Plant Root, Stem, and Leaf Modifications: Structures, Functions, and Economic Uses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
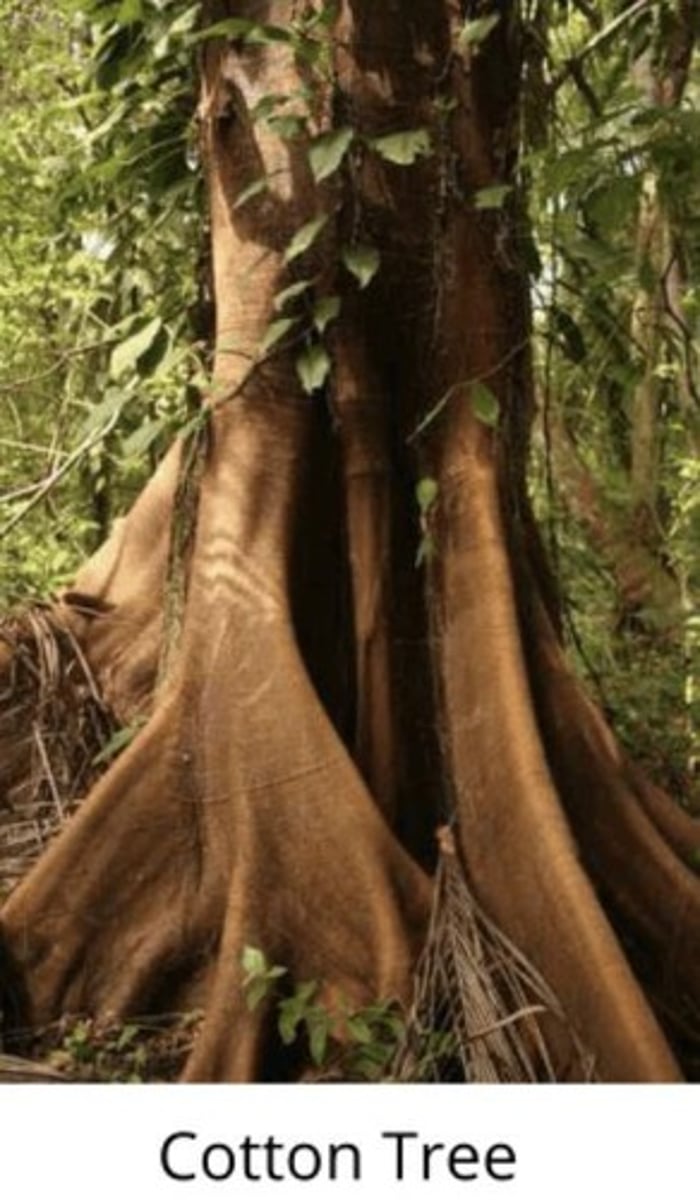
Buttress Roots
Aerial roots that look like buttresses give architectural support to the trunks of trees.

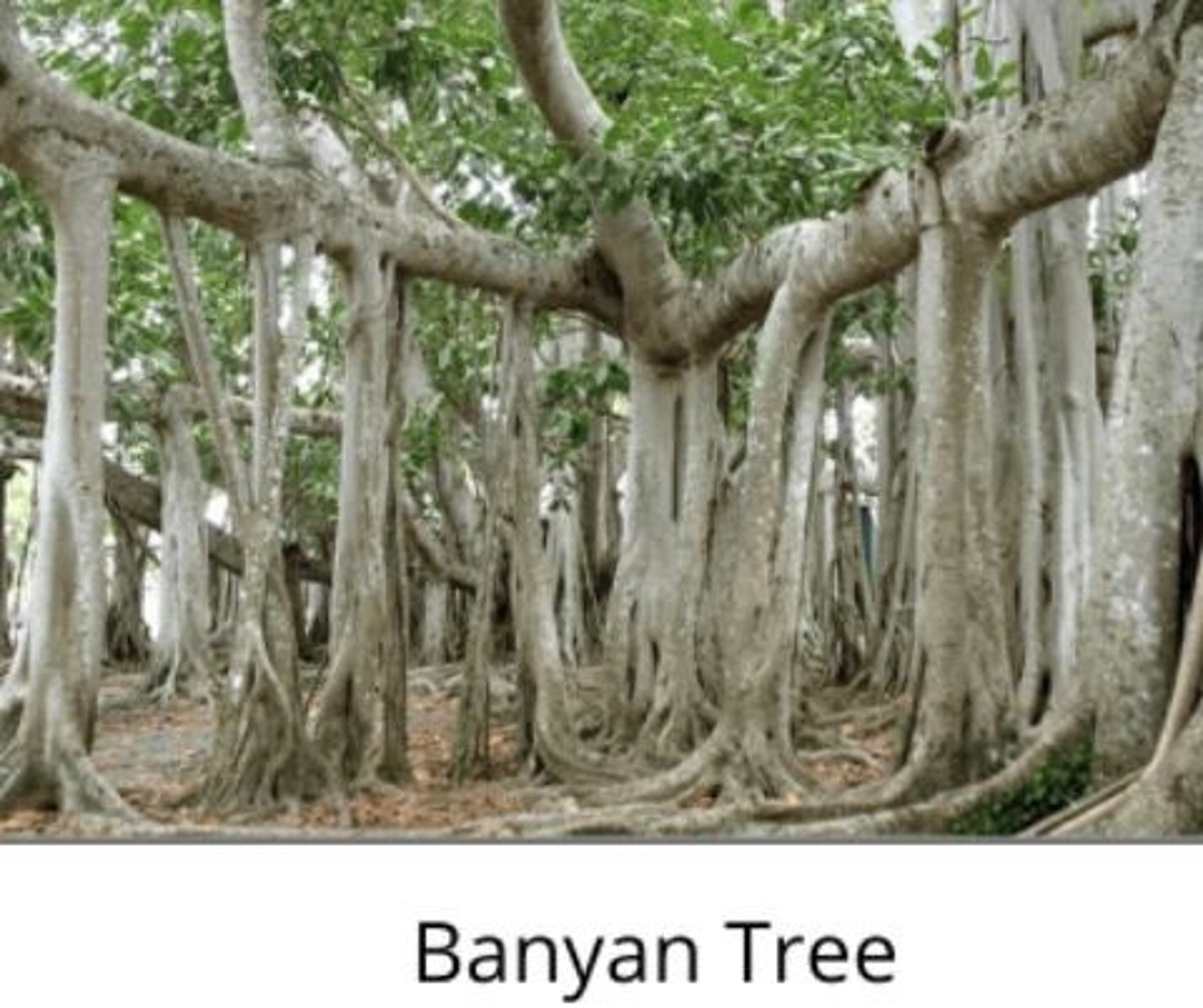
Prop Roots
Prop roots are examples of adventitious roots, which arise from any plant part other than the roots (like leaves and stem).
Aerial Roots
Many epiphytes have aerial roots for a variety of reasons, including climbing, photosynthesis, and capturing moisture.

Pneumatophores
Specialized roots of some trees grow up into the air, allowing oxygen to diffuse in.
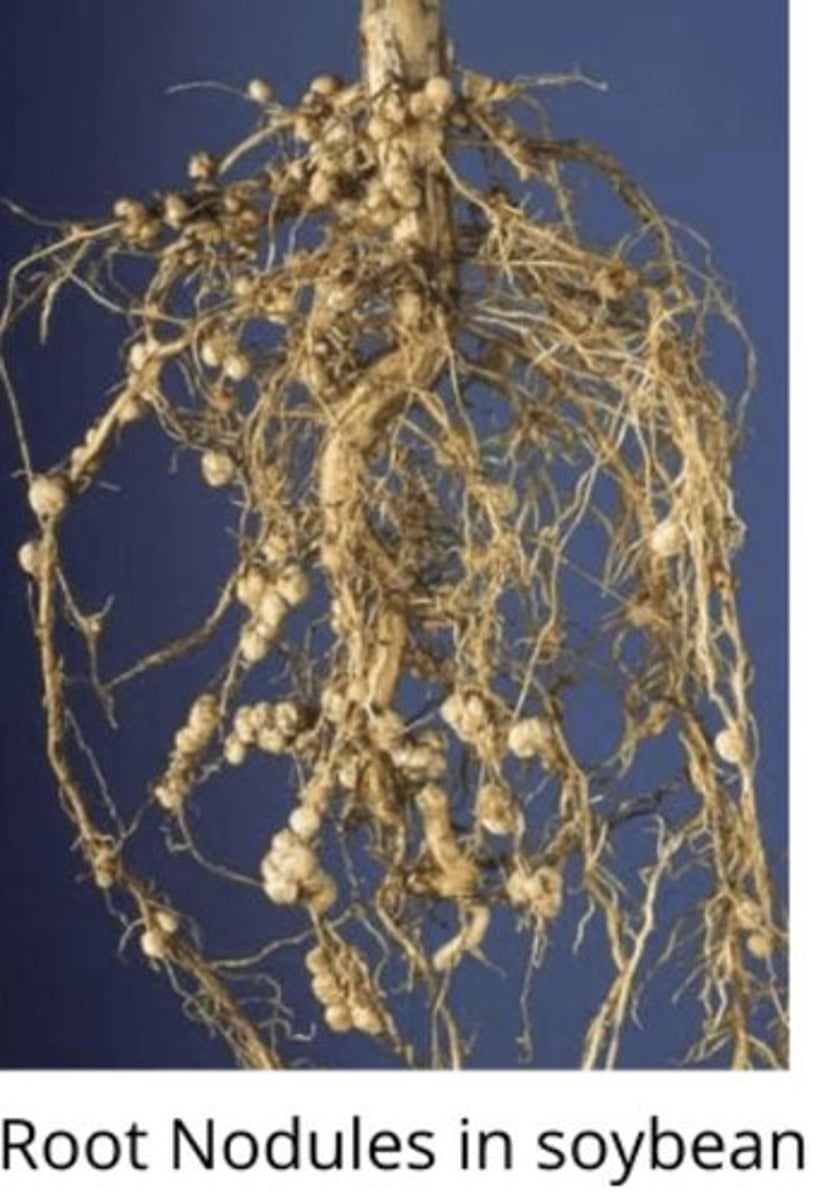
Nodules
Symbiotic interactions with soil bacteria or fungi that increase a plant's ability to absorb water and minerals.

Storage Roots
Some roots are enlarged and store large quantities of starch.
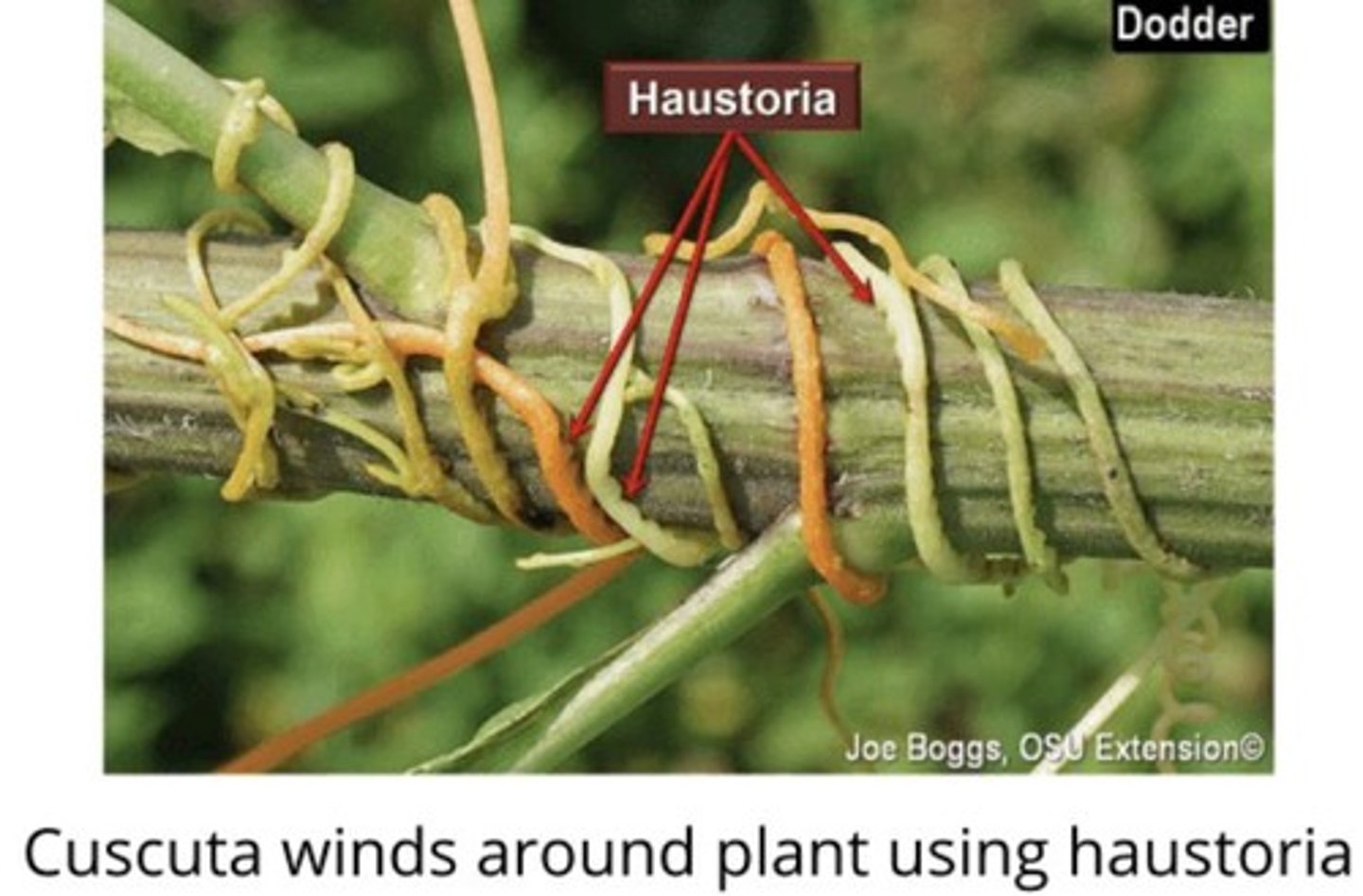
Parasitic Roots
Some roots absorb nourishment from the host plant.

Stolons
Horizontal stems that sprout from an existing stem and grow aboveground, forming roots and new shoots at their nodes.

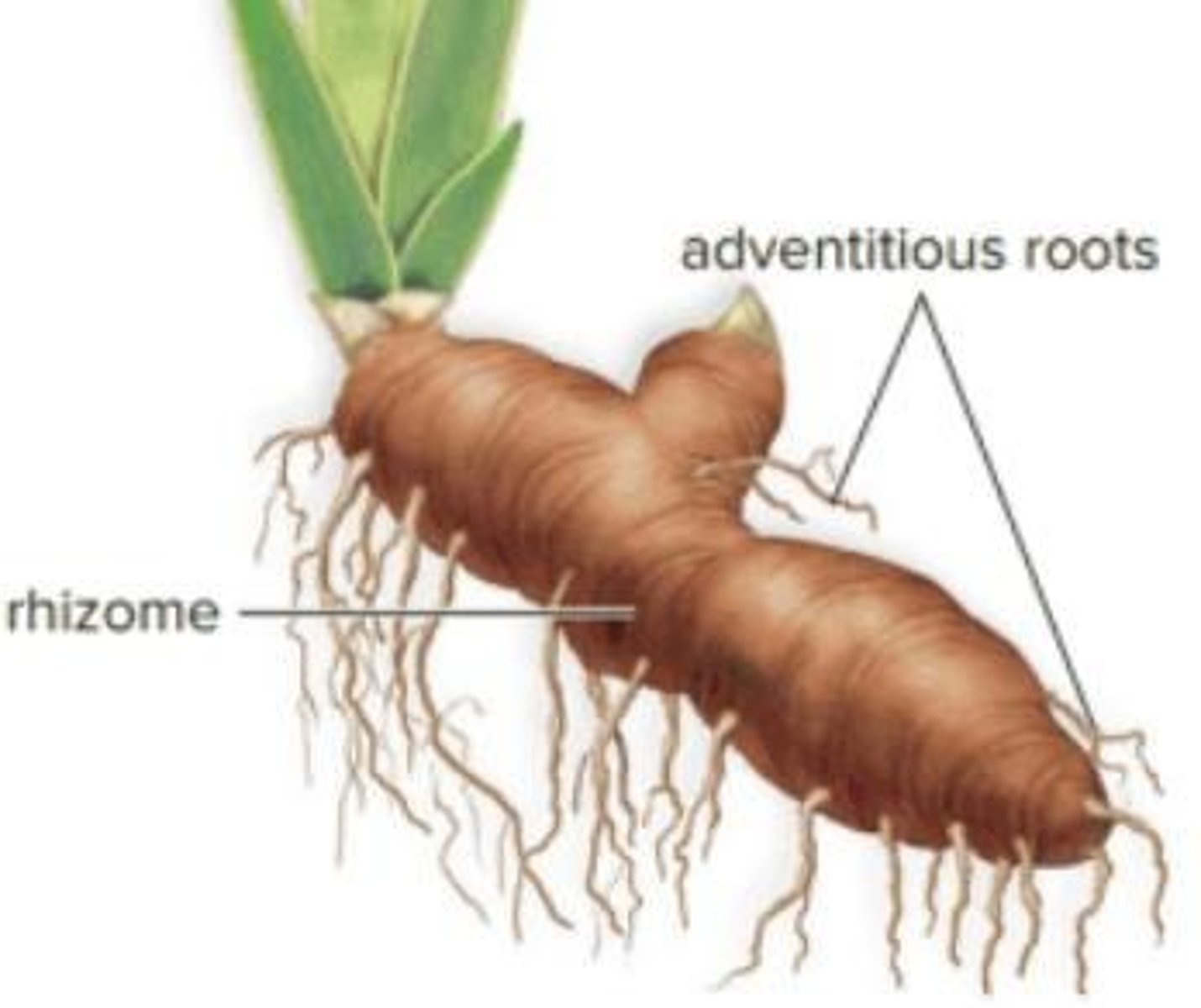
Rhizomes
Thickened, underground horizontal stems that produce shoots and roots.
Tubers
Swollen regions of rhizomes or stolons that store starch.

Corms
Bulbous underground stems that lie dormant during winter.
Succulents
Specialized photosynthetic stem for water storage.
Thorns
Thorns are modified branches appearing as hard, woody, sharp outgrowths that protect the plant.
Tendrils
Allow a plant to climb from the forest floor to the canopy, maximizing its exposure to sunlight.
Tendrils & Hooks
Tendrils and hooks are leaves modified to attach the plant to a support.
Spines
The spines of a cactus are leaves that protect the fleshy stem from herbivores.
Bulb
A bulb consists of a short, flattened stem encased in overlapping layers of thickened modified leaves called scales.
Bracts
Leaves in some species are modified to have different colors and look like petals.
Trichomes
Sticky trichomes for trapping, sensitive trichomes act as triggers, and trichomes secrete digestive enzymes.
Plantlets
Some plant species produce tiny, identical plantlets, each of which may fall to the ground and take root.
Economic Value of Roots
Source of Income, Food Source, Medicinal Source, Soil Preservation.
Economic Value of Leaves
Food, Medicine, Industry, Dyes, Fibers.