Lecture 9 - Congestion Control
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Congestion Control is implemented at the ____ Layer
Transport
Congestion Control measures capacity and demand in…
bps
When demand exceeds supply…
Que fills up
Packets are dropped
Traffic Jam
Too many packets on the network, wait in que, eventually transmit.
Bucket with a Leak Example
Hole (link) can only handle so much (capacity), fill up bucket (queue), overflow bucket (drop).
End-To-End Principle
Have “intelligent” end hosts and “dumb” core network
The senders manage…
End to end connections and congestion
Network provides
Acknowledgement (ACK) packets, recall CSMA
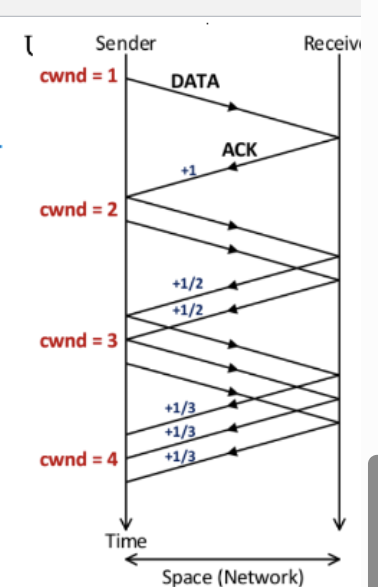
Under TCP, each sender keeps a congestion window
Limit on the number of unacknowledged packets a device can have. When ACK received, “slide” and receive
Sliding Windows are similar to Netflix DVD policy because…
Both allow you fixed number of m ovies at one time, pay for larger “window”
Under no congestion, cwnd should…
Grow, as it efficiently utilizes the network and TCP increases it linearly
Increase cwnd
By 1, if all outstanding packets received, by 1/cwnd for every packet that comes back
Inferring Congestion 1
If a sender waits a long time with no ACK, packet was probably lostfR
Round Trip Time (RTT)
Time to receiver and back
Inferring Congestion Assumption 2
IIf sender received ACK for many future packets, packet was probably lost. Think of them going sequentially.
TCP Congestion Control: Loss-based
All or nothing approach.
Problem: often too late by the time losses are occurring
Delay-based: (how late/early was the packet)
Loss Based Congestion Inference
TCP Reno - Widely used in Windows OS.
Every RTT: Have all packets been received properly?
Yes: Increases cwnd by 1
No: Cut cwnd in half
Distributed Power Control
Objective: Match measured to desired SIRs, can reach equilibrium among transmitters.
Distributed Congestion Control
Objective: Match measured to desired transmission rates.