L6 - Adaptive Immunity (B Cells)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Characteristics of the adaptive immune system
Discrimination between self & non-self
Specificity
Adaptiveness
Memory
Effector Functions of antibodies
Neutralisation
Precipitation
Opsonisation
Agglutination
Complement fixation
Steps of Bone Marrow Development
Developing B-cells acquire functional B-cell receptors
B-cells whose Ig receptors bind to ‘self’ are eliminated
B cells leave bone marrow & move to secondary lymphoid tissue
B-cells come into contact with specific antigen
B-cells proliferate
B-cells differentiate
Clonal selection
Process by which specific B-cells that recognise an antigen are activated to proliferate and develop into memory or plasma cells.
Clonal expansion
Process by which activated B-cells rapidly proliferate to produce a large number of identical cells, enhancing the immune response against a specific antigen.
Clonal Deletion
Process by which B-cells that strongly recognise self-antigens are eliminated during development to prevent autoimmune reactions.
Surface Ig
Molecules expressed on the surface of B-cells that function as antigen receptors, allowing them to bind specific antigens and initiate an immune response.
Secreted Ig
Antibodies produced by activated B-cells that circulate in the serum and help neutralise pathogens by binding to specific antigens.
5 Classes of Immunoglobulin
IgM
IgD
IgG
IgA
IgE
Immunoglobulin Structure
Immunoglobulins are Y-shaped molecules composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, forming variable and constant regions that determine their antigen-binding specificity.
Fc
Crystallisable fragment at the stalk of the Y, which is composed of only the constant region of an immunoglobulin, responsible for interactions with immune cells and complement proteins.
Fab
Antigen-binding fragments that are composed of a constant & variable region, formed by the combination of one heavy chain and one light chain of an immunoglobulin.
Constant region
The part of an immunoglobulin that remains the same among different antibodies, providing structural support and mediating interactions with other immune cells.
Variable Regions
The part of an immunoglobulin that differs among antibodies, allowing for the specific binding to various antigens. It is formed by the combination of heavy and light chains.
Bonds connecting antibody together
Disulfide bonds
How many segments is the variable domain of the heavy chain?
3 segments - V, D, J.
How many segments is the variable domain of the light chain?
V, J.
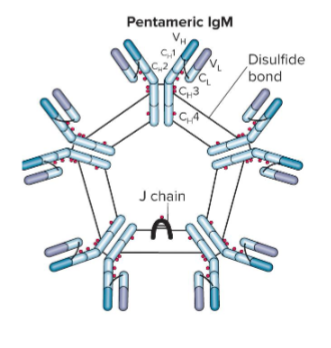
IgM
The first antibody produced in response to an infection, characterized by a pentameric structure and important in early immune response.
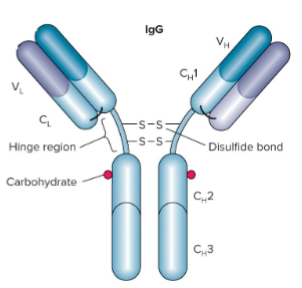
IgG
Major class in the secondary response, activates complement and can cross the placenta
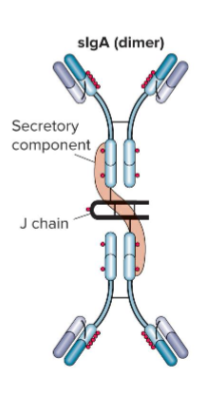
IgA
Antibody found in mucosal secretions with 4 antigen-binding sites
IgD
Antibody that is co-expressed in IgM that is rarely seen in a secreted form
IgE
Antibody associated with allergic reactions and defense against parasitic infections, binds to mast cells and basophils.
What type of antibody do all antibodies start at?
IgM