Geography Exam Set
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Last updated 10:47 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Population density
the number of people living in a square kilometre
2
New cards
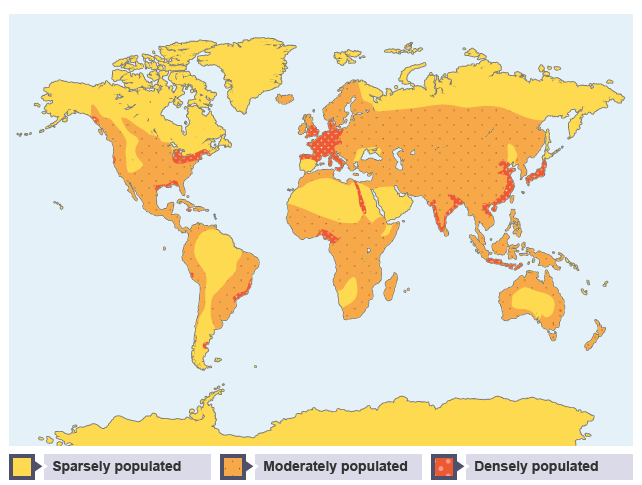
Population distribution
how people are spread out across an area
3
New cards
Relief
describes the shape and height of the land
4
New cards
Infrastructure
provision of services (water supply, electricity, roads etc) within an area
5
New cards
Positive factors affecting population density
access to services, fertile soil, high employment, accessible, varied climate, few natural natural disasters
6
New cards
Negative factors affecting population density
conflict, lack of services, poor soil, unemployment, pollution, few natural resources, extreme climate, land relief
7
New cards
Birth rate
no. of babies born per 1000 people in a year
8
New cards
Death rate
no. of people who die per 1000 people in a year
9
New cards
infant mortality rate
no. of babies who die before their first birthday
10
New cards
Reasons for a low birth rate
* childcare is expensive
* birth control/contraception available
* improved status of women
* education of girls
* birth control/contraception available
* improved status of women
* education of girls
11
New cards
Reasons for high birth rates
* early marriage
* lack of family planning and contraception
* children needed to work
* cultural tradition for large families
* lack of family planning and contraception
* children needed to work
* cultural tradition for large families
12
New cards
Reasons for low death rates
* old age pensions
* clean water supply
* improved healthare
* reliable food supply
* sanitation
* mechanisation in working
* clean water supply
* improved healthare
* reliable food supply
* sanitation
* mechanisation in working
13
New cards
Reasons for high death rates
* disease or illness
* war
* food shortage
* high infant mortality rate
* lack of clean water and sanitation
* war
* food shortage
* high infant mortality rate
* lack of clean water and sanitation
14
New cards
Population structure
number and distribution of different age groups in a population
15
New cards
Population pyramids
a graph made up of two bar graphs showing the number of males and females in each 5 year age group
16
New cards
Young dependants
someone under the age of 15 - no income as they do not work so relies on the state and their parents to provide for them
17
New cards
Economically active
aged 16-64 who are working - help to provide for others by paying taxes
18
New cards
Elderly dependants
people aged 65+ who no longer works and do not pay income tax so depend on the state
19
New cards
Consequences of youthful population
* land must be ==farmed intensively== to supply food
* many people in urban areas ==shanty towns==
* ==unemployment== rates if not enough jobs
* demand for ==education== and services goes up
* many people in urban areas ==shanty towns==
* ==unemployment== rates if not enough jobs
* demand for ==education== and services goes up
20
New cards
Solution to youthful population
* promotion of family planning
* keeping girls in education
* increasing legal age of marriage
* keeping girls in education
* increasing legal age of marriage
21
New cards
Benefits of an ageing population
* some businesses make more profit
* more childcare and support form grandparents
* more childcare and support form grandparents
22
New cards
Problems of an ageing population
* fewer people of working age so ==fewer tax payers==
* ==rise in retirement age==
* lack of young workforce
* increase in ==cost of health care==
* ==rise in retirement age==
* lack of young workforce
* increase in ==cost of health care==
23
New cards
Development
any improvement made in the standard of living
24
New cards
What are social development indicators about?
to do with the quality of life of individuals in the country
25
New cards
What are economic development indicators about?
those to do with the wealth of individuals in the country
26
New cards
Social indicator examples
* life expectancy
* birth and death rate
* literacy rate
* infant mortality
* food intake
* birth and death rate
* literacy rate
* infant mortality
* food intake
27
New cards
Economic indicator examples
* GDP (totals money by all workers)
* GDP per capita (wealth shared out equally)
* energy per person
* people per doctor
* primary employment
* GDP per capita (wealth shared out equally)
* energy per person
* people per doctor
* primary employment
28
New cards
Human Development Index (HDI)
composite indicator used by UN of life expectancy, literacy rate and GDP per capita to cover health, education and economy in a country.
29
New cards
Mouth
where the river flows into sea/lake
30
New cards
Tributary
a river that joins a larger river
31
New cards
Catchment
area from which water drains into a particular drainage basin
32
New cards
Source
upland area where river begins
33
New cards
Watershed
boundary diving two drainage basins
34
New cards
Confluence
point at which two rivers join
35
New cards
Wetted perimeter
where the river water touches the beds and banks
36
New cards
Erosion
wearing away of the land
37
New cards
Hydraulic action
the strong of river dislodges particles from bed and banks
38
New cards
Abrasion
when bed and banks are worn down by the rivers load
39
New cards
Altrition
material in river bumps into each other - smoothed and broken into smaller particles
40
New cards
Corrosion
chemicals in river slowly dissolve beds and banks
41
New cards
Traction (1)
boulders and pebbles rolled along river bed at highest discharge
42
New cards
Saltation (2)
Sand sized particles bounce along bed in a leap frog movement
43
New cards
Suspension (3)
fine clay/sand particles carried at low discharge
44
New cards
Solution (4)
minerals dissolved into water - very little energy
45
New cards
Deposition
rivers deposit load when energy is lost
46
New cards
V-shaped valley
Upper course feature - vertical erosion of the river causes a V-shaped valley
47
New cards
Interlocking spurs
Upper course feature - when river meets areas of harder rock that is difficult to erode it winds round it and hills form on either side
48
New cards
Formation of a waterfall
river meets a bander a softer rock and erodes it more quickly, undercutting the hard rock - this overhang collapses and the waterfall retreats upstream
49
New cards
Gorge
a steep sided river valley created from the waterfall retreating
50
New cards
Meander
middle course feature - a river flows around bends causing areas of faster and slower water - lateral erosion
51
New cards
Ox-bow lake
middle cruse feature - a flood cuts across a meander and take a new course so an horse shoe shaped lake is remaining
52
New cards
Levees
lower course feature - when a river floods, the heaviest particles of its load are deposited first - creating a natural embankment
53
New cards
Physical features of river you could describe
width, length, straightness, direction of flow, features, tributaries
54
New cards
Physical features of valleys could describe
shape, gradient, height, interlocking spurs, features
55
New cards
Land uses around the River Tay
farming, forestry, renewable energy, recreation and tourism, industry and settlement
56
New cards
Upper course land uses
* sheep farming
* HEP
* tourism eg. rafting
* foresty
* windfarms
* HEP
* tourism eg. rafting
* foresty
* windfarms
57
New cards
Middle course land uses
* dairy/arable farming
* tourism eg. camp sites
* fishing
* tourism eg. camp sites
* fishing
58
New cards
Lower course land uses
* arable farming
* dairy farming
* industry eg. ships
* tourism eg. boat trips
* dairy farming
* industry eg. ships
* tourism eg. boat trips
59
New cards
Conflicts on the River Tay
* wind-farms vs. tourists
* white water rafting vs. fishermen
* white water rafting vs. fishermen
60
New cards
Examples of high order services
leisure centres, chain stores, hospitals
61
New cards
Examples of low order services
post offices, doctors, newsagents
62
New cards
Central Business District
city centre where most of the shops, offices are and where transport routes meets
63
New cards
Inner City
old industrial part of the city directly next to CBD. where old 19th century housing and factories are found
64
New cards
Suburbs
Residential and shopping areas on the edge of the city with plenty of space
65
New cards
Most expensive land values
in the CBD as space is limited
66
New cards
Buildings in the CBD
old historic buildings such as cathedrals, museums, galleries
67
New cards
Retail in the CBD
shopping malls, high order shops, dapeament stores
68
New cards
Transport in the CBD
Route centre where all the arterial roads meet, has the main bus and train station
69
New cards
Tourist services in the CBD
tourist info centre, chain restaurants and bars, theatres, hotels
70
New cards
Changes to Edinburgh's CBD - shopping
The new St James Centre shopping mall was built to improve the visual appearance of the city centre and attract shoppers back into the city by protecting them from the Scottish weather.
71
New cards
Changes to Edinburgh's CBD - cycle lanes
Cycle lanes have been introduced to reduce traffic in the CBD and encourage cycling to reduce air pollution.
72
New cards
Changes to Edinburgh's CBD - New concert hall
To boost Edinburgh's image as a centre for arts and provide another venue for the International Festival.
73
New cards
Changes to Edinburgh's CBD - High ends shops such as Multrees Walk
To attract shoppers to the CBD to improve and economy and provide retails experience to compete with online shopping.
74
New cards
Housing in the Inner City
19th century tenement housing in high density, built orginally for factory workers
75
New cards
Brownfield sites
empty derelict land in the inner city form old industrial buildings
76
New cards
Grid iron street pattern
long straights rows of houses in the inner city
77
New cards
Housing in the rural/urban fringe
detached housing with gardens and driveways in cul-de-sacs
78
New cards
Industry and shopping in the rural/urban fringe
Modern industry such as shopping centres, financial services and quaternary industry
79
New cards
Greenbelt
protected countryside which has strict strict planning controls at edge of the city to stop urban sprawl
80
New cards
Greenfield sites
farmland which is ideal for building on
81
New cards
Advantages of urban sprawl
* space for businesses to expand
* cheap land values
* flat land easy to build on
* affordable housing for growing population
* cheap land values
* flat land easy to build on
* affordable housing for growing population
82
New cards
Disadvantages of urban sprawl
* wildlife habitats destroyed
* increased traffic congestion in edge of city
* spoils countryside's natural beauty
* inner city areas become run down as people move away
* increased traffic congestion in edge of city
* spoils countryside's natural beauty
* inner city areas become run down as people move away
83
New cards
Urbanisation
movement of people form the countryside to the city
84
New cards
Solutions to shanty towns - **Dharavi redevelopment project**
Project plans to %%demolish%% parts of Dharavi and %%build high rise flats to regime people%%. Many don't like this as they won't have their businesses
85
New cards
Solutions to shanty towns - **Slum Rehabilitation**
Government would provide toilets, piping, reinforced housing, schools, healthcare facilities to improve the shanty town
86
New cards
Solutions to shanty towns - **Self Help schemes**
Encourage residents to improve the area themselves - they can ask gov for loans to build toilets, water supply and negotiate with authorities about electricity etc
87
New cards
Solutions to issues in shanty towns - Navi Mumbai
reducing over population by taking the overspill out of Mumbai to new part of the city
88
New cards
Bottom Up management advantages
* residents get a say
* doesn't cost gov as heavily
* areas improved
* doesn't cost gov as heavily
* areas improved
89
New cards
Bottom Up management disadvantages
\
* cannot do sewage/toilets themselves
* only works on a small scale
* cannot do sewage/toilets themselves
* only works on a small scale
90
New cards
Top-down management advantages
* better safer housing created with toilets, running water etc- safer for children
* improved life
* improved life
91
New cards
Top-down management disadvantages
* low tax - gov don't have enough money-
* may be rehoused far way and have to change job
* construction often stalled to lack of finance
* may be rehoused far way and have to change job
* construction often stalled to lack of finance
92
New cards
Bedding planes
horizontal cracks in the limestones created when the sediment was building up in layers
93
New cards
Joints
vertical cracks formed when tectonic activity lifted limestone
94
New cards
Permeable
Water can pass through limestone's bedding planes and joints
95
New cards
What is limestone made of?
calcium carbonate
96
New cards
chemical weathering
when rainfall combines with carbon dioxide and creates a weak carbonic acid which dissolves limestone
97
New cards
Formation of limestone pavements
1. bedding planes due to layers of sediment and joints due to tectonic activity
2. during glaciation, ice scraped away topsoil
3. bare rock is permeable
4. carbonation dissolve rock, carried in solution
5. continued chemical weathering widens and deeps bedding planes and joints
6. Blocks called clints and gaps called grikes
98
New cards
Formation of swallow holes
1. bedding planes and joints
2. surface water passes over impermeable rock until reaches permeable limestone
3. water flows down a joint and dissolves rock to form a swallow hole
4. process of carbonation causes hole to become larger over time
99
New cards
Formation of intermittent drainage
1. streams flowing onto limestone disappear down swallow holes
2. they flow along bedding planes and down joints
3. when stream hits impermeable rock, they have to flow overtop until they reach the surface
4. when underground water comes to surface it is called a resurgence stream
100
New cards
Formation of caves and caverns
1. joints and bedding planes = permeable
2. water flows underground through a swallow hole until it reaches impermeable rock
3. carbonation takes place and dissolves limestone
4. areas with lots of BPs and joints close together means large areas of rock are dissolved quickly
5. the space left is a cave or caverns
6. walls may be eroded further by abrasion due to water carries stones
Explore top notes
Chapter 23 - The Building of European Supremacy: Society and Politics to World War I
Updated 1262d ago0.0(0)
Chapter 23 - The Building of European Supremacy: Society and Politics to World War I
Updated 1262d ago0.0(0)