Cardiovascular System—Systemic Circulation
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
measurement unit of perfusion
mL/min/g
capillaries
sites of exchange between arteries and veins
tunica intima is made up of
endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) and subendothelial layer (areolar connective tissue)
tunica media is made up of
smooth muscles in circularly arranged layers
tunica media is responsible for
vasoconstriction and vasodilation
vasa vasorum
small arteries supplying blood to very large vessel walls
arteries have a thicker ____ and a narrower ____
tunica media, lumen
capillaries contain only
tunica intima, made up of endothelium and basement membrane with intercellular clefts
thin capillary walls allow for rapid exchange of
gas and nutrients
as arteries branch into smaller vessels extending from the heart, they
decrease in lumen diameter, decrease in elastic fibers, increase in relative amount of smooth muscle
elastic arteries
largest arteries, conduction of blood from heart to medium arteries
muscular arteries
medium arteries, external elastic lamina and internal elastic lamina
arterioles
smallest arteries
vasomotor tone
smooth muscle somewhat constricted to regulate systemic blood pressure and blood flow, regulated by vasomotor center in brainstem
continuous capillaries
intercellular clefts, most common, found in CNS lungs muscle and skin
fenestrated capillaries
pores (fenestrations) allow for movement of smaller plasma proteins and fluid, found in intestine and glomerulus
sinusoid capillaries
endothelial cells form incomplete lining with large gaps, basement membrane incomplete or absent, allows for large substances to be transported, found in liver spleen bone marrow
capillary bed structure
arterioles → met arterioles → true capillaries → thoroughfare channels → venules
precapillary sphincter relaxation
permits blood flow to flow into true capillaries to meet tissue nutrition needs
precapillary sphincter contraction
causes blood to bypass true capillary bed when tissue needs have been met
venule diameter
8-100 um
post capillary venues
drain the capillary bed
venules become veins when
diameter > 100 um
most large veins contain
valves
venous valves are made up of
tunica intima, elastic and collagen fibers
at rest, __% of blood is in systemic circulation
70
at rest, __% of blood is in systemic veins
55
vaso/venoconstriction of veins
shifts blood from systemic venous reservoir to systemic circulation
vaso/venodilation of veins
shifts blood from systemic circulation to systemic venous reservoir
vasodilation of arteries causes
increase in local blood flow at capillary bed
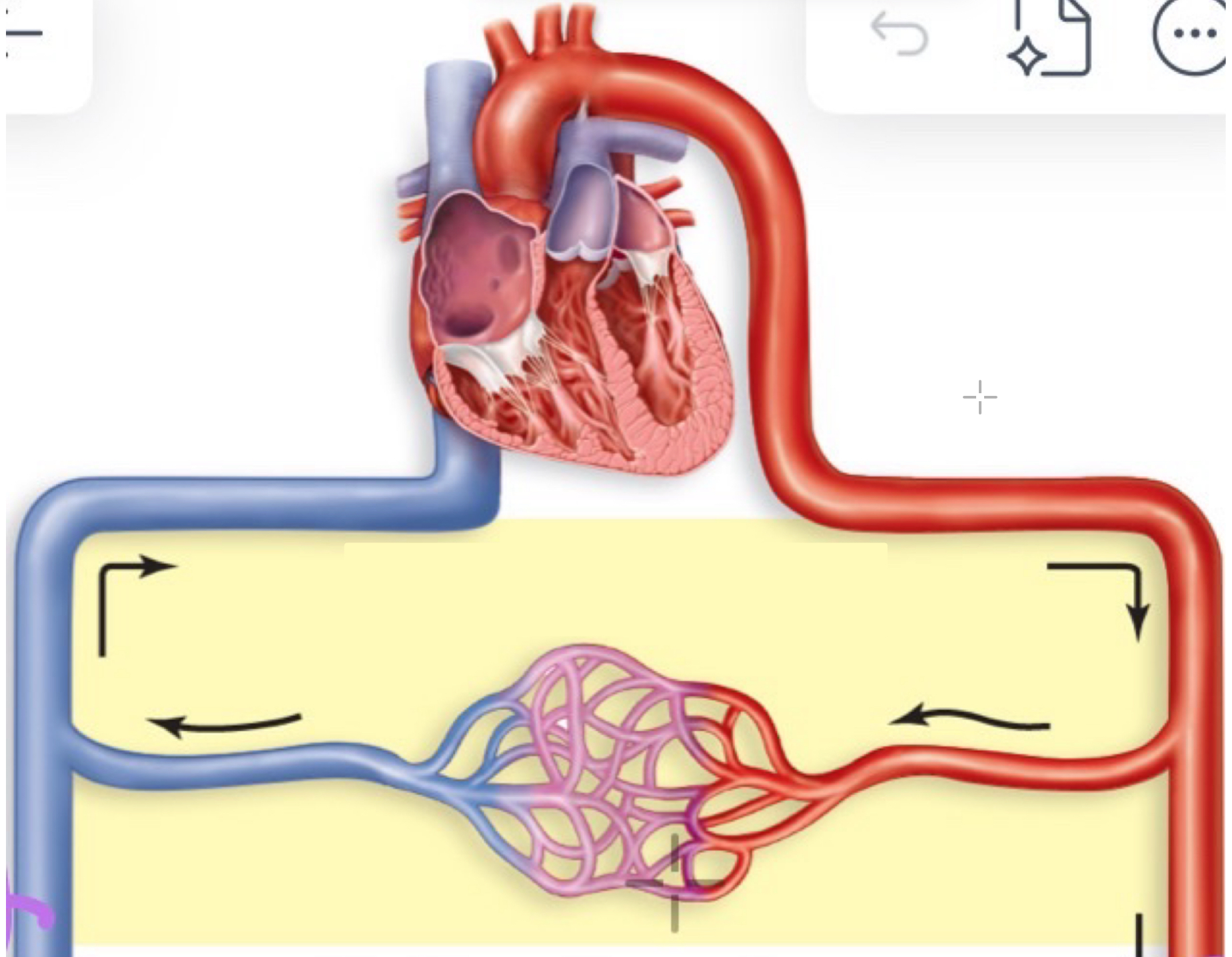
simple pathway
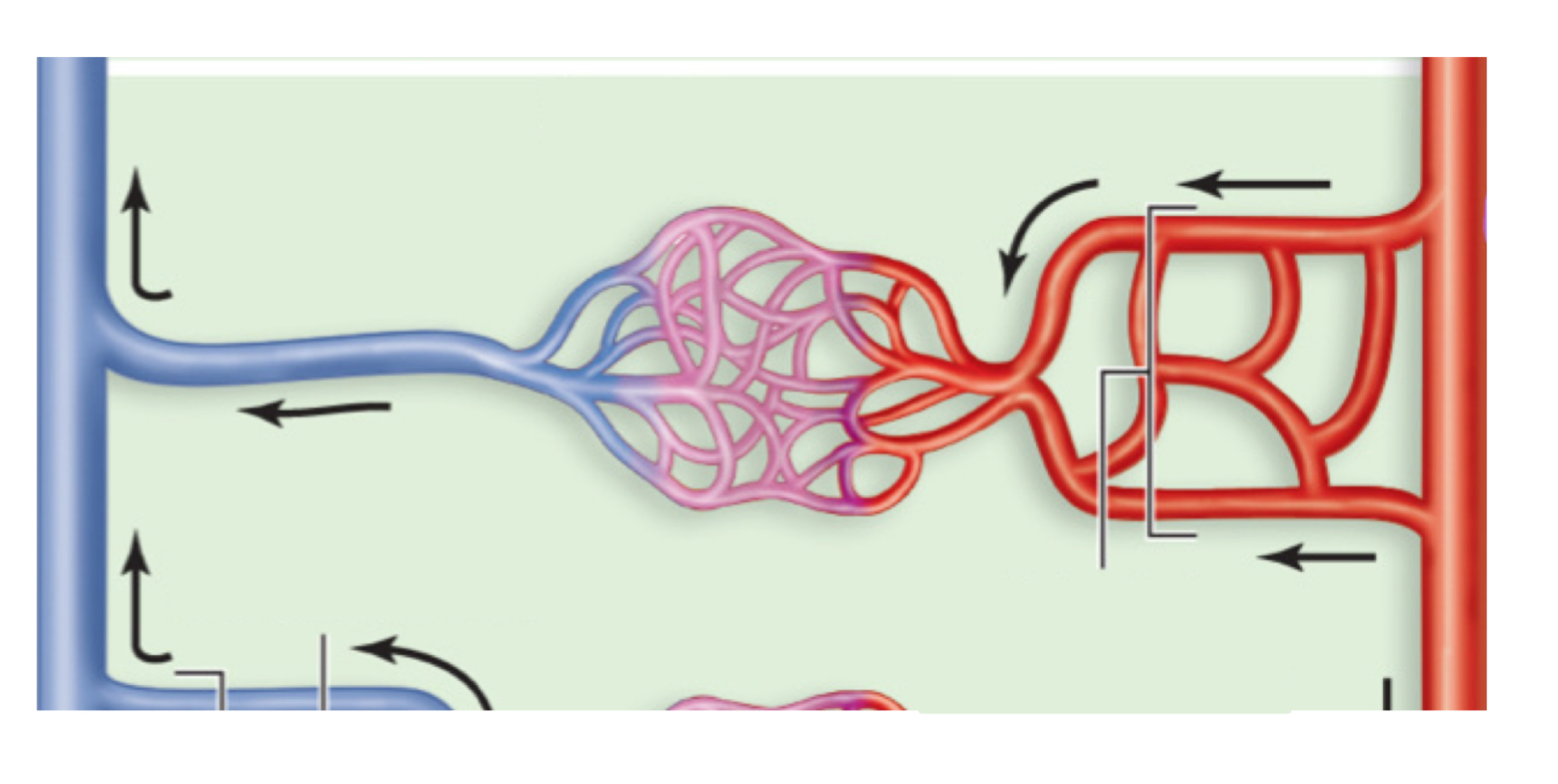
arterial anastomosis
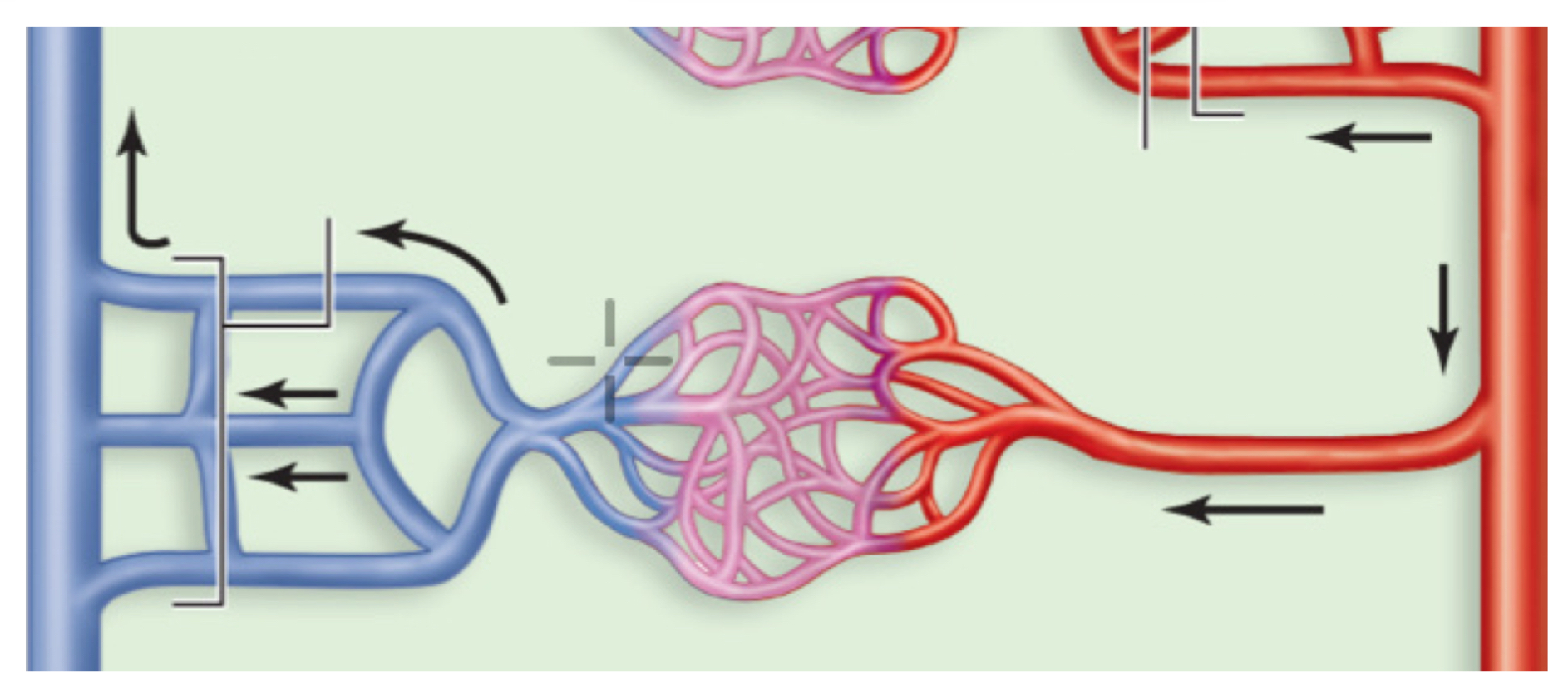
venous anastomosis
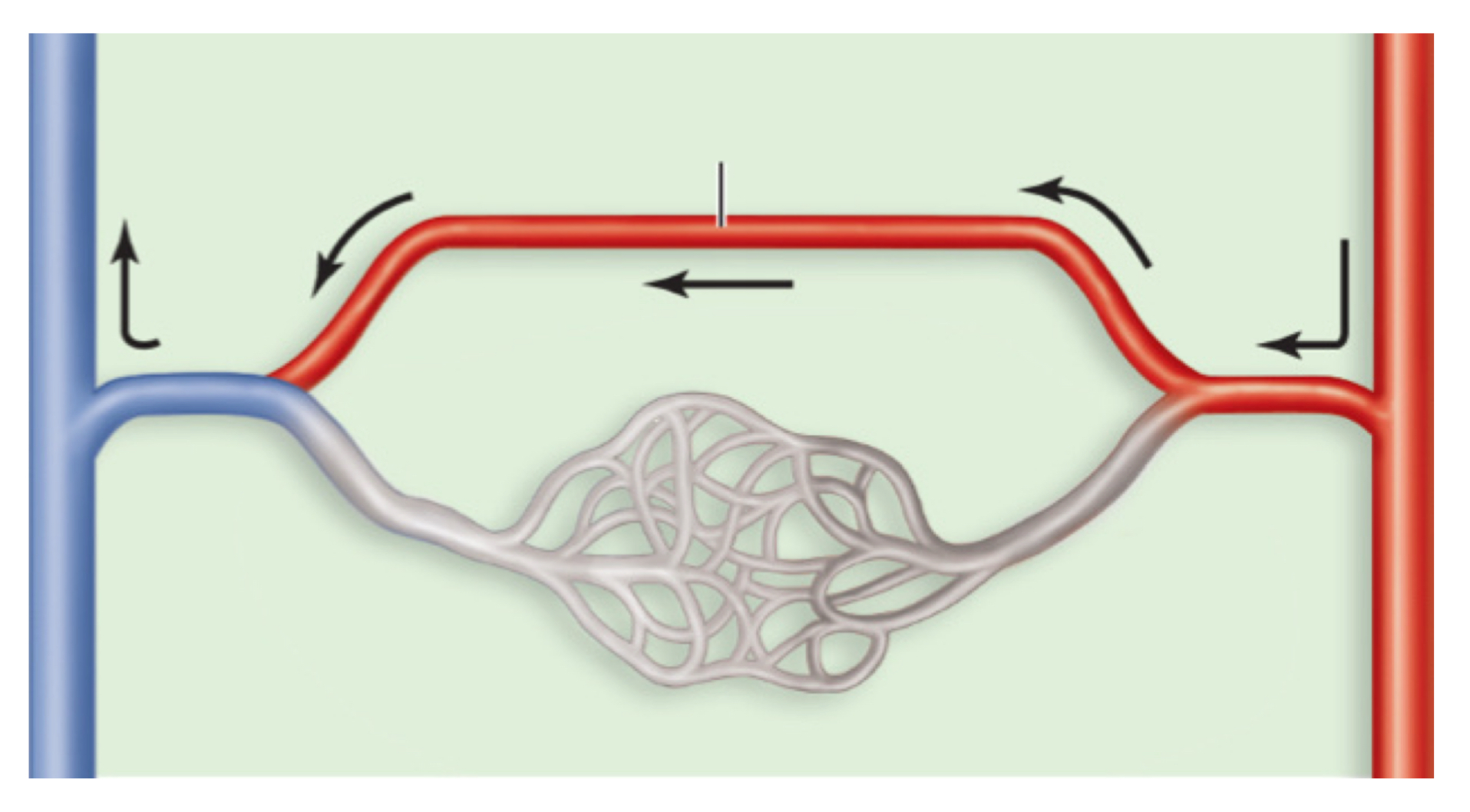
arteriovenous anastomosis
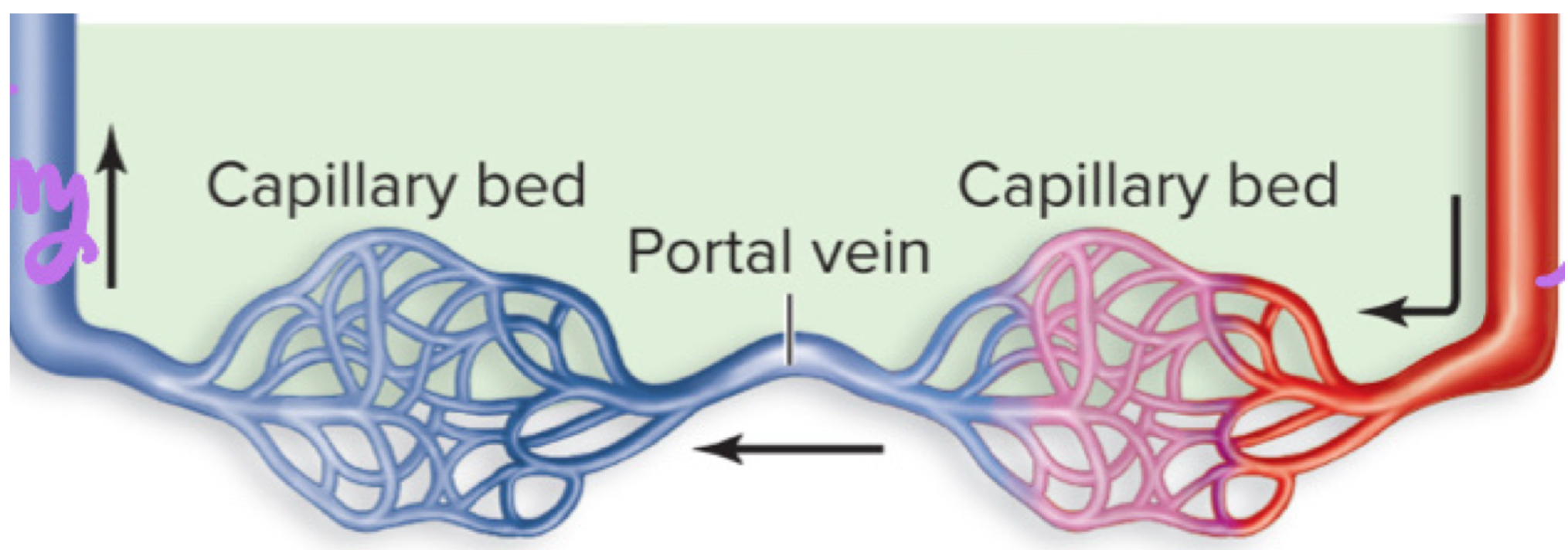
portal system
simple pathway examples
splenic artery and splenic vein
arterial anastomosis examples
superior and inferior epigastric arteries
venous anastomosis example
most common, brachial and cephalic veins
blood flow velocity and total cross-sectional area are
inversely related
diffusion
concentration gradient (high to low)
route of diffusion depends on
particle size
vesicular transport
endothelial cells use pinocytosis and exocytosis to transport hormones and fatty acids
bulk flow
fluids flow down a pressure gradient
filtration
fluid and small solutes flow easily through capillary openings, away from blood (occurs at arterial end)
reabsorption
fluid moves back into blood (occurs on venous end of capillary)
blood hydrostatic pressure
force exerted per unit area by blood on vessels wall; promotes filtration from capillary
interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
force of interstitial fluid on outside of blood vessel, close to 0 in most tissues
in systemic capillary, blood hydrostatic pressure ___ interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
greater than
high blood pressure causes
high net hydrostatic pressure of capillary and increased net filtration pressure
low blood pressure causes
low net hydrostatic pressure of capillary and decreased net filtration pressure
colloid osmotic pressure
pull on water due to the presence of proteins in the blood
net filtration pressure (NFP)
difference between net hydrostatic pressure and net colloid osmotic pressure
NFP is higher at ____ and lower at ____
the arterial end; the venous end
tissues with high vascularity
are metabolically active; ie brain heart liver skeletal muscle
higher degree of vascular dilation means
greater potential for local blood flow
structures with little vascularity
are avascular; cornea and lens of eye, epithelia, cartilage, tendons, ligaments
angiogenesis increases
perfusion of a local tissue
angiogenesis occurs during
exercise, muscle conditioning, loss of adipose tissue
when metabolic activity increases
oxygen and nutrient levels decline, carbon dioxide lactic acid H+ and K+ increase, varied stimuli signal inadequate perfusion and act as vasodilators
nitric oxide
vasodilator
leukotrienes and thromboxane A2
vasoconstrictor
increased cardiac output will increase
blood pressure
blood pressure
force of blood against a vessel wall
blood pressure is highest in ____ and lowest in ____
arteries; veins
systolic pressure
when ventricle contracts, highest pressure generated
MAP (Mean Arterial Pressure) =
diastolic pressure + 1/3 (systolic - diastolic)
normal = 70-100
skeletal muscle pump
as muscle contracts, veins are squeezed
assists venous return from limbs
blood is pushed and valves prevent back flow
blood is moved more quickly during exercise
respiratory pump inspiration
diaphragm contracts, abdominal pressure increases, thoracic pressure decreases
respiratory pump expiration
diaphragm releases, thoracic pressure increases, abdominal pressure decreases
peripheral resistance
resistance of blood in blood vessels
in atherosclerosis, sustained increased levels of resistance lead to
increase in arterial pressure to maintain adequate blood flow
when vessels are longer, resistance is
greater
increased peripheral resistance results during
weight gain (= angiogenesis)
decreased peripheral resistance is associated with
weight loss (= vessel regression)
peripheral resistance is directly related to ____ and inversely related to ____
vessel length; vessel radius
as diameter increases, resistance ___ and flow ____
decreases; increases
flow is proportional to
radius of the fourth power
blood flow is directly related to ____ and inversely related to ____
pressure gradient; resistance
cardioacceleratory center
sympathetic nervous system, stimulates SA node and myocardium
vasomotor center
stimulates sympathetic neurons to release norepinephrine (NE) and adrenal medulla to release epinephrine (EPI)
epinephrine and norepinephrine cause
vasoconstriction
if blood pressure decreases
baroreceptor firing rate decreases
activates the cardioacceleratory center
increases cardiac output
if blood pressure increases
baroreceptor firing rate increases
stimulates the cardioinhibitory center
decreases cardiac output and heart rate
baroreceptor reflexes are best for ____, but are ineffective for ____
quick changes in blood pressure; long-term blood pressure regulation
chemoreceptors stimulate vasomotor center when
high carbon dioxide, low pH, very low oxygen
if chemoreceptors stimulate vasomotor center, then
increase in blood pressure and shift blood to the lungs
renin converts ____ to ____ in blood
angiotensinogen; angiotensin I
angiotensin II effects
vasoconstrictor
raises blood pressure
stimulates thirst center
acts on kidneys to decrease urine formation
why does angiotensin II decrease urine formation?
to ensure less fluid loss from the blood and maintain blood volume
aldosterone effects
increases blood pressure
decreases urine output
hormones that cause an increase in blood pressure
epinephrine, aldosterone, ADH
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) effects
stimulates vasodilation
decreases blood pressure
increases urine output
hypertension
may damage blood vessel walls, causing atherosclerosis
may thicken arteriole walls, arteriosclerosis
essential hypertension
hypertension without any cause; starts between 30-50 years old
secondary hypertension
has an underlying cause; before age 30 or after age 50
labile hypertension
high blood pressure caused by stress (50% will end up with essential hypertension)
isolated systolic hypertension
seen in the elderly where systolic BP > 140 & diastolic < 90
pseudo hypertension
secondary to a stiff non-compressible blood vessel
during exercise
total blood flow increases
increased blood flow to coronary arteries, skeletal muscle, skin
decreased blood flow to abdomen, kidney, GI and GU track