Angiosperms pt 1, 2, 3
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
251 Terms
What are the basic characteristics of plant kingdoms?
autotrophic, eukaryotic, multicellular, non-mobile, cellulose-rich cell walls, alternations of generations life cycle, special adaptations for life on land
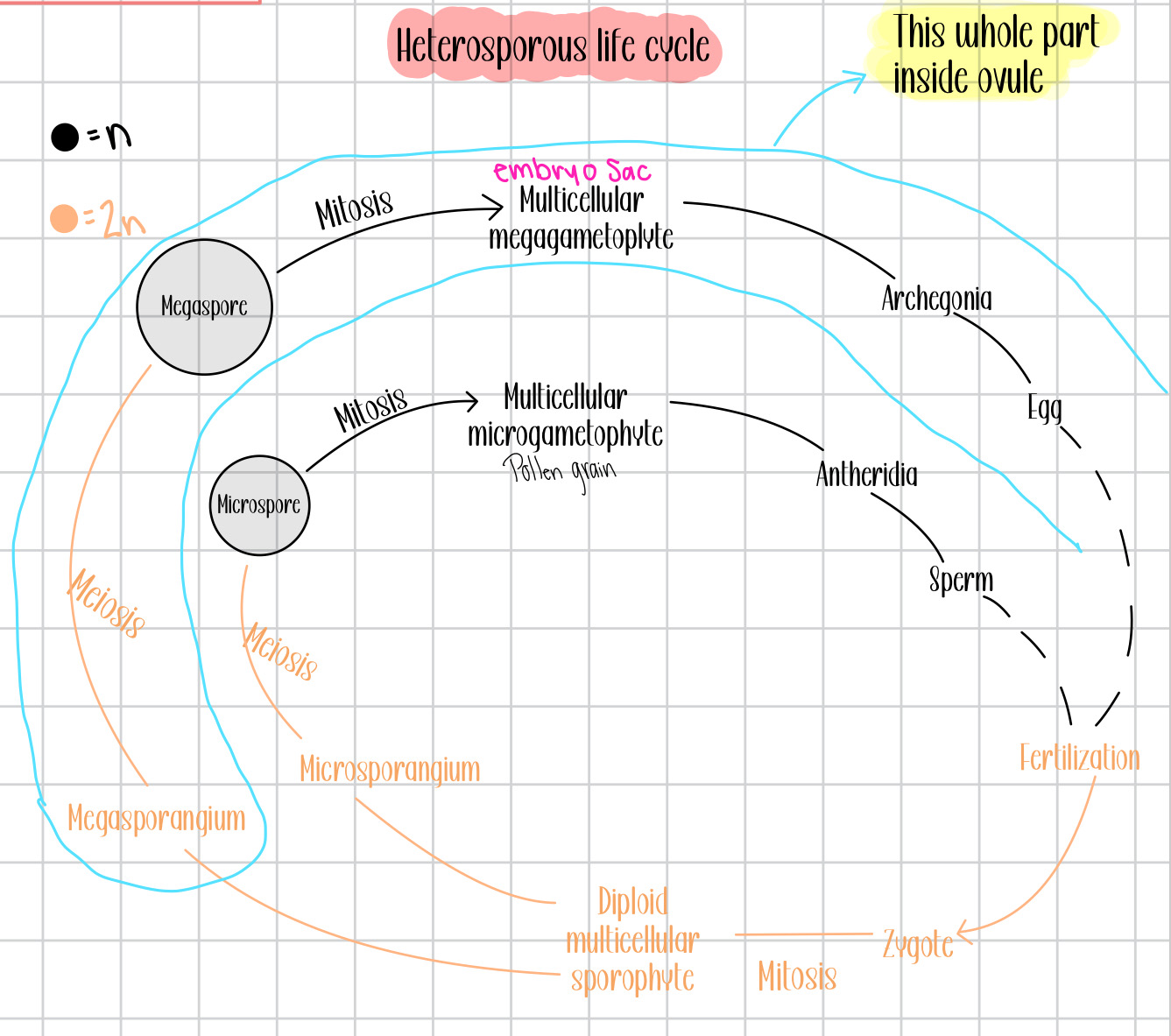
Draw the heterosporous life cycle
Angiosperms are also called ___ ____
flowering plants
Angiosperms seeds are….
enclosed within a fruit
Angiosperms are the most ____ group of extant plants and vary in ____
diverse, size
What are the uniting characteristics of angiosperms? (vascular & seed plants)
flowers, seeds borne in fruits, double fertilization
What are the 2 major groups of angiosperms?
monocot, dicot
Monocot
petals in groups of 3s, parallel veins in leaf
Dicot
petals in groups of 4s or 5s, netted veins in leaf
What are flowers?
a modified shoot that produces sporophylls
What are sporophylls?
leaves modified to have spores
Ovules are borne in ____
carpels
What are carpels?
female parts of the flower
What are flowers composed of?
sterile & fertile reproductive parts attached to a receptacle
What is a receptacle?
attachment point of all flower parts
What are the main parts of the flower?
sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
What does the sterile part of the flower mean?
no gametes
What are the sterile parts of the flower?
sepals, petals
Sepals are the ____ layer
outer
Function of sepals
protect developing flower that is still in bud form
Appearance of sepals
green
Collective name of sepals
calyx
Petals are the ___ layer
inner
Function of petals
attract pollinators for pollination
Appearance of petals
bright colored, smell good
Collective name of petals
corolla
What are tepals?
when petals & sepals are indistinguishable
What is the collective name for petals and sepals all together?
perianth
What are the fertile parts of the flower?
stamen, carpels
Stamens are the ___ parts of the flower
male
What do stamens produce?
pollen
Stamens are ______
microsporophylls
What are microsporophylls?
modified leaves associated with microsporangia
Stamens consist of ____ & ____
anther, filament
What is an anther?
bud-like structure, produces pollen
What is a filament?
stalk that supports anther
What are anthers and filaments called?
androecium (house of man) or stamen
Carpels are the ____ part of flowers
female
Where do seeds originate?
in carpels
What do carpels produce?
ovules
Carpels are _______
megasporophylls
What is the whole female part of the flower called?
gynoecium (house of woman)
Carpels consist of what 3 parts?
stigma, style, ovary
What is a stigma?
bulb in the middle of flower, catches pollen for fertilization
What is a style?
tube-like structure that holds up stigma
What is an ovary?
contains & produces ovules
After fertilization, the ovary becomes a ____
fruit
What is the collective name for stigma, style, ovary
carpel
What is floral symmetry?
arrangement of parts of the flower
What are the 2 types of floral symmetry?
actinomorphic, zygomorphic
Actinomorphic symmetry
radial symmetry, can cut infinite ways and always get mirror image
Zygomorphic symmetry
bilateral symmetry, can only cut once and get mirror image
What is floral fusion?
flower parts can be fused or separated
What are the 2 types of floral fusion?
connation, adnation
Connation
fusion of 1 layer of the flower (all petals)
Adnation
fusion of 2 different layers of flower (petals, sepals)
What are perfect flowers?
bisexual, have both male & female parts
What are imperfect flowers?
unisexual, have only male or only female parts
What is a whorl?
sepals, petals, stamens, carpels
What is a complete flower?
have all 4 whorls
What is an incomplete flower?
missing 1 of the 4 whorls
Superior ovary
ovary is above sepals & petals
Inferior ovary
ovary is below sepals & petals
Peduncle
central stalk
Pedicel
individual flower stalk attaching flower to central stalk
What is an inflorescence?
2 or more flowers in a cluster arranged various ways
What are the elongated types of inflorescence?
solitary, spike, raceme, panicle
Solitary inflorescence
1 flower on main axis
Spike inflorescence
unbranched main axis with sessile flowers
What does sessile mean?
no stalk
Raceme inflorescence
unbranched main axis with stalked flowers
Panicle inflorescence
multi-branched, each branch has multiple flowers
What are the flat-top inflorescence types?
umbel, corymb/cyme
Umbel inflorescence
flat-topped, individual pedicels originate from same point
Corymb/cyme inflorescence
flat-topped, individual pedicels originate from different points
Catkin inflorescence
unisexual, spike-like, hang off branch
What is an example of a catkin inflorescence?
oak tree
What catkin characteristics let you know that they are not insect pollinated?
wind pollinated, have no petals, no smell
Head inflorescence
looks like a single flower, hundreds of tiny flowers arranged on a structure
Head inflorescence are common in the _____ family
aster
What is an example of head inflorescence?
sunflower, daisy
What are disk flowers?
each individual flower in the middle of a whole flower (brown dots in sunflower)
What are ray flowers?
a petal with an ovary attached at the end (yellow petal on sunflower)
In the stamen, each anther is composed of….
4 pollen sacs (microsporangia)
Within each microsporangia are ____ _____
diploid microsporocytes
Microsporocytes undergo ____ to produce ___ _____
meiosis, haploid microspores
What is a sporocyte?
diploid cells inside a sporangium that undergo meiosis to produce 4 spores
Each microspore develops into a ___ ____, also called a ________
pollen grain, microgametophyte
What does the microgametophyte produce?
sperm
The pollen grain is covered in _____
sporopollenin
What is sporopollenin?
hard outer layer, prevent drying out when flying through air
The pollen grain consist of what 2 cells?
tube cell, generative cell
Tube cell
grows into pollen tubes
Generative cell
splits into 2 sperm cells
Ovules are located within the _____
ovary
What does a young ovule consist of?
integuments, nucellus, diploid megasporocyte
A nucellus is also called a ______
megasporangium
Each megasporocyte undergoes ____ to produce what?
meiosis, 4 haploid megaspores
What happens to the 4 megaspores?
3 disintegrate, leaving 1 functional megaspore
The functional megaspore undergoes _____ how many times to produce what?
mitosis, 3 times to produce 8 nuclei