Exam 1 - Criminological Theory
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is theory?
A theory is a set of statements that explain how two or more “things” are related. Theory not only informs, but implies action.
What constitutes a good theory?
Logical consistency (statement or propositions should flow logically), reasonable scope, testable, applicable, and supported by empirical evidence.
What does Sutherland’s definition of criminology include?
Criminology is the study of the “entire process of law making, law breaking, and law enforcement.”
Describe the three levels that theory might take in criminology.
Micro - studies individuals and one-on-one interactions
Meso - studies groups
Macro - studies institutions and policies
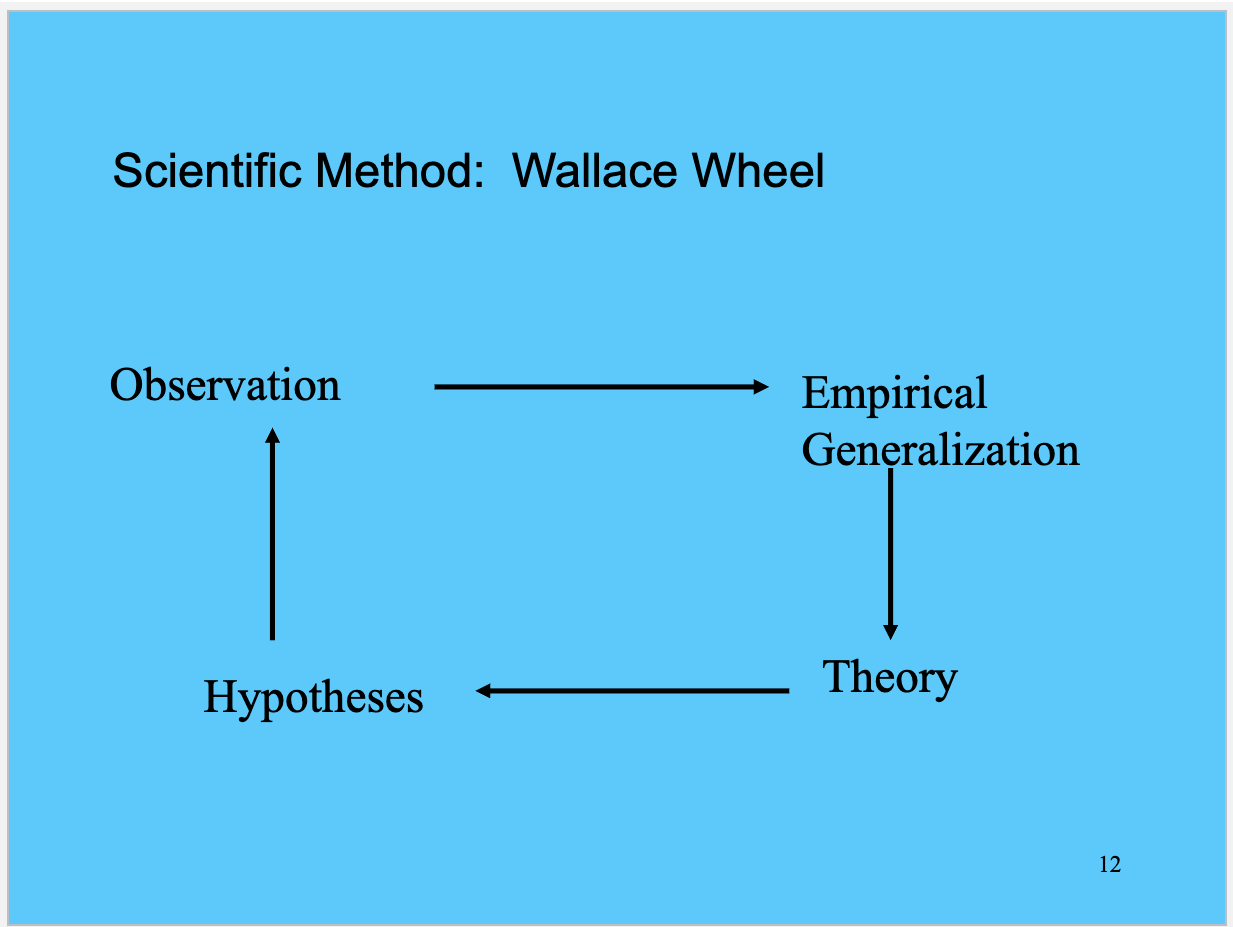
What is the Wallace Wheel of Science and why is it useful?
The Wallace Wheel of Science is a model that illustrates the relationship between theory, research, and practice in criminology. It is useful for guiding researchers in formulating hypotheses, collecting data, and applying findings to real-world issues.
Who were Bentham and Beccaria and what did they stand for?
Bentham and Beccaria were social philosophers who focused on legal and penal reform rather than “why did they do it?” Founders of classical criminology.
Beccaria - developed “academy of fists,” and essay on crimes and punishments, believes people are rational and have free will, founder of deterrence theory.
Bentham - founded utilitarianism (actions are right or good if they benefit the most people and promote happiness), certainty is most important aspect of deterrence theory.
What are the basic components of deterrence theory?
Certainty - the likelihood of being caught and punished, most important
Severity - punishment that fits the crime, cost and benefit
Celerity - swiftness of the punishment
What is specific and general deterrence?
Specific - caught and punished swiftly and correctly, individual is less likely to reoffend, deter a specific individual
General - state’s actions affect other potential criminals, deter general public
What is Positive School?
The philosophy that emphasizes the scientific method, assumes behavior is determined by external stimuli and social experiences.
What were the basics of Lombroso’s theory?
Criminality is inherited and atavistic (genetic throwbacks), 1/3 of worst criminals had distinct physical types.
What did Stephen Gould have to say about Lombroso?
Rejected Lombroso, agreed criminals are born with criminal traits, not atavistic but have a defective physique and intelligence, anthropomorphism (the attribution of human characteristics or behavior to a god, animal, or object).
What are the policy implications of Lombroso’s theory?
Discriminatory practices against those with certain physical characteristics.
According to David Rowe, what biological factors appear to be related to crime and how?
Deficits in prefrontal cortex
Rowe offers two explanations of the sweaty hand/resting heart rate and delinquency relationship. What are they and which makes more sense to you?
Lower state of arousal and lack of fear.
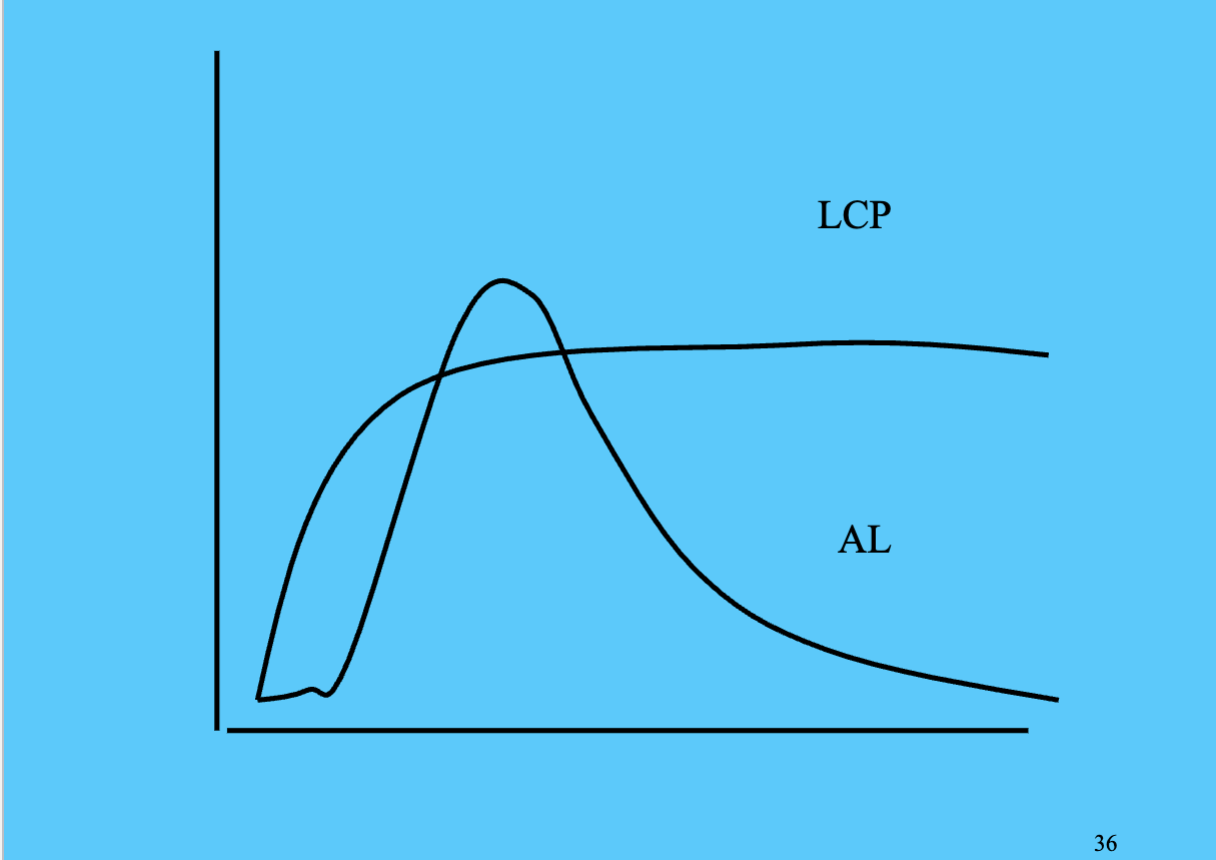
According to Moffit’s theory, there are two types of criminals. What does she call them and how do their trajectories differ? Can you draw the trajectories? What are the causes of the two trajectories? How are they similar and different?
Two types of criminals are life course persistent (LCP) and adolescent limited offenders (ALO). Biological and social factors are important and they interact.
ALO - mimic “criminals” in attempts to rebel adults
LCP - “environmental” (biosocial) factors, neurological deficits, poor social environment, parents with deficits
What are the policy implications of the newer biosocial theories?
Deterministic, eugenics, psychological/social intervention.
Describe Freud’s three separate functions of the mind. What are his stages of development? What might be most important for criminology?
Id - unconscious, assumption, selfish, temper, aggressive
Ego - conscious, reality and vision of reality, rational element of the mind
Super ego - conscious, remorse, empathy, moral element of the mind
Stages - oral, anal, phallic, latency, mature
How does the Capsi’s study bring psychology back into the study of crime? What did they do and what did they find?
Capsi’s study used multiple samples, multiple measures, and predictor-criterion overlap, offers different perceptions of reality, neurobiological origins combined with differential socialization, three concepts are negative emotionality, positive emotionality, and constraint.
Describe the empirical tests of psychological based interventions of the 50s and 60s and what were the outcomes? How are newer programs different and how effective are they?
Good, systematic evaluations, all show few differences for the better or worse effects.
What is Classical School?
The philosophy that emphasizes free will and rational choice, the purpose of punishment is to promote justice and defer future criminal behavior.
What did Charles Goring comparative research look like? What did he find?
Compared outside people with prisoners characteristics. Found no difference on psychological traits, found prisoners to be less intelligent.
What did E.A. Hooten’s research look like? What did he find?
Biological theorist who found that prisoners are organically inferior, no physical difference.
What are the three common traits of a psychopath?
Conceitful, deceitful, manipulative, and aggressive
What did Robert Hare find about psychopaths?
20% of prison inmates are psychopaths, responsible for 50% of crime, recidivism rate is three times higher.
Is psychological counseling effective? What evaluation is used?
Psychological counseling is not effective, uses sound evaluations.
Freudian and early psychological theories have been criticized for…?
A. For being tautological and largely untestable
B. Placing too much attention on social factors affecting criminality
C. Emphasizing psychological counseling
D. Not being deterministic in nature
Which of the following DOES NOT characterize psychopaths?
A. Conceitful
B. Deceptive
C. Empathy
D. Manipulative
The field studies conducted in the 1950s and 60s, evaluating programs based on psychological theories, can be best summarized as…
A. Promising but the methodology was not strong enough to confirm or reject the programs
B. Good systematic evaluations showing strong positive effects of individual level counseling
C. Good systematic evaluations showing strong positive effects of group counseling
D. Good systematic evaluations but not having strong positive effects and some showing even worse outcomes
Capsi and his colleagues made important strides to develop studies that were not “compromised by predictor-criterion overlap.” What do they mean by this?
A. Measures of personality do not include measures of the behavior they are designed to predict (criminality and deliquency)
B. Measures of crime and criminality need to be based on explicit criterion
C. Measures of personality need to be based on formal psychological theories
D. Measures of personality that are expected to predict crime must include behavioral measures of crime
Capsi and colleagues offer several new personality characteristics that include ALL BUT which of the following?
A. Remorselessness
B. Constraint
C. Negative emotionality
D. Positive emotionality
Lombroso argued that about 1/3 of criminals were “atavistic,” by which he meant they were…?
A. Anthropomorphized
B. Habitual offenders
C. Violent offenders
D. Genetic throw backs
Lombroso and virtually all of his students supported…?
A. Psychological counseling
B. The death penalty
C. Deterrence theory
D. Anthropomorphic determinism
Charles Goring found that criminals did not differ from noncriminal on 37 physical traits. He did conclude, however, that…
A. Criminals had similar physiques but lower intelligence
B. Smaller brain capacity (literally skull sizes)
C. Criminals have defective physiques and lower intelligence
D. Large brain capacity (more room in the skill but he could not measure the size of the brain)
E.A. Hooten building and critiquing on the work of Charles Goring concluded that…
A. Criminals are not “organically inferior” to noncriminals
B. In some ways firemen and the police are actually more like criminals than are other members of the public
C. Biology and genetics are important but so are social factors in explaining criminal behavior
D. Social factors were not important in distinguishing criminal from noncriminals
Modern biological criminologists generally believe that…
A. Biology is important but so are social factors in theories of criminal behavior
B. Social factors play almost no role in criminal behavior
C. Social factors are more important than biological factors but biological factors are important
D. The only way advance criminology is to advance technology so we can better measure the inner workings of the brain