1.6 Network Topologies & Architectures
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Why are network topologies useful?
For planning a new network
For troubleshooting and understanding signal flow
Star / Hub and spoke Network
All devices are connected to a central device
Usually a switched ethernet
What is the most common network topology
Star / Hub and spoke
Mesh network
Multiple links to the same place
If one link fails it can use anotherWh
Where are mesh networks usually used
WANs
Benefits of mesh network
Redundancy
Fault tolerance
Load balancing
Hybrid Networks
Combination of multiple physical topologies
Most networks use this
Spine and Leaf architecture
All “leaf” switches connected to every higher “spine” switches
leaves do not connected to each other, nor do spinesB
Benefits of Spine and leaf acrhitecture
Simple cabling
Redundant
FastDi
Disadvantages of spine and leaf
additional switches may be costly
Point to point network
Common on old WAN
Can use with LAN to connect buildings
Three tier architecture
Very common
Includes:
Core: centre of network - web servers, databases, applications
Distribution: Midpoint of core and users - communication betweek access switches
Access: where users connect - end stations, printers
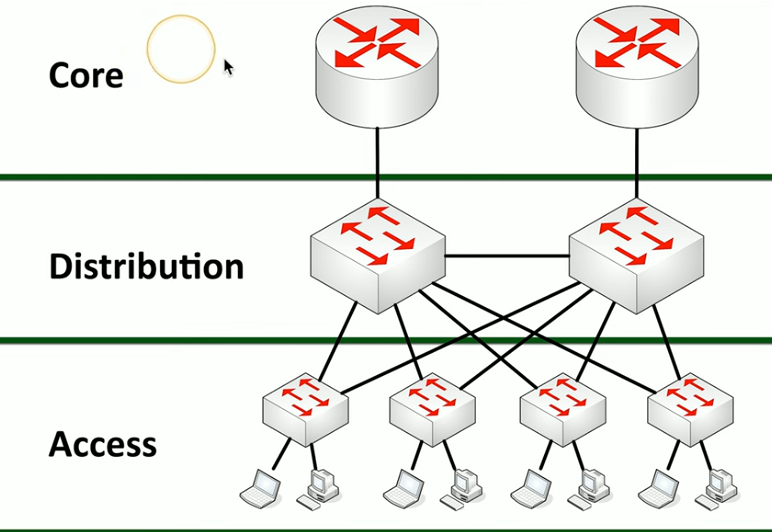
How is three tier architecture often layed out?
Connection between buildings
Collapsed core architecture
two tier architecture
Combines core and distribution layers
Advantages and disadvantages of collapsed core
Simpler, less expensive, less resilient
East west Traffic flow
Traffic between devices in the same data centre
fastN
North south traffic flow
Ingress/egress to an outside device
Different security posture to inside devices