Meat Science Exam 3
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Top 10 pathogens
Staphylococcus (from humans)
Salmonella (everywhere/polutry)
E. coli (beef/ruminats
Listeria (fruits/dairy)
Clostridium botulinum (canned food/neurotoxin)
Hepatitis A (dirty water)
Taenia solium (tapeworm)
Liver fluke
How many cases each year does CDC estimate are from food-born illness?
48 M cases
How many hospitalizations each year does CDC estimate are from food-born illness?
128,000 hospitalizations
How many deaths each year does CDC estimate are from food-born illness?
3,000 deaths
How much cost each year does CDC estimate are from food-born illness?
$6.9 B For top 5 foodborne pathogens
What direction does Monotrichous flagella come from? What is the use for this?
Flagella comes one direction
Can go through blood-brain barrier
Use action myosin to travel
Pass from mothers to babies in womb
Ex: L. Monocytogenea
What direction does Peritrichous flagella come from? What is the use for this?
Flagella comes from multiple directions
Ex: salmonella
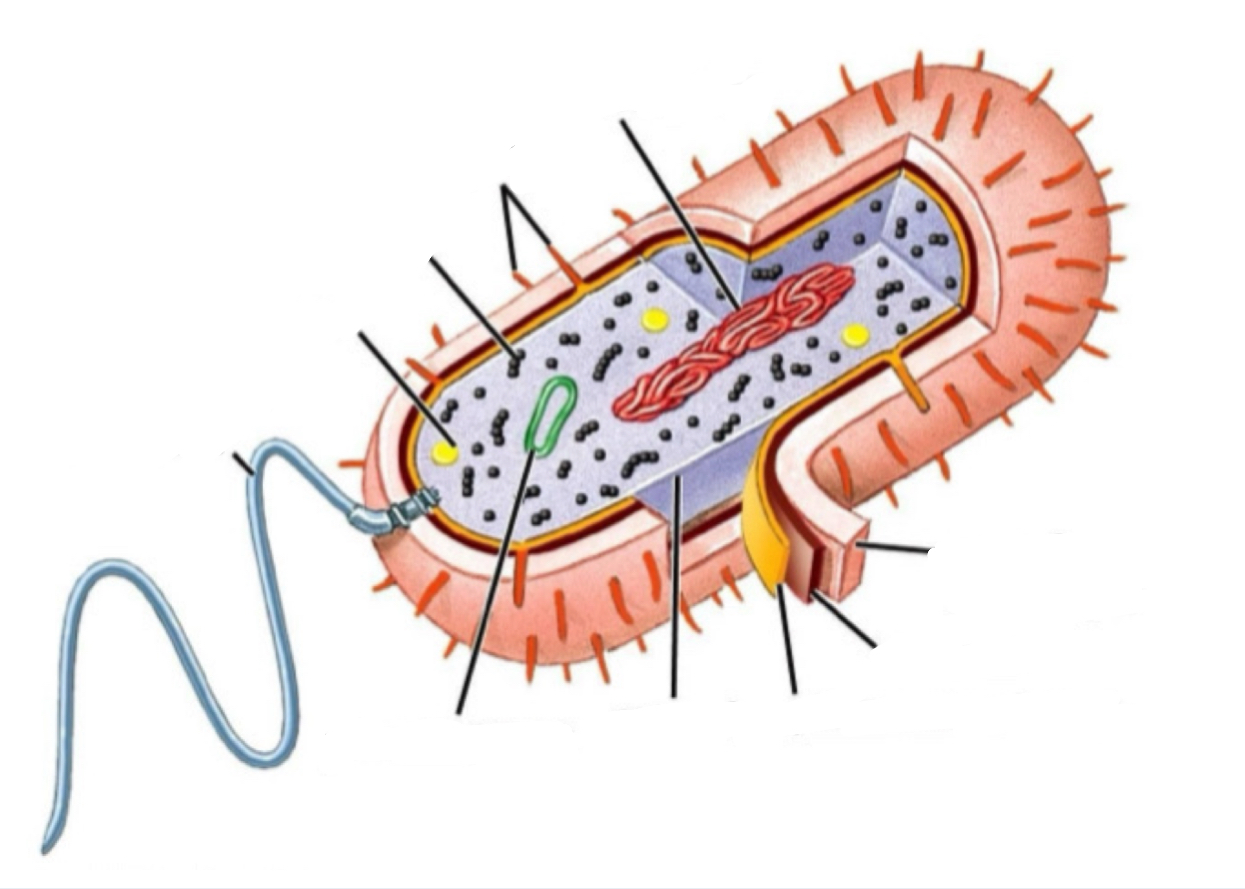
Label the following structure on the bacteria (chromosomes, capsule, cell wall, plasma membrane, cytosol, ribosomes, food granule, flagella, plasmid, pili)
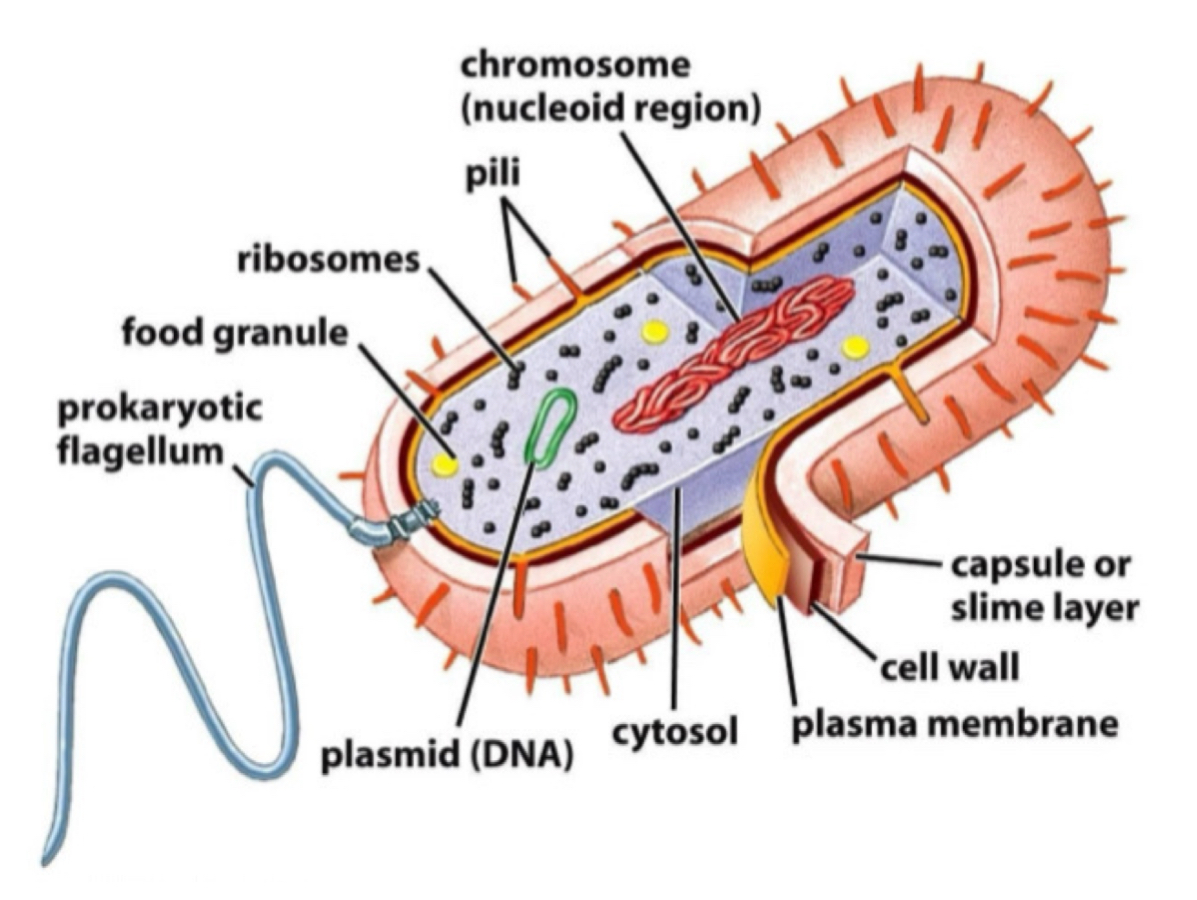
What is the function of plasmid?
It contains DNA that carries anti microbial genes for antibodies resistance
Layers of gram positive bacteria
Peptidoglycan (protein, sugar) thick/gram multilayer, purple
Periplasmic space (nutrients, cushion)
Plasma membrane
Layers of Gram Negative Bacteria
Lipopolysaccharide (lipid, many sugar) and protein
Has PORIN (drugs/molecules enter cell through)
Antibodies kill easily but cause release endotoxins
Periplasmic space
Peptidoglycan (mono layer/thin layer)
Periplasmic space
Plasma membrane
Ex: salmonella, E. coli.
Gram Staining Process ???
Fixation → crystal violet → iodine treatment → decolorisation → counter stain with safranin
Crystal violet form covelent bond with iodine in cell
Decolorisation (gram (-), loose color since it has thin Peptidoglycan layer) (gram (+) turns purple)
Safranin stains pink in gram (-)
What are microbes?
microorganisms not visible to naked eye
Ex: bacteria, parasites, viruses and fungi
How often do bacteria multiple on average?
every 20 minutes
In 6hrs 1 cell becomes 1 M cells
What are fungi?
Single, or multi-celled organisms such as yeast, mold, mushrooms
What are viruses?
Non-living, non-cellular organisms that require a host to grow
What are bacteria?
Living, single called organisms
What organisms are parasites?
Flatworms (taenia, round worms)
Round worms (anisakis)
Protozoa (eukaryotic, single-cell, motile)
How often do clostridium borfringens multiple and where are they found?
multiply every 9 minutes and thrive in anaerobic conditions (no oxygen) Ex: canned food, meats
-can cause can to be distorted from gas byproduct
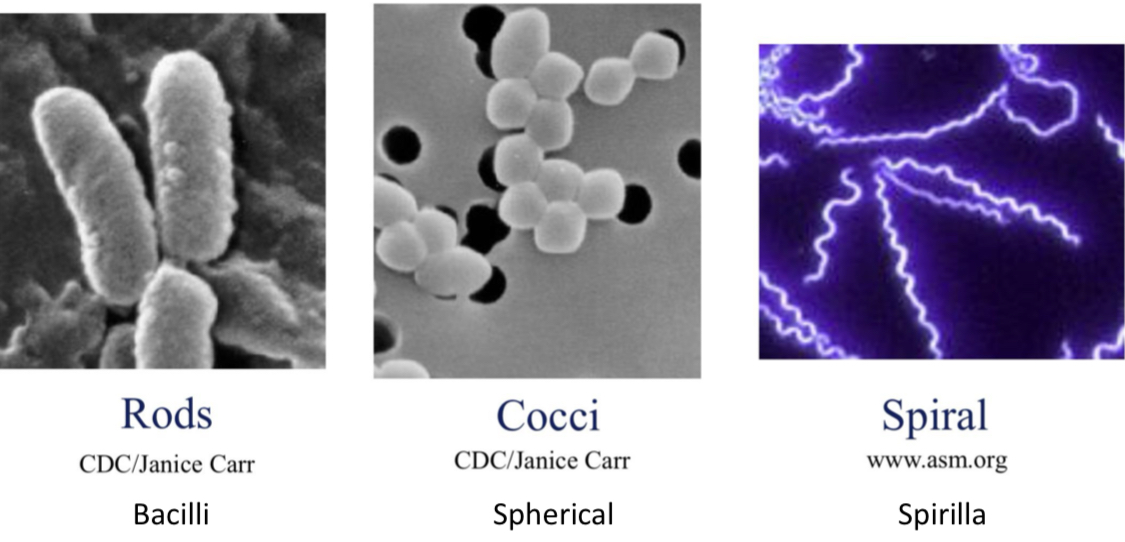
What do Rods, Cocci, and Spiral bacteria look like?
Rods - bacilli or diplobaccilli (2 rods)
Cocci - spherical, dipolococci (2 spheres)
Spiral - spirilla

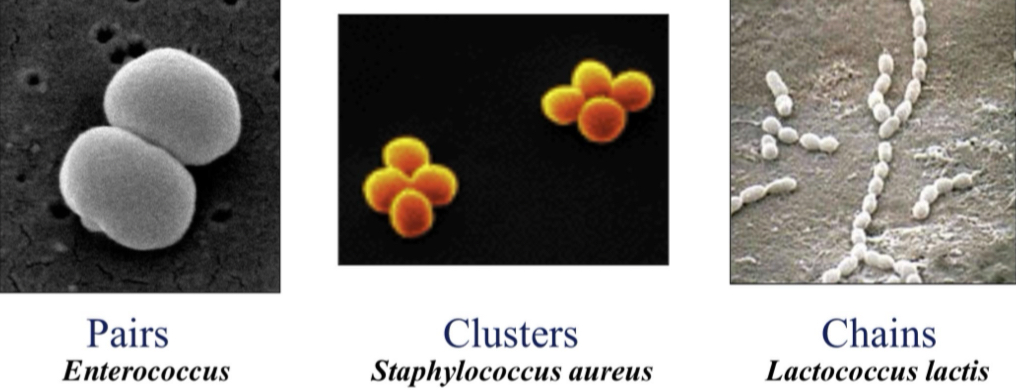
What does pairs, clusters and chains bacteria look like? Give example of each
Pairs - enterococcus
Clusters - staphylococcus aureus
Chains - lactococuslactis
What temperature do you cook food at to prevent clostridium bacteria from multiplying?
> 140 F -1hr→ 70 F -4 hrs→ <40 F (hold), total: 5 hrs , no more than 6
How long does it take CDC to be notified of food-borne illness outbreak?
Hospitalized (day 3) → Lab results out (day 5) → Presumptive positive (day 7) → people surveyed to find origin (takes 7-10 days)
Total time: 28 days until CDC notified
What is an infection?
Pathogen is ingested and living pathogen multiplies inside body
What is an Intoxication?
Pathogen produced toxins that were ingested
Toxin mediated infection
Living pathogen inside body and produces toxin in body
What does it mean to be susceptible?
inability to prevent or overcome invasion
What does it mean to be immunocompromised?
weak immune system from disease or treatments
Ex: old age, health (AIDs, cancer), pregnancy, nutritional status, meds
At what temperature and for how long should steak be cooked at?
145 F for 3 minutes or less of steak is sterile and handled by hygienic people
What does FATTOM standard for?
include factors of food that support microbial growth
Food, Acidity, Time, Temp, Oxygen level, Moisture
Which of the FATTOM are intrinsic factors?
Inside factors that affect microbial growth
Food, acidity, moisture
Which of the FATTOM are Extrinsic?
outside factors affecting microbial growth
Time, temp and oxygen level
How does pH affect bacteria?
Low pH (lots of H+) penetrated gram (-) bacteria through their PORIN and kill them, gram (+) has thicker membrane - more resistant to low pH
What is the pH for ideal pathogen growth, meat/poultry and prevent microbial growth?
ideal pH for pathogen: 4.6 - 7.5
pH of meat & poultry: 5.1 - 6.4
pH to prevent microbial growth: < 4.6
At what temperatures does pathogen grow? What temperature is recommended for storage, display, and transport of meat?
Pathogens grow at 41 F - 135 F
Meat should be kept at 28 F
Where is contamination is from?
Farm, commodity/ingredient/packaging/processing, retail, consumer
How does food become contaminated?
Contaminated ingredient or packaging material, improper processing (undercooking, bad cooling, bad holding), cross contamination, poor personal hygiene