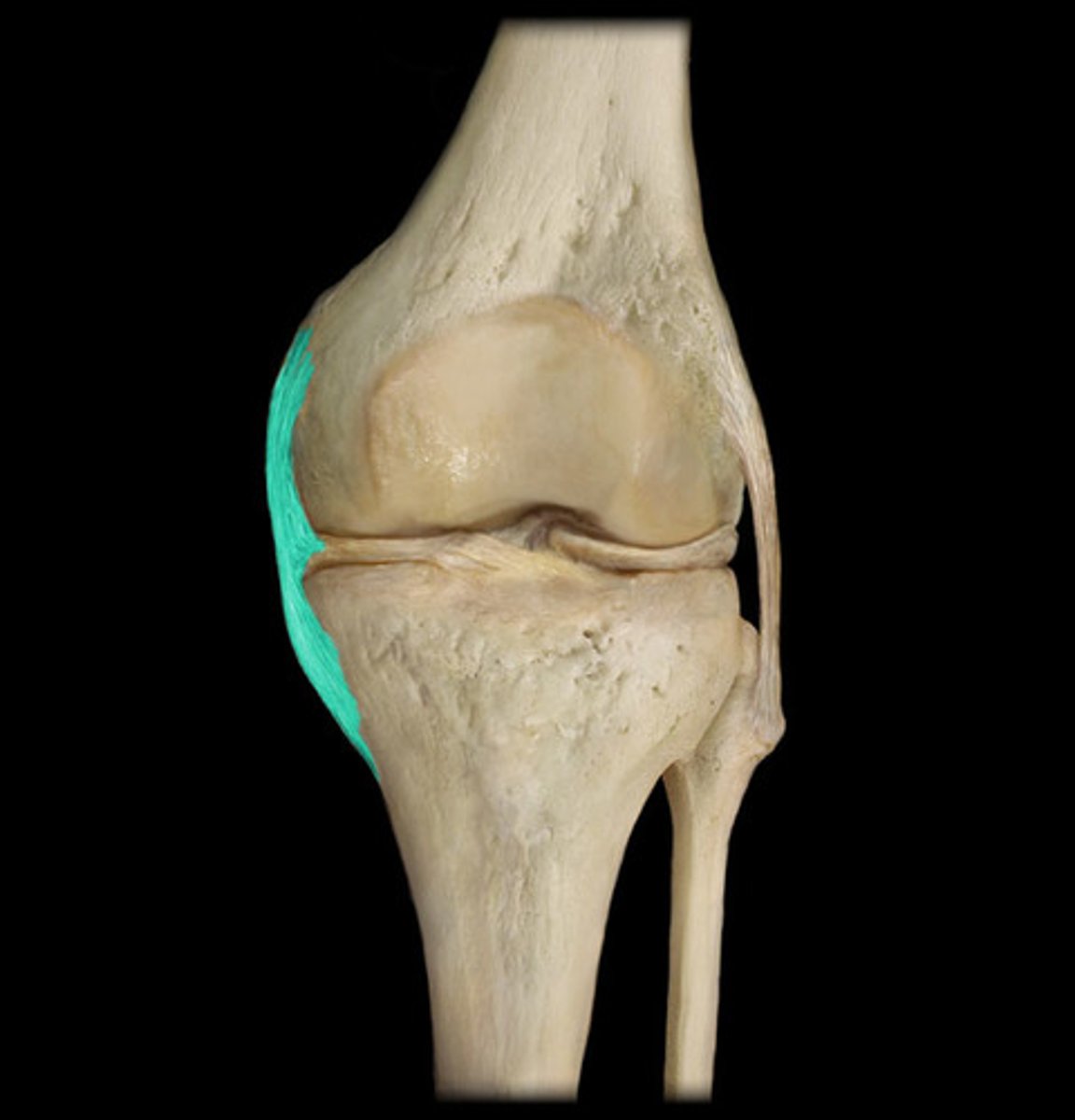
medial collateral ligament (MCL)
One of four ligaments that are critical to the stability of the knee joint; spans the distance from the medial end of the femur to the top of the medial tibia
lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
One of four ligaments that are critical to the stability of the knee joint; distal end of the femur to the proximal end of the fibula (may also touch the tibia as well)
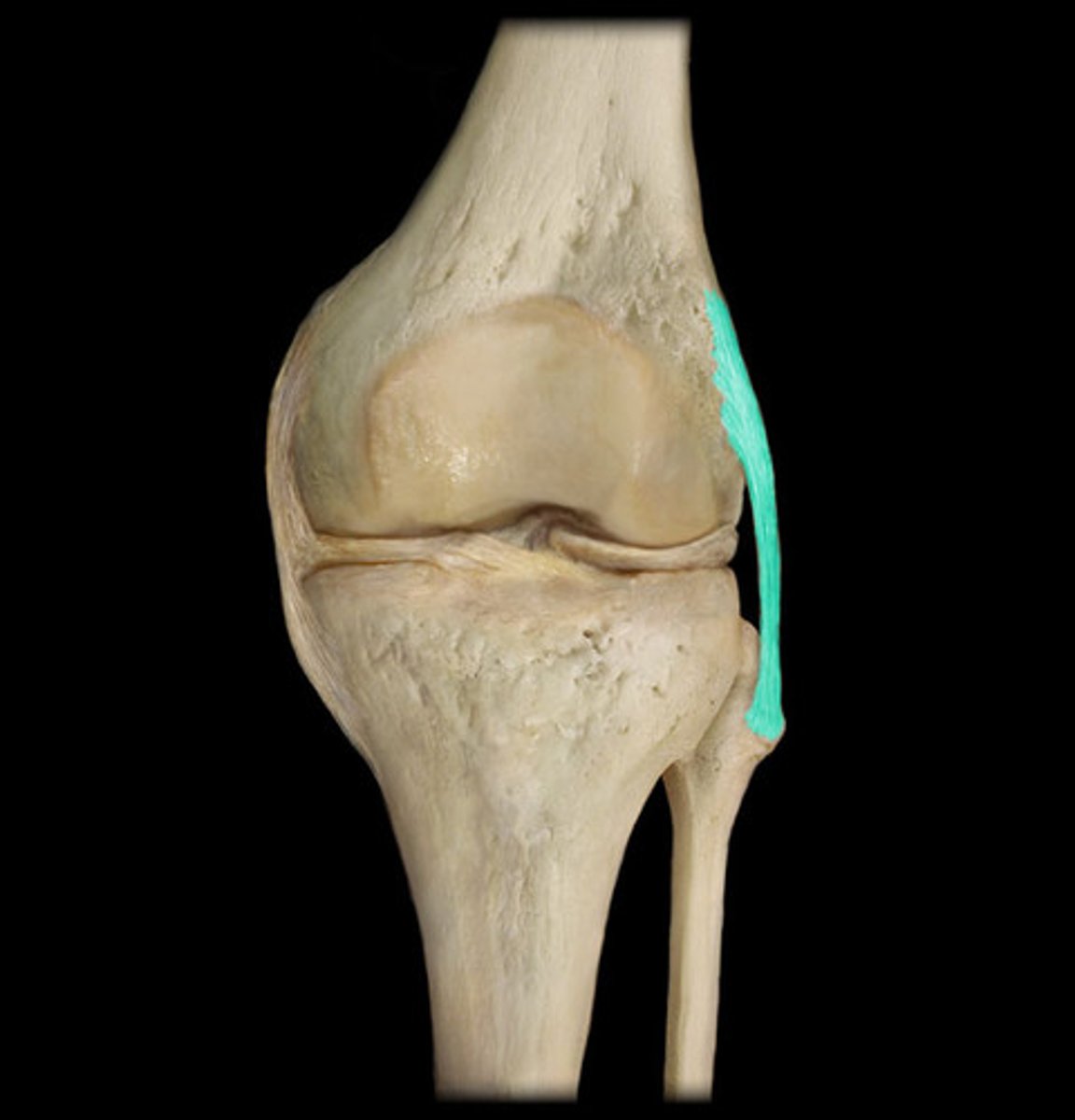
medial meniscus
Cartilage in the knee between the femoral condyle and the medial tibial plateau
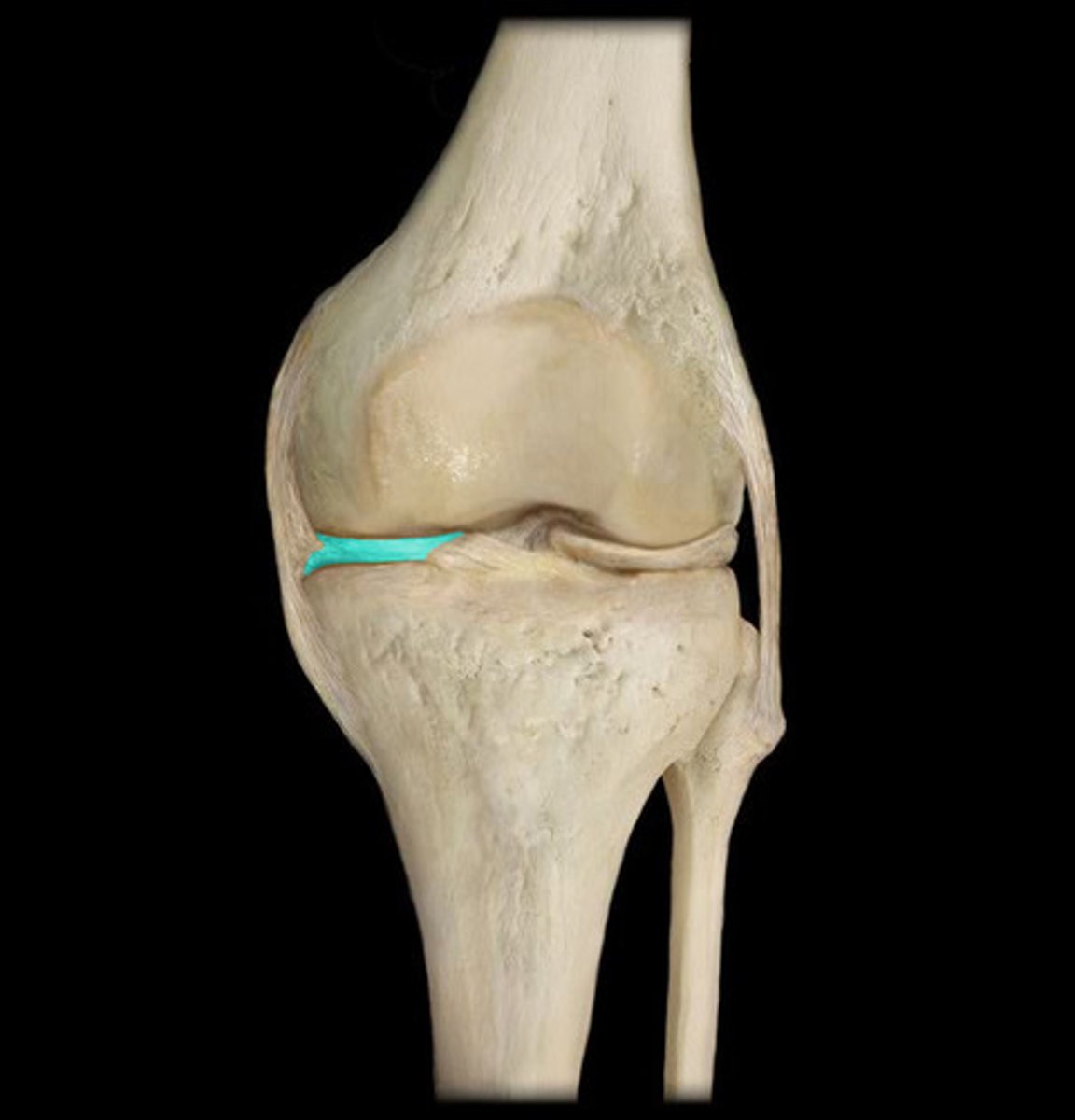
lateral meniscus
Cartilage in the knee between the femoral condyle and the lateral tibial plateau
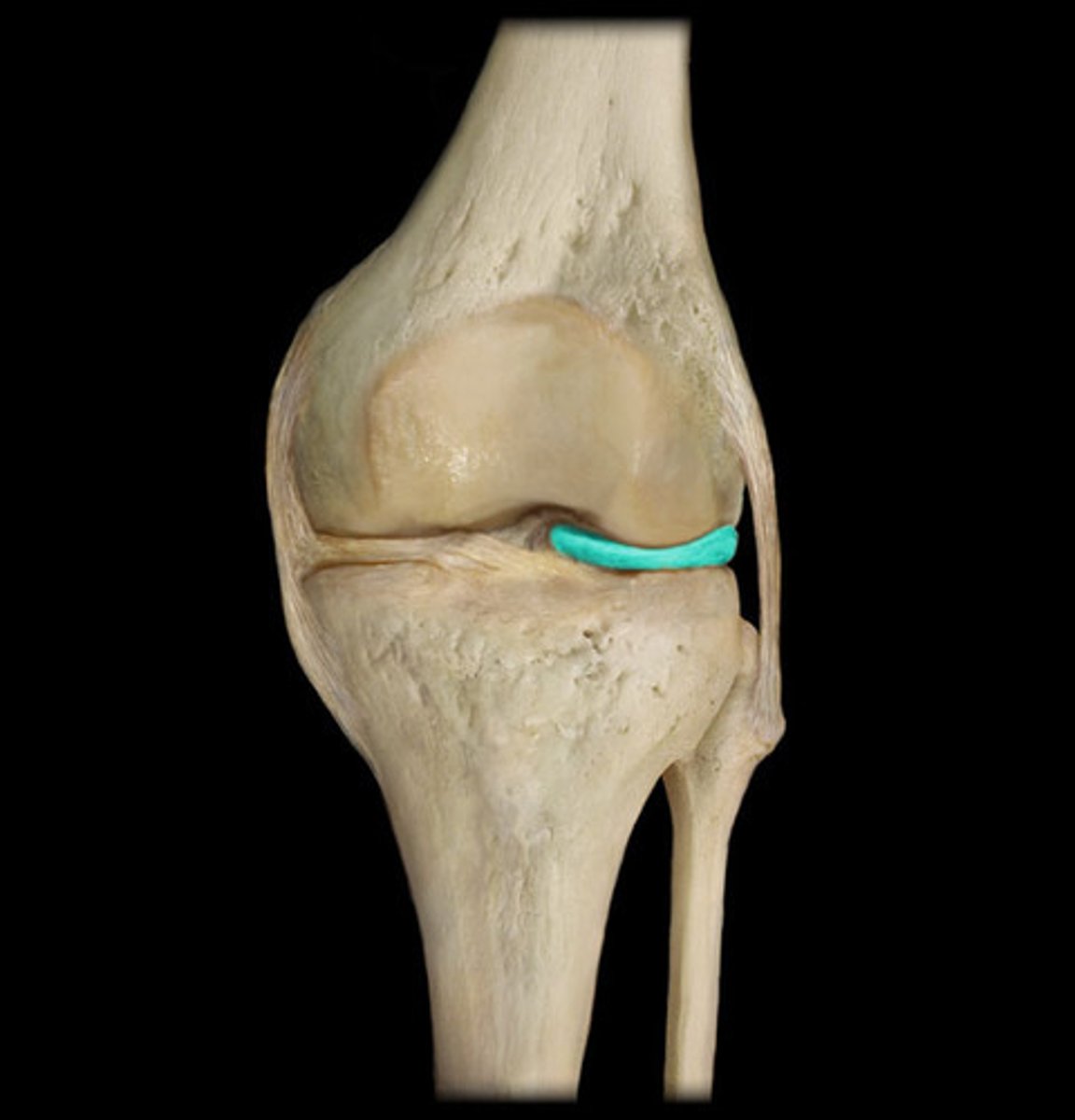
coronary ligament
attaches medial and lateral miniscus to the tibia