biochem midterm 2 review (pass session)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
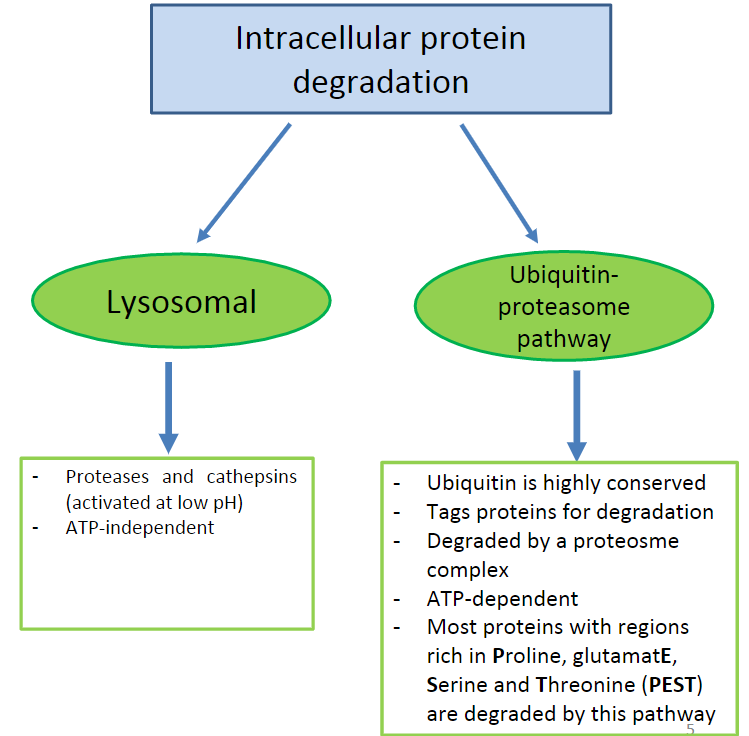
Cathepsins are activated in the lysosomal pathway **(True/False)**
**True**
2
New cards
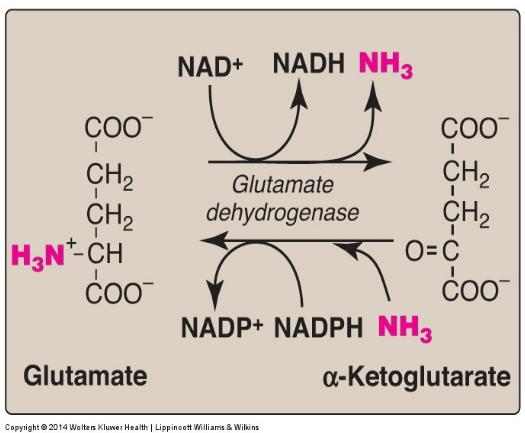
Glutamate dehydrogenase is bidirectional. **(True/False)**
**True** - from glutamate to alpha ketoglutarate with high ammonia concentration and the opposite direction with low ammonia concentration
3
New cards
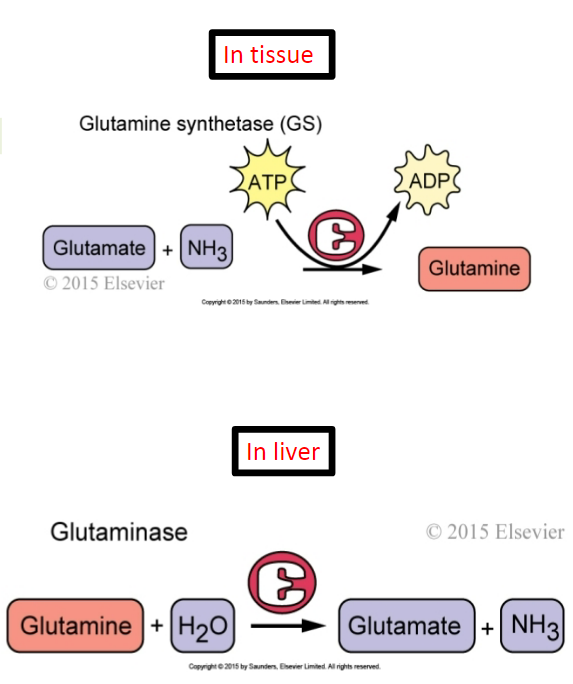
Glutamine synthetase acts in the liver. **(True/False)**
**False** - its helping to synthesize glutamine (glutamate + ammonia → glutamine). Glutamine is synthesized in the tissues because you don’t want free-floating ammonia in your body. Your body wants to pick it up from the tissues, transport and deposit it into the liver to undergo the urea cycle.
4
New cards
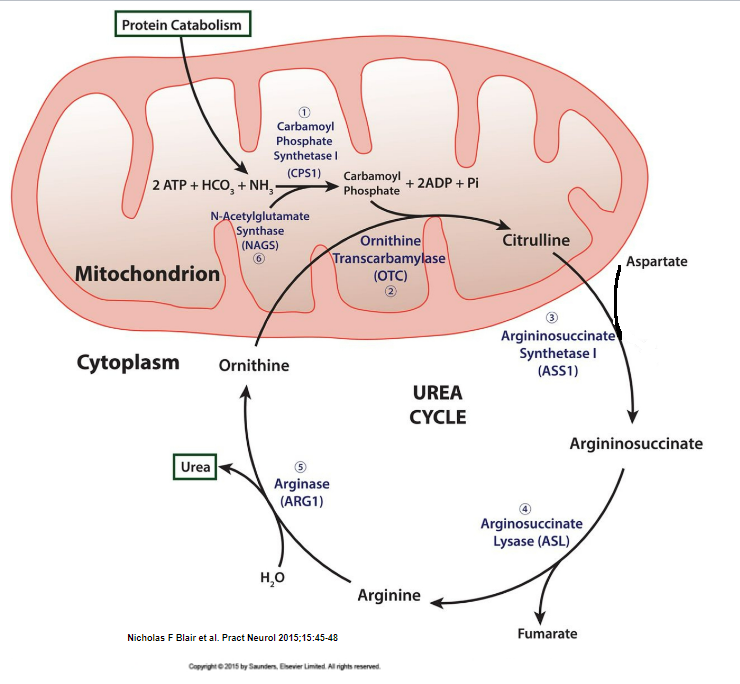
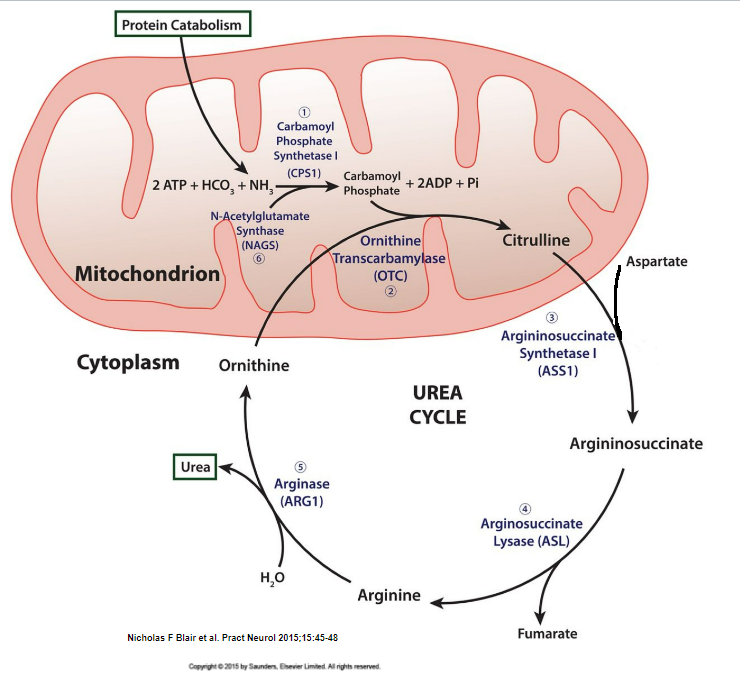
Which reacts with carbamoyl phosphate to generate citruline?
1\. aspartate
2\. fumarate
3\. ornithine
4\. ornithine transcarbamylase
1\. aspartate
2\. fumarate
3\. ornithine
4\. ornithine transcarbamylase
3. ornithine because ornithine + carbamoyl phosphate → citruline and the enzyme that helps this reaction occur is ornithine transcarbamylase
5
New cards
Urea is produced in the kidneys. **(True/False)**
**False** - urea is produced in the liver because the urea cycle occurs in the liver cell’s mitochondrion and cytoplasm
6
New cards
A treatment of hyperammonemia is a high protein diet. **(True/False)**
**False** - need a low protein diet because protein contains amino groups which can be converted into ammonia
7
New cards
The main source of non-erythrocyte heme is in:
1. bone marrow
2. spleen
3. liver
4. kidney
1. bone marrow
2. spleen
3. liver
4. kidney
3. Liver
8
New cards
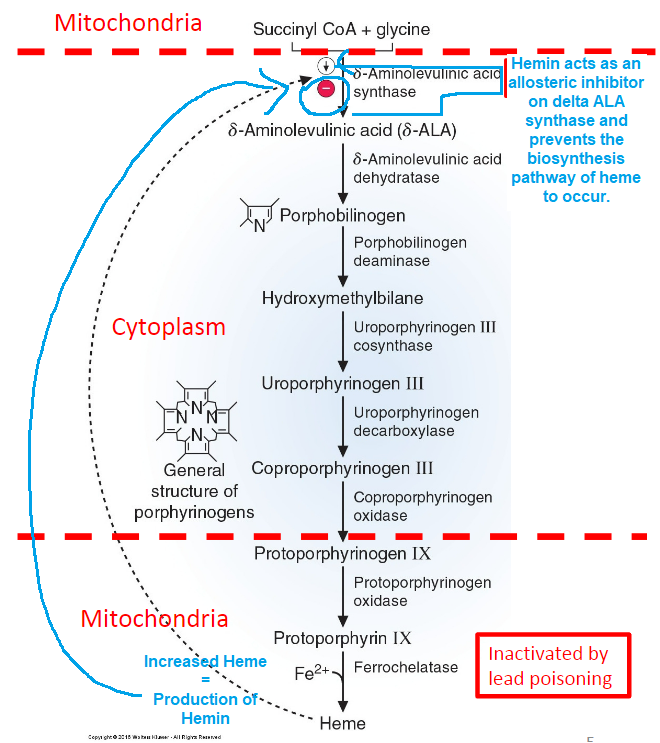
Hemin is produced when there is reduced heme production. **(True/False)**
**False** - when there’s an abundance of heme it becomes oxidized (loss of H+) and becomes hemin
9
New cards
Hemin acts as an allosteric inhibitor. **(True/False)**
**True** - the abundance of heme results in the production of hemin (heme undergoes oxidation to become hemin). Hemin acts as an allosteric inhibitor to ***delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase*** to prevent the production of ***delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)*** and thus overall reduces heme production.
10
New cards
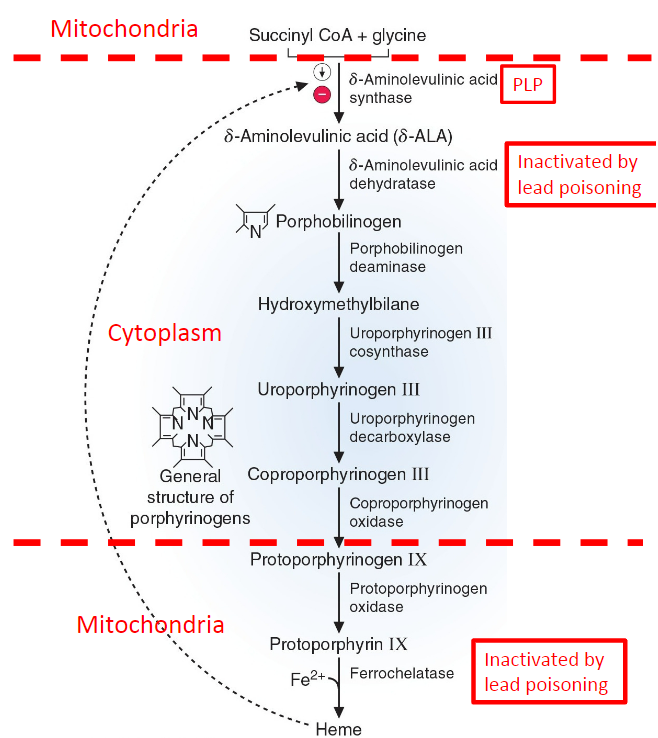
when 2 delta-aminolevulinic acids (delta-ALA’s) react, what is formed?
porhphobilinogen - the 1st ring of heme
11
New cards
What is added to protoporphyrin IX to become heme?
1. Phosphate
2. Iron
3. Carboxylic Acid
4. Oxygen
1. Phosphate
2. Iron
3. Carboxylic Acid
4. Oxygen
2. Iron (Fe 2+)
12
New cards
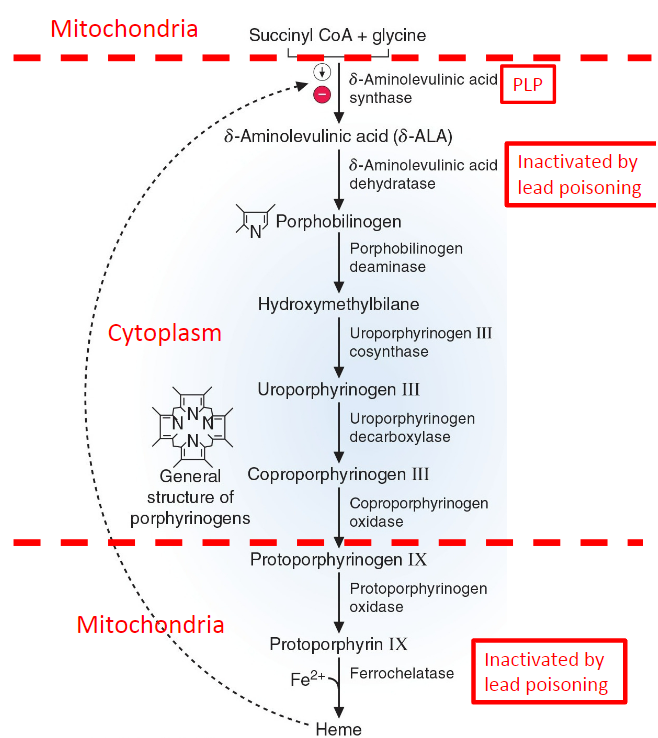
Increased sensitivity of the skin is a symptom of porphyria. **(True/False)**
**True** - porphyria cutanea tarda occurs when there’s a deficiency of ***uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase***
13
New cards
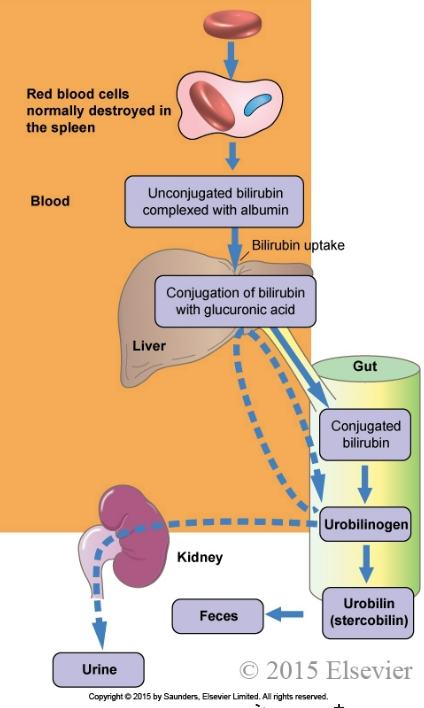
Where does bilirubin get conjugated with gluconic acid?
1. hepatocytes
2. spleen
3. bile
4. kidneys
1. hepatocytes
2. spleen
3. bile
4. kidneys
1. hepatocytes - liver cells
14
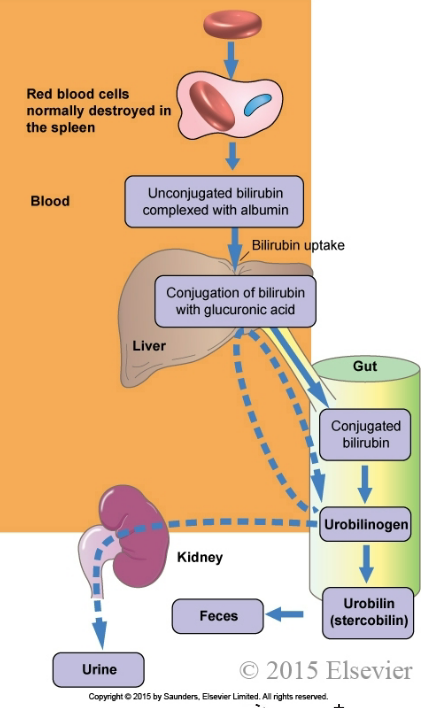
New cards
When liver damage occurs, there is high levels of conjugated bilirubin. **(True/False)**
**False** - if liver damage occurs, bilirubin cannot become conjugated and there would be high levels of unconjugated bilirubin.
15
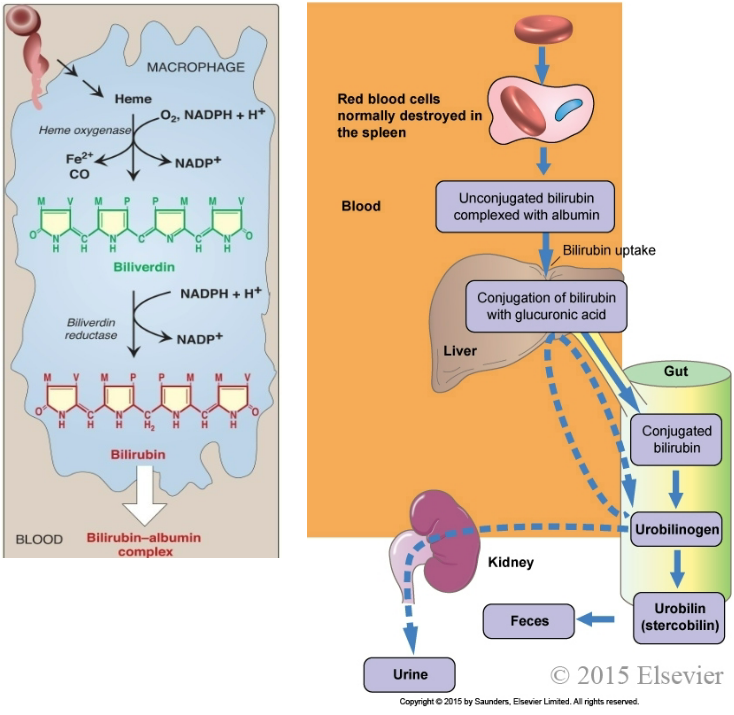
New cards
UDP - glucuronyltransferase helps reduce biliverdin to bilirubin. **(True/False)**
**False** - Biliverdin reductase helps to reduce biliverdin to become bilirubin and UDP-glucuronyltransferase helps conjugate bilirubin in the step afterwards
16
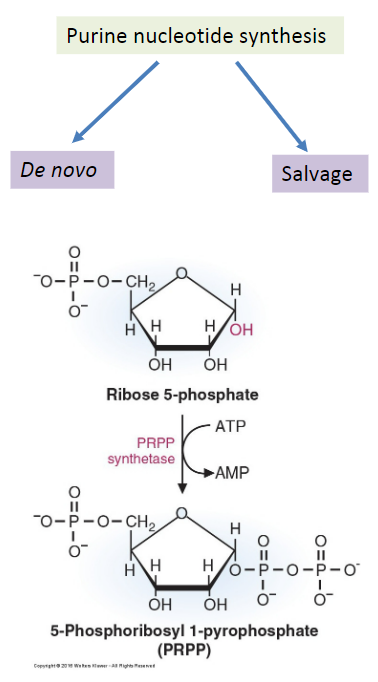
New cards
What is required to begin De Novo synthesis?
1. Glutamate
2. 5-phosphoribosyl 1-amine
3. Aspartate
4. Ribose 5-phosphate
1. Glutamate
2. 5-phosphoribosyl 1-amine
3. Aspartate
4. Ribose 5-phosphate
4. Ribose 5-phosphate
17
New cards
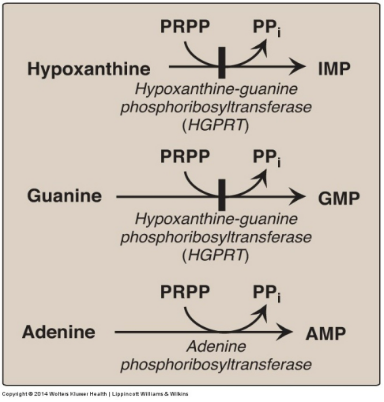
Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase catalyzes the transformation of adenine to AMP. **(True/False)**
**True** - this occurs in the purine salvage pathway in which PRPP (5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate) gives it’s ribose 5-phosphate to adenine, converting it into AMP.
18
New cards
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome involves reduced levels of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP). **(True/False)**
**False** - it involves an increased level of PRPP, an increase in purine de novo synthesis, and an increase of uric acid resulting in gouty arthritis, neuropathology, and self mutilation
19
New cards
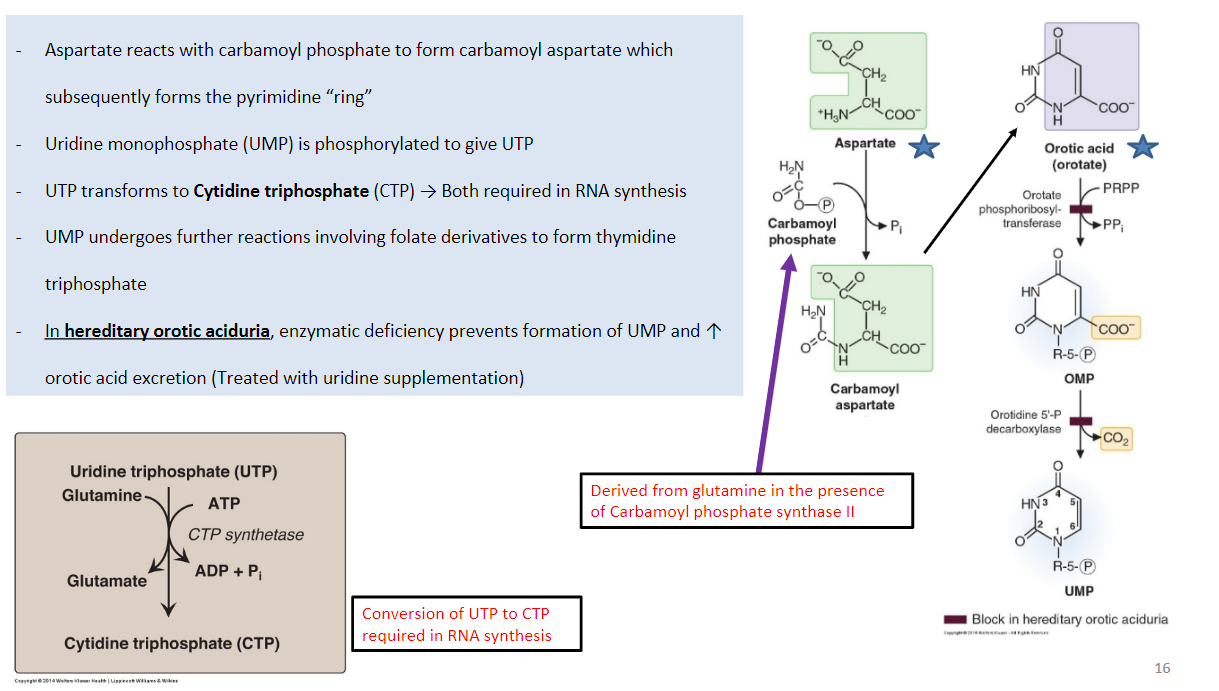
In pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis, uridine triphosphate converts to uridine monophosphate. **(True/False)**
**False** - It goes from uridine monophosphate gets phosphorylated → uridine triphosphate → cytidine triphosphate.
\
In addition, uridine monophosphate → thymidine triphosphate
\
In addition, uridine monophosphate → thymidine triphosphate
20
New cards
Adenine is a pyrimidine with two rings. **(True/False)**
**False** - adenine is a purine with two rings.
\
Tip: Purines sounds like pure, and babies make GAGA sound and are pure. G - guanine A - adenine = GA, and it’s said twice for two rings (GAGA).
\
Tip: Purines sounds like pure, and babies make GAGA sound and are pure. G - guanine A - adenine = GA, and it’s said twice for two rings (GAGA).
21
New cards
Heme is the most prevalent metalloporphyrin in the human body. **(True/False)**
**True**