ANAPHY Lab ACTIVITY 3 HUMAN TISSUES: EPITHELIAL AND CONNECTIVE
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
• Found in different areas
• Body coverings
• Body linings
• Glandular tissue
• Functions
• Protection
• Absorption
• Filtration
• Secretion
•Cells fit closely together
•Tissue layer always has one free surface
•The lower surface is bound by a basement membrane
•Avascular (have no blood supply)
•Regenerate easily if well nourished
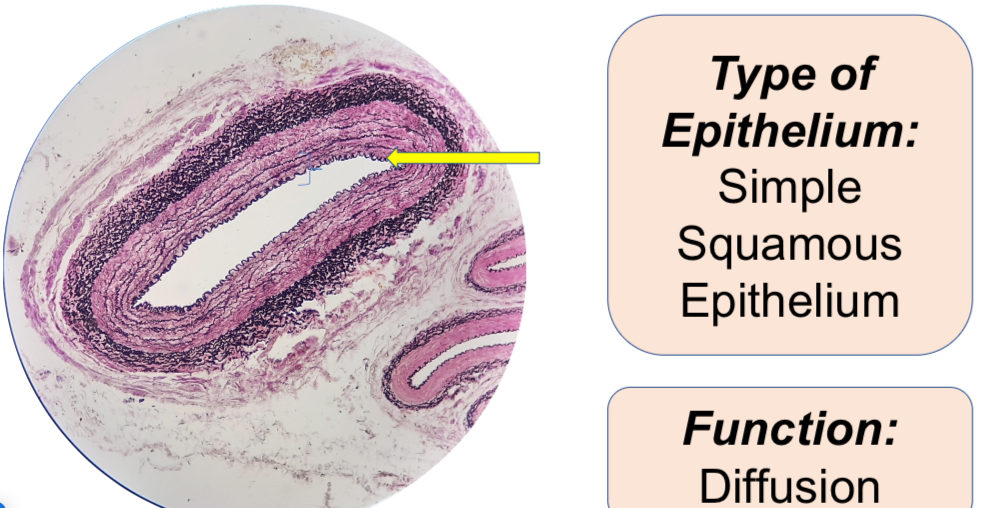
1. X-S Human Artery
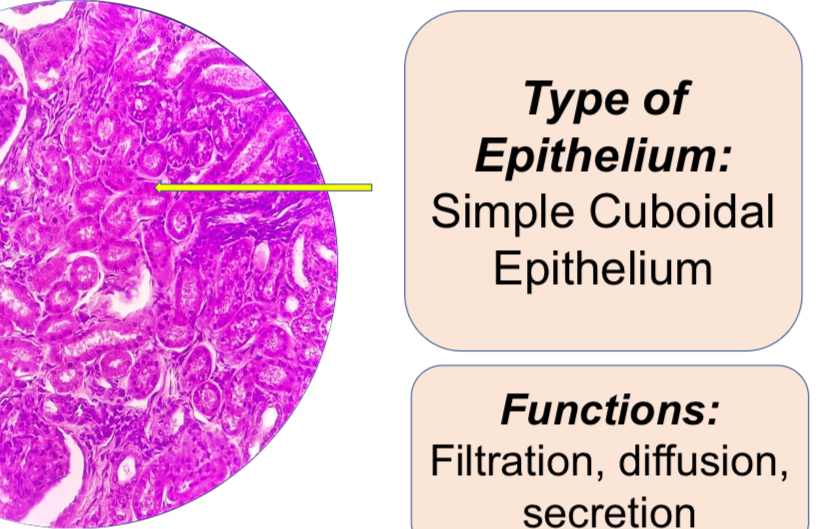
2. X-S Renal (Kidney) Tubules
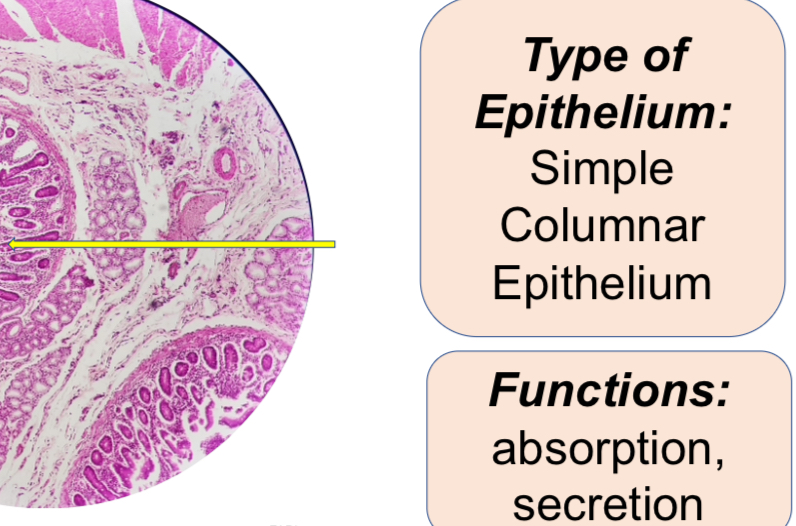
3. X-S Duodenum
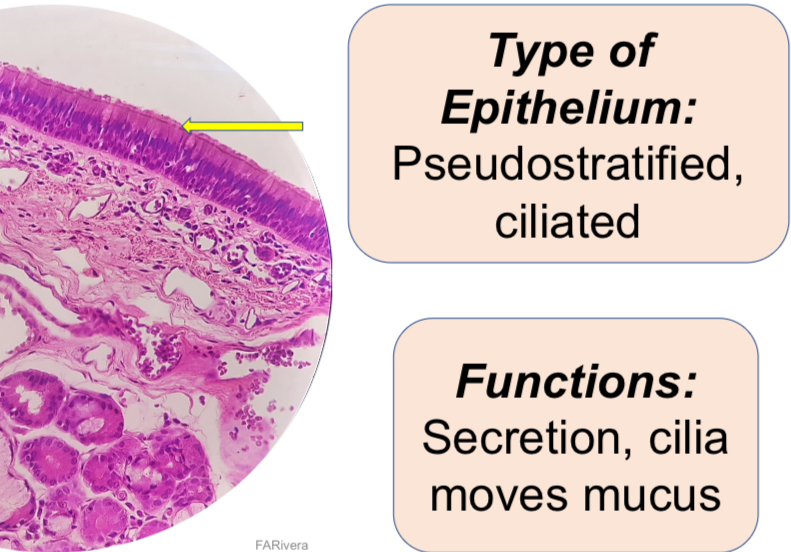
4. X-S Trachea
5. X-S Esophagus
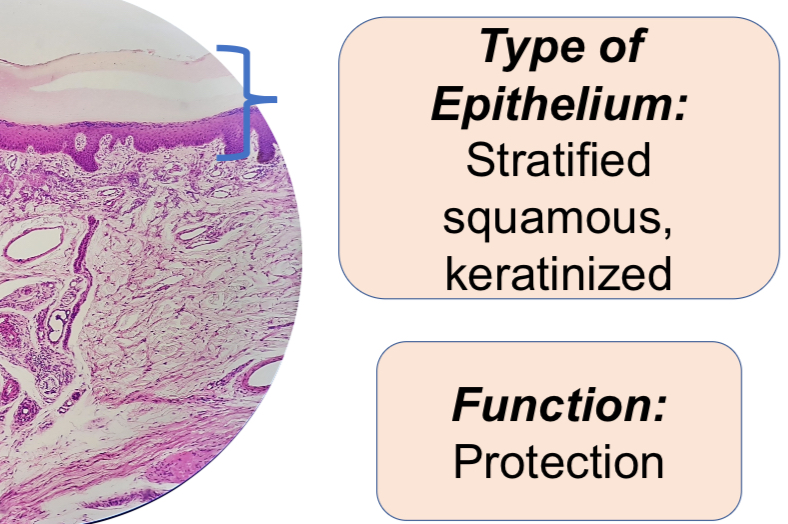
6. X-S Human palm skin -epidermis
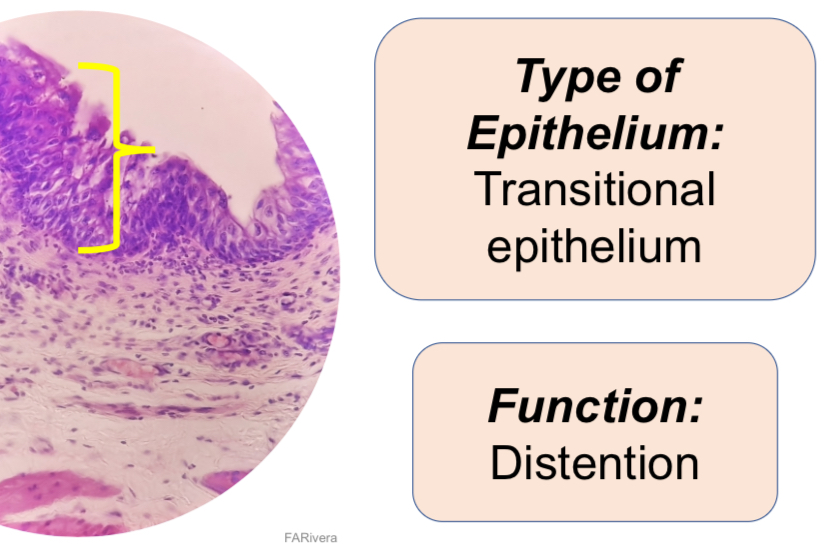
7. X-S Urinary bladder
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Artery Medium, X.S. LPO, 100x
Human Kidney, X.S. (Renal Tubules) HPO, 400X
Human Duodenum X.S
Human Trachea, X.S
Esophagus, X.S. HPO, 400
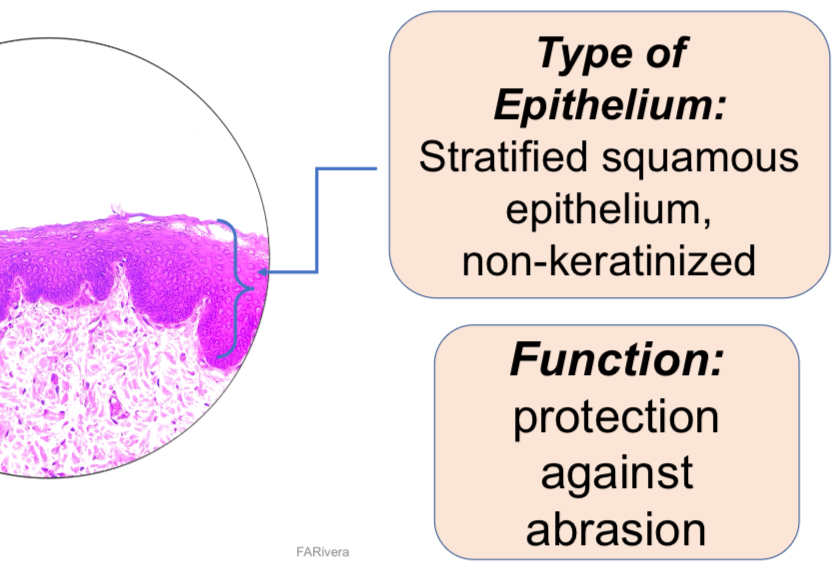
Human Palm Skin, X.S.
Urinary Bladder, X.S. HPO, 400x
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
•Found everywhere in the body
•Includes the most abundant
and widely distributed tissues
•Functions
•Binds body tissues together
•Supports the body
•Provides protection
• Variations in blood supply
• Some tissue types are well
vascularized
• Some have poor blood
supply or are avascular
• Extracellular matrix
• Non-living material that
surrounds living cells
•Two main elements
•Ground substance – mostly water along with adhesion
proteins and polysaccharide molecules
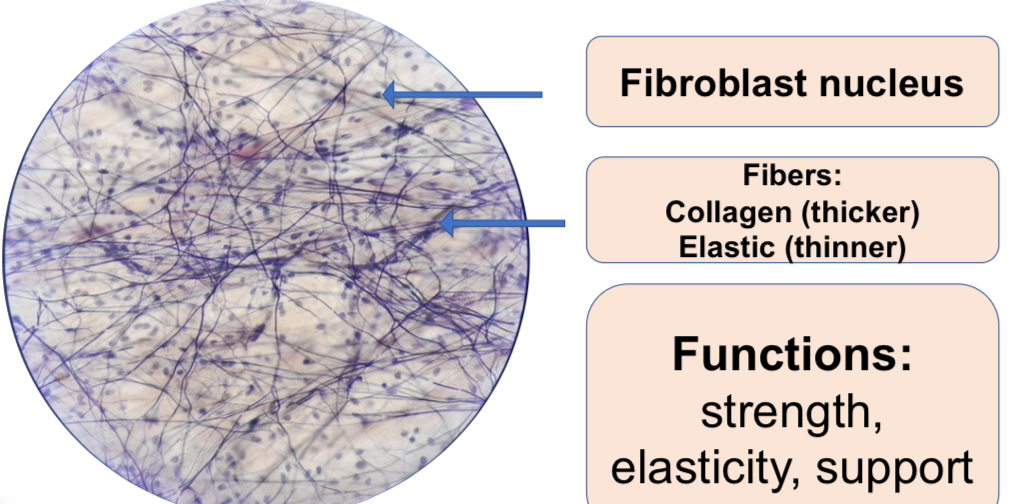
•Fibers
•Produced by the cells
•Three types
•Collagen fibers
•Elastic fibers
•Reticular fibers
COMPONENTS OF THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
a.1. Areolar connective tissue
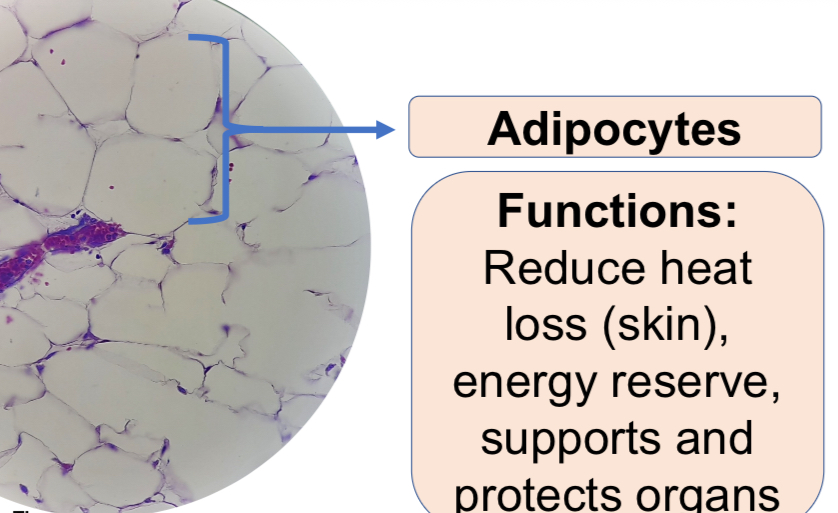
a.2. Adipose connective tissue
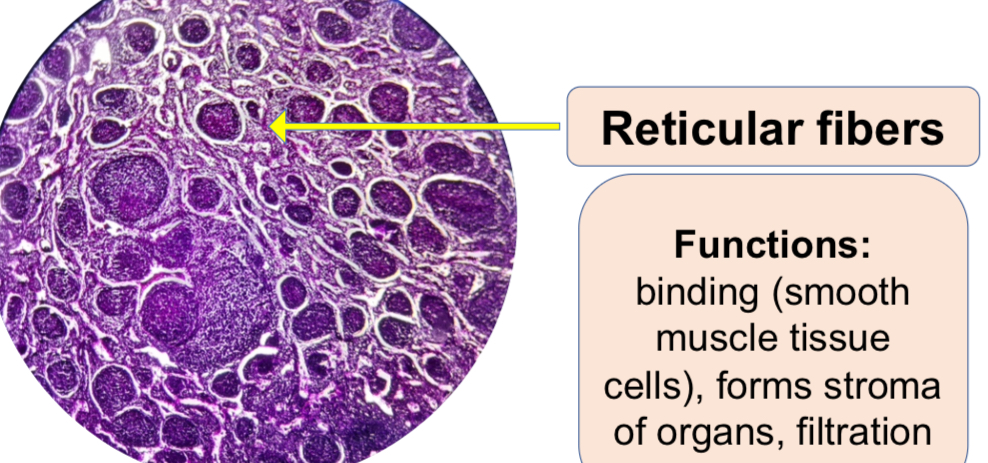
a.3 Reticular connective tissue
A. Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar Connective Tissue
Adipose Connective Tissue
Mammal Reticular Tissue
B. Dense Connective Tissue
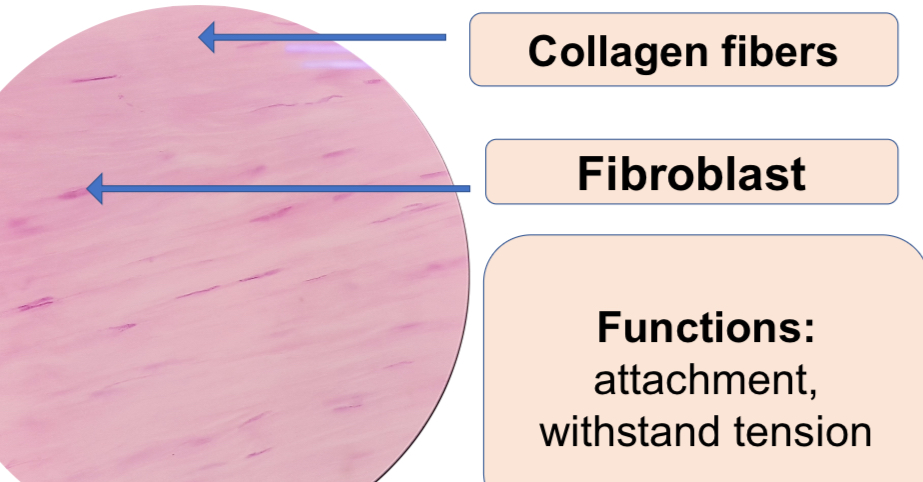
b.1. Dense regular (tendon)
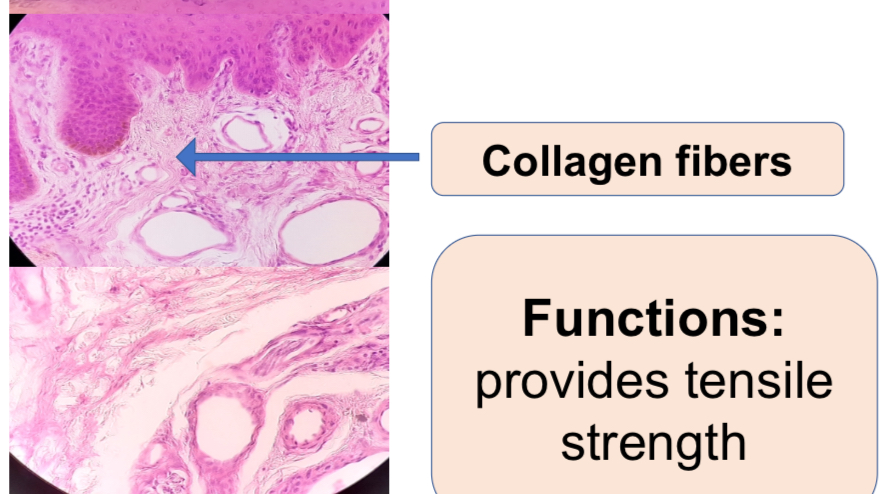
b.2. Dense irregular (human dermis)
Human Tendon
Human Dermis
C. Supporting Connective Tissue
c.1. Elastic cartilage
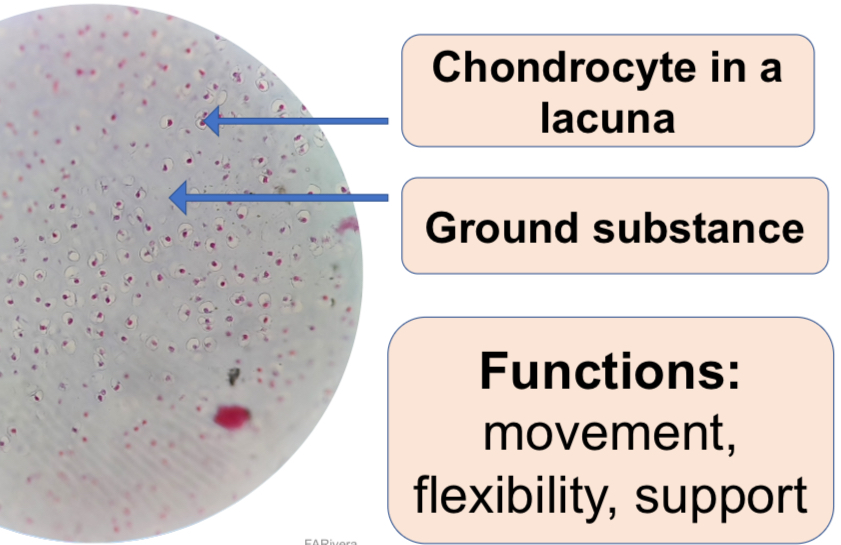
c.2. Hyaline cartilage
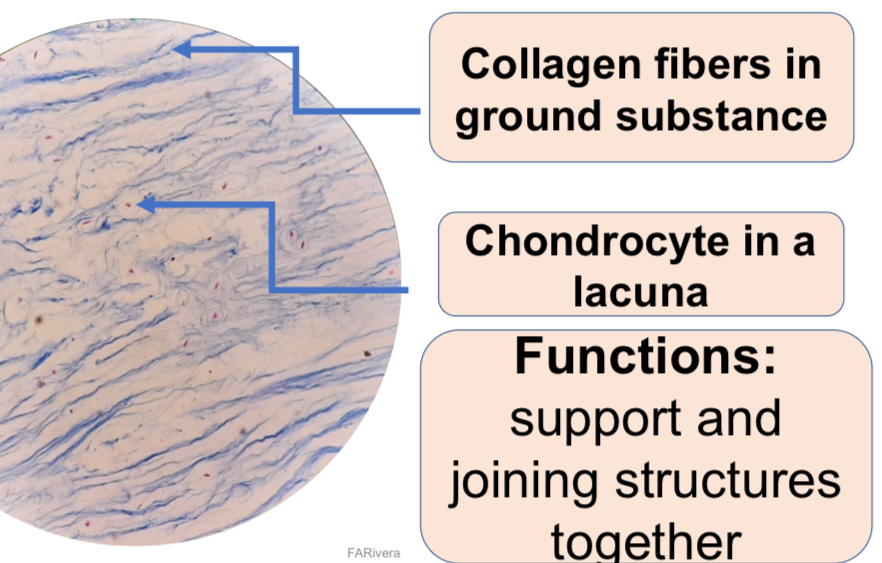
c.3. Fibrocartilage
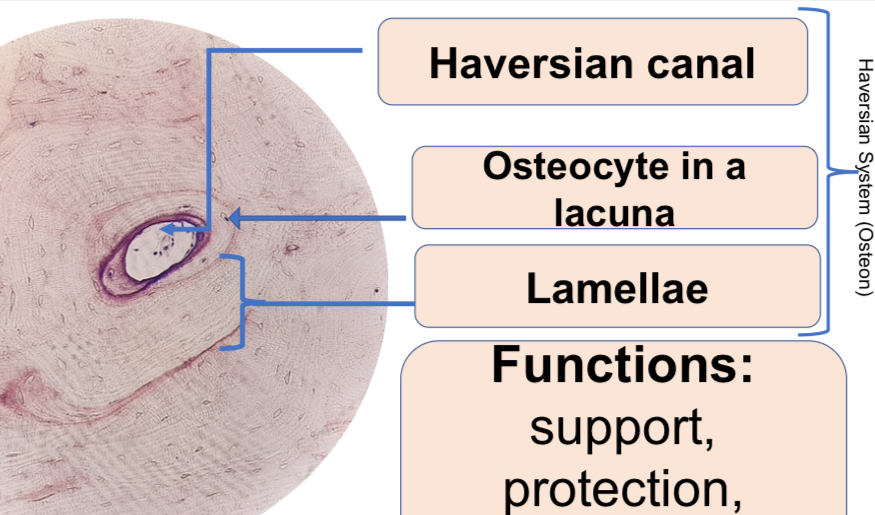
c.4. x-s of the human bone
Elastic Cartilage
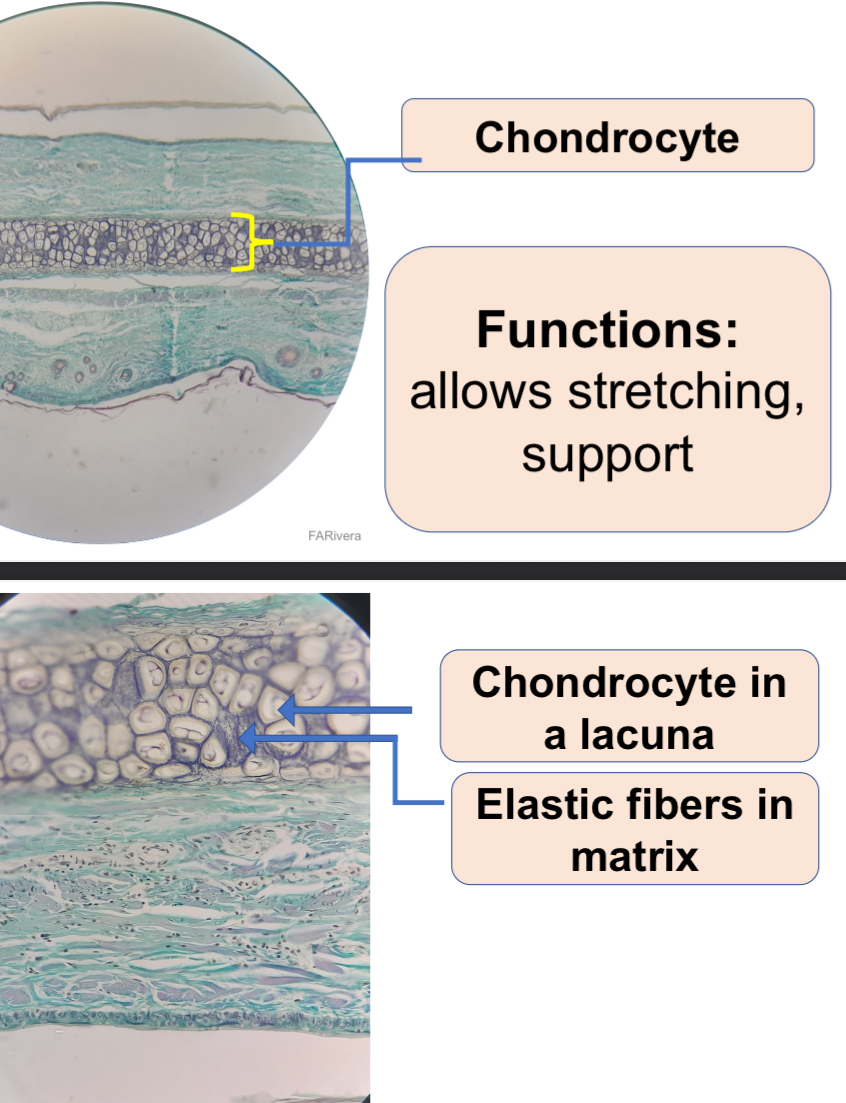
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Human Bone Decalcified, X.S.
D. Vascular (Fluid) Connective Tissue
d.1 Human blood smear
Human Blood Smear
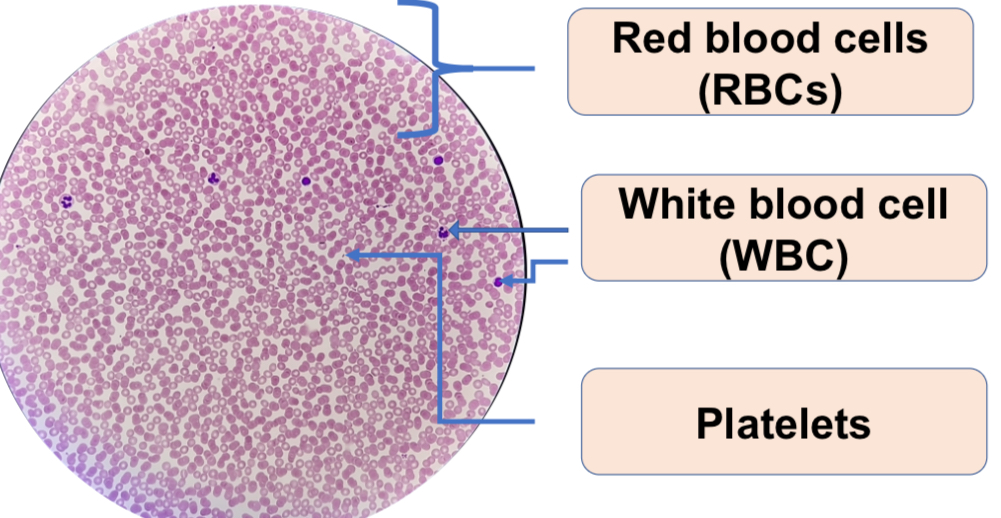
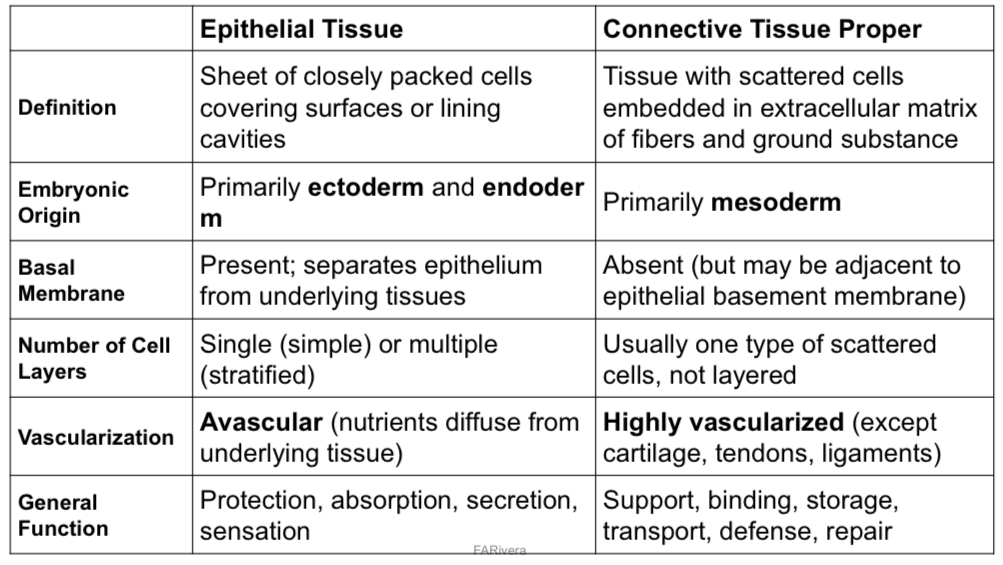
1. Differentiate epithelial from connective tissue proper in terms of the following: definition, embryonic origin, basal membrane, number of cell layers, vascularization, general function. Tabulate your answer.
Effect on Sensation
• Loss/altered touch & pain perception (Tortora &, 2022)
• Pain → numbness as depth increases (Guyton & Hall, 2021)
Nursing Interventions
• Pain management (analgesics, relaxation)
• Sterile wound care & infection prevention
• Support skin integrity (topicals, grafting)
• Psychological support (anxiety, body image)
• Rehabilitation for sensory/mobility recovery
2. A patient sustains a severe burn that damages the skin and underlying connective tissues. As a nurse, how would this injury affect the patient’s sense of touch and pain perception, and what nursing interventions would you provide to address the physical changes and impacts to him/her as a person?