Barriers and epithelial cells
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Recall the anatomy of the immune system
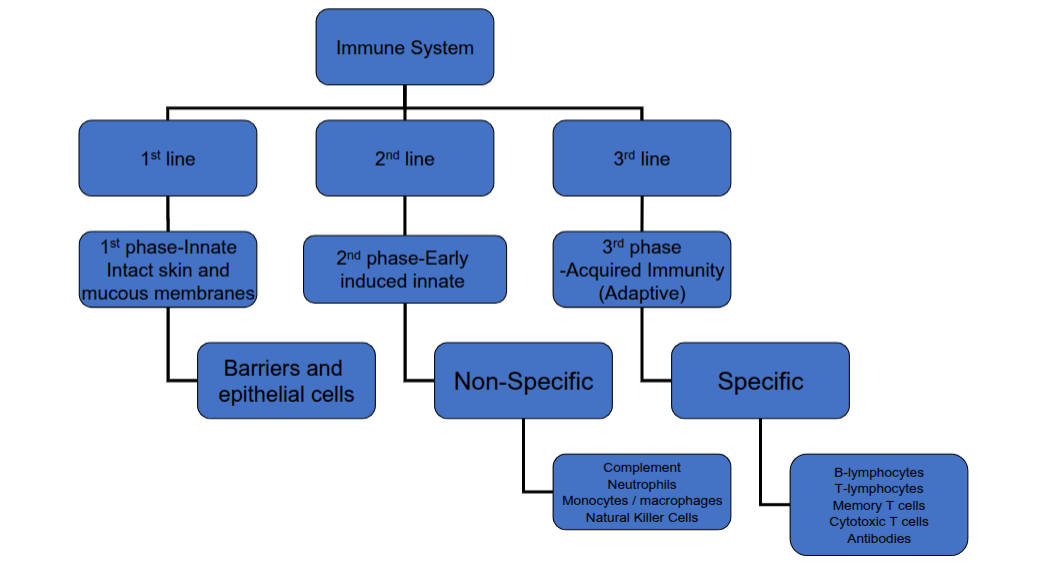
What are the differences between innate and adaptive immunity

What are the two phases of the innate immune response?
The innate phase and the early-induced phase
What happens during the innate phase?
Immediate action using preformed mediators to kill, weaken, or mark a pathogen.
What happens during the early-induced phase?
Sensing of pathogens, recruitment of immune cells, and inflammation.
What are the main anatomical barriers to infection?
Skin, mouth and upper alimentary canal, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, airway and lungs, urogenital tract, and salivary, lacrimal, and mammary glands
What three types of barrier composition exist?
Mechanical, chemical, and microbiological.
What defines a mechanical barrier?
Physical movement or force preventing pathogen entry
What defines a chemical barrier?
Enzymes or active molecules that damage or neutralise pathogens
What defines a microbiological barrier?
The normal human flora that competes with pathogens.
What are the main defences of the skin?
Longitudinal flow of air and fluid, lamellar bodies, fatty acids, α- and β-defensins, S100 proteins (e.g. psoriasin, calprotectin).
What is the role of lamellar bodies in the skin?
They secrete lipids that waterproof and hydrate the skin, sealing the barrier.
What are the main stomach defences?
Low pH (~2–3), enzyme digestion (pepsin), muscular contractions, and fluid flow.
What barriers exist in the small intestine?
Digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, trypsin, chymotrypsin), antimicrobial peptides, and fluid flow to the large intestine
What barriers exist in the large intestine?
Normal intestinal flora and movement of fluid/faeces to expel waste.
How do the airways and lungs defend against infection?
Coughing, sneezing, mucociliary clearance, macrophages, and surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D
What barriers exist in the urogenital tract?
Flushing by urine, urinary mucins, lower pH (~6), antimicrobial peptides, and vaginal secretions.
What barriers are provided by these glands?
Flushing by secretions and antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, lactoferrin, and calprotectin
What are the main functions of epithelial cells?
Acting as a barrier, protecting underlying tissues, permitting nutrient movement, and secreting or absorbing substances.
How are epithelial cells joined together?
By tight junctions, forming a cobblestone-like barrier layer.
How do epithelial cells contribute to innate immunity?
By producing antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), chemokines (e.g. IL-8), cytokines (e.g. IL-6), and mucins
How do epithelial cells detect microbes?
Through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and NOD-like receptors (NLRs).
What do PRRs recognise?
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
What are the main epithelial cell types in the skin?
Stratified squamous epithelial cells differentiating from basal stem cells; the stratum spinosum produces defensins and lamellar bodies form a waterproof stratum corneum.
What epithelial cells are found in the lungs?
Ciliated epithelium, type I and type II pneumocytes, and goblet cells producing mucus.
What are type I and type II pneumocytes?
Type I are thin cells for gas exchange; type II are secretory cells producing surfactant.
What epithelial cells are found in the gut?
Epithelial cells, goblet cells, endocrine cells, and Paneth cells (which produce AMPs)
What are antimicrobial peptides?
Small, cationic peptides (7–100 amino acids) shared across all life forms, that form part of innate immunity.
What are the main structural types of AMPs?
Linear (amphipathic α-helices) and cyclic (β-sheets)
How do AMPs disrupt membranes?
By inserting into the lipid bilayer, forming pores, and damaging the membrane.
What are the two major mammalian AMP families?
Cathelicidins and defensins
What are the three subfamilies of defensins?
α-defensins, β-defensins (both human), and θ-defensins (non-human primates)
Name other antimicrobial molecules besides AMPs.
Lysozyme, azurocidin, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin
What is mucus?
A biological hydrogel coating epithelial surfaces that lubricates, protects, and selectively filters particles.
What is the main structural component of mucus?
Mucins—large glycoproteins.
What are mucins composed of?
High molecular weight glycoproteins (~200 kDa) that are 50–90% sugar by weight.
How do mucins form networks?
Via disulphide bonds and reversible hydrophobic/electrostatic interactions.
What happens when epithelial PRRs are activated?
NF-κB signalling triggers pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, leading to neutrophil recruitment and macrophage activation
What skin diseases are linked to barrier failure?
Ichthyosis and atopic dermatitis (linked to filaggrin gene mutation)
What gut condition results from barrier dysfunction?
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
What lung diseases arise from defective barrier mechanisms?
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) and cystic fibrosis (CFTR mutation).