Pre & Post Op Evaluation - Clin Med 6
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What does this refer to
pre-anesthetic evaluation should be made several days in advance.
Testing for lung function
Testing for other body systems that affect lungs. (kidneys, heart, cranial nerves, etc)
Pre-operative
What does this refer to
Any medical history of complications previously
Any concerns with overall health during surgery
Perioperative
What does this refer to
Is the patient able to recover from surgery, respiratory related? Will they need more assistance with the pulmonary system after surgery?
Post-Operative
What does this refer to
Pre-op is performed to assess patient for surgical candidacy
Evaluation
What does this refer to
What medical history does the patient have that may put their health at risk if they are cleared for surgery?
Risk
What does this refer to
Is there any additional complications that may occur with this patient and not with a healthy individual?
Complication
What does this refer to
H&P
Essential tool in estimating severity of pulmonary compromise and extent of pulmonary reserve.
S/S of important clues to the pulmonary status pre-operatively.
Heart Failure
OSA
Determination
Base on symptoms of cough, SOB, dyspnea, recent lung infections, COPD, can the patient walk normally, fluid retention, edema
Medical History-Smoker, Asthma
Concerning-Self-reported symptoms, extensive smoking hx (>20pk/yrs), maximal laryngeal height <4cm or less and <45 years of age.
Estimate the risk
What does this refer to
Essential tool in estimating severity of pulmonary compromise and extent of pulmonary reserve.
S/S of important clues to the pulmonary status pre-operatively.
Heart Failure
OSA
H&P (to estimate the risk)
What does this refer to
Base on symptoms of cough, SOB, dyspnea, recent lung infections, COPD, can the patient walk normally, fluid retention, edema
Medical History-Smoker, Asthma
Concerning-Self-reported symptoms, extensive smoking hx (>20pk/yrs), maximal laryngeal height <4cm or less and <45 years of age.
Determination (to estimate the risk)
What does this refer to
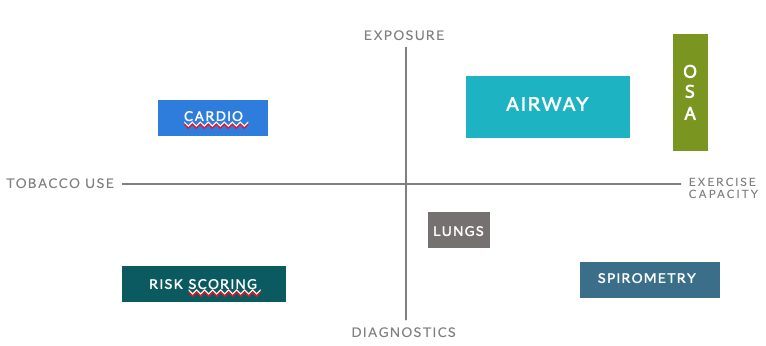
Determinates
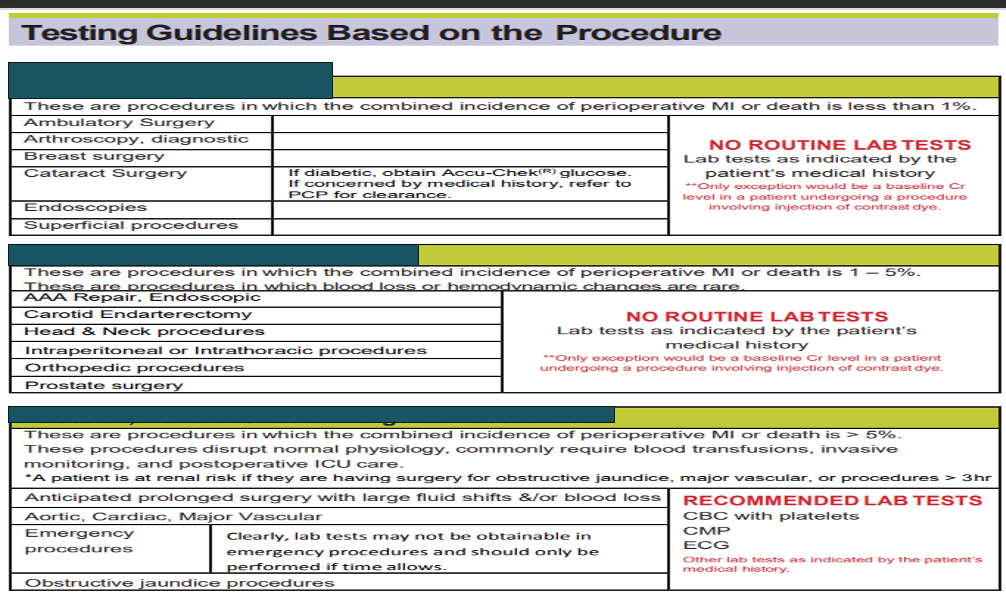
What type of procedure is the top box
Low risk procedure
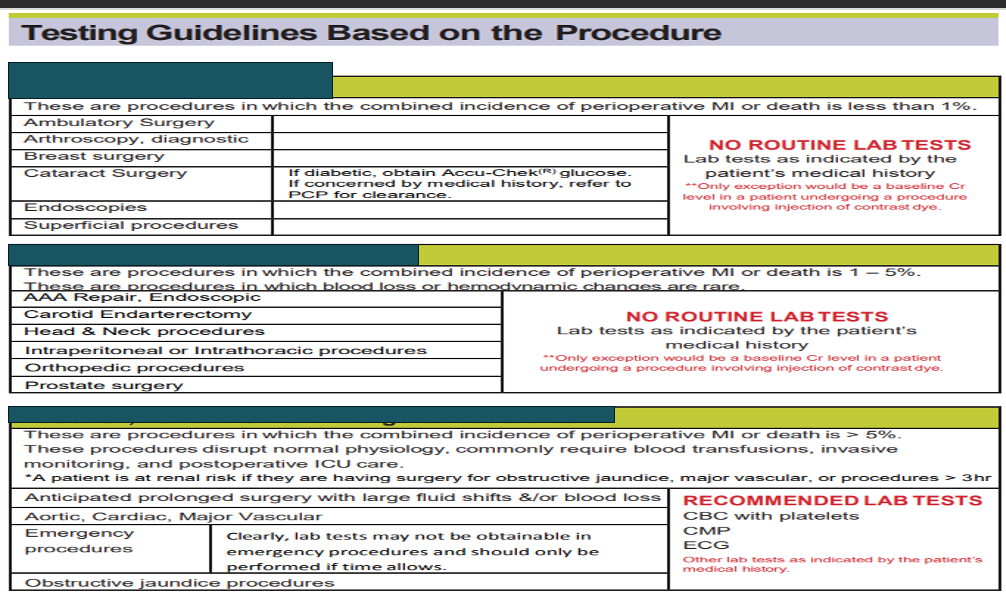
What type of procedure is the middle box
Intermediate Risk Procedure
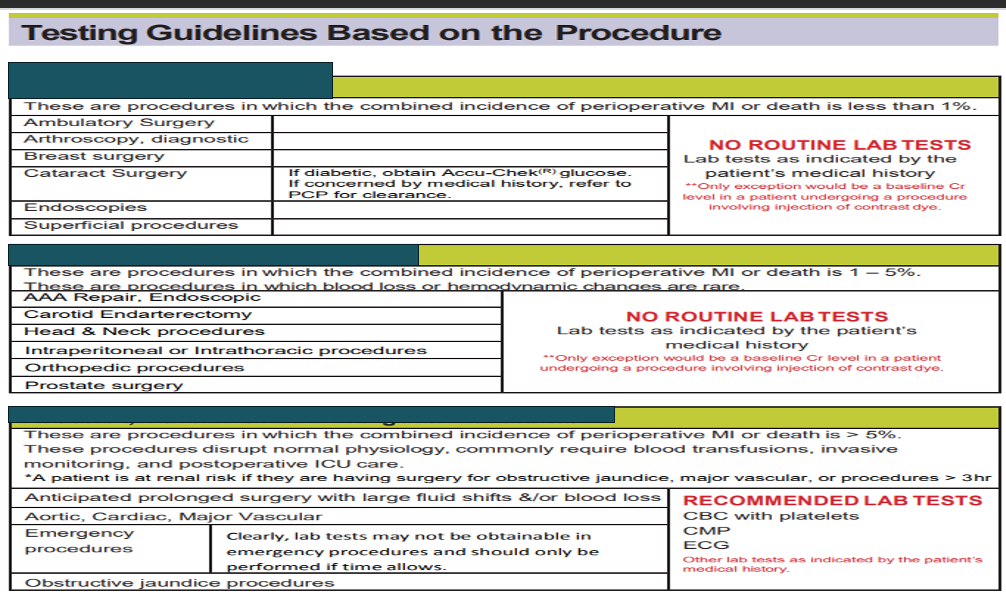
What type of procedure is the bottom box
Vascular, Renal risk, or emergent procedures
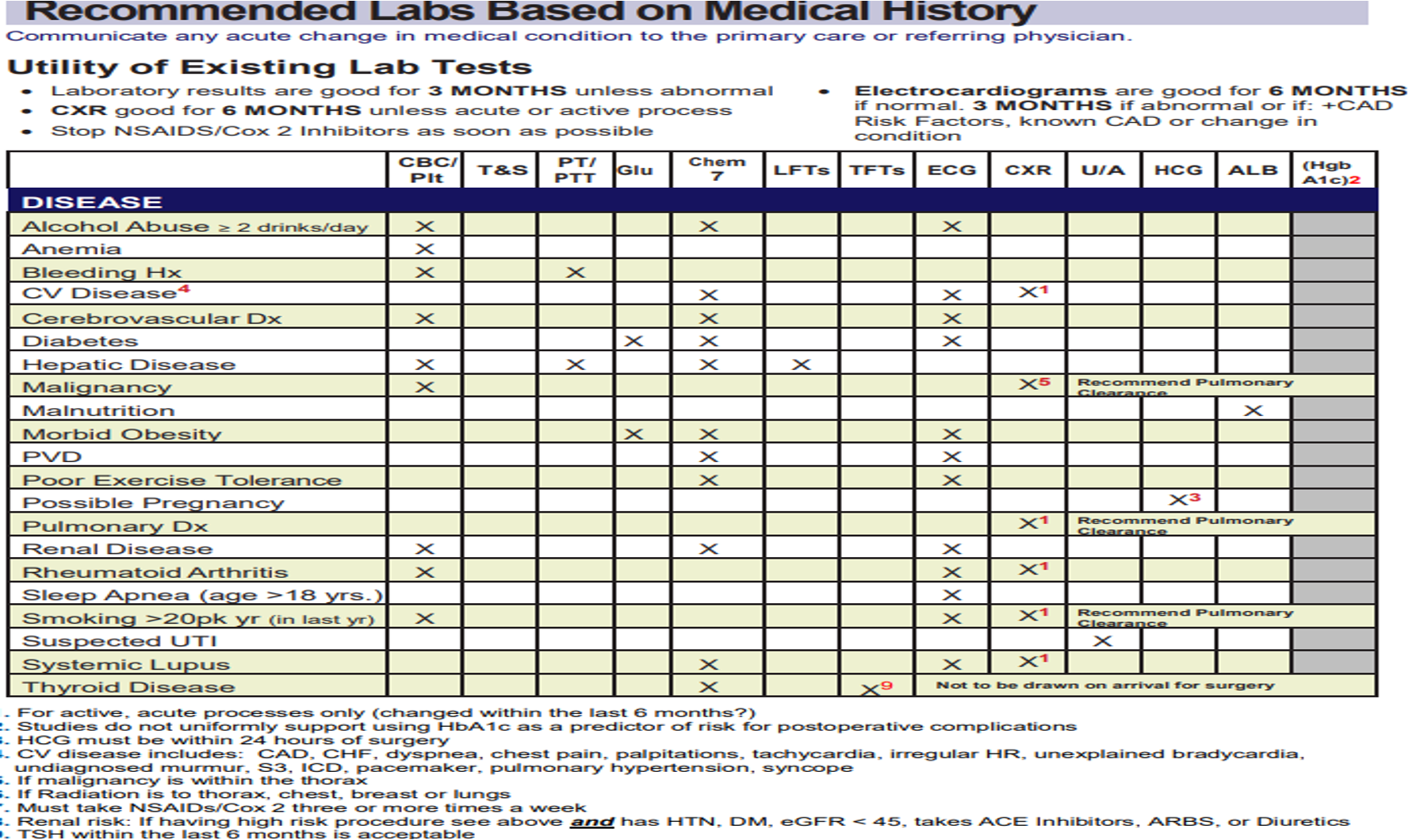
What does this refer to
Recommended labs based on medical history
What does this refer to
Goal of ____________ is to help the patient to arrive to the operating room with sedation, hypnosis, prevention of nausea and vomiting, and with preemptive analgesia
Pre-Anesthetic Medication
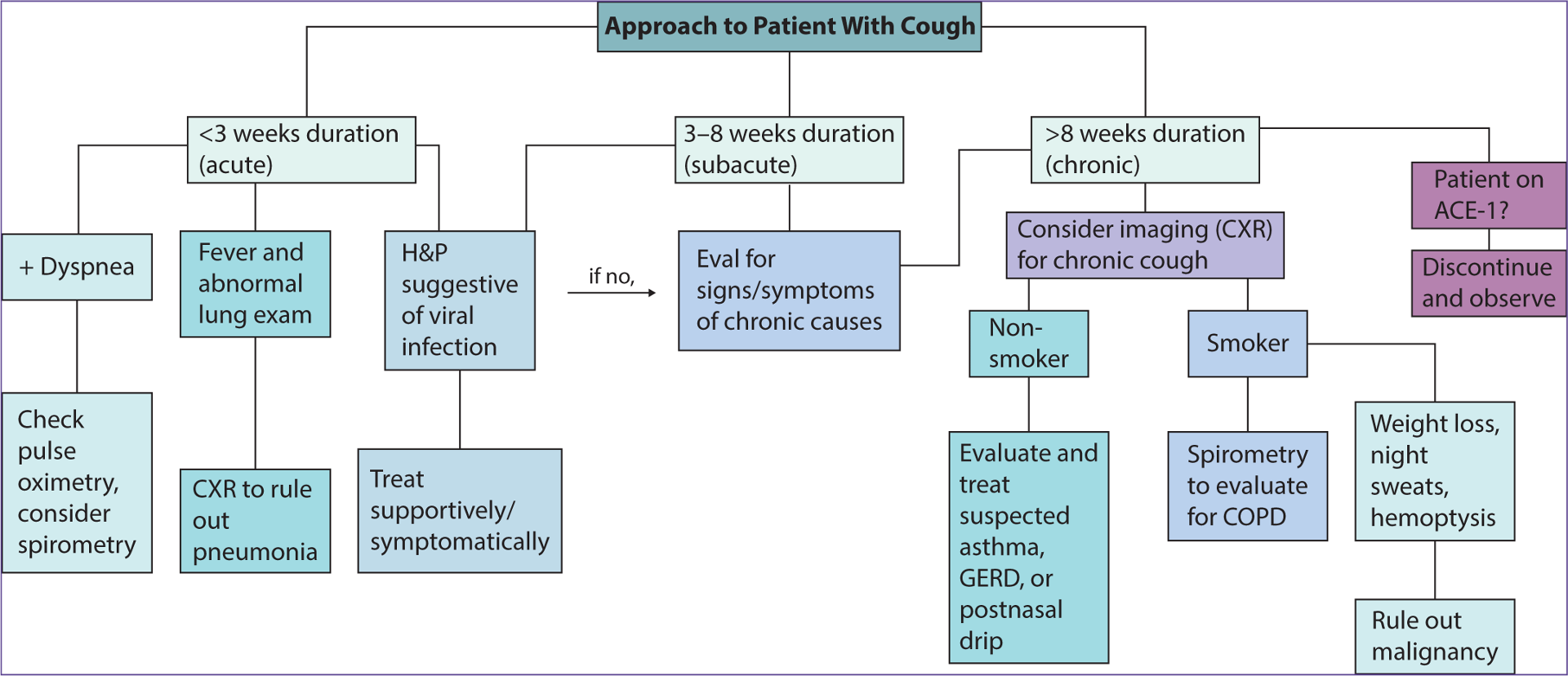
What does this refer to
Approach to patient with cough
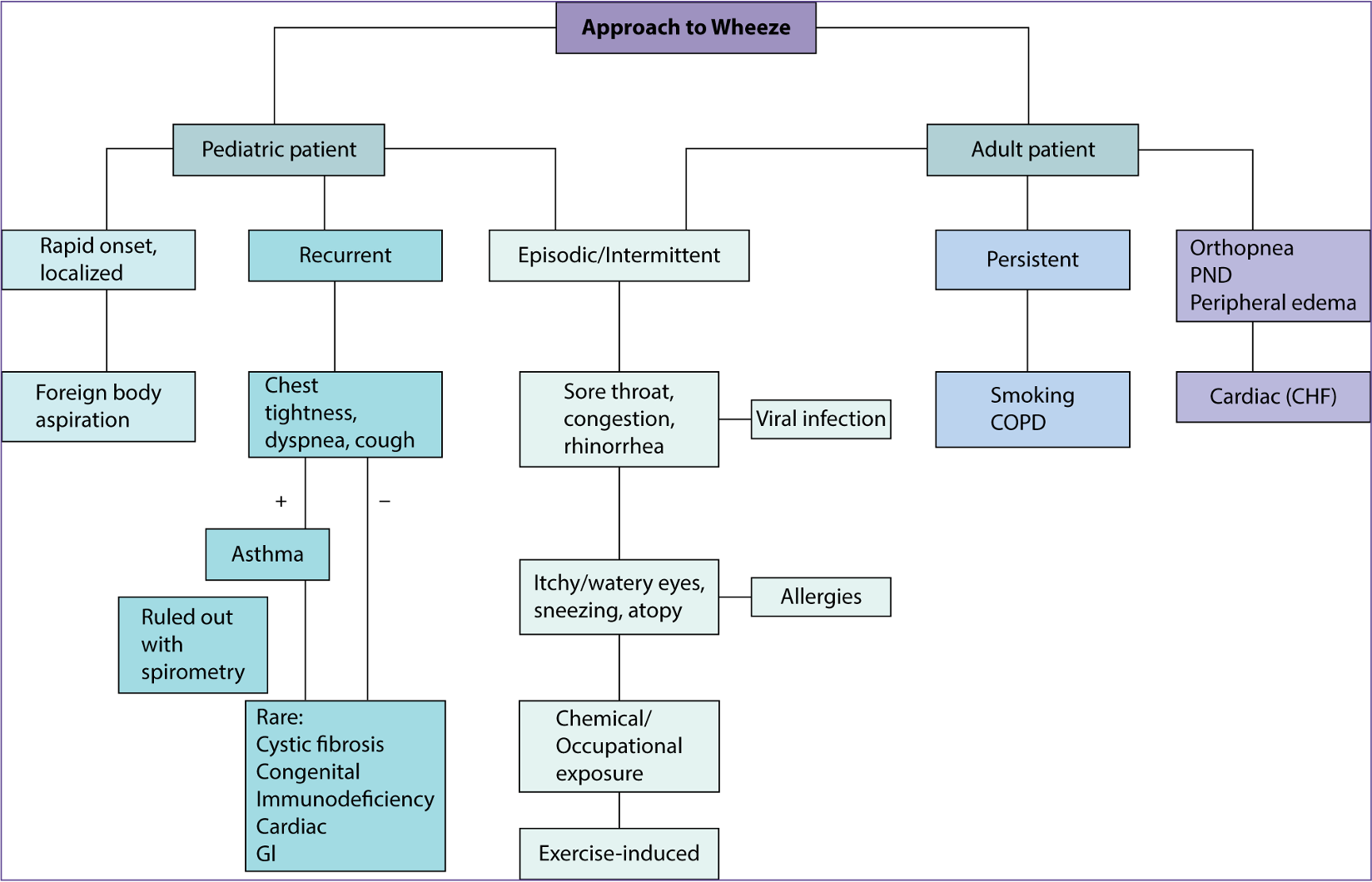
What does this refer to
Approach to patient wheezing
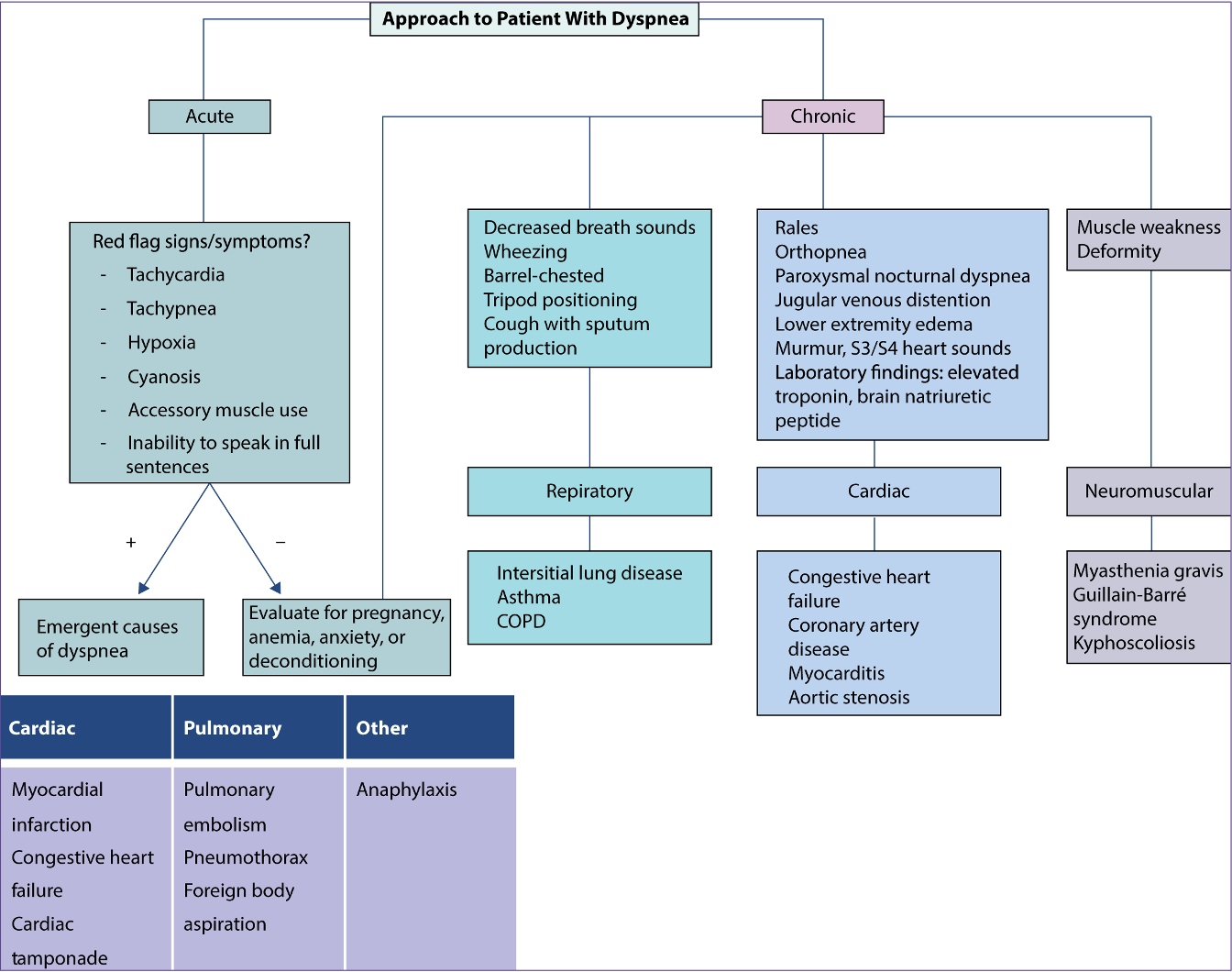
What does this refer to
Approach to patient with dyspnea
What does this refer to
Benzo
Melatonin
Doperidol and Decadron
Pre-Anesthetic Medication
What does this refer to

Medication not to continue prior to procedures (may be taken on day of surgery)
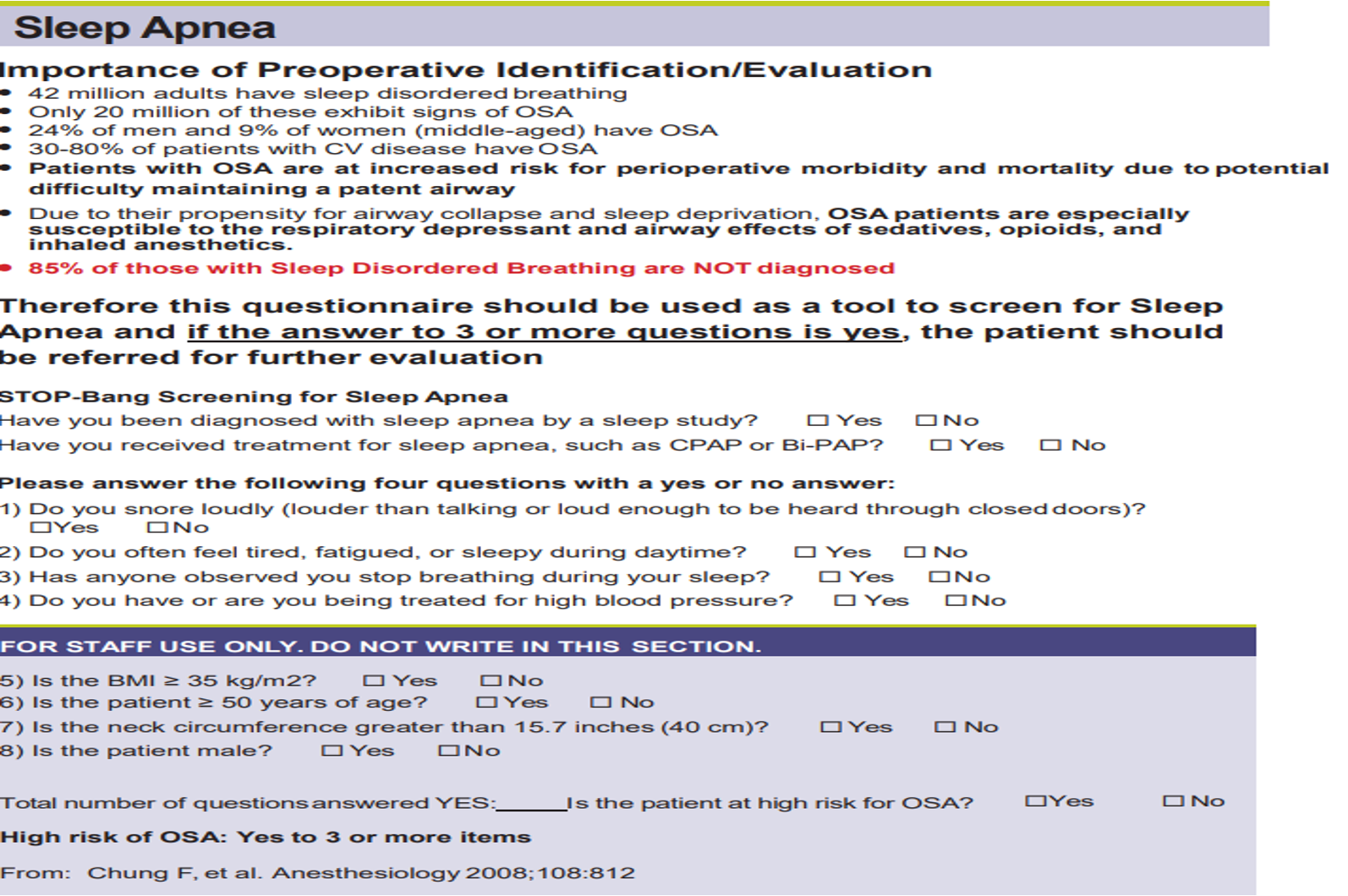
What does this refer to
Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to
Pulmonary function testing
Labs
EKG
CXR
Pre-anesthesia consultation
What does this refer to
Restrictive respiratory disease
Interstitial Lung Disease
Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia
Intrinsic lung disorders
What does this refer to
Increased chest wall impedance
Limited spacing
Costovertebral disorders
Congenital abnormality
Traumatic abnormality
Extrinsic restrictive disorders
What does this refer to
Increased intraabdominal pressure
Central obesity
Ascites
Pregnancy
Related to Lung Dx
What does this refer to
COPD
Heart Failure
OSA
Metabolic
Pulmonary HTN
Factors
Post-operative pulmonary complication (POPC)
What does this refer to
Hgb
Albumin
BUN
Metabolic (post-operative pulmonary complication)
Why is pulmonary HTN a concern of post-operative pulmonary complication (POPC)
Increase morbidity and mortality
What does this refer to
Risk factors
Surgery > 2 hour
General anesthesia risk
Factors or Post-operative pulmonary complications (POPC)
What does this refer to
Determines pulmonary complication (risk of pneumonia post op and risk of respiratory failure)
For postoperative pulmonary complicaiton
for patients undergoing surgery under general, neuraxial, or regional anesthesia.
ARISCAT Score
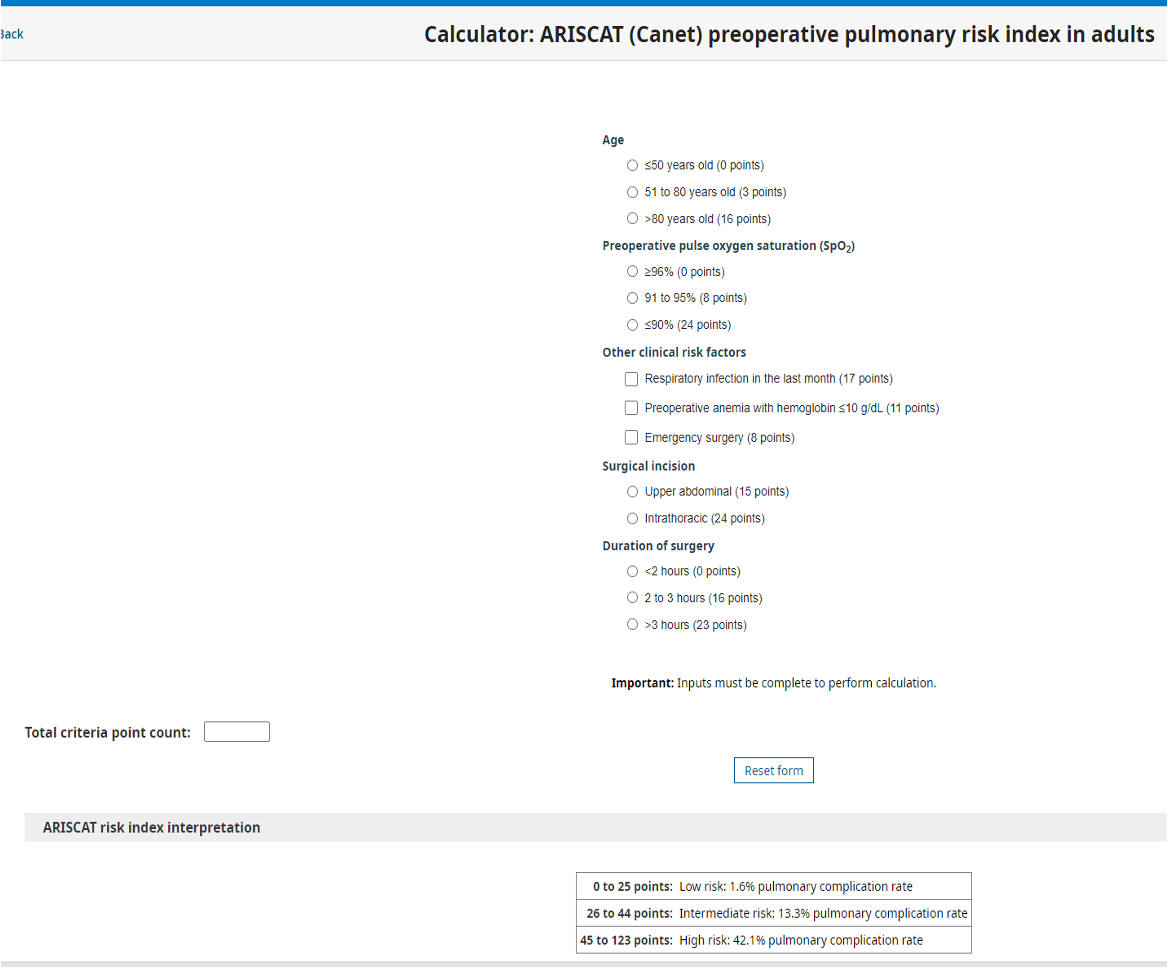
What does this refer to
Monitored anesthesia care
Airway management
Selection of anesthetic agents
Intraoperative Management
What does this refer to
Hypoxemia
V/Q Mismatch
Impaired Diffusion
Decreased mixed venous oxygen content
Management of Intraoperative Complications

What does this refer to
Choice of Anesthetic technique
What does this refer to
antiemetic requirements were higher in general anesthesia
Conscious sedation
What does this refer to
Neuraxial anesthesia
Regional Anesthesia
What does this refer to
Spinal anesthesia
allow early home discharge
As clinicians, you will want to keep your patients from being in harm’s way and how can you do that without assessing the patient and the situation?
Thorough history and physical
What does this refer to

Management in the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit