Organic Chemistry Midterm Study
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1, 3, 4, 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Ionic bond
EN difference greater than 2.0
Polar covalent bond
EN difference between 0.5-2.0
Nonpolar covalent bond
EN difference between 0-0.5
Formal charge
= how many valence does it like - how much is it using
Linear
SP, 180, 2 domains
Trigonal planar
SP2, 120, 3 domains
Tetrahedral
SP3 109.5, 4 domains
CH4
methane
C2H6
ethane
C3H8
propane
C4H10
butane
C5H12
pentane
C6H14
hexane
C7H16
heptane
C8H18
octane
C9H20
nonane
C10H22
decane
Alkane equation
C_nH_2n+2, representing saturated hydrocarbons
Cyclo (pentane, hexane, propane, butane)
Closed ring structures
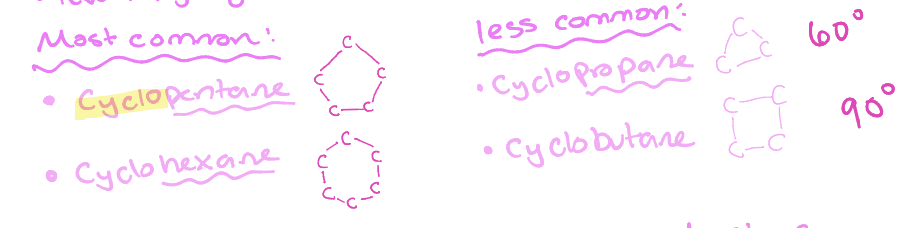
No angle strain
5-6 membered rings
Angle strain
3-4 membered rings
What is unique about naming cyclic structures
start with alphabetical, then move to closest substituent
n-butyl
alphabetize by b

iso-butyl
(alphabetize this by first letter)

sec-butyl
alphabetize by b

tert-butyl
alphabetize by b

Isomer
Same formula, different compound
Constitutional isomer
Same formula, different compound due to order of atom connection
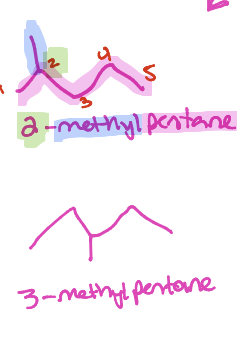
Compounds with ONE possible combo
methane, ethane, propane
Compounds with TWO possible combos
C4H10 (butane, methylpropane)
Compounds with THREE possible combos
C5H12 (pentane; 2-methylbutane; 2,2-dimethylpropane)
Compounds with FIVE possible combos
C6H14 (hexane; 3-methylpentane; 2,2-dimethylbutane; 2,3-dimethylbutane; 3,3-dimethylpentane)
Compounds with NINE possible combos
C10H22 (heptane; 2-methylhexane; 3-methylhexane; 2,2-dimethypentane; 2,3-dimethylpentane; 3,3-dimethylpentane; 3-ethylpentane; 2,2,3-trimethylbutane)
What are the two newman projection types
staggered and eclipsed
Which newman projection SPECIFIC type is the most stable
Staggered in anti (180 degree separation) (bonds are on opposite sides/spread max spread out)
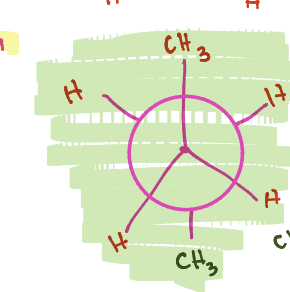
Which newman projection type is the least stable
Eclipsed (bonds overlap and are closest to each other)
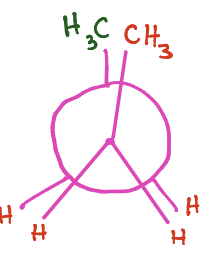
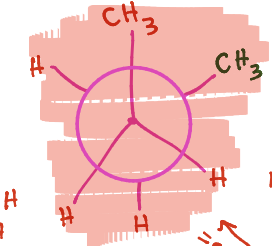
What kind of newman projection is being shown?
Gauge (60 degree separation)
What are two newman projections called that are identical in degree of separation?
degenerate
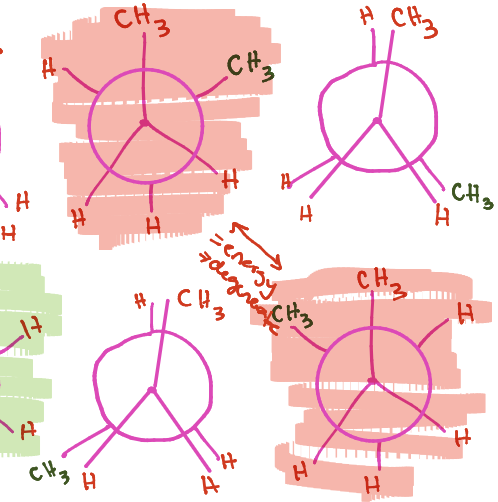
What is steric strain
Repulsion between electron clouds of close, unbonded atoms

What is the high point called, what is it associated with
energy maxima, eclipsed (unstable)
what is the low point called
energy minima, staggered (stable)
What is this?
Newman projection
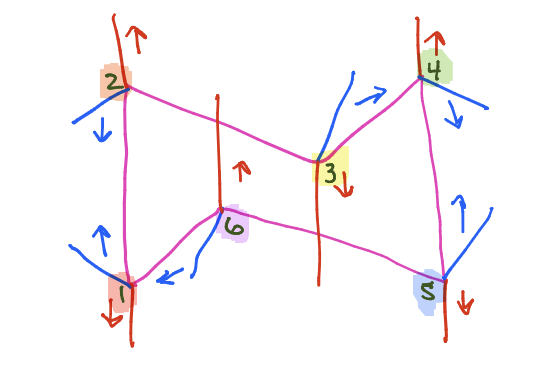
What is this?
Chair conformation
Axial orientation
Straight up or down
Equatorial orientation
Leaning out and away
What is important about the boat conformer
The boat conformation is a less stable form of cyclohexane with two hydrogens eclipsing each other, leading to greater steric strain compared to chair conformations
Why is a major chair more stable than a minor chair
The steric strain is less with opposite sides not feeling presence, while same side feels greater steric repulsion due to eclipsing interactions
What are diaxial interactions
Diaxial interactions are steric interactions that occur between axial substituents on a cyclohexane ring, leading to increased strain and instability
What is a cis chair
A configuration of cyclohexane where substituents on adjacent carbon atoms are on the same side of the ring. This arrangement can lead to increased steric strain compared to its counter part (trans)
What is a trans chair
A configuration of cyclohexane where substituents on adjacent carbon atoms are on opposite sides of the ring. This arrangement minimizes steric strain compared to its counterpart (cis).
What is a stereoisomer and what does it include
A stereoisomer is a molecule with the same molecular formula, but differs in the three-dimensional orientation of its atoms. It includes cis/trans isomers and asymmetric centers (enantiomer + diatereomer)
What is an enantiomer
A type of stereoisomer that is a non-superimposable mirror image of another molecule, often involving asymmetric carbon atoms.
What is a cis-trans steroisomer
isomers that have groups that differ in position around a double bond or ring
What is a asymmetric center stereoisomer what types are there
Asymmetric center stereoisomers contain one or more chiral centers, leading to distinct configurations
enantiomers and diastereomers.
What is a diasteromer
isomers that are not mirror images of each other and may have multiple chiral centers
Example of cis-trans
cis 1-3 (both on hatch/solid wedge), trans 1-3 (one on hatch other on solid wedge)
What is chirality
property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image, often due to the presence of one or more chiral centers
What are characteristics of a chiral compound
nonsuperomposable (stackable on its mirror image), bonded to 4 different groups, optically inactive
What are characteristics of an achiral compound
Superimposable on its mirror image, may be identical, internal plane of symmetry
Characteristics of enantiomers
non-superimposable mirror images of each other, have same physical properties, differ in rotation of light and in living systems
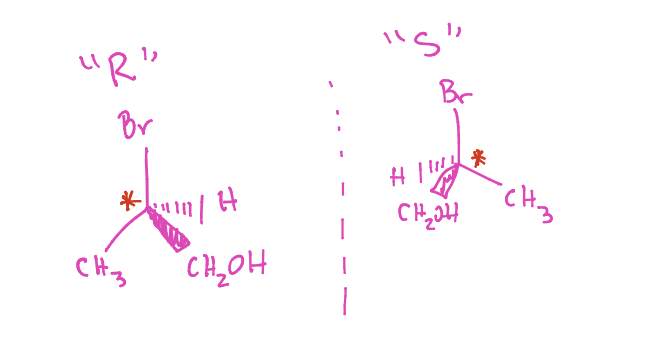
What is this
Perspective drawing
How to name enantiomers
Rank molecules based on mass
Orient lowest priority (4) in the back (dashed wedge)
Orient highest priority (1) in the front (hatch wedge)
Draw a circle following 1 —> 2 etc.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If you switch H to hatch, you made the enantiomer (original should be opposite, R becomes S vise versus)
What does it mean for a compound to be optically active?
The compound can rotate plane-polarized light due to the presence of chiral centers
What is the relation of achiral compounds and polarized light?
do not rotate plane-polarized light
optically inactive

Name this substituent
Methyl
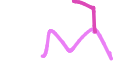
Name this substituent
Ethyl

Name this substituent
Propyl
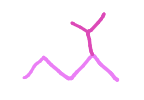
Name this substituent
Isopropyl
What is the relation of chiral compounds and polarized light?
can rotate polarized light in a specific direction, either to the left (levorotatory) or to the right (dextrorotatory)
What is the difference btween “R” “S” and “l” “d”
first can be examined, second must be experimentally determined
What is observed rotation
the angle at which a chiral compound rotates plane-polarized light
What is specific rotation
standardized measure of a chiral compound's ability to rotate polarized light, expressed in degrees per g/mL in a 1.0 dm long @ specific T and wavelength
Relation os optical activity and “R” “S” enantiomers
rotate light in equal, opposite directions
What is a 50:50 mixture of R and S
racemic mixture (±)
What about racemic mixtures is important
they have 0 degree optical rotation
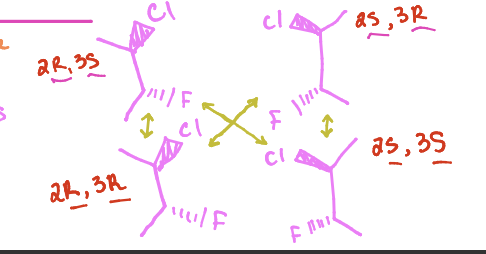
What do the yellow arrows represent
pairs of diastereomers
What is a meso compound?
A compound that has multiple stereocenters
achiral due to an internal plane of symmetry
What are the two qualifications of a meso compound
must have 2+ chiral centers (C atoms bonded to 4 diff. molecules)
Have same four attatchments to each chiral centerand an internal plane of symmetry.
What is a nucleophilic substitution reaction
A chemical reaction where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule, resulting in the formation of a new product
What is an alkyl halide
A hydrocarbon backbone w/ halogens
different chemical and physical properties than normal hydrocarbons
What is bond polarity?
Bond polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charge over the atoms involved in a bond, resulting from differences in electronegativity
Why do alkyl halides have different properties and what effects are seen
bond polarity, physical effects, chemical effects
What physical effects are there in alkyl halides
molecules with polar bonds stick together (higher bp)
higher solubility in water (polar in polar)
What chemical effects are there in alkyl halides
+/- interaction can be overcome (atom breaking off)
polarity (often) increases chemical reactivity
Alkyl halides are _____
Polar
What is a substrate
the main organic molecule experimented on
SN2 reactions are ___ ____
one step
how a reaction occurs =
mechanism
each step requires __________ ______ where uphill is bond ______ and downhill is bond ______ and is ____ in energy than the beginning
activation energy, formation, breaking, lower
SN2 reaction
nucleophile + substrate → product + leaving group
SN2 rates are represented by what equation
rate = k[OH-][CH3Br]
What is present at the Transition State
nucleophile and substrate
What kind of reaction is a SN2
Bimolecular (2 molecules are involved in the Ts of the RDS)
What is the slowest step called
rate-determining step (RDS)
Kinetics and SN2 reactions
concentrating chemicals in the RDS will speed up the reaction
Adding chemicals not involved in RDS will not speed up the reaction

What is a backside attack
A mechanism in SN2 reactions where the nucleophile approaches the electrophile from the opposite side of the leaving group, leading to inversion of stereochemistry (opposite configuration)
What are steric effects of SN2
the size and spatial arrangement of substituents around the electrophile can facilitate nucleophilic attack, influencing reaction rates and outcomes
Order of most reactive to least/too unreactive (order of increasing steric hinderince)
methyl > primary > secondary > tertiary
Relative basicities of halide ions (most to least stable)
I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Relative basicities of halide (most to least stable)
RI > RBr > RCl > RF