IR spectroscopy (+ mass spectrometry)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
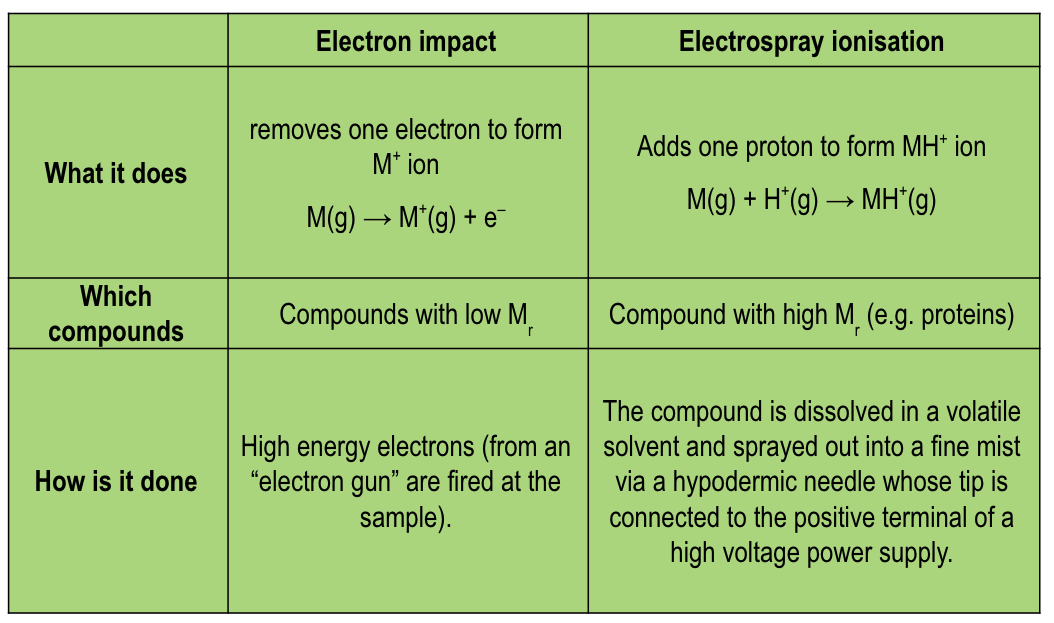
compare the e- process, types of compounds and method of the 2 types of ionisation techniques in mass spectrometry:
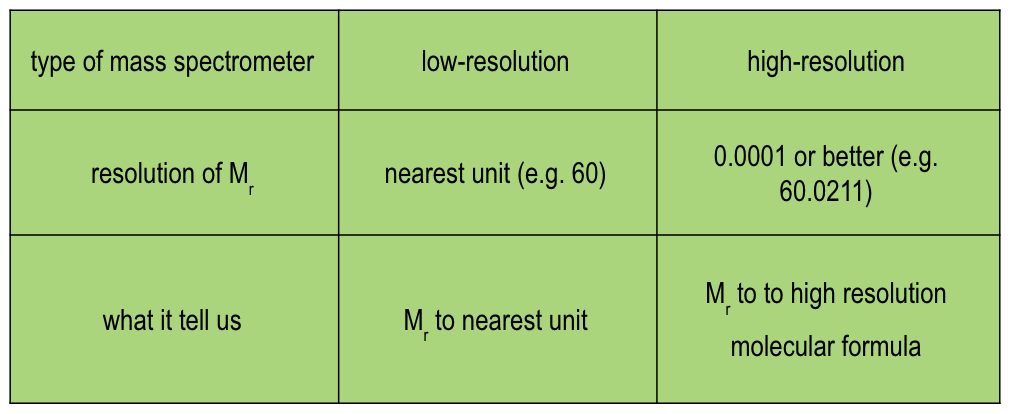
compare the type of mass spectrometer, resolution of Mr and what this shows of the 2 types of mass spectrometry:
electron impact, electrospray (respectively)
why is it useful to have Mr s at high resolutions?
some compounds w/ diff molecular formulae may have the same Mr at a low resolution but different Mr s at a high resolution

what are the different types of bond vibration?
stretching (symmetric/assymetric)
bending
what does the frequency at which bonds vibrate at depend on?
mass of atoms
bond strength
type of vibration in bond
how does infreread (IR) spectroscopy work?
vibrating bonds can absorb radiation at the same frequency as the bond vibration - for organic molecules, the radiation lies in the IR region of the EM spectrum
when the molecules absorb IR radiation, the degree of stretching/bending increases, meaning the bonds absorb specific frequencies when IR radiation is passed through them
this allows an IR absorption spectrum to be formed
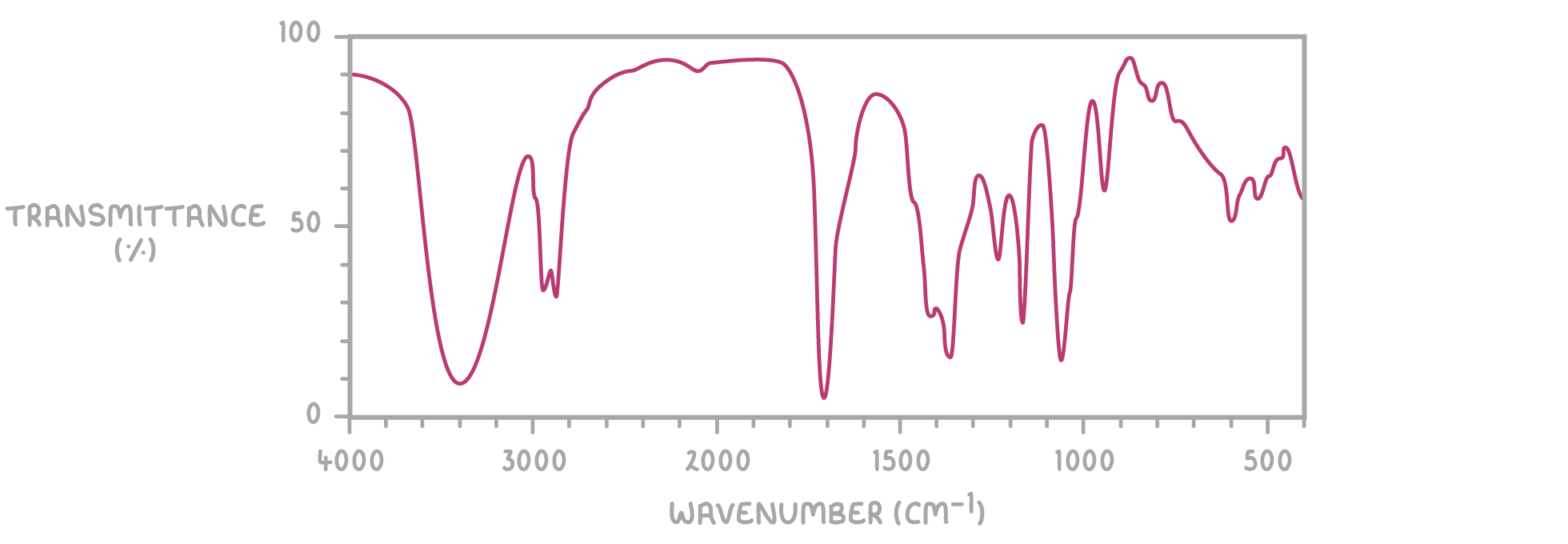
what are wavenumbers? how can they be calculated?
used as a measure of the freq of the absorption\
measured in cm-1
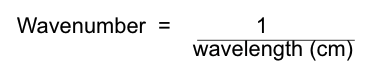
what is a wavenumber above 1500 cm-1 used for?
to identify functional groups
what is a wavenumber below 1500 cm-1 used for?
fingerprinting
what is the ‘fingerprint’ section and what is its significance?
part of the spectrum which is unique for every molecule
allows identification of a molecule by comparison of spectra
can be used to check for impurities as extra peaks in this region indicate the presence of impurities
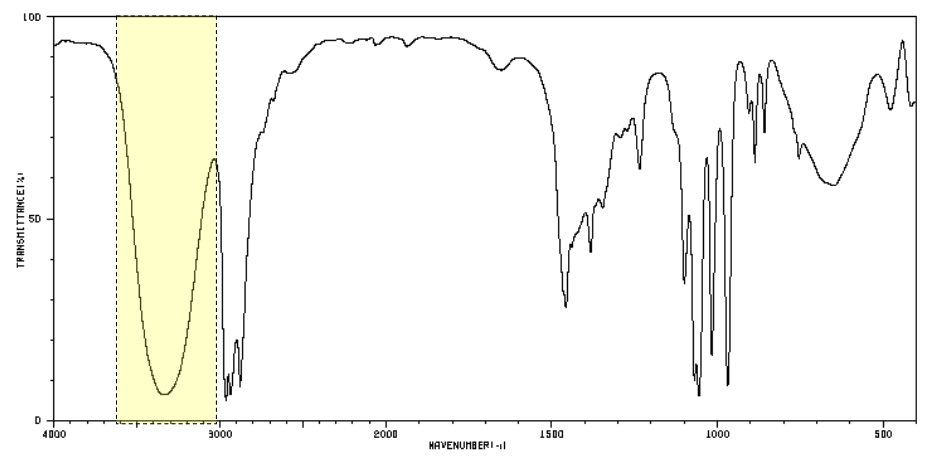
which functional group does this peak indicate?
alcohol -OH
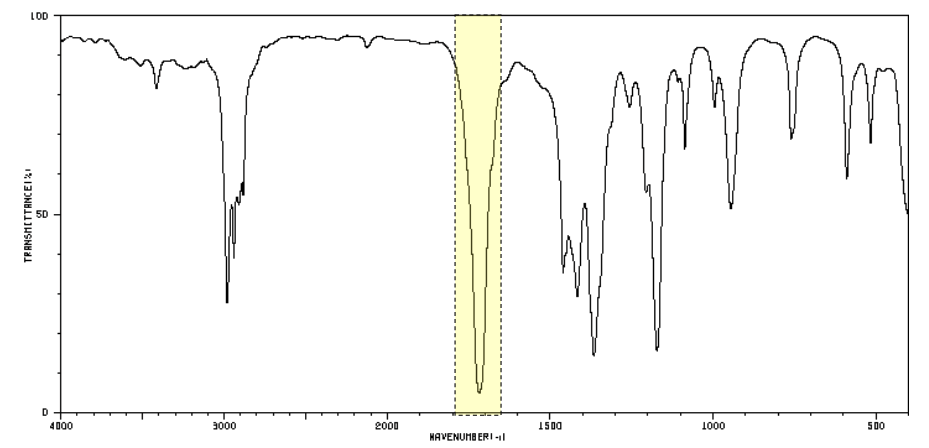
which functional group does this peak indicate?
C=O (carbonyl)
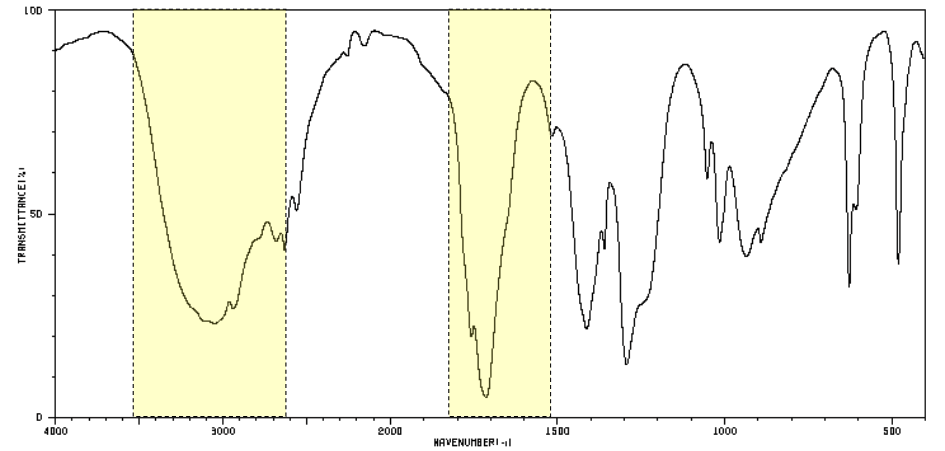
which two functional groups do these peaks indicate?
respectively:
acid -OH
C=O
(→ carboxylic acid)
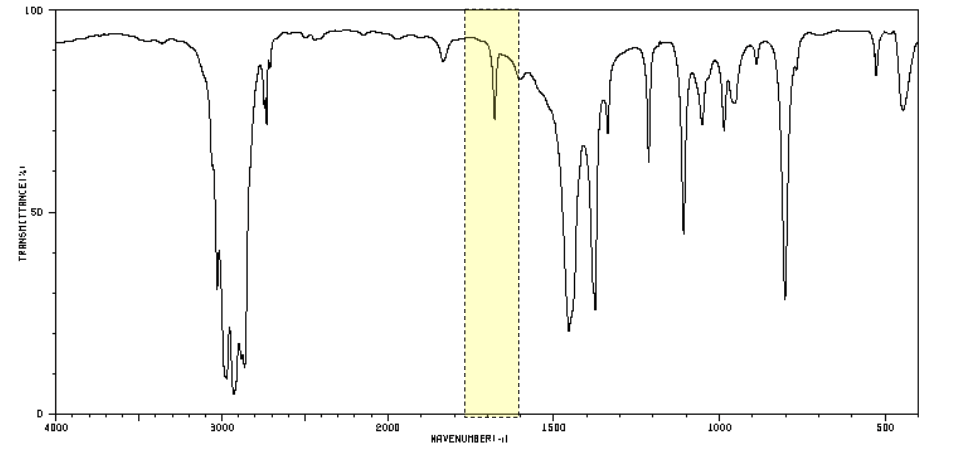
which functional group does this peak indicate?
C=C