Regulation of Gene Expression
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Overview of enhancers and promoters
multiple per gene
enhancers differ in places in diff tissues
TFs are different in diff tissues
How are motifs derived experimentally?
based on binding to either a polynucleotide (SELEX) or (ChIP-Seq) where the DNA is complexed with histones
Transcription factor classes
based on the DNA binding domain …
How is trabscription factor activity regulated
transcription factors must be in the nucleus to function, this a common mechanism is regulation of its nuclear or cytoplasmic localization
sythesis
ligand binding
covalent formation
regulated nuclear
release from a membrane
Synthesis TF regulation
ex. includes c-fos, ERK, and Elk-1
ERK kinase phosphorylates Elk which inducts the c-phos gene
Elk
has a DNA binding domain which is normally blocked by another TF
when elk is phosphorylated it can bind to DNA and its second domain binds to SRF (weak transcription activator) (stabilizes it)
…
complex formation TF regulation
COvalent modifications causing dimerization TF regukation
Ligand binding TF regukation
Release from membrane TF regulation
sequesters TF outside of nucleus and TF that binding to a DNA binding protein
Histone modifications
can activiate or repress transcription
all histones are modified, but much research is done on H3
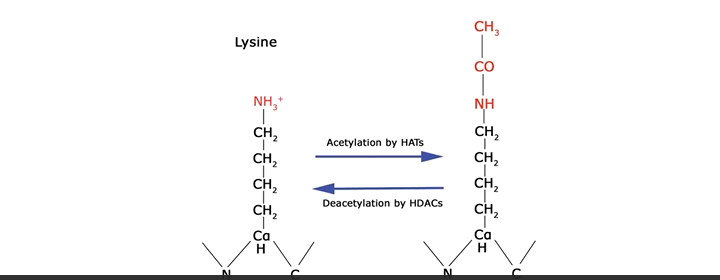
Histone modification: acetylation
loosens DNA from the histones to increase transcription
positive charge of lysine is removed
reduces affinity for negatively charged DNA
Histone Modification: methylation
steric hindrance on lysine and arginine
does not change charge
lysine’s can be methylated in different amounts which have different effects/functionality
assosiation of methylation with transcription and distinct locations within genes
distinct histone methylations are associated with active and repressed regions
epigenetic processes can be classified into
writers
putting on the modifications
Erasers
remove methyl’s and acetyl groups
histone deacetylases
readers
binding to the modification and bringing in other proteins for specific functions (ex. chromatin remodeling)
…
Histone ubiquitin
added to the histone tail
strong steric effect
Chromatin remodeling
essential for transcription and is one of the methods for regulating efficiency …
Bromo domain: recognizes acetyletes lysines