Angina and MI Drugs Ch. 28 (N241)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
angina
chest pain due to heart's lack of oxygen, possibly as a result of a possible obstruction and activity that increases the demand of the heart
fats
non-pharm managements of angina:
- limit alcohol
- limit foods that are high in bad ______, such as trans fat, saturated fat, LDL
- no smoking
- BP management
- weight management (treat obesity)
- exercise
- euglycemia
- low sodium diet
oxygen
the overall goal of pharmacological management of angina is to reduce myocardial ___________ demand
- slow HR
- reduce preload
- reduced contractility
- reduced afterload
betablockers
what drug class slows heart rate?
nitrate
what drug reduces preload and is a potent vasodilator?
statins
drugs used to lower cholesterol in the bloodstream
contraindications: pregnancy
- check AST/ALT liver levels
- call provider if muscle or joint pain / cramps
- check if cholesterol decreases to see drug effectiveness
nitrates
potent vasodilator
use: angina
MOA: reduces preload and afterload and dilates coronary arteries
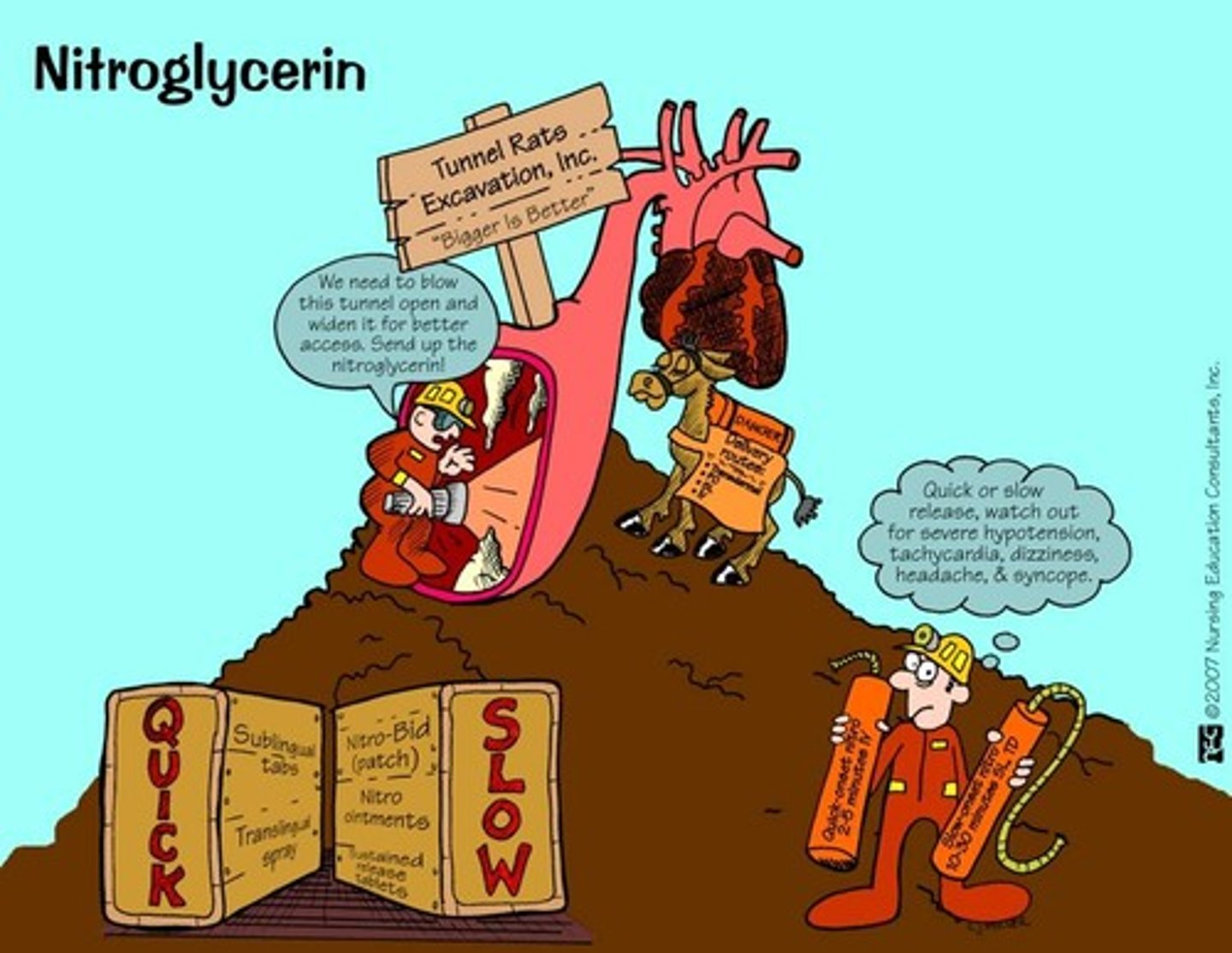
nitroglycerin
class: nitrate
use: angina
MOA: dilates veins and decreases preload --> decreases cardiac oxygen demand
A/E: H/A, orthostatic hypotension
contraindication: do NOT take with Sildenafil (Viagra) or Tadalafil (Cialis) since they are both potent vasodilators; pregnancy
sublingual route is short acting (2-4 minutes) and if the patient is at home, they may go up to 3 doses
- patient should call provider if chest pain does not subside after 1 dose
- drug should be kept in a dark place and at room temp
betablockers
which class of drugs?
stable angina prophylaxis
TU: reduce cardiac workload and treats angina
ex. metoprolol, propranolol
- monitor especially patients with asthma or COPD (bronchoconstriction) and diabetic patients (masks hypoglycemia)
calcium
what ion is necessary for muscle contraction?
the blockage of this ion results in the limiting of muscular contraction and the relaxation of smooth muscles of arteries / decrease in vascular resistance
therefore:
- reduces afterload
- decreases cardiac workload
- dilates coronary arteries
blood pressure
if we use calcium channel blockers for angina, we should assess the patient's heart rate and _________ ____________ since it may contribute to peripheral edema
diltiazem (verapamil)
class: calcium channel blocker
use: angina
S/E: dizziness, edema