Trade, Trade Restrictions and Liberalisation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
International Trade
The exchange of goods and services between countries, otherwise known as exporting and importing. Including, primary, secondary and tertiary products.
Specialisation
When countries are not self-sufficient but concentrate on producing certain goods and services and trading the surplus with others. This is done to increase the world output of a good.
Absolute Advantage
The ability of an individual, a firm, or a country to produce more of a good or service than competitors, using the same or fewer amount of inputs/resources.
Comparative Advantage
The ability of a country to produce a good at a lower relative opportunity cost than another country can.
Protectionism
The use of trade barriers such as tariffs to favour domestic suppliers at the expense of foreign suppliers.
Tariff
A tax on imports, otherwise known as import or customs duty.
Quota
A limit placed on the quantities of a product that can be imported
Subsidies
A grant given to domestic firms which lowers the price of a good, designed to encourage competition or production of a good.
Non-tariff barriers
Regulations which increase cost to foreign producers and act as barriers to trade. Such as product specifications, health and safety regulations, environmental regulations and product labelling.
Infant Industry / Sunrise Industry
A new domestic industry that has not had time to establish itself and achieve comparitative advantage and therefore may be unable to compete with more mature competitor firms from abroad. This is used as a strong argument for trade protection policies in developing countries.
Dumping
Selling products in a foreign country at lower prices than those charged in the producing country as you have a surplus of the good or an absolute advantage. In extreme cases, a company may deliberately sell at a loss to drive domestic producers out of business, so it can then raise prices and enjoy a monopoly.
Trade liberalisation
The move towards greater free trade through the removal of protectionist barriers to trade where specialised good surpluses are trade.
Pattern of trade
What goods and services a country trades, with whom, and in what direction.
Terms of Trade
the relationship between the value of a country's export prices and its import prices
Trade Barrier
Any measure which artificially reduces international trade.
WTO / World Trade Organisation
the organisation that regulates world trade helping to set the rules of international trade
Structural Adjustment
The reallocation of factor inputs from one sector of the economy to another, in response to changing economic circumstances - criticism of David Ricardo's comparative advantage theory which doesn't account for this.
Assumptions of a tariff diagram
All goods are homogeneous, domestic supply curve is upwards sloping (due to incentives to produce more), price of imported goods are determined in the world market.
Tariff Diagram
Shows the impact of a tariff on imports of a good, and how the gap between quantity demanded and supplied (Filled by importing goods) narrows as a tariff is levied on prices.
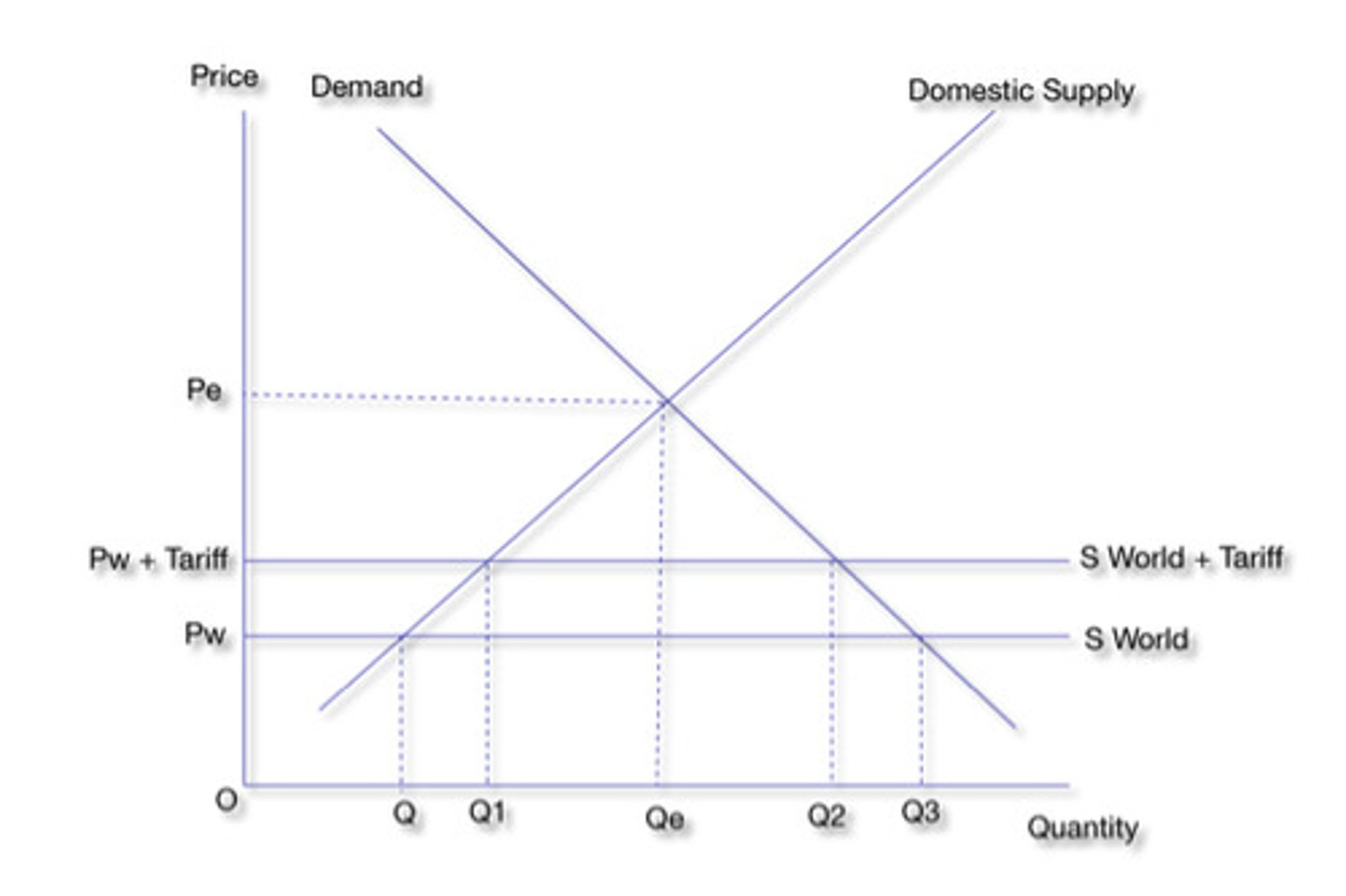
Consumer Surplus
the difference between the highest price a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and the actual price the consumer pays
Producer Surplus
The difference between the lowest price a firm would be willing to accept for a good or service and the price it actually receives
Sunset Industry
An industry in decline that needs protection for its displaced workers, especially from dumping and low cost foreign competition.
Law of comparative advantage
David Ricardo's law that a nation is better off when it produces goods and services for which it has a comparative advantage, as it can trade the surplus and maximise the use of its resources.
Non-discrimination
A principle that a country cannot make distinctions in trade among its trading partners. A tariff reduction applied to one nation should apply to all with which it trades.
Reciprocity
the obligation to return in kind what another has done for us, applies to tariff reductions being mutual under WTO rules.
Safety Valves
The permission of tariff usage by the WTO...The use of tariffs in relataliation to offset illegal subsidies or to protect infant industries/domestic industries critical for domestic employment, or quotas to correct a balance of payment crisis.
Embargo
a government order imposing a blanket ban on imports and trade with another country/trading bloc.
Size of the tariff on Chinese steel that Donald Trump imposed in 2019 (leading to a 25% tariff from China on American imports)
25%
Average cost of Trump's first term tariffs on US consumers
$480 per year