Aetiology of skin conditions - other skin lecture is more important this one don't need to know in too much detail
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How long is cell turnover?
28 days - longer cycles as you age
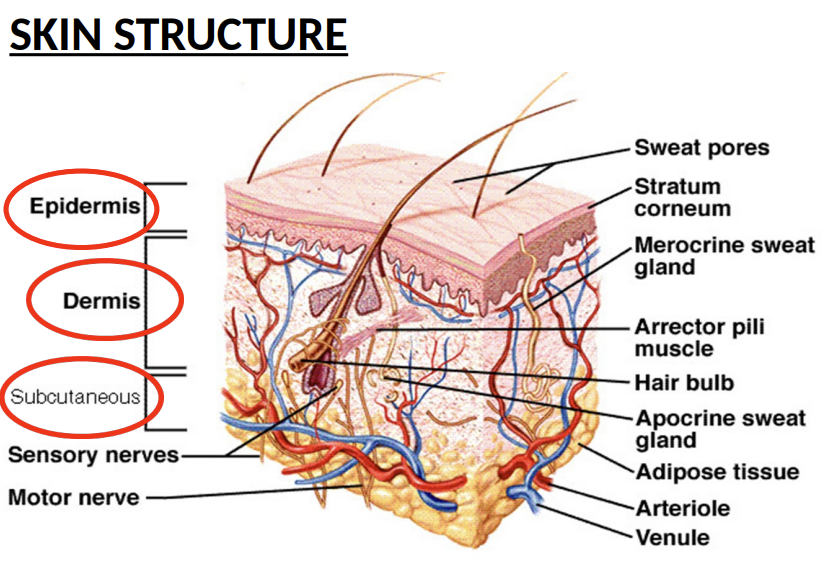
What are the layers of the Skin structure and what seperates these layers
Epidermis: thin tough outer layer, prevents loss of water and body fluids and acts as protective layer, thickness depends on part of the body
Dermis - elastic tissue, where collagen, elastin and fibrinogen are = flexibility and stretch of skin, decompromises as you get older. Also contains nerve ending s
Subcutaneous tissue - Fatty layer that insulates body and acts as padding and energy storage
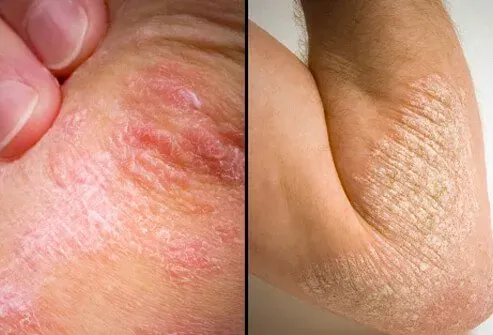
What is Psoriasis?
• Chronic inflammatory skin disease
• Increased epidermal cell turnover = thickening and scaling
• Inflammatory cell infiltration
• Relapsing / remitting
Note : affects men and women the same
BIG HINT THIS PART WILL BE IN THE EXAM AS A CASE QUESTION: What is the cause of Psoriasis?
T-cells (Th1 & Th17) become overactive due to faulty signaling of Immune mediated antigen
These T-cells release inflammatory cytokines (IL-17, IL-23, TNF-α).
These cytokines accelerate skin cell growth (keratinocyte hyperproliferation). Epidermal hyper proliferation
Normally, skin cells replace every 28-30 days—in psoriasis, this happens in 3-4 days, leading to thick, scaly plaques.
—
Trigger (e.g., stress, infection, trauma) →
Immune mediated antigen →
T cell activation →
Release of inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL 23 or 17 etc.) - these are updriven in psoriasis →
Epidermal hyper proliferation
= Plaques
—
Genetic factor also
What else can trigger Psoriasis (what are the precipitating factors)?
• Injuries such as cuts, abrasions, sunburn
• Streptococcal infection
• Hormonal events – often improves during pregnancy and relapses in the postpartum period
• Sunlight – usually improves but 10% will get worse
• Drugs (beta-blockers, lithium, NSAIDS, antimalarials, withdrawal of systemic steroids) - KEY FOR THE EXAM!!!!!
• Alcohol
• Smoking
• Stress
• Obesity
What area the different types of Psoriasis ?
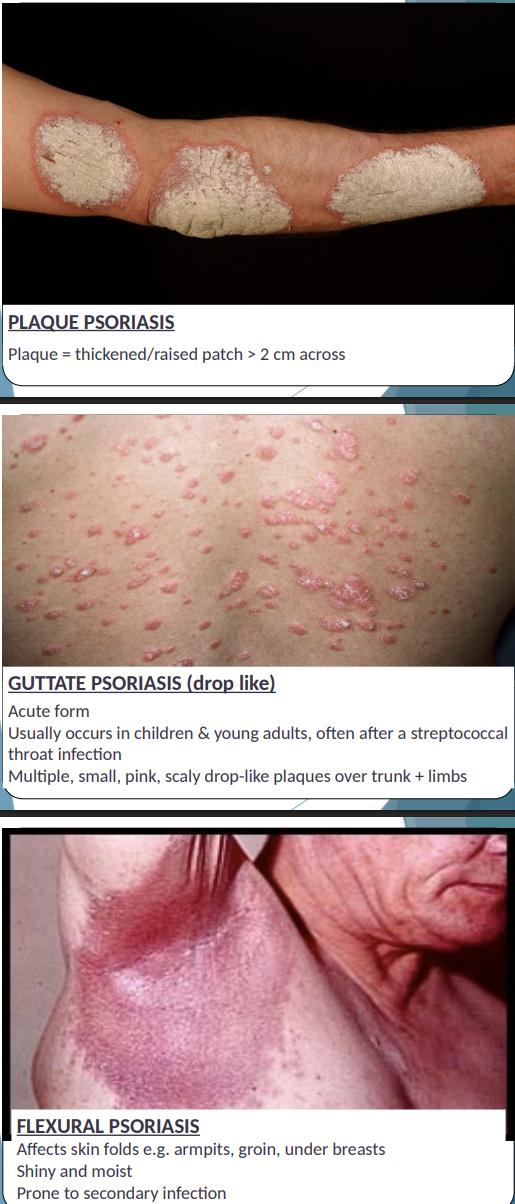
CHRONIC PLAQUE PSORIASIS: - MAIN ONE
Plaque = thickened/raised patch > 2 cm across
Red plaques – well defined edge covered with silvery scales
Plaques can be any size
Scale = flakes of stratum corneum, accumulate or shed
Can affect any area (usually scalp, kness/shins, outside of elbows, lower back)
Plaques can crack and bleed – scratching/removing scales → pinpoint bleeding
Usually symmetrical in distribution across the body
GUTTATE PSORIASIS (drop like):
Acute
Children and young adults usually
Often after a streptococcal throat infection
Multiple, small, pink, scaly drop-like plaques over trunk + limbs
FLEXURAL PSORIASIS:
Affects skin folds e.g. armpits, groin, under breasts
Shiny and moist
Prone to secondary infection
What is the difference between eczema and dermatitis ?
Eczema is endogenously caused [Internal factors (genetics, immune dysfunction, skin barrier defects)]
Dermatitis is cause by exogenous factors e.g. allergic or irritant contact dermatitis
What is eczema and what is it caused by ?
• Impaired barrier function of skin
Dry, itchy, cracked skin (due to impaired barrier function).
Redness, swelling, and recurrent flares (acute: oozing; chronic: thickened skin).
Commonly affects flexures (e.g., elbows, knees) in children, but can occur anywhere.
1. Genetic Factor: Filaggrin (FLG) Mutation
Filaggrin is a protein crucial for:
Binding keratinocytes (skin cells) together.
Producing natural moisturizing factor (NMF) to retain water.
FLG mutations → weak skin barrier →:
Transepidermal water loss (dry, cracked skin).
Easier penetration of irritants/allergens (soap, pollen, microbes).
2. Immune System Overreaction
Allergens/irritants trigger Th2 immune response → release of IL-4, IL-13, IL-31 (cause itching/inflammation).
Chronic inflammation → skin thickening (lichenification).
Can be acute or chronic
What is atopic eczema ?
A genetic tendency to develop allergic diseases
Genetic factors involved – 70% have family history of eczema/ asthma/ hay-fever/ urticaria
e.g. eczema - affects children mostly
Suggested due to immature immune system and high IgE levels (also in asthma)
Asymmetrical appearance
Red skin, scratched bleeding
Precipitating factors:
- Dry skin
- Stress
- Extremes of temperature
- Infection
What is allergic contact dermatitis??
Allergy to usually harmless substances that have been in contact with the skin
E.g. nickel, components of creams/ointments, fragrances, rubber gloves, plants
Cause: Activation of T-cells → release of cytokines
Visible in 48 / 96 hours after contact with allergen
Patch testing can be useful in patients
Questions to ask patient with suspected allergic contact dermatitis
area affected
timing
exposure?
What is irritant contact dermatitis?
Caused by Chemical / Mechanical irritation of the skin
E.g. detergents, abrasives, water
Irritants remove oils and lipids from stratum corneum → deeper penetration of irritant → triggers inflammation
No allergy involved
What do irritants do ?
Irritants remove oils and lipids from stratum corneum → deeper penetration of irritant → triggers inflammation
What is acne ?
Inflammation of the sebaceous glands in the skin
Usually affects face/back/chest where sebaceous glands most numerous and active
How do we assess severity of acne ?
• Mild = non-inflam, <20 comedones
• Severe = extensive nodular cysts, scarring, >125 lesions
What are the types of acne and their symptoms?
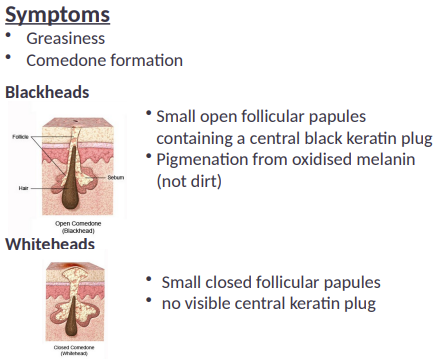
Symptoms of acne in general:
• Greasiness
• Comedone formation
Blackheads:
•Small open follicular papules containing a central black keratin plug
•Pigmenation from oxidised melanin (not dirt)
Whiteheads:
• Small closed follicular papules
• no visible central keratin plug
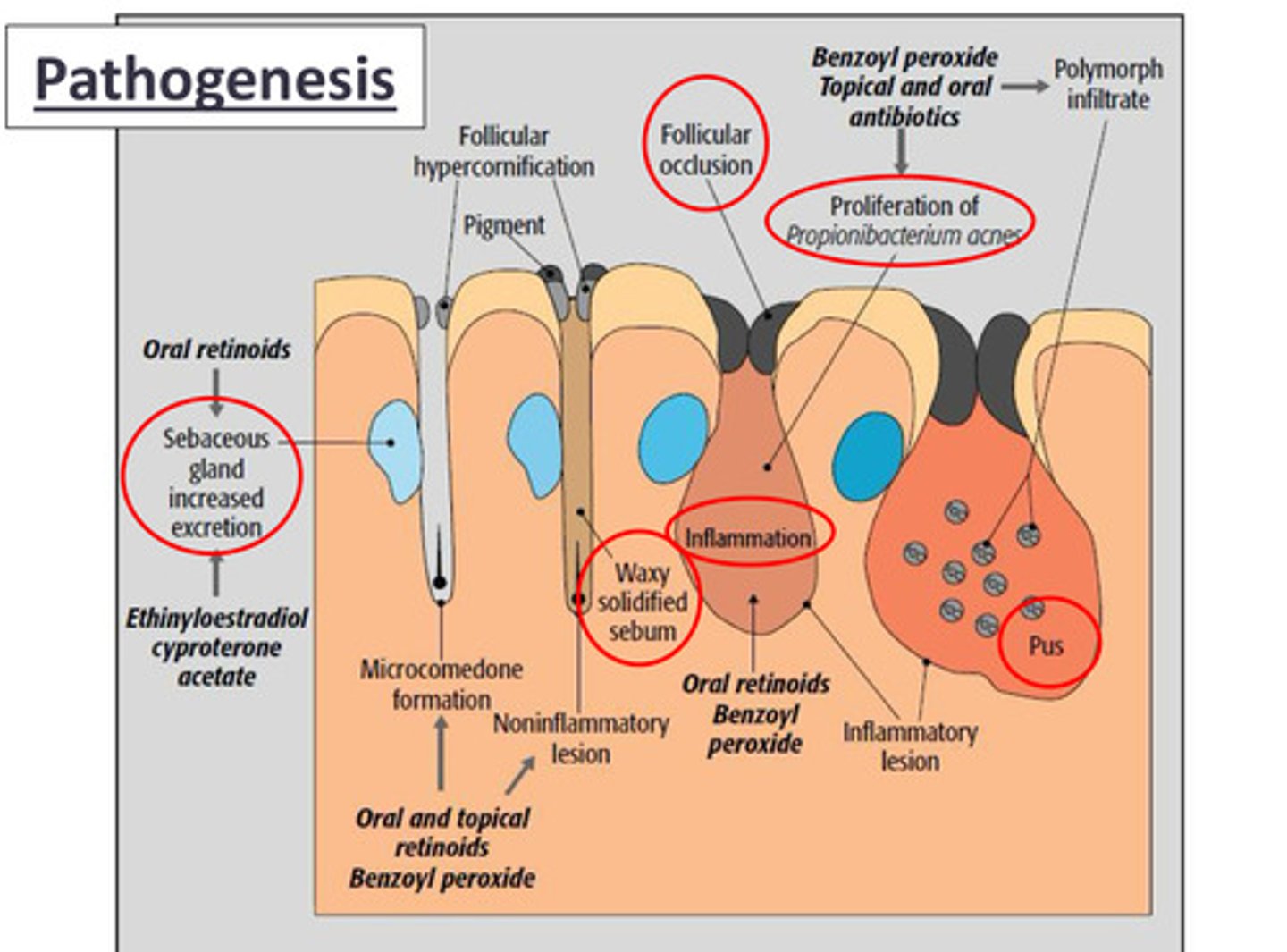
Pathogenesis of Acne
Driven by sebaceous glands
Bigger sebaceous glands can cause an increased activity by androgens (hormones) that effect the formation of comodones as more sebum is being produced
Keratin plugs stop the outflow of the sebum produced by the sebaceous glands = build up of sebum comodone formation