NURS 317 - Community Health Midterm
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What were some of the earliest forms of Healthcare in Canada
turtle island (Canada)
- Indigenous peoples would provide holistic healthcare, curative midwifery, and education regarding health and healing
- settlers would receive this care and learn fromf them
What did the 17th century of nursing look like?
;religious orders would provide healthcare and support the sick
- Grey nuns
a lot to do with social justice
- no divide between community and hospital healthcare and both in rural and urban places
What did nursing look like in the 18th and 19th century?
Nation Building and Nightingale Era
- Canada developed = immigration = new diseases indigenous people were not ready for = federal laws
- provincial health not federal responsibility with the social unrest and epidemics
- hospitals became centre of healthcare
- Nightingale is founder of nursing (great at epidemiology)
What factors have influence the history of nursing
racism
patriarchy
healthcare resource competition
gender bias
Socio-ecological context
challenges due to epidemics, immigration, inability to provide basic health to settlers and Indigenous peoples
nightingale and seacole used the epidemiology, statistics, awareness of environmental factors and SDoH for health promotion
military nursing: competencies of CHN, population health, prevention, emergency preparedness and disaster nursing
What did the 20th century nursing look like?
1. hospital: the shift to less emphasis on SDoH as the funding went there as you can SEE the outcome
2. private-duty
3. public health and home visit (self-employed CHNs, specialized and elite)
What were the first two sub specialities
1. public health nursing: started with school-aged children and evolved to maternal and in fact care
2. district nursing: home health nursing, early form of primary health care
Canada Health Act Principles
1. Public Administration
2. Comprehensiveness
3. Universality
4. Portability
5. Accessibility
- health promotion, prevention of disease and injury, health protection, and home health was not emphasized in the act
What are some big documents that have caused a shift in community health nursing?
Lalonde Report: environment, lifestyle, human biology, and the healthcare system are the 4 DOH
Alma Ata: primary health care
The Epp Framework and the Ottawa Charter: health promotion
Ottawa Charter: enabling people to increase control over and improve their health
Attributes of CHN
RELATIONAL!
- primary health care and advocacy
- political in nature to drive public and health policy change
six basic principles of collaboration
1. focus on the client
2. a population health approach
3. quality care and services
4. access
5. trust and respect
6. communication
Population health promotion
taking action on the interrelated SDoH that affects the population to create healthy change
reduce inequities, maintenance or improvement of health
*best change to facilitate social justice
primary prevention
impact specific risk factors so that incidence of disease is reduce (immunizations)
- UPSTREAM THINKING
Secondary prevention
identify disease processes as early as possible - at preclinical stage to reduce prevalence/duration of disease (PPD screening)
upstream thinking
a "big picture" population health approach that takes in the SDoH and more a primary prevention perspective
Power
is the ability to act so as to achieve a goal, ethically neutral
impacts health equity/inequity and social justice/injustice
health equity
every person has an opportunity to achieve optimal health regardless of the colour of their skin, level of education, gender identity, sexual orientation, the job they have, the neighbourhood, or if they are disabled
public health nursing
0focus on disease and injury prevention, health promotion, community development, program/policy planning
home health nursing
deals with disease care and treatment that requires surgical or medical interventions
- helps people live independently in their communities
tertiary prevention
reduce impact of long-term disease and disability by eliminating or reducing impairment or disability
- want to reduce persistence and progression
quaternary prevention
population at risk for over-diagnosis and overmedialization
- ADHD children
Why do CHN Standards of practice matter?
- Inspire excellence
- Foundation for certification
- Set criteria and expectations for safe and ethical care
- Define the scope and depth of practice
- Support human resource management
- Strengthen education and professional development
CHN Professional Practice Model
client is at the centre and the categories of
1. community health nurses and nursing practice
2. community organizations
3. system
all surround it
PARTNERSHIP MODEL
CHNC standards of practice
1. Health Promotion
2. Prevention and Health Protection
3. Health Maintenance, Restoration and Palliation
4. Professional Relationships
5. Capacity Building
6. Health Equity
7. Evidence Informed Practice
8. Professional Responsibility and Accountability
How do the standards work in practice
Health promotion, prevention and health protection, and health maintenance, restoration and palliation are WHAT WE DO IN PRACTICE
Professional Relationships capacity building, health equity, evidence informed practices, professional responsibility DESCRIBE HOW WE PRACTICE AND WHAT WE EXPECT TO ACHIEVE
The five Ottawa Charter health promotion strategies:
1. build healthy public policy
2. create supportive environments
3. strengthen community actions
4. develop personal skills
5. reorient health services
health promotion
is the process of enabling people to increase control over and to improve their health
LOOK AT EXAMPLES OF THE STANDARDS
Capacity building
focus is to recognize barriers to health and to mobilize and build on existing strengths
- PARTNERSHIP IS KEY!
What values must the CHN uphold
ones in both the CNA code of ethics and Canadian Community Health Nursings Standards of practice
morals vs values
morals: shared and generational societal norms about what constitutes right or wrong conduct
values: beliefs about the shared worth or importance of what is desired or esteemed within a society
purpose of the code of ethics
aspirational and regulatory: self-regulating professional and we strive to meet them
attributes of social justice
equity, human rights, democracy and civil rights, capacity building, just institutions, enabling environments, poverty reduction, ethical practice, advocacy, and partnerships
-assumes that all societies experience systematic oppression and inequities which affect some people more than others
- everyone contributes unintentionally or intentionally
social justice in community nurses framework
1. approaches tend to he concerned with the ethical use of power in health care
2. approach tends to view persons relationally as unique, connected to others, and vulnerable and unequal in power
3. tends to elicit concern for issues of everyday life and not primarily with crisis issues
ethical issues in CHN
pertain to capacity building, access and equity, negligence, and professional responsibly and accountability
Advocacy
act in the persons best interest and in their wishes, keep them informed, carry out instructions with diligence and competence, act impartially, maintain confidentiality
inequalities
must identify root causes of inequities
privilege vs oppression
P: societally granted, unearned advantages accorded to some people and not others. These are systemic or structural advantages based on identity factors
O: societally constructed disadvantages and disenfranchisement due to holding a marginalized identity.
race/racialization
social construction with biological consequences
importance of theory
roots that anchor both practice and research in the nursing discipline
guide practice and support understanding of why things are the way they are
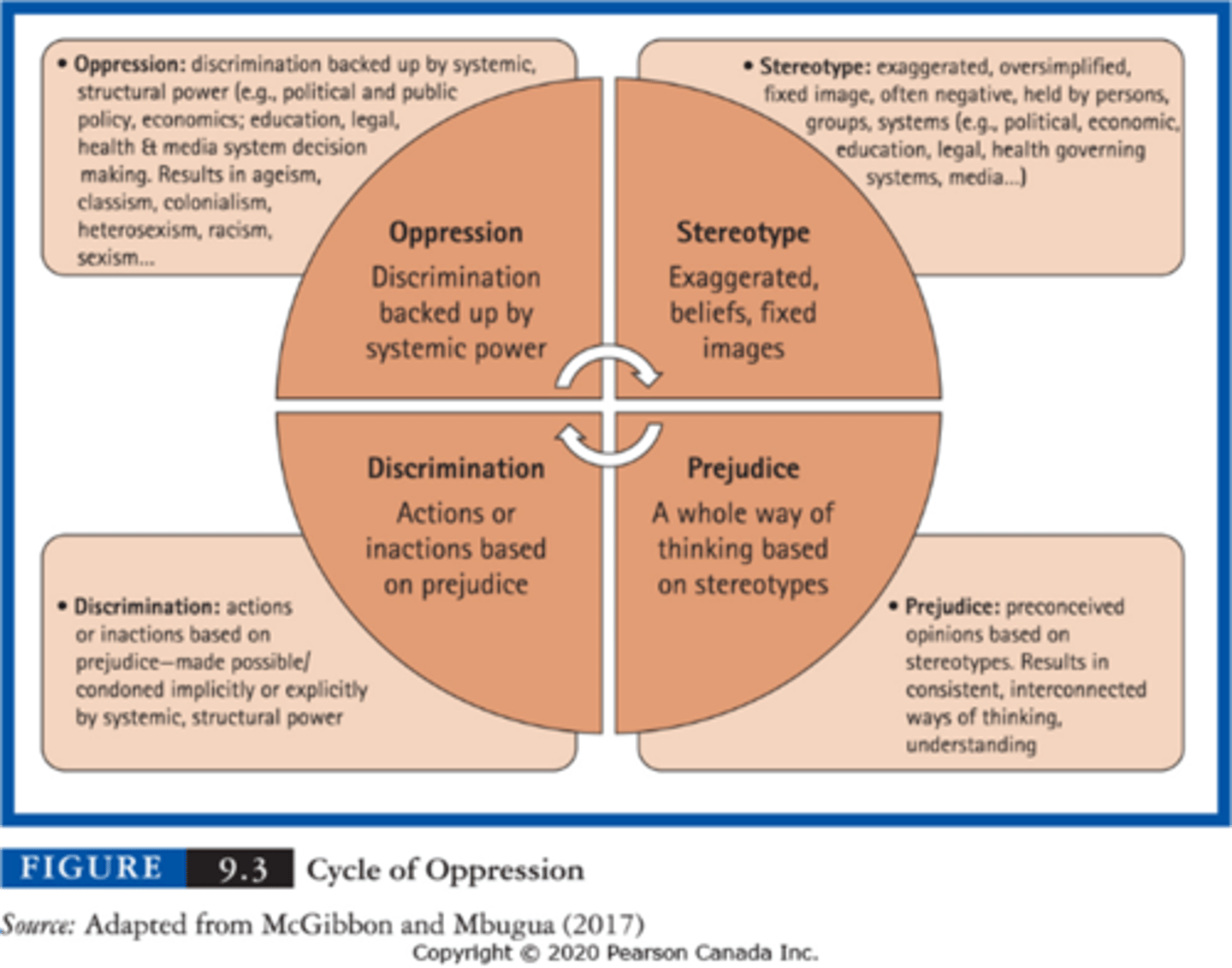
cycle of oppression
Characteristics of Culture
Culture: language, gestures, tools, customs and traditions defining a group's values and organize social interactions
- culture is a social construction
- culture is shared
- culture shapes us at an unconscious level
- culture is fluid and dynamic
cultural competence
an ongoing process, not an outcome
process of respect, accept, and apply knowledge and skills appropriate to client interactions and not letting personal beliefs to influence the clients differing views
cultural safety, cultural awareness, and cultural sensitivity
cultural safety: knowing our own culture and its influence on interacting with someone, knowing the power imbalance favouring the HP and address it, learning and applying new foundational skills
Cultural awareness (an initial understanding that variations exist) and cultural sensitivity (showing respect and valuing cultural diversity) are steps towards cultural safety
cultural humility
a commitment to actively taking responsibility for seeking to understand the culture and experiences of others, being comfortable not being the expert, we cannot fully understand all aspects of a person
tips for working with interpreters
1. share information: gives information to the client, using plain language
2. confirm understand: ask to repeat back using their own words
3. rephrase or clarify: if further explanation is needed
4. continue on
- sit in circle, clear and simple sentences, ask open-ended questions, pause frequently
primordial prevention
measure that alter societal structures and there changing underlying determinants of health (changing public policies)
social control
a group's formal and informal means of enforcing its norms
"Mickey Mouse concept as it is used in a broad array of means
formal social control pertains to a legalized right to enforce order
facemasks, vaccinations, and social distracting are all tools made use of in controlling behaviour in the name of collective advantages
evidence informed decision making
research is used with clinical expertise, client preference, and available resources
PICO (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes)
critical appraisal of research
see who else had problem, use surveillance to see what you know about the problem in your community, context, document what happened
epidemiology
the study of the occurrence and distribution of health-related states or events in specific populations, including the study of the determinants influencing such states and the application of the knowledge to control the health problem
- look at who what when and where
- go on to the how and why
- started with John snow
association vs causality
A: occurs when there is reasonable evidence that a connection exists between a stressor or environmental factor and a disease or health challenge
C: an association that has been confirmed and there is a definite, statistical, cause-and-effect relationship between a particular stimulus and occurrence of a disease
- web of causation, two important concepts are necessary and a particular stressor must be present and sufficient amount of exposure is required
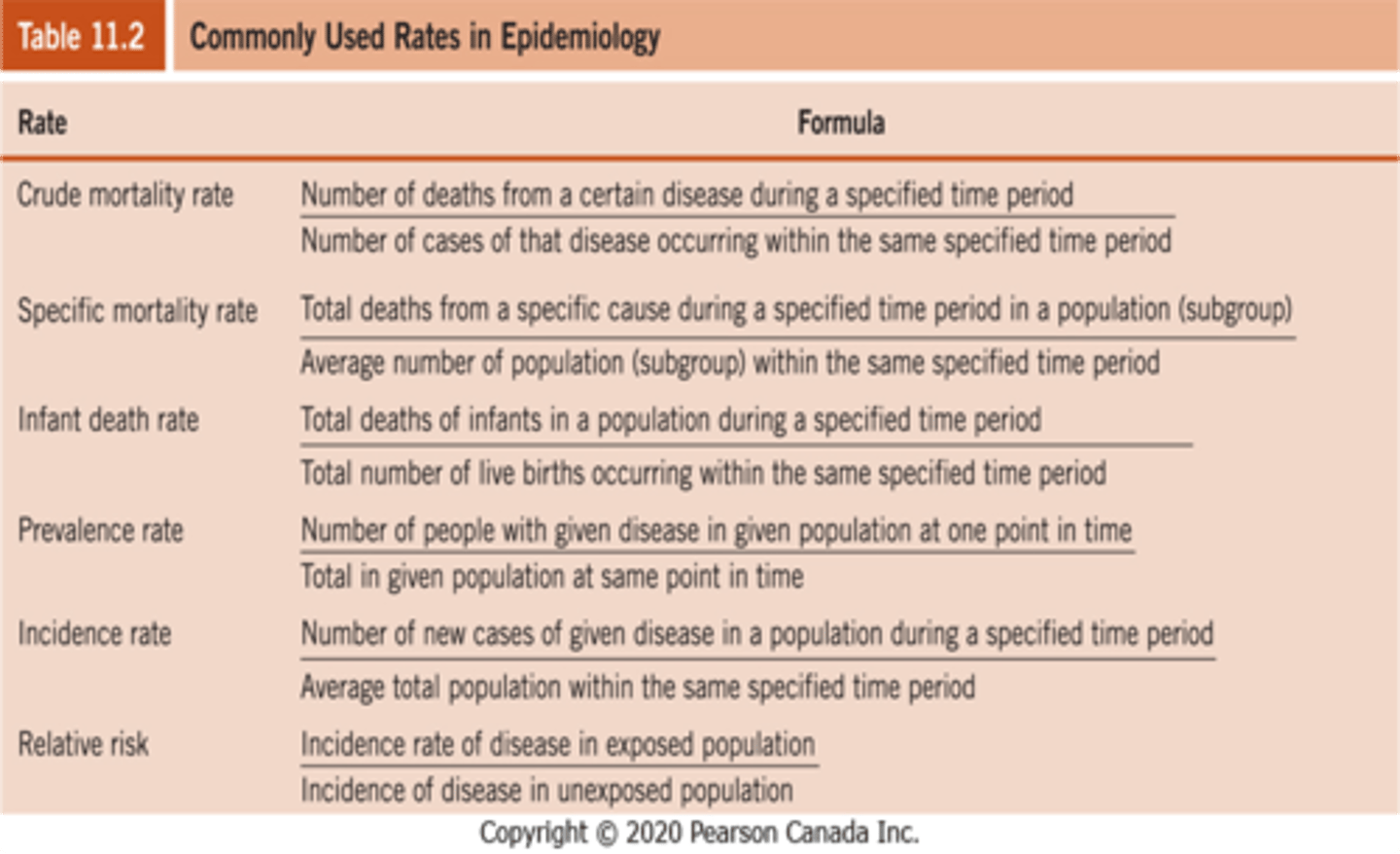
measurements in epidemiology
mortality: deaths
survival: describe the effect of a given disease and can be used to compare the efficacy of various treatments
morbidity: picture of a population and disease over time, questions population susceptibility and effectiveness of health promotion or treatment
prevalence vs incidence
P: the number of all cases of a specific disease in a population at any one given point in time / relative to the population at risk
I: identification of NEW cases of disease in a population over time (usually one year) / relative to the population at risk
screening and surveillance
screening: secondary prevention
case finding: contact tracing determine individuals whose health status is at risk
surveillance: constant monitoring of disease to assess patterns and identify events that do not fit the pattern
- screening tests need high sensitivity, need high specificity
epidemiologic triangle
host: human being in which disease occurs
agent: contagious/ non-contagious force that begins or prolongs a health problem
environment: context that promotes the epos sure of the host to the agent
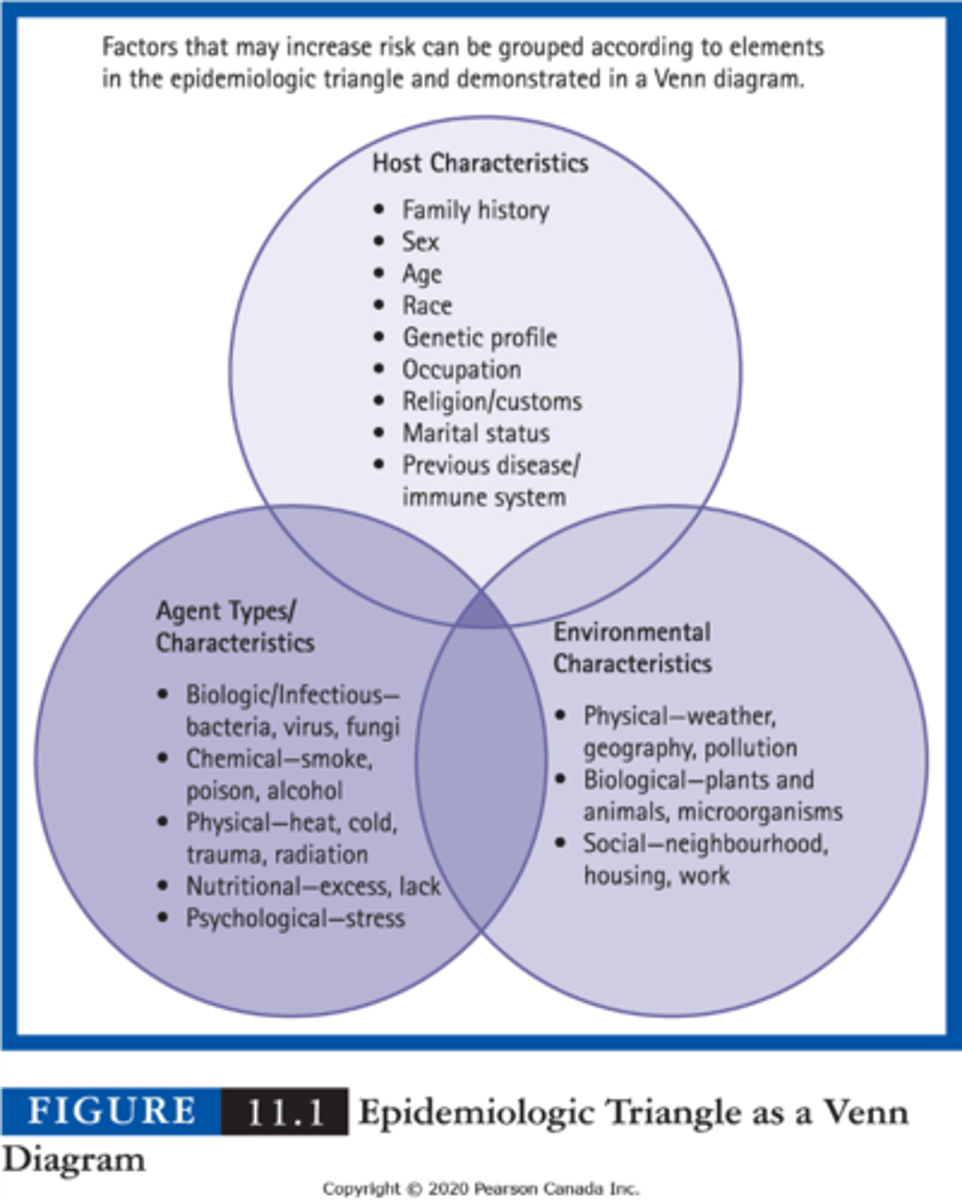
epidemiological research methods
descriptive: the person-place-time model
analytical: how and why (examine associations and test hypothesis)
observational studies: cross-sectional/correlational studies, retrospective, prospective
experimental studies: clinical trials
attributable risk
burden of disease in a population based on risk factors, how much of the disease is caused by this risk factor
outbreak
sudden occurrence of a disease in a community which has never experienced the disease before OR causes occur in > numbers than expected
- two incubation periods have passed without any then it is over!
epidemic vs endemic
Epidemic is a a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time.
An endemic is a diease regularly found amongst people in a certain area
how to find the rates