el physiology final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:46 AM on 5/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
homeostasis
(1) Define ___________ . State of dynamic constancy in the internal environment (no fluid changes)
\
dynamic constancy: correction in opposite direction of deviation-move it back to set point; Continuous process, always fine adjustments to stay in homeostasis
\
dynamic constancy: correction in opposite direction of deviation-move it back to set point; Continuous process, always fine adjustments to stay in homeostasis
2
New cards
sensors, control, effector
(1) Explain negative feedback
____ in the body to detect change and send information
(ex. nerve cells in the brain)
_____ which assesses change around a set point
_____ which can make the appropriate adjustments to counter the change from the set-point
____ in the body to detect change and send information
(ex. nerve cells in the brain)
_____ which assesses change around a set point
_____ which can make the appropriate adjustments to counter the change from the set-point
3
New cards
ok
reminder to go look at the negative feedback images
4
New cards
stimulus
positive feedback
1\.______ causes deviation from set point
2\.Cellular response amplifies deviation
3\.Further deviation leads to additional cellular response
4\.And so on and so on until stimulus stops (slow return to set point)
\*end product stimulates process
1\.______ causes deviation from set point
2\.Cellular response amplifies deviation
3\.Further deviation leads to additional cellular response
4\.And so on and so on until stimulus stops (slow return to set point)
\*end product stimulates process
5
New cards
reproductive
continuation of the species
6
New cards
digestive
breakdown of food into molecules
7
New cards
urinary
regulation of blood volume and composition
8
New cards
respiratory
gas exchange
9
New cards
immune
defense of the body against invading pathogens
10
New cards
circulatory
movement of blood and lymph
11
New cards
muscular
movements of the skeleton
12
New cards
skeletal
movement and support
13
New cards
endocrine
secretion of regulatory molecules called hormones
14
New cards
nervous
regulation of other body systems
15
New cards
integumentary
retention, thermoregulation
16
New cards
K+
•Membrane is most permeable to ___ therefore a change in it will have the greatest effect
•K = -90 mV
•Na = +66mV
•In most cells, the resting potential is between -65mV and -85mV.
•Neurons are usually at −70mV.
•These numbers are also derived mathematically:
•*Nernst Equation*
•*Goldmann-Hodgkin-Katz equation*
•K = -90 mV
•Na = +66mV
•In most cells, the resting potential is between -65mV and -85mV.
•Neurons are usually at −70mV.
•These numbers are also derived mathematically:
•*Nernst Equation*
•*Goldmann-Hodgkin-Katz equation*
17
New cards
Na, K
\
__ is mostly in plasma & interstitial fluid
__ is mostly in intracellular fluid
Cl- is mostly in intersitial fluid & plasma
__ is mostly in plasma & interstitial fluid
__ is mostly in intracellular fluid
Cl- is mostly in intersitial fluid & plasma
18
New cards
\-90
Membrane Potential (K+)
•The resulting potential difference measured in voltage would be the equilibrium potential (EK) of ___ mV.
oThis means the inside has a voltage 90mV lower than the outside.
\-negative indicates polarity inside the cell
•The resulting potential difference measured in voltage would be the equilibrium potential (EK) of ___ mV.
oThis means the inside has a voltage 90mV lower than the outside.
\-negative indicates polarity inside the cell
19
New cards
12, 145
•Sodium is important for establishing membrane potential.
•The concentration of sodium in a normal cell is __mM inside and 145mM outside.
•The concentration of sodium in a normal cell is __mM inside and 145mM outside.
20
New cards
\+66
Membrane potential (Na+)
To keep so much sodium out, the inside would have to be positive to repel the sodium ions.
•The equilibrium potential is ___mV.
To keep so much sodium out, the inside would have to be positive to repel the sodium ions.
•The equilibrium potential is ___mV.
21
New cards
osmolality
(4) Explain how the body detects changes in the ________ (# of solutes) of plasma and describe the regulatory mechanisms by which a proper range of plasma osmolality is maintained.
(look at the solution)
(look at the solution)
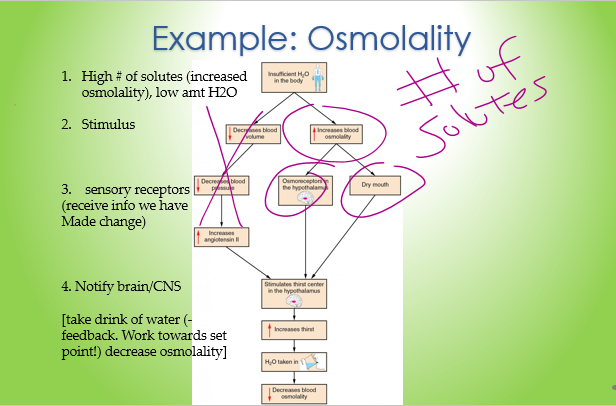
22
New cards
tonicity
_______: effect of solution on osmotic movement
23
New cards
isotonic , isosmotic
•**________** solutions have the __same__ concentration of *nonpenetrating* solutes as normal plasma.
•Plasma has the same osmolality as a 0.3m glucose or a 0.15m NaCl solution.
Solutions __________ to plasma:
1)0.9g NaCl/100mL water – normal saline
2)5% dextrose – 5g glucose/100 mL water
24
New cards
hypo
____**tonic:** a solution with a lower solute concentration compared to the plasma or cell (another solution)
________**-osmotic** solutions have a __lower__ solute concentration, Lower osmolality.
oThe cell will Lyse (swell / burst)
25
New cards
hyper
______**tonic:** a solution with a greater solute concentration compared to the plasma or cell DEHYDRATION. LOW OSMOLALITY
________ **osmotic** solutions have a __higher__ concentration than the cell.
oThe cell will **CRENATE (SHRINK)**
________ **osmotic** solutions have a __higher__ concentration than the cell.
oThe cell will **CRENATE (SHRINK)**
26
New cards
primary, secondary
(4) Describe active transport:
•Involves the use of **energy (ATP)** to “pump” a molecule against its gradient (low to high)
•Molecule specific and limited by saturation and the rate of conformational change.
•There are two types of active transport based on the source of energy:
\
including _______:
uses atp, pump is an enzyme
\
(always pumping, transporter high affinity for na +, reduces affinity for Na+ and affinity is now for K switching protein back to extracellular side
\
•Na/K –ATPase pump
•Moves 3 Sodium to extracellular fluid, 2 Potassium to intracellular.
•Both against the concentration gradient
•Maintains distribution of high intracellular K and low Na
•Found in every cell
•Shape & Affinity of transporter changes
\
__Why the pump?__
1\.Na + gradient (Na + is used in secondary transport)
2\.Prevents constant osmosis
3\.Maintain membrane potential - Counter K + leaks
•Involves the use of **energy (ATP)** to “pump” a molecule against its gradient (low to high)
•Molecule specific and limited by saturation and the rate of conformational change.
•There are two types of active transport based on the source of energy:
\
including _______:
uses atp, pump is an enzyme
\
(always pumping, transporter high affinity for na +, reduces affinity for Na+ and affinity is now for K switching protein back to extracellular side
\
•Na/K –ATPase pump
•Moves 3 Sodium to extracellular fluid, 2 Potassium to intracellular.
•Both against the concentration gradient
•Maintains distribution of high intracellular K and low Na
•Found in every cell
•Shape & Affinity of transporter changes
\
__Why the pump?__
1\.Na + gradient (Na + is used in secondary transport)
2\.Prevents constant osmosis
3\.Maintain membrane potential - Counter K + leaks
27
New cards
secondary
\
_______: uses electrochemical gradient across membrane
•Transported molecules can be moved in the same or opposite directions **(cotransport, countertransport)**
• **Co-transport: symport**
o**Ex. K+/Cl- (renal system)**
• **counter transport: antiport**
o**Ex. HCo3-/Cl- (respiratory system)**
\
•The movement of a molecule (Na+) with its electrochemical gradient is coupled with the movement of a second molecule (ex. glucose)
•Requires that proteins have two binding sites (one for each molecule)
•Primary AT will move Na+ back out of the cell maintaining the gradient
_______: uses electrochemical gradient across membrane
•Transported molecules can be moved in the same or opposite directions **(cotransport, countertransport)**
• **Co-transport: symport**
o**Ex. K+/Cl- (renal system)**
• **counter transport: antiport**
o**Ex. HCo3-/Cl- (respiratory system)**
\
•The movement of a molecule (Na+) with its electrochemical gradient is coupled with the movement of a second molecule (ex. glucose)
•Requires that proteins have two binding sites (one for each molecule)
•Primary AT will move Na+ back out of the cell maintaining the gradient
28
New cards
faciliated, active
Explain how active transport differs from facilitated diffusion. Use examples.
both are _____ mediated transport (slower)
_______: no energy is required, channel is specific and movements are diffusional, hight to low (ex glucose)
_______: uses atp & against gradient
both are _____ mediated transport (slower)
_______: no energy is required, channel is specific and movements are diffusional, hight to low (ex glucose)
_______: uses atp & against gradient
29
New cards
diffusion
Define ________, give examples and list the factors that influence the rate.
oLipid soluble molecules, Ions through channel proteins, Water
-Random movement of molecules from regions of **higher** concentration to regions of **lower** concentrations
\-Molecules are __always__ moving & colliding
\-simple/passive/ no enegy
__Affected by:__
• Concentration difference (gradient)
•distance
•Membrane permeability to each molecule
•Neural membrane at rest is more permeable to K+ than Na+
•Temperature
oLipid soluble molecules, Ions through channel proteins, Water
-Random movement of molecules from regions of **higher** concentration to regions of **lower** concentrations
\-Molecules are __always__ moving & colliding
\-simple/passive/ no enegy
__Affected by:__
• Concentration difference (gradient)
•distance
•Membrane permeability to each molecule
•Neural membrane at rest is more permeable to K+ than Na+
•Temperature
30
New cards
semipermeable
diffusion examples:
•**_________**: some materials allowed through, others not
•Nonpolar molecules diffuse rapidly
oLipophilic (lipid-loving) substances move through easily.
oEx. Steroid hormones, O2, CO2, fatty acids
•Polar molecules and hydrophilic (water-loving) do not diffuse readily through the membranes without the help of special molecules and structures.
oEx. Organic molecules
•**_________**: some materials allowed through, others not
•Nonpolar molecules diffuse rapidly
oLipophilic (lipid-loving) substances move through easily.
oEx. Steroid hormones, O2, CO2, fatty acids
•Polar molecules and hydrophilic (water-loving) do not diffuse readily through the membranes without the help of special molecules and structures.
oEx. Organic molecules
31
New cards
epithelial
osmosis:
•A difference in concentration of solutes exists on either side of the membrane
•Membrane must be **selectively permeable** making the water move
•The net movement of water is from the side with more water (diluted, low solute) to the side with less water (concentrated, high solute).
oWater will move faster with a higher concentration
Ex. **__________ cells** of kidneys have LOTS of aquaporins, varying slightly.
32
New cards
idk about this
(5_ Step-by-step, explain how an action potential is produced (get from turning point)
33
New cards
neurotransmitter
(5) Describe the sequence of events by which action potentials stimulate the release of _______________from presynaptic axons.
\
__**Chemical**__
•Axon terminals hold synaptic vesicles
•Pre-synaptic neurons release **__________**
•which is a chemical messenger that travels across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on post-synaptic neurons
**SNARE complex:** proteins loosely dock vesicles
Calcium Ions trigger a change in the SNARE proteins that lead to the fusion & release of the neurotransmitter
\
__**Chemical**__
•Axon terminals hold synaptic vesicles
•Pre-synaptic neurons release **__________**
•which is a chemical messenger that travels across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on post-synaptic neurons
**SNARE complex:** proteins loosely dock vesicles
Calcium Ions trigger a change in the SNARE proteins that lead to the fusion & release of the neurotransmitter
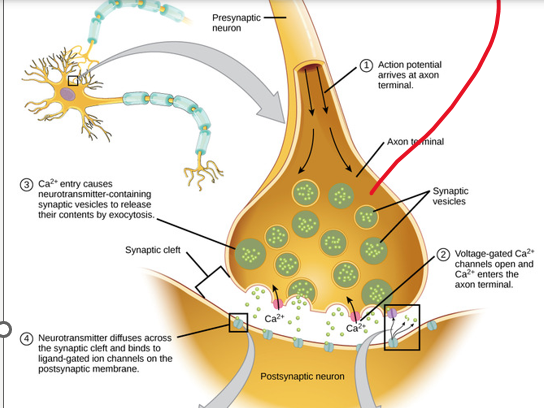
34
New cards
post
at the ___synapse
•Neurotransmitters come in large amounts across the synapse to ensure binding to a post synaptic receptor, unused neurotransmitters are transported away from the site
•Neurotransmitters come in large amounts across the synapse to ensure binding to a post synaptic receptor, unused neurotransmitters are transported away from the site
35
New cards
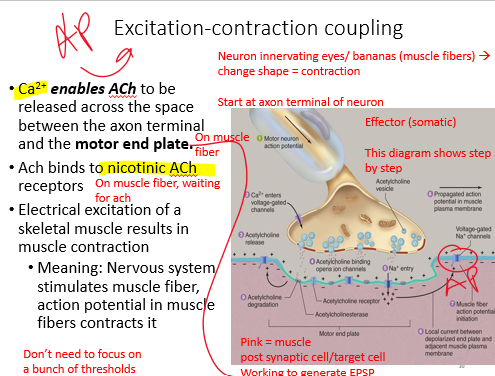
nicotinic
(5) NT @ the synapse
Remember these channels are ligand gated (binds the Ach).
_______ Ach receptors
•Ach binds at post synaptic cell,
o ex. Skeletal muscle cells (how muscles contract)
–Agonist: nicotine; Antagonist: curare
Explain how ligand-gated channels produce synaptic potentials, using the _________ACh receptor as an example.
•Binding of 2 acetylcholine molecules opens a channel
•Due to electrochemical gradient, more Na+ flows in than K+ out, EPSP is begun
Remember these channels are ligand gated (binds the Ach).
_______ Ach receptors
•Ach binds at post synaptic cell,
o ex. Skeletal muscle cells (how muscles contract)
–Agonist: nicotine; Antagonist: curare
Explain how ligand-gated channels produce synaptic potentials, using the _________ACh receptor as an example.
•Binding of 2 acetylcholine molecules opens a channel
•Due to electrochemical gradient, more Na+ flows in than K+ out, EPSP is begun
36
New cards
muscarinic
__**_______Ach receptor**__
•Ach binds at post synaptic cell
o ex. Digestive cells or cardio cells
–Agonist: muscarine
–Antagonist: atropine
•Binding at the receptor opens ion channels indirectly by using a G-protein. (secondary messenger)
–Dopamine and norepinephrine receptors do this too!
monoamines help w/ depression
37
New cards
EPSP
(5) Compare EPSPs and IPSPs and explain how action potentials can be stimulated by EPSP
•Opening Na+ or Ca2+ channels results in a graded depolarization called an **________ postsynaptic potential (EPSP)**
•Brings postsynaptic membrane closer to threshold (Depolarizing).
•Is a graded potential
-below -55 =NOT AP
•Opening Na+ or Ca2+ channels results in a graded depolarization called an **________ postsynaptic potential (EPSP)**
•Brings postsynaptic membrane closer to threshold (Depolarizing).
•Is a graded potential
-below -55 =NOT AP
38
New cards
inhibitory
5) •Opening K+(out) or Cl−(in) channels results in a graded hyperpolarization called **______ postsynaptic potential (IPSP)**
•Brings postsynaptic membrane further from threshold (Hyperpolarizing)
•Decreasing the likelihood of an action potential
in these, it is hyperpolarizing (more negative)
39
New cards
summation
(5)EPSP & IPSP are **graded potentials** – amplitude decreases as signal moves toward axon hillock.
–Action potentials can begin at the hillock due to high amt of Na+ and K+ channels
•**_________& lack of a refractory period** are characteristics of graded potentials
•Graded potentials *may* lead to action potentials
40
New cards
homeostasis
(7) Define the main functions of the central nervous system
•Composed of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Functions:
1\.Receives input from sensory neurons and directs activity of motor neurons
2\.Association neurons integrate sensory information and help direct the appropriate response to **maintain ________** and respond to the environment.
3\.Humans are capable of learning and memory adding a layer of modification to our behaviors
•Composed of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Functions:
1\.Receives input from sensory neurons and directs activity of motor neurons
2\.Association neurons integrate sensory information and help direct the appropriate response to **maintain ________** and respond to the environment.
3\.Humans are capable of learning and memory adding a layer of modification to our behaviors
41
New cards
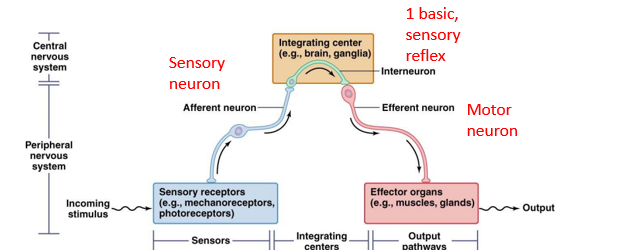
sensory, motor
(7) Describe the neural pathways and structures involved in a reflex arc
•Reflex responses to stimuli is a multi-step process.
•A **stimulus** occurs at the receptor of a **_____ neuron**. This is sent along the **afferent neuron** as a nervous impulse and is received by the **central nervous system**
•The interneuron makes connections to the **_______ neuron**. The motor neuron transmits the impulse to the **effector organ**.
Some reflexes require many association areas and interneurons in the brain
• Ex. crossed extensor reflex
**Muscle Stretch Reflex:** link afferent & efferent neurons directly together
• Ex. Knee-jerk reflex
•Reflex responses to stimuli is a multi-step process.
•A **stimulus** occurs at the receptor of a **_____ neuron**. This is sent along the **afferent neuron** as a nervous impulse and is received by the **central nervous system**
•The interneuron makes connections to the **_______ neuron**. The motor neuron transmits the impulse to the **effector organ**.
Some reflexes require many association areas and interneurons in the brain
• Ex. crossed extensor reflex
**Muscle Stretch Reflex:** link afferent & efferent neurons directly together
• Ex. Knee-jerk reflex
42
New cards
medulla
(7)•**Autonomic nervous center functions:** cardio and respiratory (heart pace!)
•All ascending and descending tracts between the brain and spinal cord pass through the medulla.
• relay sensory info to the thalamus
_________ = brain stem
43
New cards
autonomic
(8) compare and contrast the somatic and autonomic divisions of the PNS.
__________:
Innervate organs whose functions are not normally voluntarily controlled
Subdivisions: Parasympathetic, Sympathetic, Enteric (convergence & divergence
__________:
Innervate organs whose functions are not normally voluntarily controlled
Subdivisions: Parasympathetic, Sympathetic, Enteric (convergence & divergence
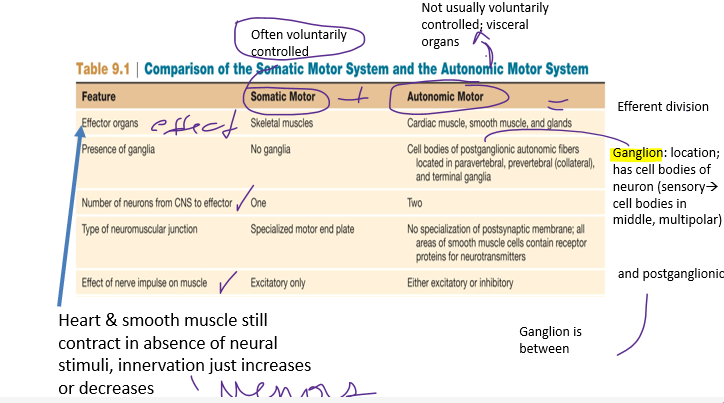
44
New cards
ganglia
\-sympathetic/parasympathetic: ________
\-Preganglionic fibers exit at different spinal locations
-Note the location of the ganglia and their proximity to the CNS
-Sympathetic on either side of the spinal cord first ganglia, second also close
-Parasympathetic ganglia located next to or in the organ
paravertebral ganglia: sympathetic chain
red = symp ; blue = para
45
New cards
synapsing
(8)Apply examples of dual innervation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic system
\
Dual innervation: one organ receiving sympathetic & parasympathetic input (______)
•__Parasympathetic__
–Decrease heart rate
–Relaxes bladder sphincter
•__Sympathetic (exciting)__
– increase heart rate
•Heart rate itself controlled by pacemaker cells
–Dilates and constricts veins
–Contracts bladder sphincter
\
Dual innervation: one organ receiving sympathetic & parasympathetic input (______)
•__Parasympathetic__
–Decrease heart rate
–Relaxes bladder sphincter
•__Sympathetic (exciting)__
– increase heart rate
•Heart rate itself controlled by pacemaker cells
–Dilates and constricts veins
–Contracts bladder sphincter
46
New cards
ganglia
•__________: clusters of cell bodies
•It doesn’t do anything… it is a LOCATION
• synapse: neuron to neuron
•Ganglia are broader: neurons = nerves (zoom in and you see synapse)
•2 sets of ganglia (sympathetic & 1 closer to target)
47
New cards
norepinephrine
(8) Describe the structure of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
fight or flight
•Divergence of impulses to ganglia of the sympathetic system and convergence of impulse within ganglia *can* result in **mass activation**-increasing activity in response to fight or flight situations
•Release of _________ from postganglionic neurons and the secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla.
•Heart rate, blood pressure increase
•Blood increases to skeletal muscles, heart and brain: the essentials you need in that moment!
fight or flight
•Divergence of impulses to ganglia of the sympathetic system and convergence of impulse within ganglia *can* result in **mass activation**-increasing activity in response to fight or flight situations
•Release of _________ from postganglionic neurons and the secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla.
•Heart rate, blood pressure increase
•Blood increases to skeletal muscles, heart and brain: the essentials you need in that moment!
48
New cards
ACH
•The parasympathetic division is antagonistic to the sympathetic division.
•Releases ___ from postganglionic neurons
•Slows heart rate (decreases rate of pacemaker cells), and increases digestive activities
•As a note: the parasympathetic division is not normally activated as a whole. In other words there is no mass activation of this division
• PSNS is specific local in responses
49
New cards
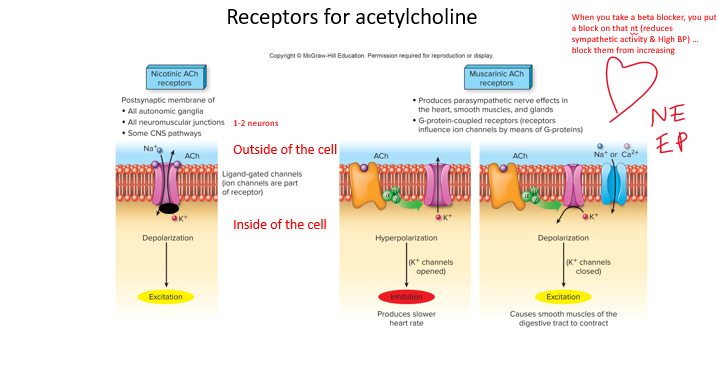
receptors
(8) Identify the neurotransmitters of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, and the hormone released by the adrenal medulla. (Review _________ for neurotransmitters)
50
New cards
anterior
(9) Explain the sequence of hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal hormones.
•The __________ pituitary is controlled via releasing and inhibiting hormones transported through the **hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system**.
•The __________ pituitary is controlled via releasing and inhibiting hormones transported through the **hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system**.
51
New cards
oxytocin
**Hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract** \n (Posterior Pituitary hormones synthesized in Hypothalamus
•Both belong to the peptide class
•_____________ is involved in the milk ejection reflex of nursing mothers and during labor. Stimuli in the nipple and cervix send neural signals to release hormone.
__Antidiuretic hormone (Vasopressin)__ is involved **in regulation of water balance and contracts blood vessels** increasing blood pressure, stimuli occurs from changing the
52
New cards
anterior
•Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system hormones \n (produced by Hypothalamus)
•Sequence (waterfall, cascade) of events:
1\.regulatory hormone (stored in hypothalamus) controls **secretion of _____ pituitary hormone**
2\. Anterior pituitary hormone then controls the secretion of a hormone from another endocrine gland
3\. The last hormone does the action on its target cell
\
Example: thyroid releases T3 and T4 hormones to do the action intended of this sequence
53
New cards
hypothalamus
(9) Distinguish between the anterior and posterior pituitary, and identify the hormones secreted by each part.
\
**Negative Feedback:** The relationship between the hypothalamus, **anterior** pituitary, and the target tissue is sometimes called an axis. Hypothalmus-pituitary-Adrenal axis…. anterior also in portal
Posterior Pituitary hormones synthesized in ___________
\
**Negative Feedback:** The relationship between the hypothalamus, **anterior** pituitary, and the target tissue is sometimes called an axis. Hypothalmus-pituitary-Adrenal axis…. anterior also in portal
Posterior Pituitary hormones synthesized in ___________
54
New cards
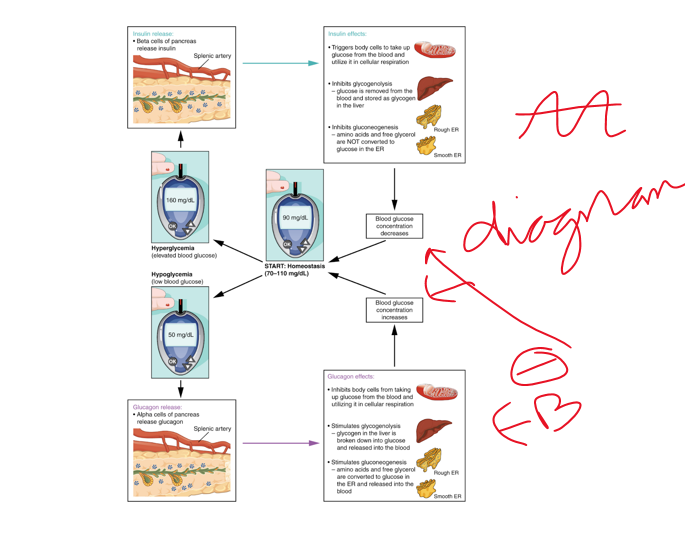
glucagon and insulin
(9) Identify the hormones of the pancreas.
55
New cards
lowers, raises
(9) Describe how insulin and glucagon secretion are affected by eating and by fasting and explain the actions of these two hormones.
• **glucagon & insulin**
•Regulate blood glucose levels, Causes an **antagonistic effect** (blocking)-insulin ______ blood glucose levels by enhancing transport of glucose, it counters any activity that would increase levels of glucose. Glucagon promotes _____ the glucose concentrations
• **glucagon & insulin**
•Regulate blood glucose levels, Causes an **antagonistic effect** (blocking)-insulin ______ blood glucose levels by enhancing transport of glucose, it counters any activity that would increase levels of glucose. Glucagon promotes _____ the glucose concentrations
56
New cards
idk about this
(10) draw a concept map to show excitation-contraction coupling in a skeletal muscle (the sequence of events from the time ACh is released from the axon terminal of a neuron to the time Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum).
57
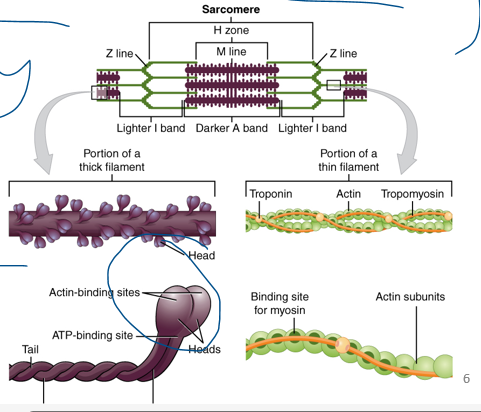
New cards
thick, thin, tropomyosin, troponin
\
_____ filaments
almost entirely of **myosin**
•Polypeptide chains form two globular heads and a tail
•Heads form crossbridge – area that exerts force on the thin filament
•Head contains ATP-binding site and actin-binding site
\
_____ filaments: Mostly made of the protein **actin**
Also include the regulatory proteins troponin and tropomyosin.
Important roles in regulating contractions
\
__**____:**__
Overlaps binding sites
blocking **cross bridges**
__**_______:**__
•**Ca2+ binding** to troponin regulates skeletal muscle contraction because it moves the tropomyosin away and allows myosin to interact with the actin.
58
New cards
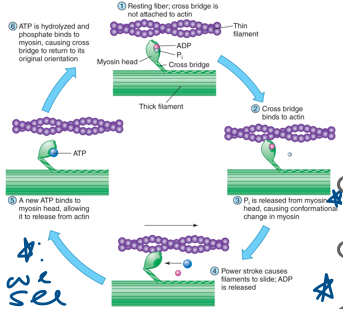
cross bridge
(10) Explain in detail a cycle of ____ _____ activity during muscle contraction and discuss the role of tropomyosin and troponin in this cycle.
•Initiated when excitation-contraction coupling increases cytosolic Ca2+ and binding sites on actin are exposed
•Each cross bridge goes through its cycle ***independently*** of other cycles
•The myosin head serves as a myosin ATPase enzyme, splitting ATP into ADP + Pi.
•The head binds to actin when the muscle is stimulated. (energy)
1/2: Energy present; ca concentration increased; excitement already occurred; binding to troponin and tropomyosin
**Now we bind actin and myosin**
Release of Pi upon binding creates a conformational change on myosin head, producing a **power stroke** that pulls the thin filament toward the center.
\
3/4: Binding of actin and myosin à release of phosphate
Add more cross bridge: Power stroke/sliding
•After the power stroke, ADP is released and a new **ATP binds**.
•This makes myosin release actin.
•ATP is split.
\
5/6:
“Resetting”
If Ca2+ is present we keep going
lose lose gain gain (p, adp, atp, energy)
•Initiated when excitation-contraction coupling increases cytosolic Ca2+ and binding sites on actin are exposed
•Each cross bridge goes through its cycle ***independently*** of other cycles
•The myosin head serves as a myosin ATPase enzyme, splitting ATP into ADP + Pi.
•The head binds to actin when the muscle is stimulated. (energy)
1/2: Energy present; ca concentration increased; excitement already occurred; binding to troponin and tropomyosin
**Now we bind actin and myosin**
Release of Pi upon binding creates a conformational change on myosin head, producing a **power stroke** that pulls the thin filament toward the center.
\
3/4: Binding of actin and myosin à release of phosphate
Add more cross bridge: Power stroke/sliding
•After the power stroke, ADP is released and a new **ATP binds**.
•This makes myosin release actin.
•ATP is split.
\
5/6:
“Resetting”
If Ca2+ is present we keep going
lose lose gain gain (p, adp, atp, energy)
59
New cards
smooth
__________ muscle cells (SMC) have a single nucleus and have the capacity to divide throughout the life of an individual.
Nerves are part of ***autonomic*** division instead of somatic. (SKELETAL)
The thick and thin (myosin and actin) filaments are not organized into myofibrils, and there are NO sarcomeres
Calcium (regulates) binds to calmodulin (differences w/ smooth: both cardiac & skeletal bind to troponin)
60
New cards
pacemaker
(10) For skeletal and cardiac muscle, list the ion channels involved in excitation-contraction coupling and what stimulus opens those channels.
cardiac: node cells have ________
cardiac: node cells have ________
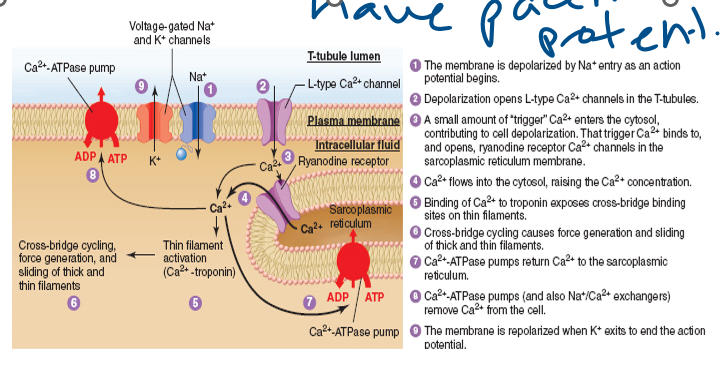
61
New cards
skeletal
this is all about __________ muscle excitation contraction coupling
62
New cards
post
this is in the ________ synaptic muscle cell
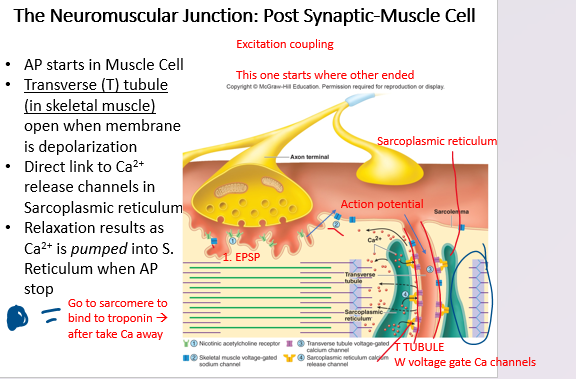
63
New cards
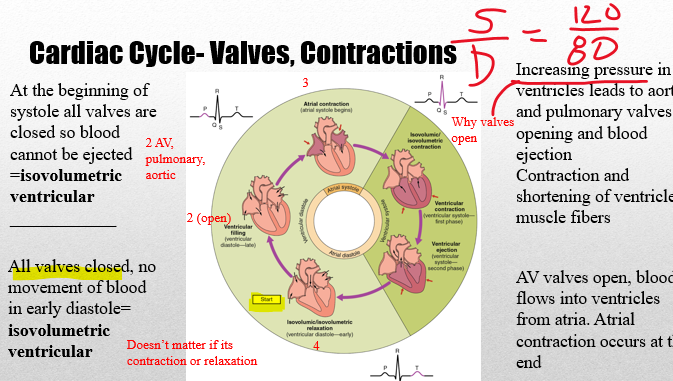
cardiac
(11)Using a drawing or flow chart, describe the sequence of events that occurs during the cardiac cycle. Indicate when atrial and ventricular filling occur and when atrial and ventricular contraction occur.
\
•The _______ cycle is all the events involved with the flow of blood through the heart during one heart beat.
•Average 72 beats/min
•Systole is the ***contraction phase*** of the ventricles where blood is ejected from the heart
•Diastole is the ***relaxation phase*** of ventricles where blood refills the ventricles
\
•The _______ cycle is all the events involved with the flow of blood through the heart during one heart beat.
•Average 72 beats/min
•Systole is the ***contraction phase*** of the ventricles where blood is ejected from the heart
•Diastole is the ***relaxation phase*** of ventricles where blood refills the ventricles
64
New cards
circulation
(11) Using a flow diagram (arrows), describe each pathway of _________ . List the valves involved in each pathway
•**Systemic:** arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
•**Pulmonary:** carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs and the pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart.
•**Systemic:** arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
•**Pulmonary:** carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs and the pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart.
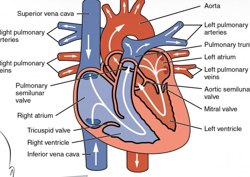
65
New cards
autonomic
(11) Discuss how the _________ nervous system is involved in heart rate and the neurotransmitters and hormones involved.
\
baroceptor reflex
\-Afferent neurons provide input to the ***arterial pressure*** (fall in BP leads to reduced action potentials firing) – _______ system responds
\-.CNS vasomotor and cardiac control centers of the medulla oblongata (controlling _______ innervation)
\
baroceptor reflex
\-Afferent neurons provide input to the ***arterial pressure*** (fall in BP leads to reduced action potentials firing) – _______ system responds
\-.CNS vasomotor and cardiac control centers of the medulla oblongata (controlling _______ innervation)
66
New cards
gas exchange
(11) explain the functions of capillaries.
•Branching in the system ensures all cells are close to capillaries. Nutrients and metabolic end products need to move between the blood in the capillaries to the cells. (through diffusion)
•__Main function of the vessels:__ supply nutrients and hormones and remove metabolic end products and other cell secretions
•Velocity ***decreases*** as blood flows from the larger aorta to smaller arteries and arterioles and then to capillaries
•The reduced velocity allows the time for products in the blood to be exchanged from the ***blood plasma to the interstitial fluid***
\
\-platelet plug @ cap
•Branching in the system ensures all cells are close to capillaries. Nutrients and metabolic end products need to move between the blood in the capillaries to the cells. (through diffusion)
•__Main function of the vessels:__ supply nutrients and hormones and remove metabolic end products and other cell secretions
•Velocity ***decreases*** as blood flows from the larger aorta to smaller arteries and arterioles and then to capillaries
•The reduced velocity allows the time for products in the blood to be exchanged from the ***blood plasma to the interstitial fluid***
\
\-platelet plug @ cap
67
New cards
all ways to excrete water
(11)Describe the effects of dehydration/overhydration on blood and urine volumes.
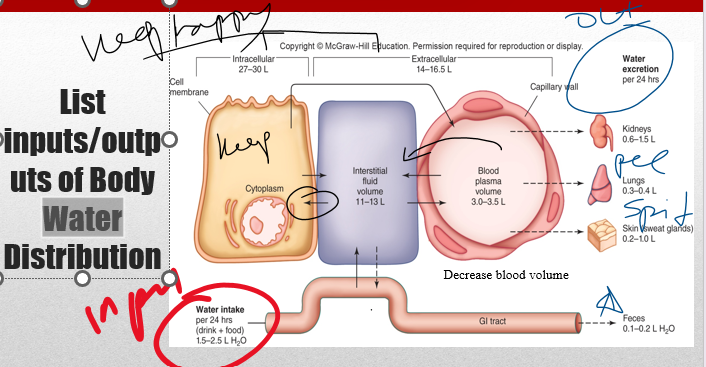
68
New cards
transportation
(11)Identify the functions and components of the circulatory system.
•The three main functions are:
__________**:** O2/CO2, products of digestion, wastes
o**Regulation:** Hormones, temperature (cycling blood through deep to surface vessels)
o**protection** Clotting, Immune
\
•**Cells:** Myocardial cells **(cardiac muscle),** Node **(**pacemaker) cells, erythrocytes, endothelial cells
•The circulatory system function is impacted by many systems: endocrine system, nervous system, respiratory and kidneys.
•This is a key physiology point-the interaction of systems!
•The three main functions are:
__________**:** O2/CO2, products of digestion, wastes
o**Regulation:** Hormones, temperature (cycling blood through deep to surface vessels)
o**protection** Clotting, Immune
\
•**Cells:** Myocardial cells **(cardiac muscle),** Node **(**pacemaker) cells, erythrocytes, endothelial cells
•The circulatory system function is impacted by many systems: endocrine system, nervous system, respiratory and kidneys.
•This is a key physiology point-the interaction of systems!
69
New cards
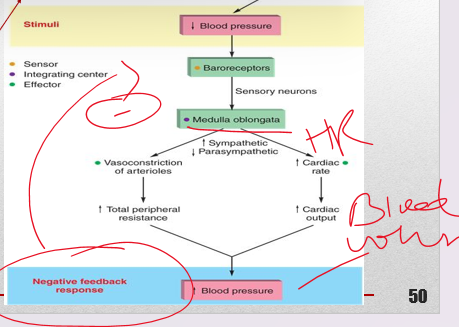
baroreceptor
(11)• Explain how the _________ reflex helps to compensate for a fall in blood pressure.
•Baroreceptors located at:
•The carotid arteries called the **carotid sinus**
•Second is the **aortic arch**
•Baroreceptors sensitive to changes in ***arterial pressure*** in the short term (beat to beat)
•Baroreceptor reflex includes:
1\.sensory receptors at the aortic arch and carotid sinus
2\.CNS vasomotor and cardiac control centers of the medulla oblongata (controlling autonomic innervation)
3\.Effectors: ***heart and blood vessels***
•Baroreceptors located at:
•The carotid arteries called the **carotid sinus**
•Second is the **aortic arch**
•Baroreceptors sensitive to changes in ***arterial pressure*** in the short term (beat to beat)
•Baroreceptor reflex includes:
1\.sensory receptors at the aortic arch and carotid sinus
2\.CNS vasomotor and cardiac control centers of the medulla oblongata (controlling autonomic innervation)
3\.Effectors: ***heart and blood vessels***
70
New cards
inspiration, expiration
(12) Explain how ventilation is regulated by the nervous system.
_______:
•Initiated by ***motor neurons*** firing action potentials to ***intercostal muscles*** (between ribs) and diaphragm
***diaphragm*** contracts and provides the most important ; active process
\
______:
Motor neurons ***decrease action potentials*** to diaphragm and intercostals, muscles relax
Air in alveoli gets compressed as lungs become smaller, air moves out, Palv > Patm, passive process
\
•Receive information regarding respiratory system
•Nervous system processes information and responds
•Muscles move and respiration occurs
_______:
•Initiated by ***motor neurons*** firing action potentials to ***intercostal muscles*** (between ribs) and diaphragm
***diaphragm*** contracts and provides the most important ; active process
\
______:
Motor neurons ***decrease action potentials*** to diaphragm and intercostals, muscles relax
Air in alveoli gets compressed as lungs become smaller, air moves out, Palv > Patm, passive process
\
•Receive information regarding respiratory system
•Nervous system processes information and responds
•Muscles move and respiration occurs
71
New cards
hypo, hyper
(12) Describe the effects of hyperventilation and hypoventilation on the blood pH.
• **______ventilation**
•Low pH, cause of respiratory acidosis
•Alveolar ventilation can’t keep up! Too slow
•High CO2
• **_____entilation**
•High pH, cause of respiratory alkalosis
•Alveolar ventilation too fast
•Low CO2
• **______ventilation**
•Low pH, cause of respiratory acidosis
•Alveolar ventilation can’t keep up! Too slow
•High CO2
• **_____entilation**
•High pH, cause of respiratory alkalosis
•Alveolar ventilation too fast
•Low CO2
72
New cards
ok
•Range for pH of blood: 7.35-7.45 (Homeostasis)
•Maintained through Lungs-CO2 and Kidneys- Bicarbonate
**Acidosis:** When plasma H+ concentration increases, pH drops below 7.4
•Arterial H+ concentration increased due to carbon dioxide: ***respiratory acidosis***
**Alkalosis:** When plasma H+ concentration decreases, pH rises above 7.4
•***respiratory alkalosis*** results from decreased arterial PCO2 and H+ concentration
73
New cards
inspiration
(12) Describe the actions of the diaphragm during inspiration and expiration.
___________: d***iaphragm*** contracts down and provides the most important inspiratory muscle
___________: d***iaphragm*** contracts down and provides the most important inspiratory muscle
74
New cards
kidney
what is the function of the _______
•The ***kidneys and the respiratory system*** work together to regulate hydrogen ion concentrations.
•Respiratory can respond quickly-within minutes-to changes in H+ (pH) until the renal system can eliminate the imbalance in a period of hours or days
•Ex. Increased arterial H+ stimulates ventilation (air moves from atmosphere to alveoli), lowers arterial PCO2, which reduces H+
\
•The kidneys eliminate or replenish hydrogen ions from the body by altering plasma bicarbonate concentration.
•The ***kidneys and the respiratory system*** work together to regulate hydrogen ion concentrations.
•Respiratory can respond quickly-within minutes-to changes in H+ (pH) until the renal system can eliminate the imbalance in a period of hours or days
•Ex. Increased arterial H+ stimulates ventilation (air moves from atmosphere to alveoli), lowers arterial PCO2, which reduces H+
\
•The kidneys eliminate or replenish hydrogen ions from the body by altering plasma bicarbonate concentration.
75
New cards
micturition
(13) Describe the process of micturition and the mechanisms that control urine release
•The bladder stores urine until it is excreted from the body by the ***micturition reflex***
•Micturition is initiated by a nervous reflex which causes the smooth muscle of the bladder walls (***detrusor muscle***) to contract and expel the urine.
•Action potentials can exhibit automaticity in response to stretch but stimulation is required for bladder emptying
(external - skeletal, internal - smooth)
•The bladder stores urine until it is excreted from the body by the ***micturition reflex***
•Micturition is initiated by a nervous reflex which causes the smooth muscle of the bladder walls (***detrusor muscle***) to contract and expel the urine.
•Action potentials can exhibit automaticity in response to stretch but stimulation is required for bladder emptying
(external - skeletal, internal - smooth)
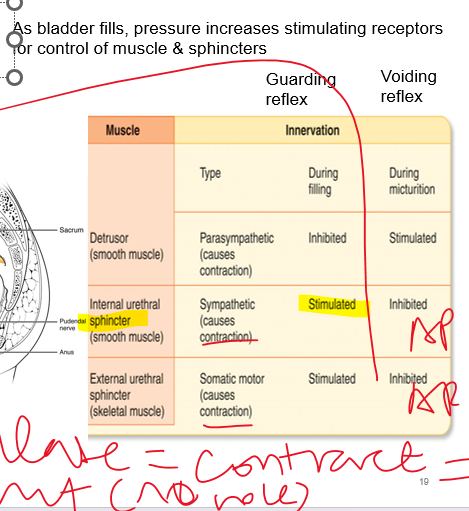
76
New cards
secretion
•A substance may enter tubules through glomerular filtration or tubular **__________c**(capillary to lumen).
•A substance may leave the tubule through **reabsorption** (passing of substances from the lumen (tubules) to the capillary) or **excretion** (out of the body)
•Reabsorption and secretion require a substance to move across a layer of epithelial cells
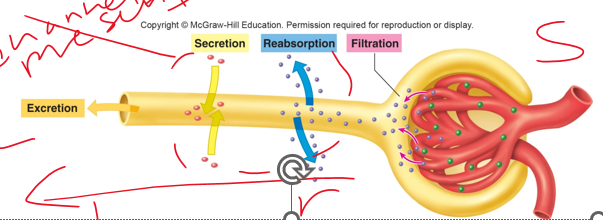
77
New cards
filtrate
•(13) Draw and label the course of the _________ (through the nephron) from the glomerular capsules to the ureter. Add the vasculature around the nephron including the afferent arteriole, glomerular capillaries, efferent arteriole, and peritubular capillaries.
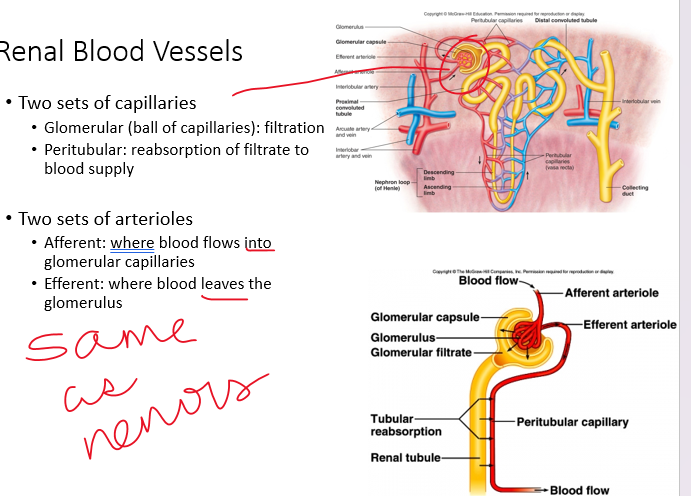
78
New cards
reabsorption
•________ occurs constantly in ***proximal and loop of Henle tubules*** and is not subject to hormonal control. Distal and collecting tubules *are* subject to this control.
Products reabsorbed at high rates:
• **Glucose & most organic nutrients**
•For products like these, the kidneys just help in ***maintaining*** plasma levels of the nutrients
•**Water and many ion**
•Kidneys can aid in ***regulating*** these
•Ex. Water intake decreases, kidneys water reabsorption increases
79
New cards
water
\-Na+ and Cl- combine to form NaCl in the interstitial fluid which will drive the reabsorption of ***_____***
-throughout tubule, Na+ is reabsorbed by ***primary active transport***
-Na+ reabsorption drives reabsorption of cotransported substances (such as Cl-) and secretion of H+
80
New cards
impermeable
•Na+ & water in proximal tubule is reabsorbed in the same proportions
But in the Loop of Henle…
•The descending loop of Henle is relatively ***__________*** to solutes and freely permeable to water.
•The ascending limb is ***permeable*** to solutes, but not water.
81
New cards
reabsorption
(13) explain how ADH (vasopressin) acts to promote water ________.
•These are the two factors that stimulate ***vasopressin (ADH)***
•More vasopressin - more aquaporins - more water retained - less water excreted
•These are the two factors that stimulate ***vasopressin (ADH)***
•More vasopressin - more aquaporins - more water retained - less water excreted
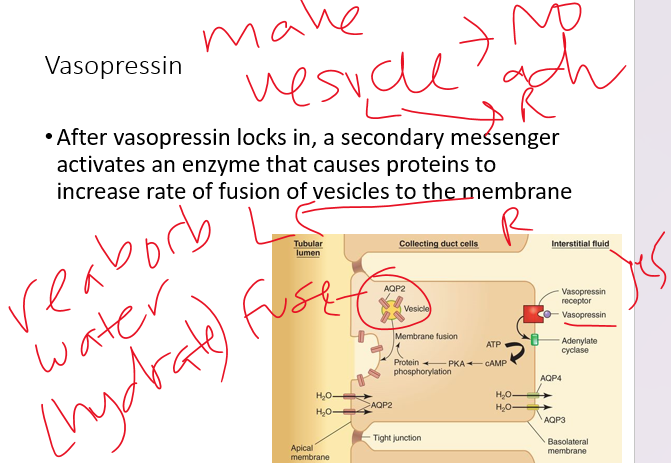
82
New cards
aquaporin
•Permeability varies depending on location in tubule and presence of ***_____***
•***Proximal tubule*** location for highest water permeability (ie highest # of aquaporins)
•Vasopressin stimulates presence of aquaporins in the collecting ducts, without it permeability is low
***Water diuresis:*** large amounts of water in urine due to low
83
New cards
low
(13) Compare respiratory and metabolic imbalances of acidosis and alkalosis.
•**Metabolic acidosis:** acidosis due to processes other than respiration, ___ blood pH
•Examples:
•Lactic acid build-up due to severe exercise
•Diarrhea (This gets rid of bicarbonates-creating more acidic environment)
•**Metabolic alkalosis** alkalosis due to processes other than respiration, rising blood pH
•Examples:
•Excessive vomiting
•Intake of excess bases - antacids
•**Metabolic acidosis:** acidosis due to processes other than respiration, ___ blood pH
•Examples:
•Lactic acid build-up due to severe exercise
•Diarrhea (This gets rid of bicarbonates-creating more acidic environment)
•**Metabolic alkalosis** alkalosis due to processes other than respiration, rising blood pH
•Examples:
•Excessive vomiting
•Intake of excess bases - antacids
84
New cards
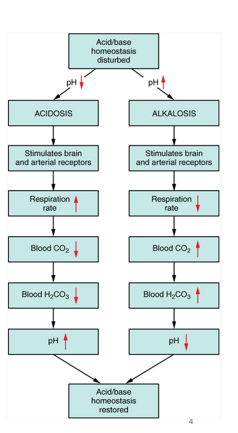
respiratory
How do I know if the cause is metabolic (renal) or respiratory
1\.Look at ph (ph reflects H+ concentrations) both systems influence ph
2\.Look for if the H+ changes (ph) aligns to CO2 or HCO3 changes outside of normal. When ph aligns to one, that variable is causing the changes (both leaning acidic, bicarbonate is responsible for ph changes à metapholic acidosis)
3\.Since both systems influence pH, if one causes a condition then the other should fix (compensate)
Co2 not regulated by renal system (_______only) , bicarbonate is not respiratory
1\.Look at ph (ph reflects H+ concentrations) both systems influence ph
2\.Look for if the H+ changes (ph) aligns to CO2 or HCO3 changes outside of normal. When ph aligns to one, that variable is causing the changes (both leaning acidic, bicarbonate is responsible for ph changes à metapholic acidosis)
3\.Since both systems influence pH, if one causes a condition then the other should fix (compensate)
Co2 not regulated by renal system (_______only) , bicarbonate is not respiratory